Interrelationships of Sleep Quality, Obesity Severity, and Clinical Headache Features among Women with Comorbid Migraine and Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Migraine Diagnosis, BMI, and Medical History
2.2. Sleep Quality
2.3. Migraine Characteristics, Clinical Features, and Allodynia
2.4. Potential Confounders
2.5. Analytic Plan
3. Results
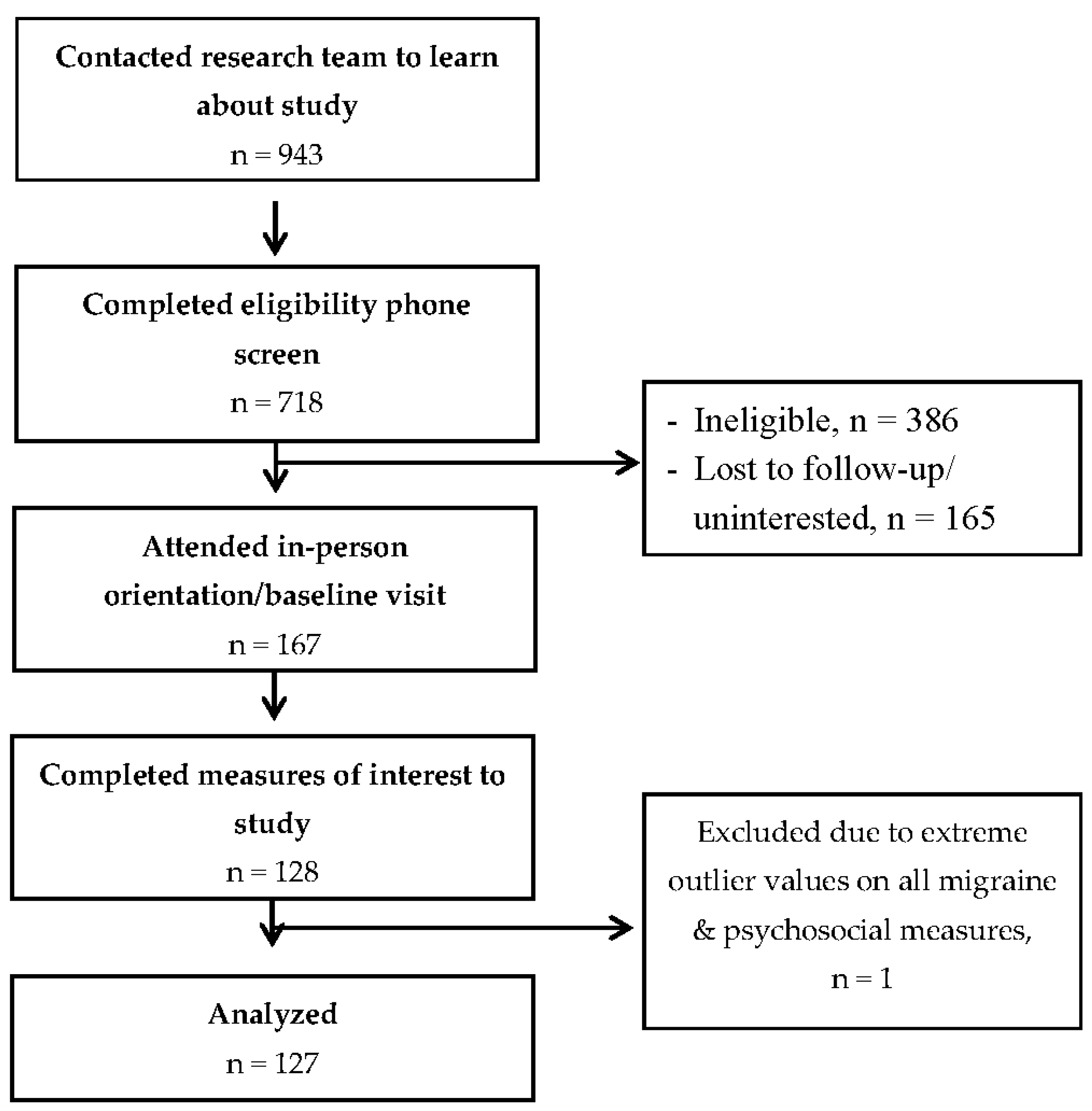
3.1. Participant Flow and Descriptive Characteristics
3.2. Migraine Characteristics/Clinical Features and BMI in Relation to Sleep Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burstein, R.; Noseda, R.; Borsook, D. Migraine: Multiple processes, complex pathophysiology. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 6619–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine: Epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, J.M.; Vieira, J.R.; Lipton, R.B.; Bond, D.S. Association between obesity and migraine in women. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2017, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.S.; Roth, J.; Nash, J.M.; Wing, R.R. Migraine and obesity: Epidemiology, possible mechanisms and the potential role of weight loss treatment. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e362–e371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatami, M.; Soveid, N.; Lesani, A.; Djafarian, K.; Shab-Bidar, S. Migraine and obesity: Is there a relationship? A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 20, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.; Manack, A.; Serrano, D.; Turkel, C.; Lipton, R. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.-J.; Cho, S.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Yang, K.I.; Yun, C.-H.; Chu, M.K. Poor sleep quality in migraine and probable migraine: A population study. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Lin, G.Y.; Lee, J.T.; Lee, M.S.; Tsai, C.K.; Hsu, Y.W.; Lin, Y.Z.; Tsai, Y.C.; Yang, F.C. Associations between sleep quality and migraine frequency: A cross-sectional case-control study. Medicine 2016, 95, e3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, A.B.; Hamer, J.D.; Smitherman, T.A. Sleep disturbance and affective comorbidity among episodic migraineurs. Headache 2014, 54, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, C.; Vacca, A.; Felbush, A.; Filimonova, T.; Gai, A.; Glazyrina, T.; Hubalek, I.A.; Marchenko, Y.; Overeem, L.H.; Piroso, S. Migraine and sleep disorders: A systematic review. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.; Pavlović, J.M. Sleep disorders and migraine: Review of literature and potential pathophysiology mechanisms. Headache 2018, 58, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Rains, J.C.; Pavlovic, J.M.; Fanning, K.M.; Reed, M.L.; Manack Adams, A.; Lipton, R.B. Sleep disorders among people with migraine: Results from the chronic migraine epidemiology and outcomes (cameo) study. Headache 2019, 59, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Bixler, E.O.; Chrousos, G.P. Obesity-related sleepiness and fatigue: The role of the stress system and cytokines. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1083, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-G.; Park, S.-P. Significance of fatigue in patients with migraine. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 50, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cho, S.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Yang, K.I.; Yun, C.-H.; Chu, M.K. Excessive daytime sleepiness is associated with an exacerbation of migraine: A population-based study. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.C.; Dawson, S.C.; Taylor, H.L.; Park, M.; Burgess, H.J.; Crawford, M.R.; Rains, J.C.; Smitherman, T.A.; Espie, C.A.; Jones, A.L. A micro-longitudinal study of naps, sleep disturbance, and headache severity in women with chronic migraine. Behav. Sleep Med. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovati, C.; D’Amico, D.; Bertora, P.; Raimondi, E.; Rosa, S.; Zardoni, M.; Bussone, G.; Mariani, C. Correlation between presence of allodynia and sleep quality in migraineurs. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 31, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajria, K.; Lee, L.K.; Flores, N.M.; Aycardi, E.; Gandhi, S.K. Humanistic and economic burden of nausea and vomiting among migraine sufferers. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.P.; Martin, P.R.; Boschen, M.J. Psychological sleep interventions for migraine and tension-type headache: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.S.; Thomas, J.G.; Lipton, R.B.; Roth, J.; Pavlovic, J.M.; Rathier, L.; O’Leary, K.C.; Evans, E.W.; Wing, R.R. Behavioral weight loss intervention for migraine: A randomized controlled trial. Obesity 2018, 26, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (HIS). The international classification of headache disorders, (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F., III; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.; Li, W.; Mostofsky, E.; Mittleman, M.A.; Bertisch, S.M. Baseline sleep quality, stress, and depressive symptoms, and subsequent headache occurrence in a six-week prospective cohort study of patients with episodic migraine. Headache 2021, 61, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.C.; Motivala, S.J.; Buysse, D.J.; Oxman, M.N.; Levin, M.J.; Irwin, M.R. Validation of a 3-factor scoring model for the pittsburgh sleep quality index in older adults. Sleep 2006, 29, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Bigal, M.E.; Ashina, S.; Burstein, R.; Silberstein, S.; Reed, M.L.; Serrano, D.; Stewart, W.F.; Group AMPPA. Cutaneous allodynia in the migraine population. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radloff, L.S. The ces-d scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 1977, 1, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.L.; Kroenke, K.; Williams, J.B.; Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The gad-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. Perceived stress scale. Meas. Stress Guide Health Soc. Sci. 1994, 10, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Unick, J.L.; Bond, D.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Vithiananthan, S.; Ryder, B.A.; Roye, G.D.; Pohl, D.; Trautvetter, J.; Wing, R.R. Comparison of two objective monitors for assessing physical activity and sedentary behaviors in bariatric surgery patients. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetten, A.A.; Batterham, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Tapsell, L. Relative validity of 3 accelerometer models for estimating energy expenditure during light activity. J. Phys. Act. Health 2014, 11, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebe, D.; Ehrman, J.K.; Liguori, G.; Magal, M.; American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 10th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, K.W.; Watson, K.; Himes, J.H.; Baranowski, T.; Rochon, J.; Waclawiw, M.; Sun, W.; Stevens, M.; Slawson, D.L.; Matheson, D. Evaluation of quality control procedures for 24-h dietary recalls: Results from the girls health enrichment multisite studies. Prev. Med. 2004, 38, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.E.; Raynor, H.A.; Howie, W.; Lipton, R.B.; Thomas, G.J.; Wing, R.R.; Pavlovic, J.; Farris, S.G.; Bond, D.S. Associations between lifestyle intervention-related changes in dietary targets and migraine headaches among women in the women’s health and migraine (wham) randomized controlled trial. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2020, 6, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahe, C.; Czira, M.E.; Teismann, H.; Berger, K. Associations between poor sleep quality and different measures of obesity. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.C.; Yang, Y.C.; Ou, H.Y.; Wu, J.S.; Lu, F.H.; Chang, C.J. The association between self-reported sleep quality and overweight in a chinese population. Obesity 2013, 21, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Cartledge, S.; Maddison, R.; Islam, S.M.S. Association of overweight and obesity with obstructive sleep apnoea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Med. 2020, 17, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaratna, C.V.; Perret, J.L.; Lodge, C.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Campbell, B.E.; Matheson, M.C.; Hamilton, G.S.; Dharmage, S.C. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in the general population: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 34, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, N.; Kulkarni, G.; Taly, A.; Rao, S.; Sinha, S. Sleep disturbances in ‘migraine without aura’—A questionnaire based study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 321, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriot, J.J.; Toga, A.W.; Prakash, N.; Ju, Y.S.; Brennan, K. Cortical sensory plasticity in a model of migraine with aura. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 15252–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robblee, J.; Starling, A.J. Seeds for success: Lifestyle management in migraine. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2019, 86, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.J.; Yun, C.H.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, W.J.; Yang, K.I.; Chu, M.K. Short sleep duration and poor sleep quality among migraineurs: A population-based study. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, W.J.; Yang, K.I.; Yun, C.H.; Chu, M.K. Insufficient sleep is prevalent among migraineurs: A population-based study. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertisch, S.M.; Li, W.; Buettner, C.; Mostofsky, E.; Rueschman, M.; Kaplan, E.R.; Fung, J.; Huntington, S.; Murphy, T.; Stead, C. Nightly sleep duration, fragmentation, and quality and daily risk of migraine. Neurology 2020, 94, e489–e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naufel, M.F.; Frange, C.; Andersen, M.L.; Girão, M.J.B.C.; Tufik, S.; Beraldi Ribeiro, E.; Hachul, H. Association between obesity and sleep disorders in postmenopausal women. Menopause 2018, 25, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlhöfer, J.; Karschin, J.; Breusing, N.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Relationship between actigraphy-assessed sleep quality and fat mass in college students. Obesity 2016, 24, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.H.; Theorell-Haglöw, J.; Janson, C.; Svartengren, M.; Elmståhl, S.; Lind, L.; Lindberg, E. Insomnia symptoms and sleep duration and their combined effects in relation to associations with obesity and central obesity. Sleep Med. 2018, 46, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.; Abdullah, H.R.; Liao, P. STOP-Bang questionnaire: A practical approach to screen for obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 2016, 149, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Befus, D.R.; Irby, M.B.; Coeytaux, R.R.; Penzien, D.B. A critical exploration of migraine as a health disparity: The imperative of an equity-oriented, intersectional approach. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2018, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begasse de Dhaem, O.; Kiarashi, J.; Armand, C.E.; Charleston, I.V.L.; Szperka, C.L.; Lee, Y.S.; Rajapakse, T.; Seng, E.K.; VanderPluym, J.H.; Starling, A.J. Ten eleven things to facilitate participation of underrepresented groups in headache medicine research. Headache 2021, 61, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla-Neto, J.; Amaral, F.G.; Afeche, S.C.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin, energy metabolism, and obesity: A review. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Full Sample (n = 127) | Participants with Poor Sleep (n = 88) | Participants with Good Sleep (n = 39) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), M (SD) | 38.3 (8.0) | 38.2 (7.7) | 38.6 (8.8) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| Black | 16 (12.6%) | 14 (15.9%) | 2 (5.1%) |
