Efficacy of CDK 4/6 Inhibitors and Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
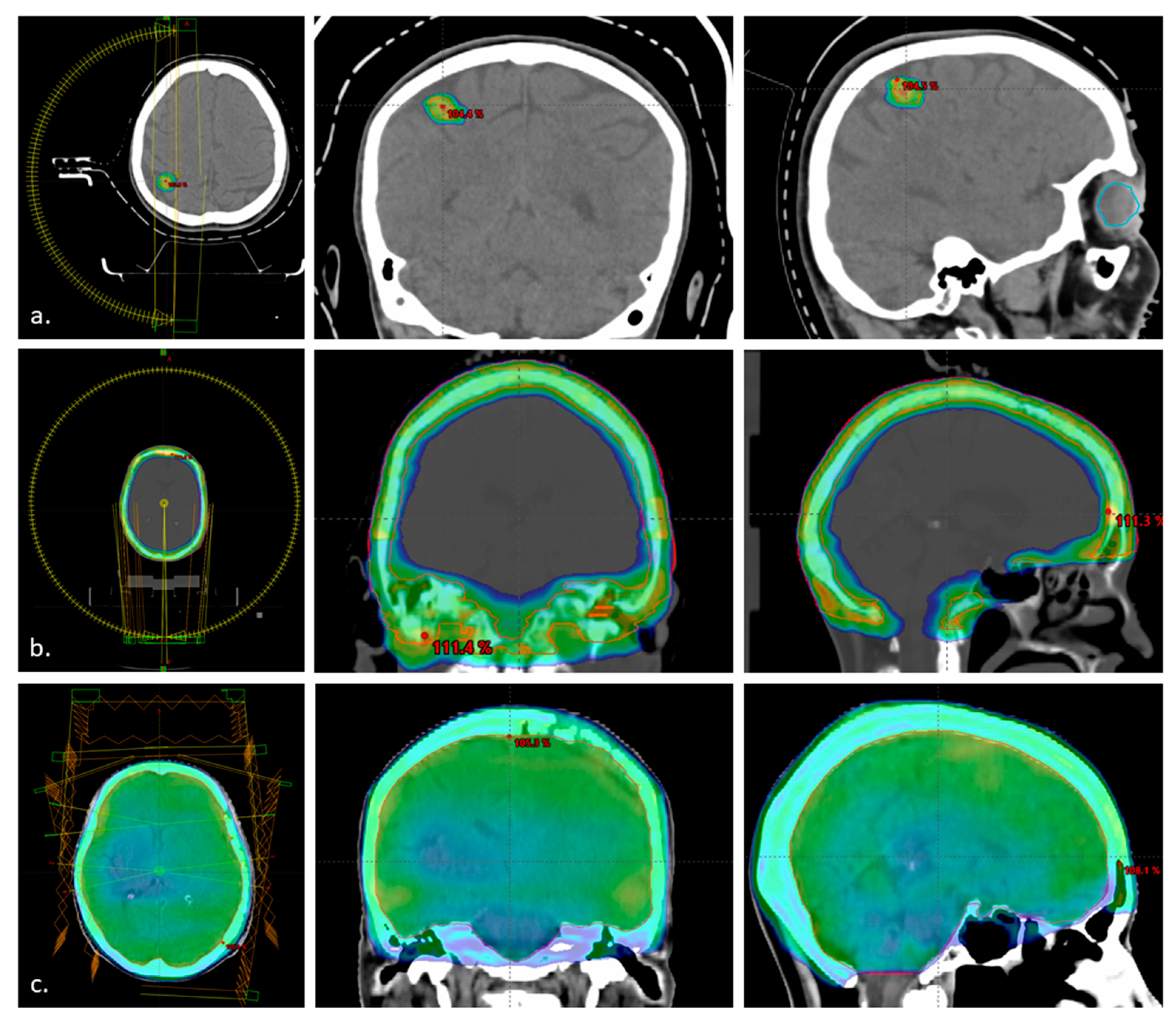
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Treatment Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Efficacy
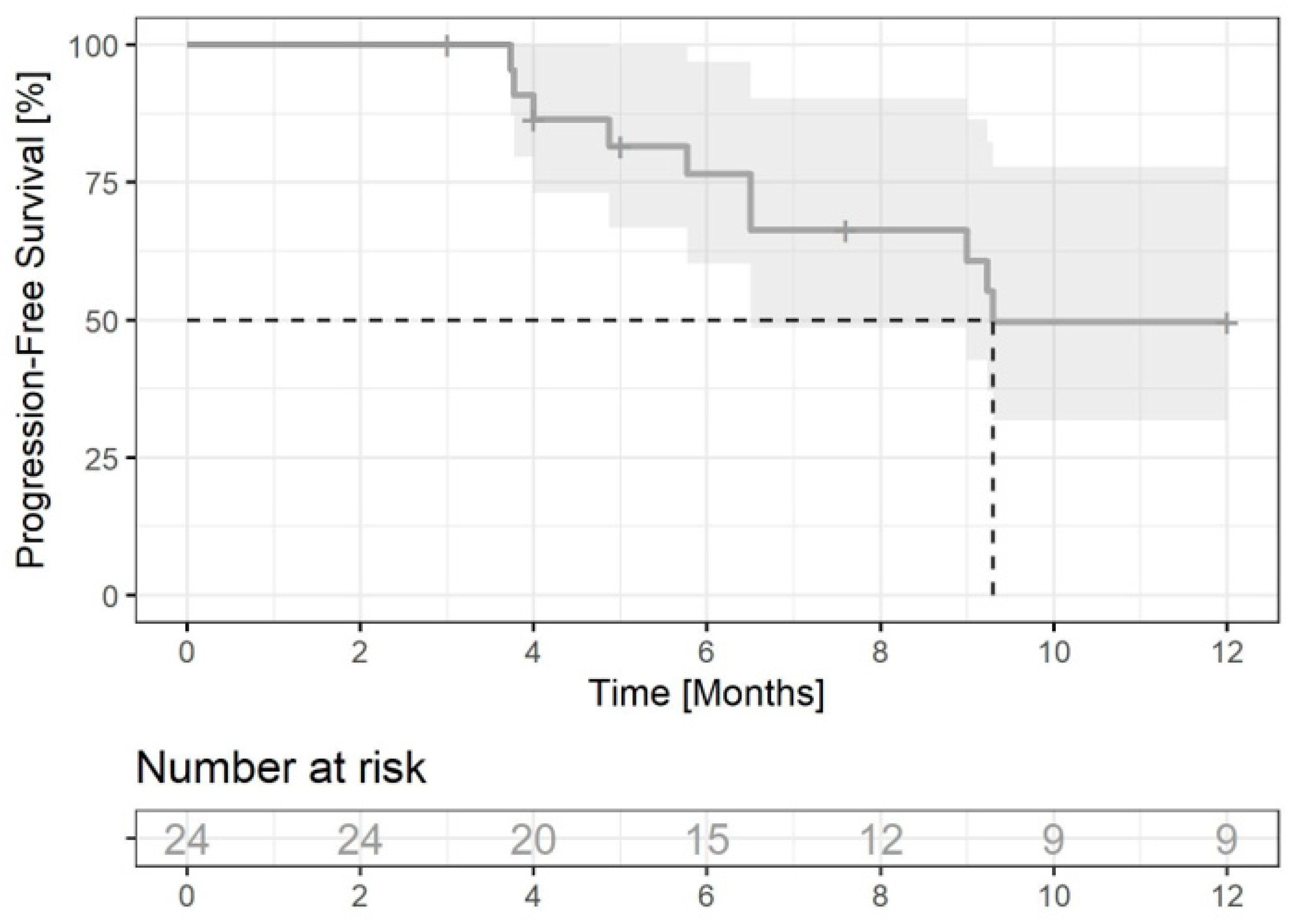
3.2.1. Progression-Free Survival
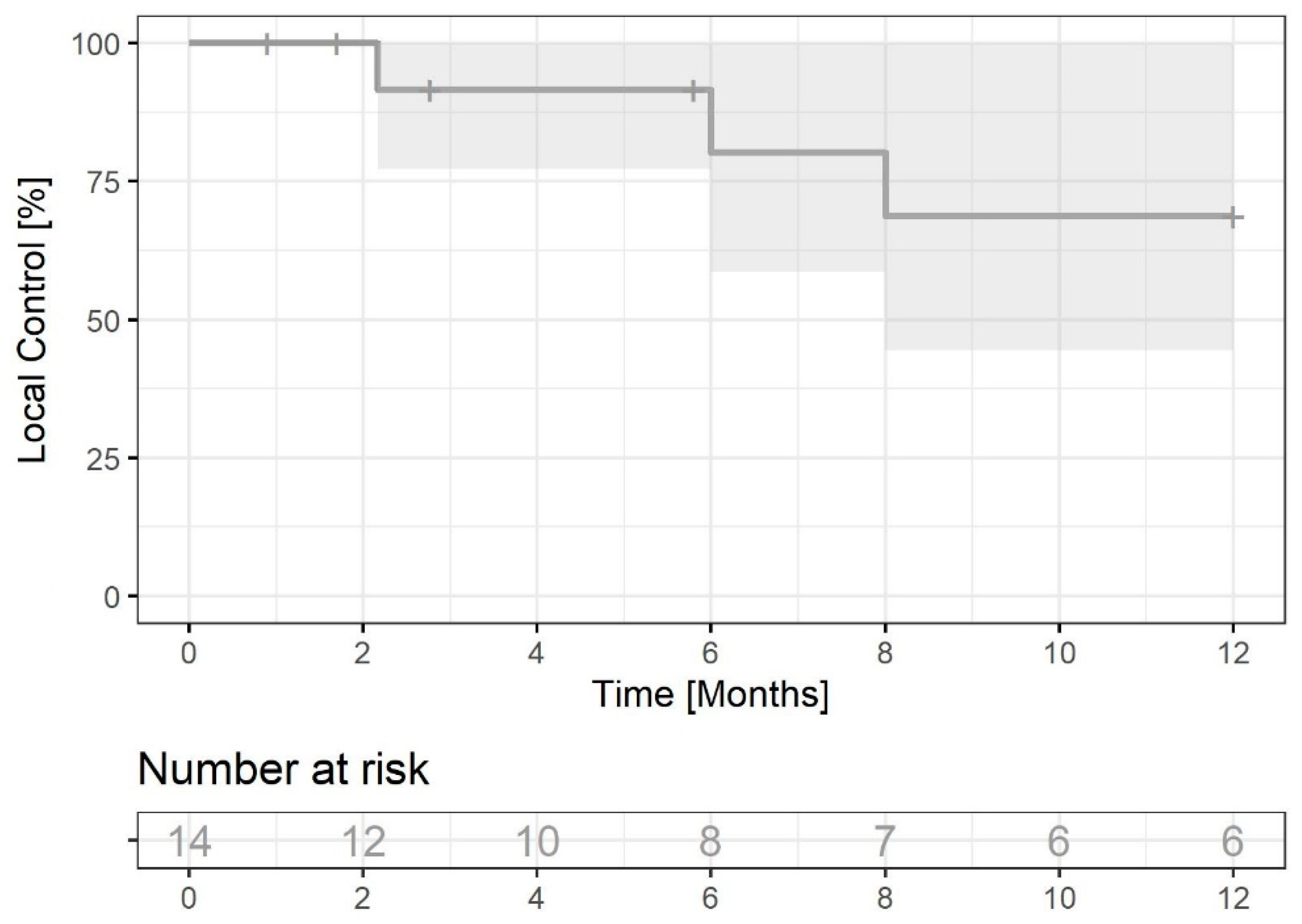
3.2.2. Local Control in the Brain
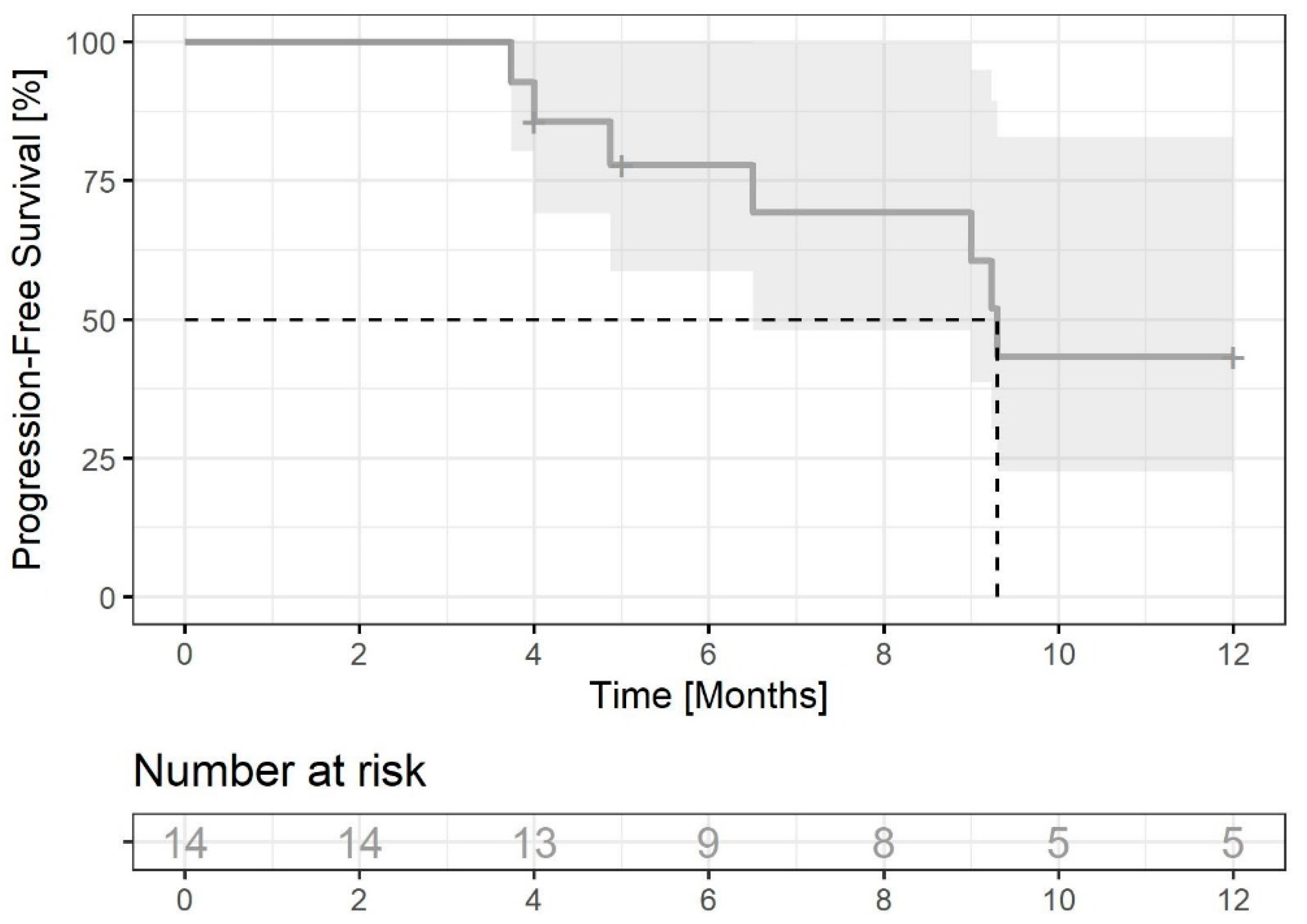
3.2.3. Results of the Treatment in Patients Treated with RT before CDK4/6i Initiation
3.3. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Davis, F.G.; Vigneau, F.D.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, R.E. Incidence Proportions of Brain Metastases in Patients Diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aversa, C.; Rossi, V.; Geuna, E.; Martinello, R.; Milani, A.; Redana, S.; Valabrega, G.; Aglietta, M.; Montemurro, F. Metastatic breast cancer subtypes and central nervous system metastases. Breast 2014, 23, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Brown, P.D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Burri, S.; Cahill, D.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gatson, N.T.N.; Gondi, V.; et al. Treatment for Brain Metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Ahmed, S.; McAleer, M.F.; Weinberg, J.S.; Li, J.; Brown, P.; Settle, S.; Prabhu, S.S.; Lang, F.F.; Levine, N.; et al. Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery versus observation for completely resected brain metastases: A single-centre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Senkus, E.; Curigliano, G.; Aapro, M.S.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; Bhattacharyya, G.S.; Biganzoli, L.; et al. 