Different Moro Zones of Psoas Major Affect the Clinical Outcomes after Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Retrospective Study of 94 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Procedures
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Outcome Observations
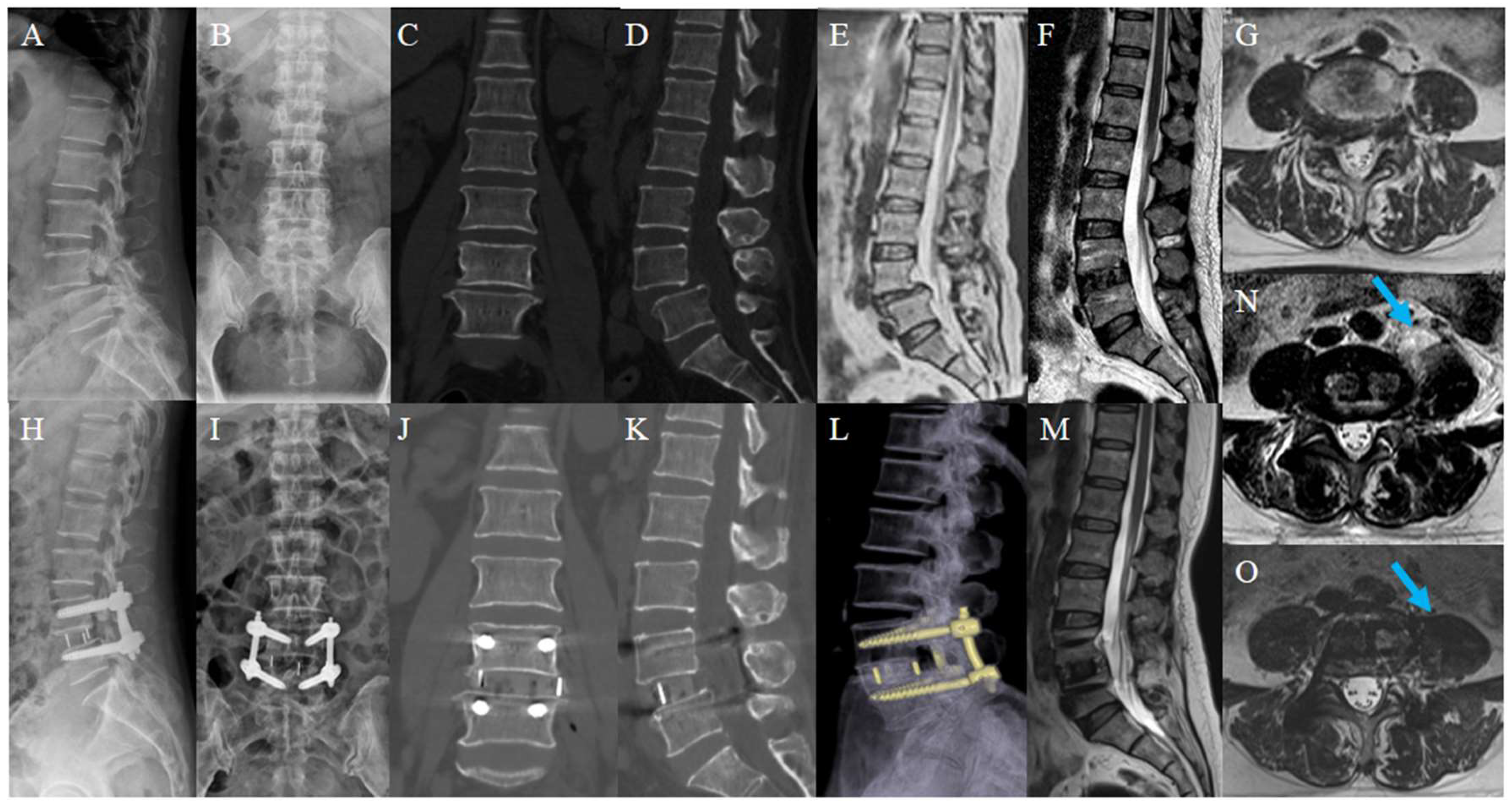
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.5. Statistical Analysis
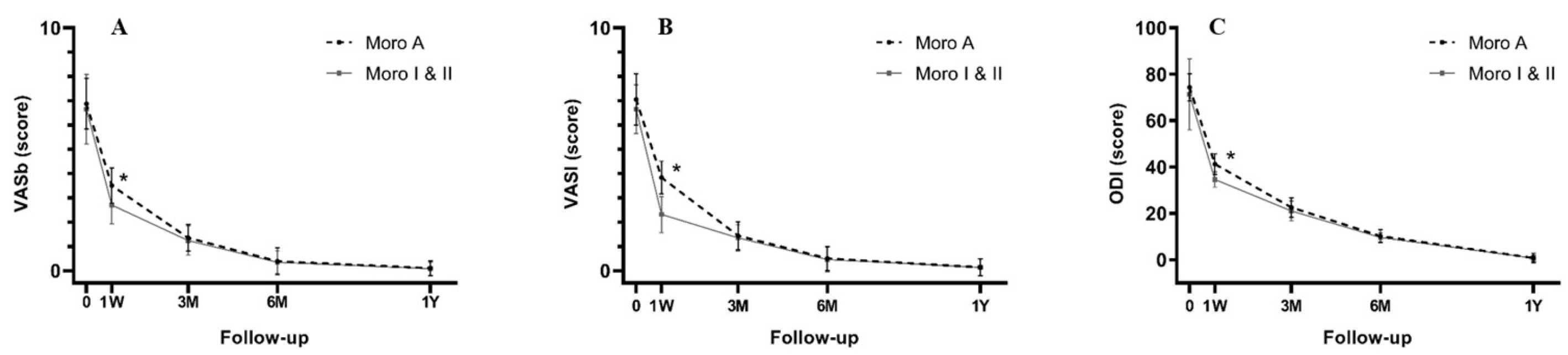
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Z.; Chang, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.M.; Feng, H. Comparing Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Lateral Screw Fixation and Transforaminal Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy (OLIF-TELD) and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) for the Treatment of Adjacent Segment Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4610128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Shao, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W. Comparison of clinical outcomes and spino-pelvic sagittal balance in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: Minimally invasive oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF). Medicine 2021, 100, e23783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Hynes, R.A.; Otsuki, B.; Kimura, H.; Takemoto, M.; Matsuda, S. Effect of indirect neural decompression through oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease. Spine 2015, 40, E175–E182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, W. Development and Application of Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.X.; Phan, K.; Mobbs, R. Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Technical Aspects, Operative Outcomes, and Complications. World Neurosurg. 2017, 98, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckland, A.J.; Ashayeri, K.; Leon, C.; Cheng, I.; Thomas, J.A.; Braly, B.; Kwon, B.; Eisen, L. Anterior column reconstruction of the lumbar spine in the lateral decubitus position: Anatomical and patient-related considerations for ALIF, anterior-to-psoas, and transpsoas LLIF approaches. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 2175–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Tan, J.; Huang, K.; Xie, H.Q. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus oblique lateral interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative disease: A meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.F.; Guo, T.C.; Chen, J.X.; Yu, W.J.; Feng, H.C.; Niu, P.Y.; Zhai, J.B. Efficacy and Safety of Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Versus Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022, 158, e964–e974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H.; Jian, F. Clinical results and complications associated with oblique lumbar interbody fusion technique. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinares, D.M.; Davis, T.T.; Fung, D.A. Retroperitoneal oblique corridor to the L2-S1 intervertebral discs: An MRI study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 24, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, T.; Kikuchi, S.; Konno, S.; Yaginuma, H. An anatomic study of the lumbar plexus with respect to retroperitoneal endoscopic surgery. Spine 2003, 28, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.P.; Kaliya-Perumal, A.K.; Tandon, A.A.; Oh, J.Y. The Oblique Corridor at L4-L5: A Radiographic-Anatomical Study into the Feasibility for Lateral Interbody Fusion. Spine 2020, 45, E552–E559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. Imaging Anatomic Research of Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in a Chinese Population Based on Magnetic Resonance. World Neurosurg. 2019, 128, e51–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhao, Q.M.; Zhang, H.H. Efficacy of Single-Position Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Combined with Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation in Treating Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Cohort Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 856022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; She, Y.; Ou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, W.; Jiang, D. Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion versus Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Single-Center Retrospective Comparative Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6693446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Sonawane, S.; Uotani, K.; Oda, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Arataki, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Takigawa, T.; Ito, Y. Comparison of Simultaneous Single-Position Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation with Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using O-arm Navigated Technique for Lumbar Degenerative Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczki, F.; Turbucz, M.; Kiss, R.; Eltes, P.E.; Lazary, A. Stability Evaluation of Different Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Constructs in Normal and Osteoporotic Condition—A Finite Element Based Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 749914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Xie, T.H.