| White | 97 (76.4%) | 63 (71.6%) | 34 (87.2%) |
| More than one race | 3 (2.4%) | 3 (3.4%) | 0 |
| Other | 11 (8.7%) | 8 (9.1%) | 3 (7.7%) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic | 23 (18.1%) | 17 (19.3%) | 6 (15.4) |
| Not Hispanic | 104 (81.9%) | 71 (80.7%) | 33 (84.6%) |
| Marital Status, n (%) | |||
| Married or living with significant other | 77 (60.6%) | 49 (55.7%) | 28 (71.8%) |
| Separated or divorced | 16 (12.6%) | 10 (11.4%) | 6 (15.4%) |
| Never married | 32 (25.2%) | 27 (30.7%) | 5 (12.8%) |
| Other | 2 (1.6%) | 2 (2.3%) | 0 |
| Educational attainment, n (%) | |||
| High school degree or less | 12 (9.4%) | 8 (9.1%) | 4 (10.3%) |
| Vocational training or some college | 38 (30.0%) | 24 (27.3%) | 14 (35.9%) |
| College/university degree | 52 (40.9%) | 37 (42.0%) | 15 (38.5%) |
| Graduate degree | 25 (19.7%) | 19 (21. | 6 (15.4%) |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | |||
| Lifetime diagnosis | 8 (6.3%) | 7 (8.0%) | 1 (2.6%) |
| Current use of CPAP machine | 4 (3.1%) | 3 (3.4%) | 1 (2.6%) |
| Continuous Variables | ||
| Variable | Mean (SD) | Median (25%, 75%) |
| PSQI overall subjective sleep quality score | 7.9 (3.7) | 8.0 (5.0, 11.0) |
| PSQI sleep efficiency score | 2.2 (1.7) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) |
| PSQI subjective sleep quality score | 3.1 (2.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 5.0) |
| PSQI daily disturbances score | 2.7 (1.0) | 3.0 (2.0, 3.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 36.1 (6.6) | 34.9 (30.3, 40.4) |
| Monthly migraine days | 8.4 (4.6) | 7.0 (5.0, 11.0) |
| Pain intensity (0–10) | 5.8 (1.6) | 5.8 (4.8, 7.0) |
| Attack duration (hours) | 18.2 (9.8) | 16.0 (12.0, 20.9) |
| Allodynia | 5.1 (3.8) | 4.0 (2.0, 7.0) |
| Perceived stress | 16.8 (6.6) | 17.0 (12.0, 22.0) |
| Average daily moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (min) | 42.9 (32.4) | 36.0 (23.9, 53.1) |
| Average daily caffeine intake (mg) | 152.6 (171.2) | 116.9 (40.7, 203.3) |
| Average daily alcohol intake (g) | 4.2 (10.8) | 0 (0, 0.3) |
| Categorical Variables | ||
| Variable | n (%) | |
| Nausea frequency | ||
| Low (0–33.3% of episodes) | 48 (38.1%) | |
| Medium (33.4–66.7% of episodes) | 42 (33.3%) | |
| High (66.8–100% of episodes) | 36 (29.9%) | |
| Photophobia (present at all episodes) | 77 (60.6%) | |
| Phonophobia (present at any episodes) | 53 (41.7%) | |
| Anxiety (GAD-7 10) | 31 (24.4%) | |
| Depression (CES-D 16) | 56 (44.1%) | |
