Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index at Hospital Admission or Discharge in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
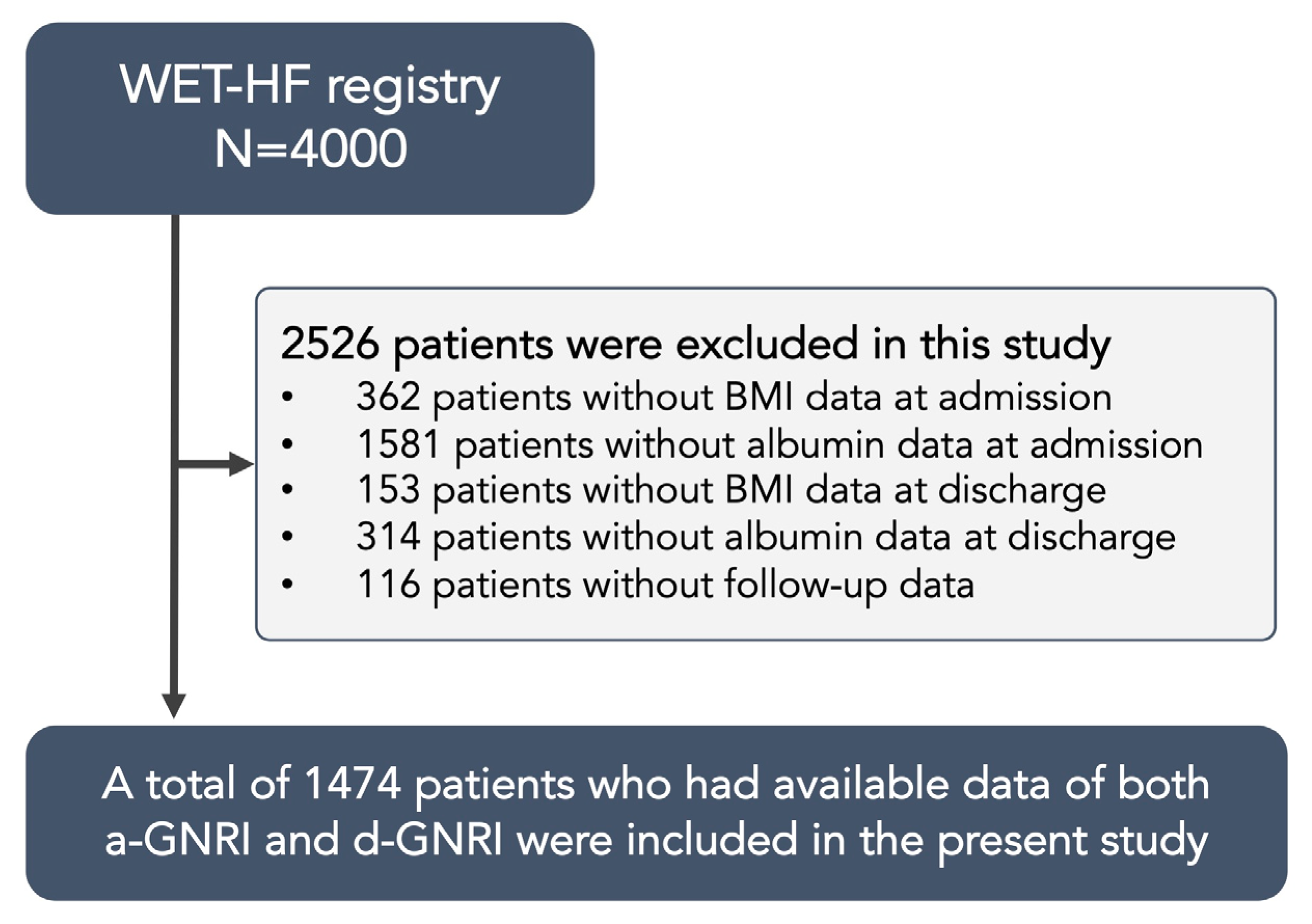
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Endpoint
2.3. GNRI
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
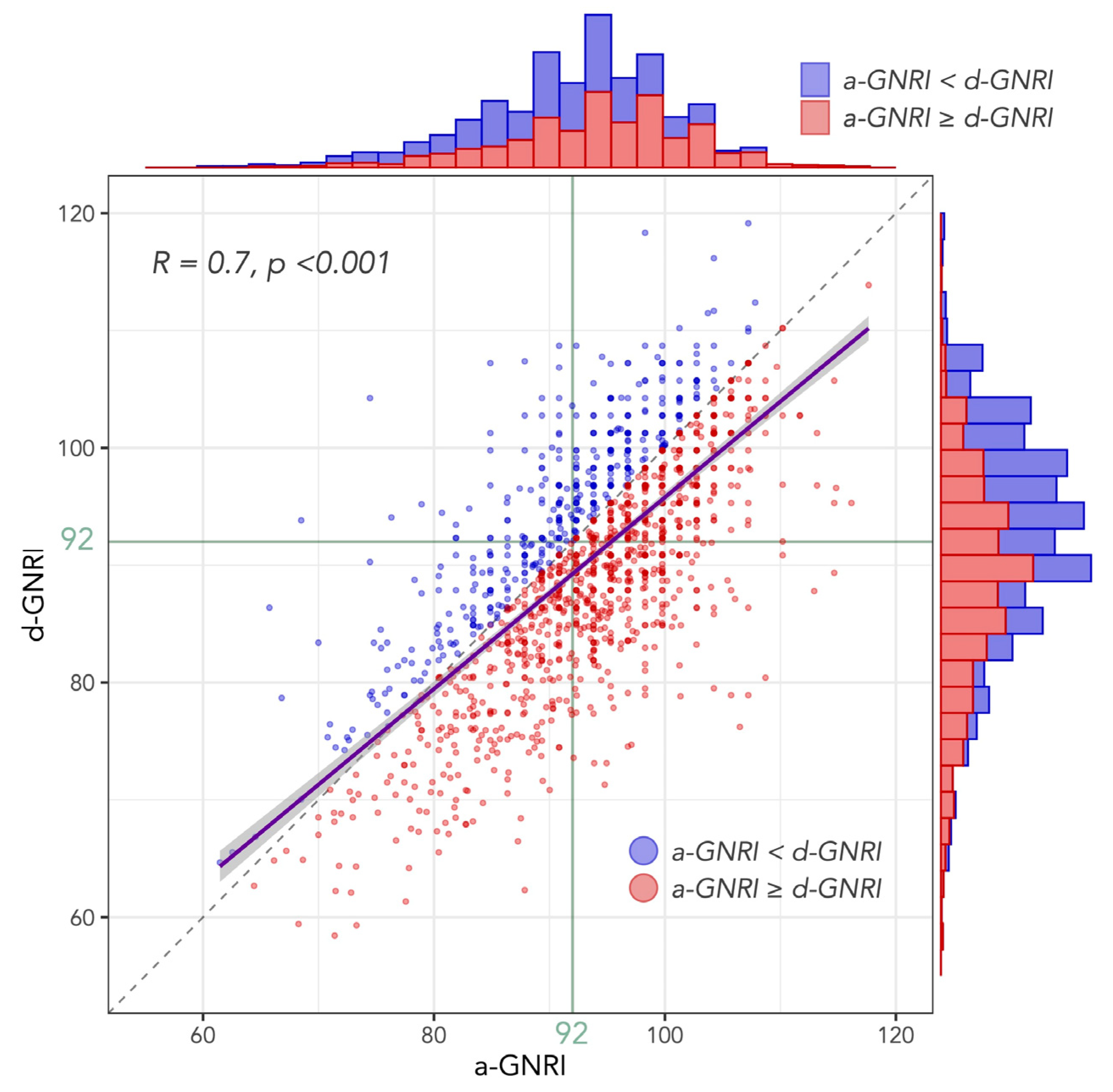
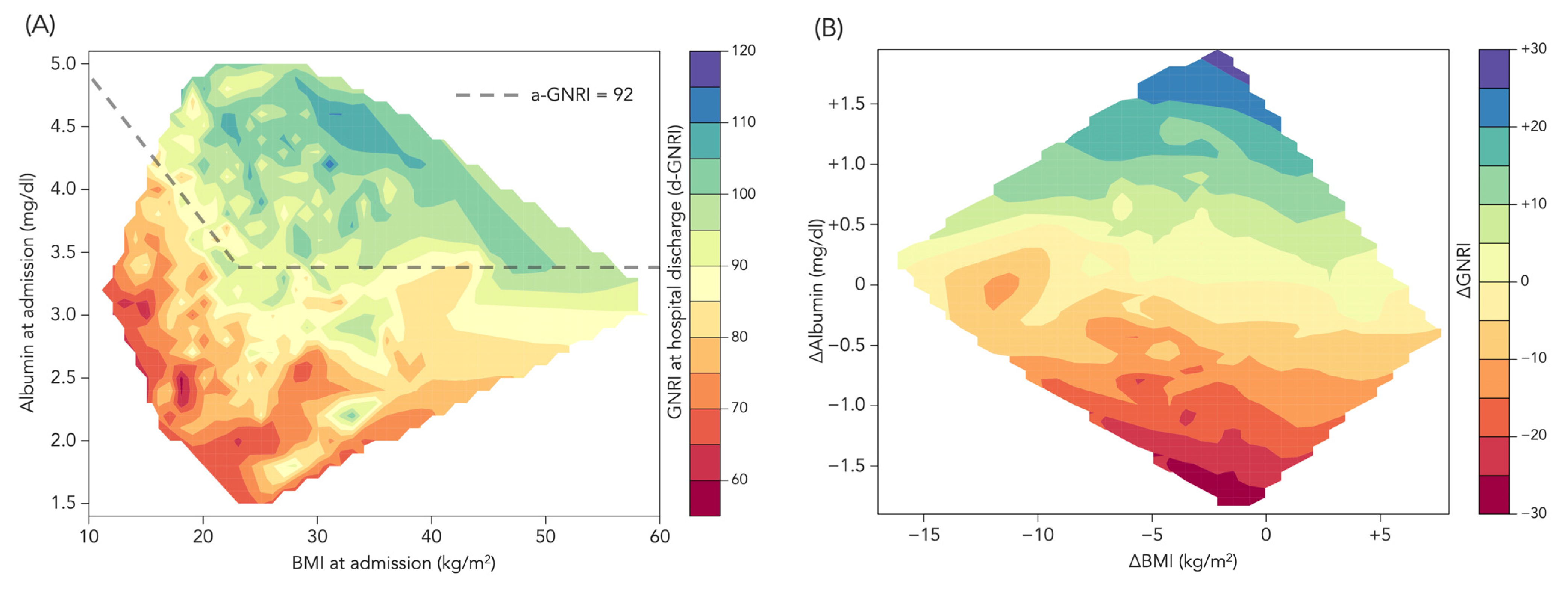
3.1. Distribution of a-GNRI and d-GNRI
3.2. Other Patient Characteristics
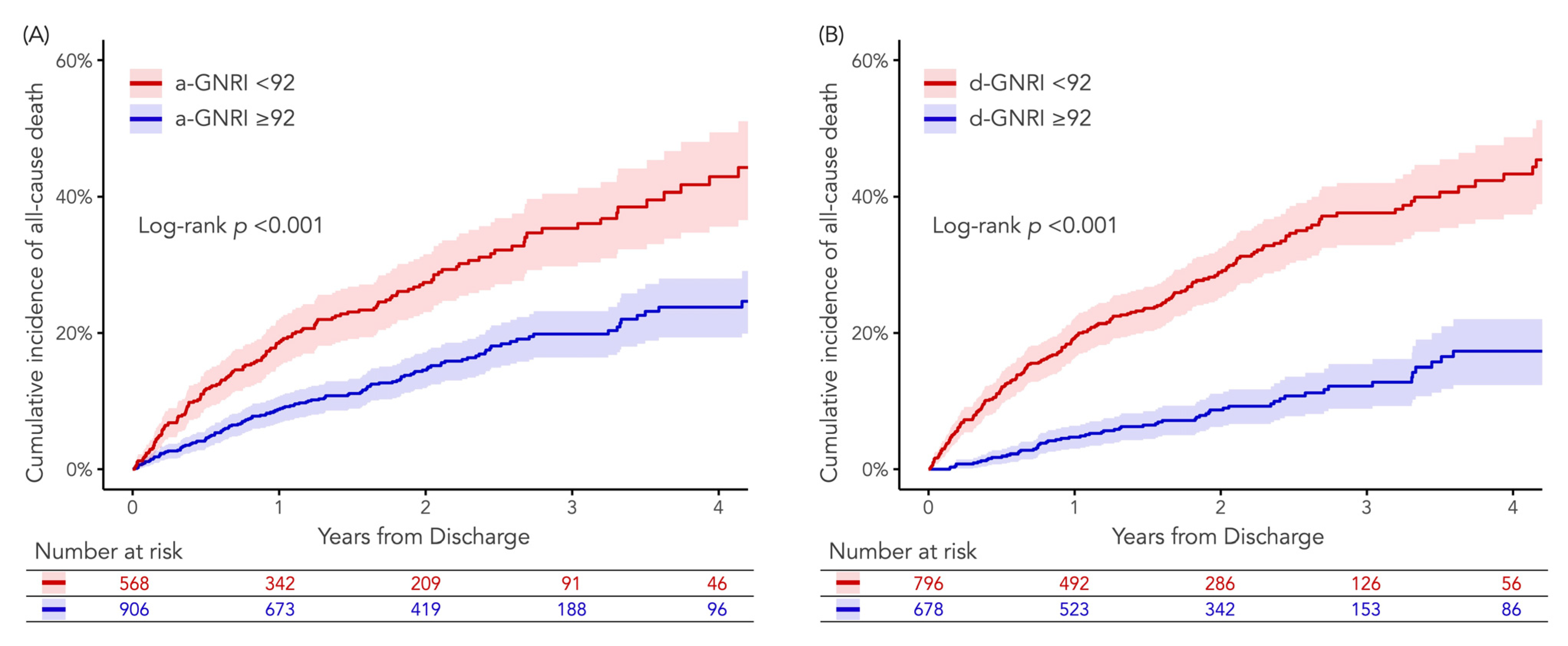
3.3. Clinical Outcomes According to a-GNRI or d-GNRI
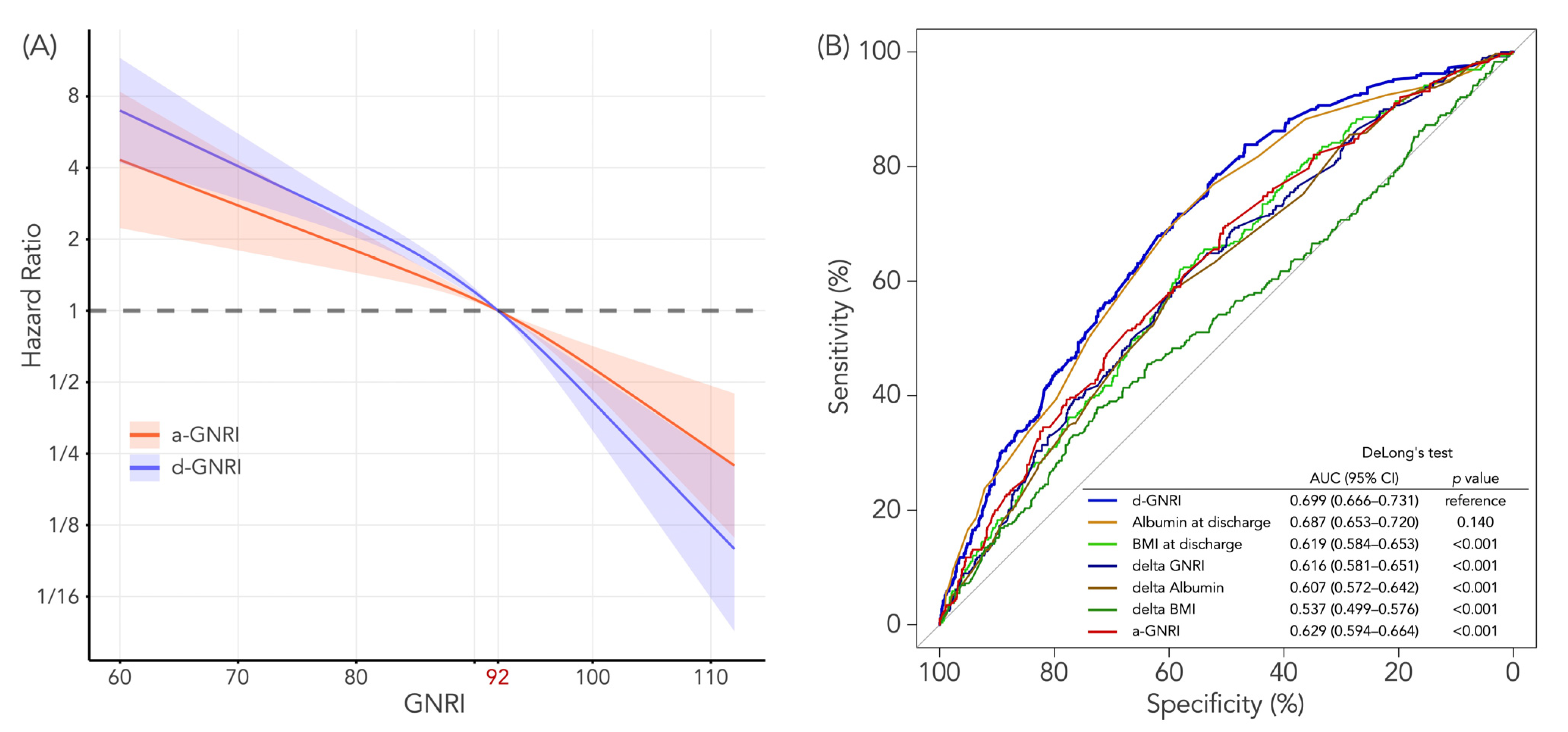
3.4. Predictive Values of a-GNRI and d-GNRI for All-Cause Death
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tevik, K.; Thürmer, H.; Husby, M.I.; de Soysa, A.K.; Helvik, A.-S. Nutritional risk is associated with long term mortality in hospitalized patients with chronic heart failure. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2016, 12, e20–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillanne, O.; Morineau, G.; Dupont, C.; Coulombel, I.; Vincent, J.P.; Nicolis, I.; Benazeth, S.; Cynober, L.; Aussel, C. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: A new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargento, L.; Vicente Simoes, A.; Rodrigues, J.; Longo, S.; Lousada, N.; Palma Dos Reis, R. Geriatric nutritional risk index as a nutritional and survival risk assessment tool in stable outpatients with systolic heart failure. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinugasa, Y.; Kato, M.; Sugihara, S.; Hirai, M.; Yamada, K.; Yanagihara, K.; Yamamoto, K. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts Functional Dependency and Mortality in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, H.; Suzuki, S.; Goto, M.; Yuzawa, Y.; Arita, T.; Yagi, N.; Murata, N.; Kato, Y.; Kano, H.; Matsuno, S.; et al. Geriatric nutritional risk index in hospitalized heart failure patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 181, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihisa, A.; Kanno, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Yokokawa, T.; Abe, S.; Miyata, M.; Sato, T.; Suzuki, S.; Oikawa, M.