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Z.T.; Song, Y.M.; Zeng, J.C. The Mismatch Between Bony Endplates and Grafted Bone Increases Screw Loosening Risk for OLIF Patients with ALSR Fixation Biomechanically. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 862951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhu, G.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Ge, Z.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Tang, J.; Ren, H.; et al. Application of offset Dingo instruments in Anterior to Psoas (ATP)/Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF) procedure: A retrospective study of 80 patients. Neuro-Chirurgie 2022, 68, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Orita, S.; Mannoji, C.; Motegi, H.; Aramomi, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Kotani, T.; Akazawa, T.; Morinaga, T.; Fujiyoshi, T.; et al. Perioperative Complications in 155 Patients Who Underwent Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Surgery: Perspectives and Indications from a Retrospective, Multicenter Survey. Spine 2017, 42, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.S.; Walker, C.T.; Godzik, J.; Turner, J.D.; Smith, W.; Uribe, J.S. Minimally invasive anterior, lateral, and oblique lumbar interbody fusion: A literature review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGiorgio, A.M.; Edwards, C.S.; Virk, M.S.; Mummaneni, P.V.; Chou, D. Stereotactic navigation for the prepsoas oblique lateral lumbar interbody fusion: Technical note and case series. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 43, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Kawakami, N.; Asazuma, T.; Ito, M.; Mizutani, J.; Nagashima, H.; Nakamura, M.; Sairyo, K.; Takemasa, R.; Iwasaki, M. Complications Associated with Lateral Interbody Fusion: Nationwide Survey of 2998 Cases During the First 2 Years of Its Use in Japan. Spine 2017, 42, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Xiu, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Zeng, J. Minimally Invasive Oblique Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Combined with Anterolateral Screw Fixation for Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease. World Neurosurg. 2020, 135, e671–e678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Zhang, R.J.; Shen, C.L. Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Versus Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Disease. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, e627–e638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.Y.; Xu, Z.W.; He, D.W.; Zhao, X.; Ma, W.H.; Ni, W.F.; Song, Y.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yu, W.; Fang, X.Q.; et al. Complications and Prevention Strategies of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Technique. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 10, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, A.R.; Bang, W.S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, D.C. Psoas weakness following oblique lateral interbody fusion surgery: A prospective observational study with an isokinetic dynamometer. Spine J. 2022, 22, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.H.; Cao, M.D.; Lu, H.; Zhang, K.B. The OLIF working corridor based on magnetic resonance imaging: A retrospective research. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, P.K.; Narain, A.S.; Hijji, F.Y.; Yacob, A.; Yom, K.H.; Phillips, F.M.; Singh, K. Radiographic Analysis of Psoas Morphology and its Association with Neurovascular Structures at L4-5 with Reference to Lateral Approaches. Spine 2017, 42, E1386–E1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyadzis, J.M.; Felbaum, D.; Rhee, J. The rising psoas sign: An analysis of preoperative imaging characteristics of aborted minimally invasive lateral interbody fusions at L4-5. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 20, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Moro A Group | Moro I and II Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 57 | 37 | |
| Age at surgery in years | 60.04 ± 10.03 | 60.68 ± 9.13 | 0.755 |
| No. of M/F | 21/36 | 10/27 | 0.323 |
| BMD in g/cm3 | −2.03 ± 0.83 | −2.00 ± 0.80 | 0.844 |
| BMI in kg/m2 | 23.65 ± 2.59 | 23.66 ± 3.09 | 0.989 |
| Symptom duration in years | 4.92 ± 4.53 | 6.22 ± 6.43 | 0.291 |
| Background diseases | |||
| CVD | 13 (22.81) | 8 (21.62) | 0.893 |
| Diabetes | 1 (1.75) | 2 (5.41) | 0.559 |
| CVD and Diabetes merge | 5 (8.77) | 0 (0) | 0.153 |
| Long-term smoking | 1 (1.75) | 1 (2.70) | 1.000 |
| Main diagnosis | |||
| Discogenic lumbago | 7 (12.28) | 3 (8.11) | 0.735 |
| Spondylolisthesis, instability | 21 (36.84) | 13 (35.14) | 0.376 |
| Lumbar spinal stenosis | 29 (50.88) | 21 (56.76) | 0.577 |
| Parameter | Moro A Group | Moro I & II Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated blood loss in mL | 64.74 ± 25.64 | 54.86 ± 17.25 † | 0.043 | |
| Operation time in minutes | 36.09 ± 5.62 | 37.14 ± 6.25 | 0.401 | |