| Continuous Variables | ||||
| Participants with Poor Sleep | Participants with Good Sleep | |||
| Variable | Mean (SD) | Median (25%, 75%) | Mean (SD) | Median (25%, 75%) |
| PSQI overall subjective sleep quality score | 9.9 (2.5) | 10.0 (8.0, 12.0) | 3.6 (1.3) | 4.0 (3.0, 5.0) |
| PSQI sleep efficiency score | 2.9 (1.5) | 3.0 (2.0, 4.0) | 0.7 (0.7) | 1.0 (0, 1.0) |
| PSQI subjective sleep quality score | 3.9 (1.8) | 3.0 (3.0, 5.0) | 1.1 (0.8) | 1.0 (0, 2.0) |
| PSQI daily disturbances score | 3.1 (0.9) | 3.0 (3.0, 4.0) | 1.9 (0.8) | 2.0 (1.0, 2.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 36.1 (6.6) | 35.4 (30.6, 40.9) | 34.0 (6.3) | 33.1 (29.7, 37.3) |
| Monthly migraine days | 8.5 (4.9) | 8.0 (5.0, 11.0) | 8.4 (4.6) | 7.0 (5.0, 11.0) |
| Pain intensity (0–10) | 6.1 (1.6) | 6.0 (5.2, 7.3) | 5.3 (1.4) | 5.4 (4.3, 6.3) |
| Attack duration (hours) | 19.0 (10.2) | 16.6 (12.6, 21.0) | 16.4 (8.9) | 14.9 (11.0, 21.0) |
| Allodynia | 5.4 (3.7) | 4.5 (2.0, 7.0) | 5.1 (3.8) | 4.0 (1.0, 8.0) |
| Perceived stress | 18.0 (6.5) | 17.5 (13.0, 22.0) | 16.5 (6.6) | 14.0 (10.0, 19.0) |
| Average daily moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (min) | 40.1 (29.4) | 32.3 (23.0, 49.6) | 49.2 (37.9) | 37.5 (24.6, 69.1) |
| Average daily caffeine intake (mg) | 165.8 (190.2) | 124.7 (43.1, 214.0) | 122.7 (114.2) | 104.8 (33.8, 185.1) |
| Average daily alcohol intake (g) | 4.5 (11.3) | 0 (0, 0.5) | 3.6 (9.4) | 0 (0, 0.2) |
| Categorical Variables | ||||
| Participants with Poor Sleep | Participants with Good Sleep | |||
| Variable | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Nausea frequency | ||||
| Low (0–33.3% of episodes) | 32 (36.8%) | 16 (41.0%) | ||
| Medium (33.4–66.7% of episodes) | 31 (35.6%) | 11 (28.2%) | ||
| High (66.8–100% of episodes) | 24 (27.6%) | 12 (30.8%) | ||
| Photophobia (present at all episodes) | 52 (59.8%) | 25 (64.1%) | ||
| Phonophobia (present at any episodes) | 40 (46.0%) | 13 (33.3%) | ||
| Anxiety (GAD-7 10) | 27 (30.7%) | 4 (10.3%) | ||
| Depression (CES-D 16) | 47 (53.4%) | 9 (23.1%) | ||
| Step | Predictor | R2 | ΔR2 | F | b | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.32 | -- | 5.99 *** | |||
| Monthly migraine days | 0.16 * | 0.03, 0.29 | ||||
| BMI | 0.02 | −0.08, 0.12 | ||||
| Anxiety | 0.75 | −0.90, 2.40 | ||||
| Depression | 1.87 * | 0.42, 3.32 | ||||
| Perceived stress | 0.12 | <−0.01, 0.23 | ||||
| Daily physical activity | −0.01 | −0.03, 0.01 | ||||
| Daily wear time | −0.01 * | −0.01, 0.00 | ||||
| Daily caffeine intake | <0.01 | <−0.01, <0.01 | ||||
| Daily alcohol intake | 0.01 | −0.05, 0.06 | ||||
| 2 | 0.32 | 0.01 | 5.46 *** | |||
| Monthly migraine days | 0.15 * | 0.02, 0.28 | ||||
| BMI | 0.02 | −0.08, 0.12 | ||||
| Anxiety | 0.78 | −0.88, 2.43 | ||||
| Depression | 1.87 * | 0.42, 3.32 | ||||
| Perceived stress | 0.12 | −0.01, 0.23 | ||||
| Daily physical activity | −0.01 | −0.03, 0.01 | ||||