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. Impact of nutritional indices on mortality in patients with heart failure. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Zeng, H.L.; Yang, B.; Pan, J. Geriatric nutritional risk index predicts all-cause mortality in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinics 2021, 76, e2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Jujo, K.; Inagaki, K.; Abe, T.; Kishihara, M.; Shirotani, S.; Endo, N.; Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, K.; Minami, Y.; et al. Nutritional status during hospitalization is associated with the long-term prognosis of patients with heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 5372–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunaga, A.; Hikoso, S.; Yamada, T.; Yasumura, Y.; Tamaki, S.; Yano, M.; Hayashi, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nakagawa, A.; Seo, M.; et al. Change in Nutritional Status during Hospitalization and Prognosis in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androne, A.S.; Katz, S.D.; Lund, L.; LaManca, J.; Hudaihed, A.; Hryniewicz, K.; Mancini, D.M. Hemodilution is common in patients with advanced heart failure. Circulation 2003, 107, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Abe, T.; Mizuno, A.; Goda, A.; Izumi, Y.; Yagawa, M.; Akita, K.; Sawano, M.; Inohara, T.; et al. Validation of the Get With The Guideline-Heart Failure risk score in Japanese patients and the potential improvement of its discrimination ability by the inclusion of B-type natriuretic peptide level. Am. Heart J. 2016, 171, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, K.; Kohno, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Nagatomo, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Goda, A.; Mizuno, A.; Sawano, M.; Inohara, T.; et al. Current use of guideline-based medical therapy in elderly patients admitted with acute heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and its impact on event-free survival. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 235, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagawa, M.; Nagatomo, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Mahara, K.; Tomoike, H.