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1623–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sledge, G.W.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Burdaeva, O.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in Combination With Fulvestrant in Women With HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer Who Had Progressed While Receiving Endocrine Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, M.P.; Toi, M.; Campone, M.; Trédan, O.; Bourayou, N.; Sohn, J.; Park, I.H.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Huober, J.; Chen, S.C.; et al. MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib As Initial Therapy for Advanced Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3638–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Petrakova, K.; Blackwell, K.L.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Updated results from MONALEESA-2, a phase III trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus letrozole in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.-A.; Lu, Y.-S.; Bardia, A.; Harbeck, N.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; Lee, K.-S.; Campos-Gomez, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Neven, P.; Chia, S.; Fasching, P.A.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.A.; Petrakova, K.; Val Bianchi, G.; Esteva, F.J.; Martín, M.; et al. Phase III Randomized Study of Ribociclib and Fulvestrant in Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: MONALEESA-3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Im, S.A.; Slamon, D.J.; Harbeck, N.; Bondarenko, I.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Palbociclib and Fulvestrant in Women with HR+/HER2- ABC: Updated Exploratory Analyses of PALOMA-3, a Double-blind, Phase III Randomized Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3433–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaney, S.M.; Sahebjam, S.; Le Rhun, E.; Bachelot, T.; Kabos, P.; Awada, A.; Yardley, D.; Chan, A.; Conte, P.; Diéras, V.; et al. A phase II study of abemaciclib in patients with brain metastases secondary to hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5310–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Kim, A.E.; Wang, N.; Lee, E.Q.; Ligibel, J.; Cohen, J.V.; Chukwueke, U.N.; Mahar, M.; Oh, K.; White, M.D.; et al. Palbociclib demonstrates intracranial activity in progressive brain metastases harboring cyclin-dependent kinase pathway alterations. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Sowers, A.; Choudhuri, R.; Wissler, M.; Gamson, J.; Mathias, A.; Cook, J.A.; Mitchell, J.B. Abemaciclib, a selective CDK4/6 inhibitor, enhances the radiosensitivity of non–small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3994–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Aken, E.S.M.; Beeker, A.; Houtenbos, I.; Pos, F.J.; Linn, S.C.; Elkhuizen, P.H.M.; de Jong, M.C. Unexpected toxicity of CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib and radiotherapy. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figura, N.B.; Potluri, T.K.; Mohammadi, H.; Oliver, D.E.; Arrington, J.A.; Robinson, T.J.; Etame, A.B.; Tran, N.D.; Liu, J.K.; Soliman, H.; et al. CDK 4/6 inhibitors and stereotactic radiation in the management of hormone receptor positive breast cancer brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 144, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisqali|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/kisqali (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Ibrance|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/ibrance (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Verzenios|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/verzenios (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Therneau, T.M.; Lumley, T.; Atkinson, E.C.C. Survival Analysis [R package survival version 3.4-0]. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Kassambara, A.; Kosinski, M.; Biecek, P.S.F. Drawing Survival Curves using “ggplot2” [R package survminer version 0.4.9]. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=survminer (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Dardis, C. Miscellaneous Functions for Survival Data. R package ver-sion 0.5.6. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/survMisc/ (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Kennecke, H.; Yerushalmi, R.; Woods, R.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Voduc, D.; Speers, C.H.; Nielsen, T.O.; Gelmon, K. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, M.J.; Keith, K.; Deal, A.M.; Garrett, A.L.; Wheless, A.A.; Green, R.L.; Benbow, J.M.; Dees, E.C.; Carey, L.A.; Ewend, M.G.; et al. A Multidisciplinary Breast Cancer Brain Metastases Clinic: The University of North Carolina Experience. Oncologist 2016, 21, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlix, A.; Louvel, G.; Fraisse, J.; Jacot, W.; Brain, E.; Debled, M.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Goncalves, A.; Dalenc, F.; Delaloge, S.; et al. Impact of breast cancer molecular subtypes on the incidence, kinetics and prognosis of central nervous system metastases in a large multicentre real-life cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, H.A.; Chan, A.; Bardia, A.; Thaddeus Beck, J.; Sohn, J.; Neven, P.; Tripathy, D.; Im, S.A.; Chia, S.; Esteva, F.J.; et al. Safety and impact of dose reductions on efficacy in the randomised MONALEESA-2, -3 and -7 trials in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, K.; Miyoshi, Y. Mechanism of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: The important role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR in estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2018, 25, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmathulla, G.; Marko, N.F.; Weil, R.J. Cerebral radiation necrosis: A review of the pathobiology, diagnosis and management considerations. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, S.; Ho, G.; Day, D.; Harris, M.; Tan, J.; Goel, S.; Hanna, G.G.; Srivastava, R.; Kruss, G.; McDowell, L.; et al. Enhanced toxicity with CDK 4/6 inhibitors and palliative radiotherapy: Non-consecutive case series and review of the literature. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosacki, C.; Bouleftour, W.; Sotton, S.; Vallard, A.; Daguenet, E.; Ouaz, H.; Cojoracu, I.; Moslemi, D.; Molekzadehmoghani, M.; Magné, N. CDK 4/6 inhibitors combined with radiotherapy: A review of literature. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 26, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 24 | 100 |
| Age (median, IQR range) | 52 (41–60) | |
| ECOG 1 | ||
| 0 | 6 | 25 |
| 1 | 14 | 58 |
| 2 | 4 | 17 |
| CDK4/6i | ||
| Ribociclib | 16 | 67 |
| Palbociclib | 6 | 25 |
| Abemaciclib | 2 | 8 |
| Endocrine therapy | ||
| Letrozole | 15 | 62 |
| Fulvestrant | 9 | 38 |