| Length of hospital stay in days | 8.54 ± 1.55 | 8.49 ± 1.68 | 0.865 | |
| Complications | ||||
| Total complication rate | 26 (45.61) | 8 (21.62) | 0.560 | |
| Cage displacement | 9 (15.79) | 3 (8.11) | 0.353 | |
| Cage subsidence/endplate injury | 3 (5.26) | 3 (8.11) | 0.677 | |
| Thigh pain/numbness, hip flexion weakness | 12 (21.05) | 2 (5.41) † | 0.042 | |
| Sympathetic chain injury | 2 (3.51) | 0 | 0.518 | |
| Parameter | Moro A Group | Moro I & II Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Op | 1-Week Post-Op | Pre-Op | 1-Week Post-Op | |
| DSD in mm | 21.18 ± 1.98 | 22.11 ± 2.10 | ||
| OW in mm | 15.81 ± 3.74 | 15.52 ± 3.69 ‡ | 17.45 ± 3.01 † | 17.36 ± 3.00 †‡ |
| PMSD in mm | 25.17 ± 3.92 | 29.64 ± 4.79 ‡ | 17.51 ± 3.34 * | 20.22 ± 3.90 *‡ |
| PMTD in mm | 29.56 ± 6.11 | 35.42 ± 6.10 ‡ | 29.42 ± 6.30 | 31.71 ± 5.09 §ψ |
| Teardrop-shaped | 12 | 1 † | ||
| Parameter | 1-Week Post-Op VASb | 1-Week Post-Op VASl | 1-Week Post-Op ODI |
|---|---|---|---|
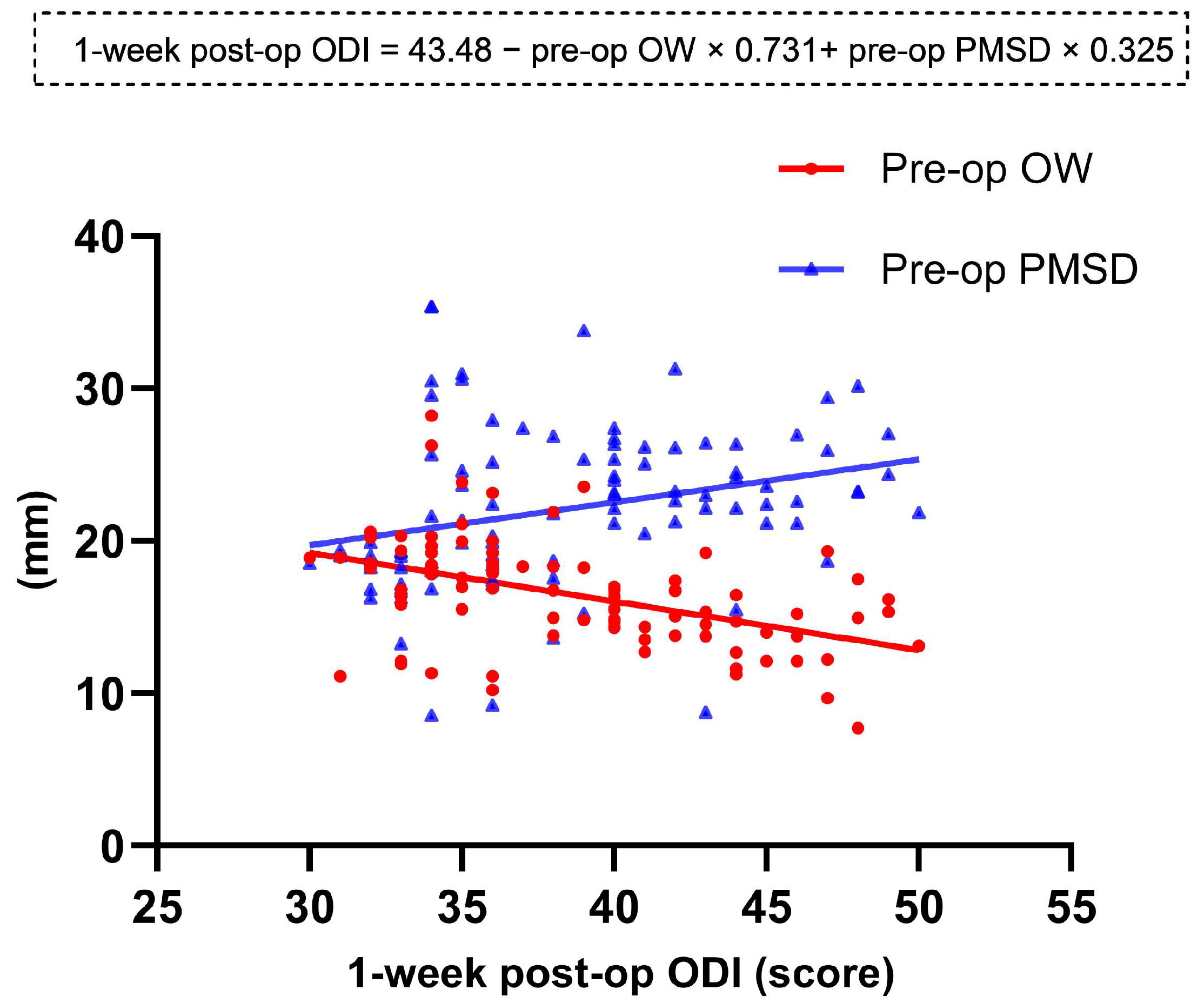
| Pre-op DSD | −0.093 | −0.132 | −0.199 |
| Pre-op OW | −0.014 | −0.018 | −0.465 * |
| Pre-op PMSD | 0.422 * | 0.621 * | 0.276 § |
| Pre-op PMTD | −0.021 | 0.076 | 0.012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, P.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; et al. Different Moro Zones of Psoas Major Affect the Clinical Outcomes after Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Retrospective Study of 94 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030989
Song Z, Chen X, Zhou Z, Chen W, Zhu G, Jiang R, Zhang P, Lin S, Wang X, Yu X, et al. Different Moro Zones of Psoas Major Affect the Clinical Outcomes after Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Retrospective Study of 94 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030989
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zefeng, Xingda Chen, Zelin Zhou, Wanyan Chen, Guangye Zhu, Rueishiuan Jiang, Peng Zhang, Shaohao Lin, Xiaowen Wang, Xiang Yu, and et al. 2023. "Different Moro Zones of Psoas Major Affect the Clinical Outcomes after Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Retrospective Study of 94 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030989
APA StyleSong, Z., Chen, X., Zhou, Z., Chen, W., Zhu, G., Jiang, R., Zhang, P., Lin, S., Wang, X., Yu, X., Ren, H., Liang, D., Cui, J., Tang, J., & Jiang, X. (2023). Different Moro Zones of Psoas Major Affect the Clinical Outcomes after Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Retrospective Study of 94 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030989