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kohno, T.; Mizuno, A.; Goda, A.; Kohsaka, S.; et al. Effect of Obesity on the Prognostic Impact of Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, M.; Kohsaka, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Goda, A.; Izumi, Y.; Yagawa, M.; Mizuno, A.; Sawano, M.; Inohara, T.; Kohno, T.; et al. Effect of estimated plasma volume reduction on renal function for acute heart failure differs between patients with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Kohno, T.; Goda, A.; Shiraishi, Y.; Saji, M.; Nagatomo, Y.; Tanaka, T.D.; Takei, M.; Nakano, S.; Soejima, K.; et al. Malnutrition in real-world patients hospitalized for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and its potential impact on generalizability of EMPEROR-Preserved trial. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 370, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitakata, H.; Kohno, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Parizo, J.T.; Niimi, N.; Goda, A.; Nishihata, Y.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Yoshikawa, T. Prognostic Implications of Early and Midrange Readmissions After Acute Heart Failure Hospitalizations: A Report From a Japanese Multicenter Registry. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, P.A.; Castelli, W.P.; McNamara, P.M.; Kannel, W.B. The natural history of congestive heart failure: The Framingham study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocock, S.J.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Collier, T.J. Statistical Controversies in Reporting of Clinical Trials: Part 2 of a 4-Part Series on Statistics for Clinical Trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2648–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driggin, E.; Cohen, L.P.; Gallagher, D.; Karmally, W.; Maddox, T.; Hummel, S.L.; Carbone, S.; Maurer, M.S. Nutrition Assessment and Dietary Interventions in Heart Failure: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Ponikowski, P.; Varney, S.; Chua, T.P.; Clark, A.L.; Webb-Peploe, K.M.; Harrington, D.; Kox, W.J.