| Daily wear time | −0.01 * | −0.01, <0.01 | ||||
| Daily caffeine intake | <0.01 | <−0.01, <0.01 | ||||
| Daily alcohol intake | 0.01 | −0.05, 0.06 | ||||
| Monthly migraine days X BMI | 0.01 | −0.01, 0.03 |
| Migraine Characteristic or Clinical Feature | PSQI Sleep Quality Measure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Score | Sleep Efficiency | Sleep Quality | Daily Disturbance | |||||
| b (95% CI) | p | b (95% CI) | p | b (95% CI) | p | b (95% CI) | p | |
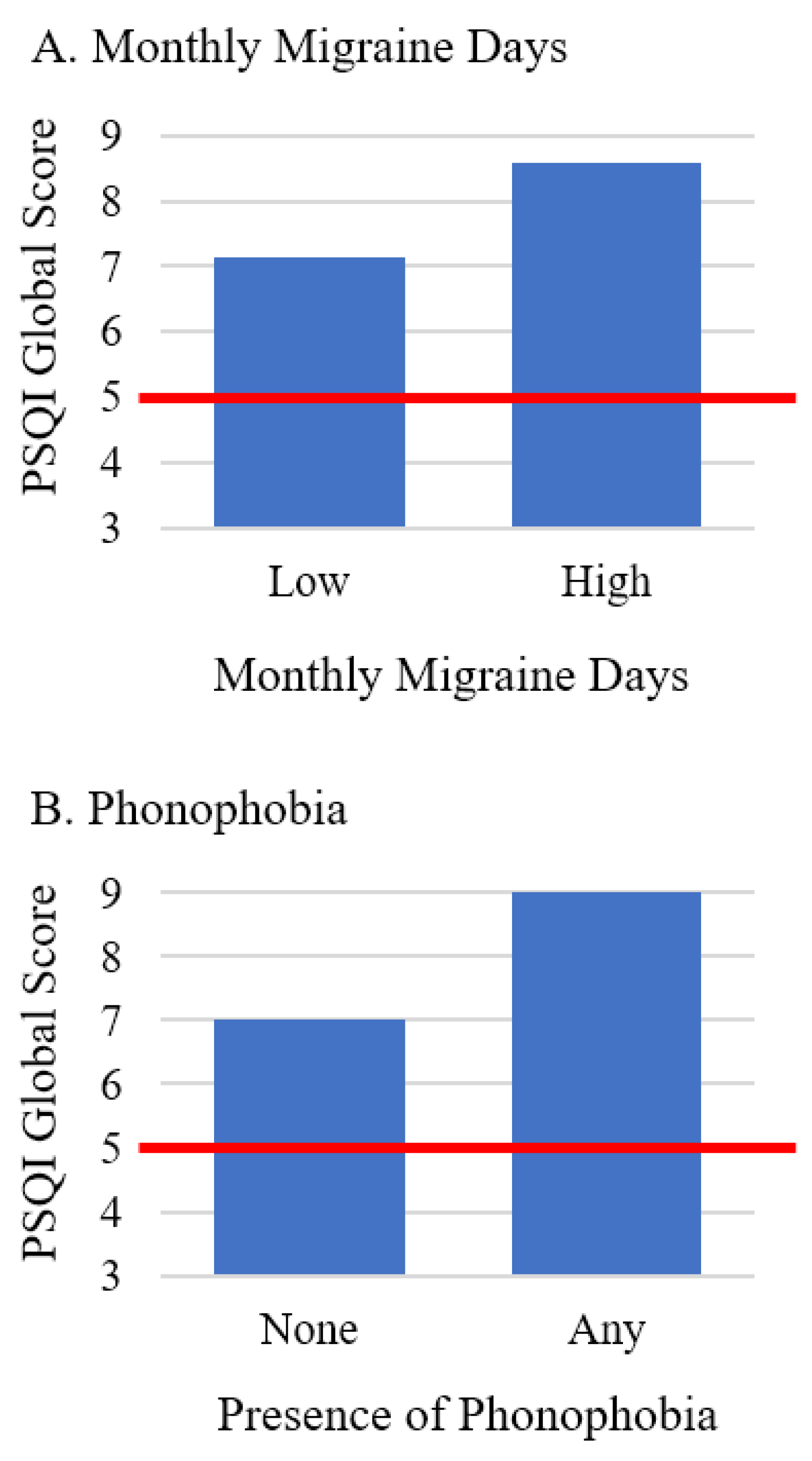
| Monthly migraine days | 0.16 (0.03, 0.29) | 0.016 | 0.02 (<0.01, 0.03) | 0.033 | <0.01 (<−0.01, 0.03) | 0.289 | 0.03 (<−0.01, 0.06) | 0.104 |
| Pain intensity | 0.32 (−0.06,0 69) | 0.097 | 0.03 (−0.02, 0.07) | 0.291 | 0.04 (−0.01, 0.08) | 0.122 | 0.07 (−0.02, 0.17) | 0.139 |
| Attack duration a | 0.03 (−0.03, 0.09) | 0.380 | 0.01 (<−0.01, 0.01) | 0.112 | <0.01 (<−0.01, 0.01) | 0.739 | <0.01 (−0.02, 0.02) | 0.872 |
| Allodynia | 0.14 (−0.01, 0.29) | 0.073 | <0.01 (−0.02, 0.02) | 0.997 | 0.02 (<−0.01, 0.04) | 0.090 | 0.04 (<−0.03, 0.08) | 0.069 |
| Nausea frequency b | ||||||||
| Medium | 1.33 (−0.08, 2.75) | 0.065 | 0.22 (0.05, 0.39) | 0.012 | 0.08 (−0.11, 0.25) | 0.413 | 0.04 (−0.34, 0.41) | 0.843 |
| High | 0.80 (−0.66, 2.26) | 0.278 | 0.06 (−0.11, 0.24) | 0.475 | 0.06 (−0.13, 0.24) | 0.553 | 0.16 (−0.23, 0.55) | 0.424 |
| Photophobia b | −0.69 (−1.89, 0.50) | 0.254 | −0.09 (−0.24, 0.05) | 0.214 | −0.04 (−0.19, 0.11) | 0.581 | −0.10 (−0.41, 0.21) | 0.541 |
| Phonophobia b | 1.85 (0.64, 3.07) | 0.003 | 0.23 (0.09, 0.38) | 0.002 | 0.12 (−0.04, 0.27) | 0.146 | 0.24 (−0.09, 0.56) | 0.147 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schumacher, L.M.; Farris, S.G.; Thomas, J.G.; Lipton, R.B.; Pavlovic, J.; Vgontzas, A.; Bond, D.S. Interrelationships of Sleep Quality, Obesity Severity, and Clinical Headache Features among Women with Comorbid Migraine and Obesity. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051742
Schumacher LM, Farris SG, Thomas JG, Lipton RB, Pavlovic J, Vgontzas A, Bond DS. Interrelationships of Sleep Quality, Obesity Severity, and Clinical Headache Features among Women with Comorbid Migraine and Obesity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051742
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchumacher, Leah M., Samantha G. Farris, J. Graham Thomas, Richard B. Lipton, Jelena Pavlovic, Angeliki Vgontzas, and Dale S. Bond. 2023. "Interrelationships of Sleep Quality, Obesity Severity, and Clinical Headache Features among Women with Comorbid Migraine and Obesity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051742
APA StyleSchumacher, L. M., Farris, S. G., Thomas, J. G., Lipton, R. B., Pavlovic, J., Vgontzas, A., & Bond, D. S. (2023). Interrelationships of Sleep Quality, Obesity Severity, and Clinical Headache Features among Women with Comorbid Migraine and Obesity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051742