| De novo disease | 6 | 25 |
| Previous CHT | 18 | 75 |
| Previous CHT < 1y 2 | 6 | 25 |
| RT in relation to CDK4/6i | ||
| Before starting CDK4/6i | 11 | 46 |
| Concurrent with CDK4/6i | 6 | 25 |
| After CDK4/6i completion | 7 | 29 |
| Technique | RT Total Dose (Gy) | RT Dose per Fraction (Gy) | No. of pts n = 24 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GammaKnife | 20 | 20 | 1 (4%) |
| CyberKnife | 15 | 5 | 1 (4%) |
| Linac Stereotactic Radiation Therapy | 24 | 8 | 2 (8%) |
| 24 | 12 | 2 (8%) | |
| 25 | 5 | 2 (8%) | |
| VMAT WBRT | 20 | 4 | 2 (8%) |
| 30 | 3 | 1 (4%) | |
| IMRT WBRT | 20 | 4 | 2 (8%) |
| 3D WBRT | 20 | 4 | 3 (13%) |
| 2D WBRT | 20 | 4 | 2 (8%) |
| VMAT—the base of the skull (tumour bed) | 30 | 3 | 1 (4%) |
| VMAT Skull bone + adjacent dura/pia | 20 | 4 | 4 (17%) |
| IMRT Retrobulbar infiltration | 20 | 4 | 1 (4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubeczko, M.; Jarząb, M.; Krzywon, A.; Gräupner, D.; Polakiewicz-Gilowska, A.; Gabryś, D. Efficacy of CDK 4/6 Inhibitors and Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052044
Kubeczko M, Jarząb M, Krzywon A, Gräupner D, Polakiewicz-Gilowska A, Gabryś D. Efficacy of CDK 4/6 Inhibitors and Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052044
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubeczko, Marcin, Michał Jarząb, Aleksandra Krzywon, Donata Gräupner, Anna Polakiewicz-Gilowska, and Dorota Gabryś. 2023. "Efficacy of CDK 4/6 Inhibitors and Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052044
APA StyleKubeczko, M., Jarząb, M., Krzywon, A., Gräupner, D., Polakiewicz-Gilowska, A., & Gabryś, D. (2023). Efficacy of CDK 4/6 Inhibitors and Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052044