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Coats, A.J.S. Wasting as independent risk factor for mortality in chronic heart failure. Lancet 1997, 349, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzeńczyk, A.; Anaszewicz, M.; Wawrzeńczyk, A.; Budzyński, J. Clinical significance of nutritional status in patients with chronic heart failure-a systematic review. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 671–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vest, A.R.; Chan, M.; Deswal, A.; Givertz, M.M.; Lekavich, C.; Lennie, T.; Litwin, S.E.; Parsly, L.; Rodgers, J.E.; Rich, M.W.; et al. Nutrition, Obesity, and Cachexia in Patients With Heart Failure: A Consensus Statement from the Heart Failure Society of America Scientific Statements Committee. J. Card. Fail. 2019, 25, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.; Pellicori, P.; Kazmi, S.; Rigby, A.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Wong, K.; Clark, A.L. Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition Using 3 Scoring Systems Among Outpatients With Heart Failure: A Comparison With Body Mass Index. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Kong, X.; Sun, G. Review of nutritional screening and assessment tools and clinical outcomes in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2016, 21, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Predicting prognosis of heart failure using common malnutrition assessment tools: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scott. Med. J. 2022, 67, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinugasa, Y.; Sota, T.; Kamitani, H.; Nakayama, N.; Nakamura, K.; Hirai, M.; Yanagihara, K.; Kato, M.; Ono, T.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Diagnostic performance of nutritional indicators in patients with heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosy, A.P.; Cerbin, L.P.; Armstrong, P.W.; Butler, J.; Coles, A.; DeVore, A.D.; Dunlap, M.E.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Felker, G.M.; Fudim, M.; et al. Body Weight Change During and After Hospitalization for Acute Heart Failure: Patient Characteristics, Markers of Congestion, and Outcomes: Findings From the ASCEND-HF Trial. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pereira, S.L.; Luo, M.; Matheson, E.M. Evaluation of Blood Biomarkers Associated with Risk of Malnutrition in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sze, S.; Zhang, J.; Pellicori, P.; Morgan, D.; Hoye, A.; Clark, A.L. Prognostic value of simple frailty and malnutrition screening tools in patients with acute heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2017, 106, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Koyama, S.; Kuragaichi, T.; Shiba, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Takatsu, Y.; Sato, Y. Prognostic Value of Rising Serum Albumin During Hospitalization in Patients With Acute Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, P.; Cui, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X. Serum albumin and the short-term mortality in individuals with congestive heart failure in intensive care unit: An analysis of MIMIC. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotsman, I.; Shauer, A.; Zwas, D.R.; Tahiroglu, I.; Lotan, C.; Keren, A. Low serum albumin: A significant predictor of reduced survival in patients with chronic heart failure. Clin. Cardiol. 2019, 42, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plitt, G.D.; Spring, J.T.; Moulton, M.J.; Agrawal, D.K. Mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and diastolic dysfunction. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2018, 16, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Empel, V.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P. Inflammation in HFpEF: Key or circumstantial? Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 189, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Palomas, J.L.; Gámez-López, A.L.; Castillo-Domínguez, J.C.; Moreno-Conde, M.; López Ibáñez, M.C.; Alhambra Expósito, R.; Ramiro Ortega, E.; Anguita-Sánchez, M.P.; Villar-Ráez, A. Nutritional Intervention in Malnourished Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure. Arch. Med. Res. 2016, 47, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Kohno, T.; Goda, A.; Nagatomo, Y.; Nishihata, Y.; Saji, M.; Takei, M.; Ikegami, Y.; et al. Potential association with malnutrition and allocation of combination medical therapies in hospitalized heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | a-GNRI < 92 N = 568 | a-GNRI ≥ 92 N = 906 | p-Value | d-GNRI < 92 N = 796 | d-GNRI ≥ 92 N = 678 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNRI | ||||||
| at admission | 86.4 (81.5–89.3) | 98.1 (95.0–101.3) | <0.001 | 89.6 (83.9–94.0) | 98.3 (94.1–102.1) | <0.001 |
| at discharge | 83.4 (77.3–89.3) | 95.3 (89.8–99.8) | <0.001 | 84.9 (78.9–88.9) | 97.4 (94.7–101.3) | <0.001 |
| Age (years) | 79.0 (69.3–85.0) | 74.0 (63.0–81.0) | <0.001 | 79.0 (71.0–85.0) | 70.0 (60.0–80.0) | <0.001 |
| Male | 51.4 (292/568) | 62.9 (570/906) | <0.001 | 51.4 (409/796) | 66.8 (453/678) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| at admission | 21.1 (18.5–24.6) | 24.0 (21.8–26.6) | <0.001 | 21.5 (19.1–24.6) | 24.7 (22.6–27.5) | <0.001 |
| at discharge | 19.3 (17.0–22.2) | 22.2 (20.2–24.9) | <0.001 | 19.7 (17.5–22.3) | 22.9 (21.1–25.5) | <0.001 |
| NYHA classification 3 or 4 | 86.7 (488/563) | 79.8 (713/894) | 0.001 | 86.3 (679/787) | 77.9 (522/670) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 72.2 (410/568) | 68.7 (622/906) | 0.161 | 73.5 (585/796) | 65.9 (447/678) | 0.002 |
| Dyslipidemia | 38.2 (216/565) | 43.9 (395/899) | 0.034 | 40.0 (316/790) | 43.8 (295/674) | 0.151 |
| Diabetes | 36.4 (207/568) | 38.6 (350/906) | 0.408 | 38.6 (307/796) | 36.9 (250/678) | 0.518 |
| Smoking | 35.5 (200/563) | 42.4 (378/892) | 0.010 | 35.7 (280/785) | 44.5 (298/670) | 0.001 |
| Hemodialysis | 4.0 (23/568) | 3.3 (30/905) | 0.475 | 5.5 (44/796) | 1.3 (9/677) | <0.001 |
| COPD | 5.1 (29/568) | 4.4 (40/900) | 0.613 | 5.6 (44/792) | 3.7 (25/676) | 0.108 |
| History of HF hospitalization | 29.8 (169/568) | 29.3 (265/905) | 0.860 | 31.5 (251/796) | 27.0 (183/677) | 0.066 |
| Etiology | ||||||
| Ischemic | 31.0 (176/568) | 28.3 (256/906) | 0.265 | 31.0 (247/796) | 27.3 (185/678) | 0.121 |
| Valvular | 25.9 (147/568) | 22.2 (201/906) | 0.115 | 27.4 (218/796) | 19.2 (130/678) | <0.001 |
| Laboratory data at admission | ||||||
| Hgb (g/dL) | 11.2 (9.8–12.8) | 12.5 (10.8–14.2) | <0.001 | 11.3 (9.9–13.0) | 12.8 (11.2–14.3) | <0.001 |
| Na (mEq/L) | 139.0 (136.0–142.0) | 140.0 (138.0–142.0) | <0.001 | 139.0 (137.0–142.0) | 140.0 (138.0–142.0) | <0.001 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 23.3 (17.1–37.1) | 20.7 (16.0–29.0) | <0.001 | 23.5 (17.6–37.1) | 19.9 (15.2–26.7) | <0.001 |
| Alb (mg/dL) | 3.2 (2.9–3.4) | 3.8 (3.6–4.1) | <0.001 | 3.4 (3.1–3.7) | 3.8 (3.6–4.1) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1.0 (0.3–3.2) | 0.3 (0.1–1.1) | <0.001 | 0.8 (0.2–2.6) | 0.3 (0.1–1.0) | <0.001 |
| BNP (pg/mL) | 906.4 (481.6–1602.2) | 632.2 (339.3–1060.3) | <0.001 | 901.0 (481.8–1585.0) | 560.3 (314.8–1005.3) | <0.001 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 5470 (2448–13218) | 3203 (1709–6655) | <0.001 | 5578 (2493–13529) | 2736 (1518–5140) | <0.001 |
| Laboratory data at discharge | ||||||
| Hgb (g/dL) | 11.0 (9.8–12.7) | 12.4 (10.8–14.0) | <0.001 | 11.0 (9.8–12.5) | 12.9 (11.5–14.5) | <0.001 |
| Na (mEq/L) | 139.0 (137.0–141.0) | 139.0 (137.0–141.0) | 0.008 | 139.0 (137.0–141.0) | 139.0 (137.0–141.0) | 0.012 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 23.8 (17.4–35.2) | 22.0 (16.5–30.0) | 0.001 | 23.6 (17.0–34.7) | 21.6 (16.5–28.7) | <0.001 |
| Alb (mg/dL) | 3.2 (2.9–3.5) | 3.7 (3.4–4.0) | <0.001 | 3.2 (2.9–3.4) | 3.9 (3.7–4.1) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.5 (0.1–1.3) | 0.3 (0.1–0.9) | <0.001 | 0.6 (0.2–1.4) | 0.2 (0.1–0.6) | <0.001 |
| BNP (pg/mL) | 319.0 (177.2–570.1) | 207.2 (102.0–442.3) | <0.001 | 351.8 (194.9–628.7) | 179.0 (94.4–341.0) | <0.001 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 2932 (1416–7688) | 1846 (1022–3205) | 0.002 | 2905 (1609–6585) | 1585 (755–2489) | <0.001 |
| LVEF (%) | 45.0 (32.0–58.4) | 43.9 (31.0–58.0) | 0.173 | 45.8 (32.2–59.0) | 40.0 (30.0–57.0) | <0.001 |
| Medications at discharge | ||||||
| ACEI or ARB | 60.7 (345/568) | 69.3 (628/906) | 0.001 | 60.4 (481/796) | 72.6 (492/678) | <0.001 |
| MRA | 38.7 (220/568) | 40.9 (370/905) | 0.444 | 37.3 (297/796) | 43.3 (293/677) | 0.022 |
| beta-blockers | 75.7 (429/567) | 79.4 (719/906) | 0.106 | 76.6 (609/795) | 79.5 (539/678) | 0.186 |
| Statines | 32.4 (184/568) | 36.6 (331/904) | 0.104 | 32.5 (258/795) | 38.0 (257/677) | 0.028 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 16 (10–27) | 14 (10–21) | <0.001 | 15 (10–26) | 14 (10–21) | 0.001 |
| All-Cause Death | Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | p Value | Adjusted HR * (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-GNRI | ||||
| Categorical (≥92 vs. <92) | 2.09 (1.66–2.63) | <0.001 | 0.77 (0.57–1.05) | 0.104 |
| Continuous (per 1 unit decrease) | 1.06 (1.04–1.07) | <0.001 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 0.341 |
| d-GNRI | ||||
| Categorical (≥92 vs. <92) | 3.82 (2.89–5.05) | <0.001 | 1.96 (1.39–2.75) | <0.001 |
| Continuous (per 1 unit decrease) | 1.08 (1.06–1.09) | <0.001 | 1.06 (1.04–1.09) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ono, M.; Mizuno, A.; Kohsaka, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kohno, T.; Nagatomo, Y.; Goda, A.; Nakano, S.; Komiyama, N.; Yoshikawa, T. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index at Hospital Admission or Discharge in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051891
Ono M, Mizuno A, Kohsaka S, Shiraishi Y, Kohno T, Nagatomo Y, Goda A, Nakano S, Komiyama N, Yoshikawa T. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index at Hospital Admission or Discharge in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051891
Chicago/Turabian StyleOno, Masafumi, Atsushi Mizuno, Shun Kohsaka, Yasuyuki Shiraishi, Takashi Kohno, Yuji Nagatomo, Ayumi Goda, Shintaro Nakano, Nobuyuki Komiyama, and Tsutomu Yoshikawa. 2023. "Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index at Hospital Admission or Discharge in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051891
APA StyleOno, M., Mizuno, A., Kohsaka, S., Shiraishi, Y., Kohno, T., Nagatomo, Y., Goda, A., Nakano, S., Komiyama, N., & Yoshikawa, T. (2023). Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index at Hospital Admission or Discharge in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051891






