SARS-CoV-2 Serum Viral Load and Prognostic Markers Proposal for COVID-19 Pneumonia in Low-Dose Radiation Therapy Treated Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Enrollment and Study Design
2.2. Blood Samples
2.3. RNA Serum Extraction
2.4. RT-PCR and SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load Quantification
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings
3.2. RT-PCR and SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load Quantification Findings
3.3. LDRT and SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load Quantification Findings
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimrane, A.; Laaradia, M.A.; Sereno, D.; Perrin, P.; Draoui, A.; Bougadir, B.; Hadach, M.; Zahir, M.; Fdil, N.; el Hiba, O.; et al. Insight into COVID-19′s epidemiology, pathology, and treatment. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.; Rajakumar, T.; Malathi, M.; Manikandan, N.; Nagaraj, J.; Santhakumar, A.; Elangovan, A.; Malik, Y.S. Epidemiology and pathobiology of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) in comparison with SARS, MERS: An updated overview of current knowledge and future perspectives. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 10, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, N.; Zaldívar-López, S.; Garrido, J.; Montoya, M. SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Proteins in Viral Pathogenesis: Knowns and Unknowns. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 708264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, S.D.; Mortaz, E.; Jamaati, H.; Tabarsi, P.; Bayram, H.; Varahram, M.; Adcock, I.M. COVID-19: Molecular and Cellular Response. Front. Cel. Infec. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 563085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajnzylber, J.; Regan, J.; Coxen, K.; Corry, H.; Wong, C.; Rosenthal, A.; Worrall, D.; Giguel, F.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; Atyeo, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketcham, S.; Bolig, T.C.; Molling, D.J.; Sjoding, M.W.; Flanders, S.A.; Prescott, H.C. Causes and Circumstances of Death among Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.; Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Y. The signal pathways and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Sig. Transd. Targ. Ther. 2021, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lan, Z.; Ye, J.; Pang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Qin, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, P. Cytokine Storm: The Primary Determinant for the Pathophysiological Evolution of COVID-19 Deterioration. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 589095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Therapeutics and COVID-19: Living Guideline, 16 September 2022; (WHO/2019-nCoV/therapeutics/2022.5); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, M.; Algara, M.; de Febrer, G.; Rubio, C.; Sanz, X.; de la Casa, M.A.; Vasco, C.; Marín, J.; Fernández-Letón, P.; Villar, J.; et al. Could pulmonary low-dose radiation therapy be an alternative treatment for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia? Preliminary results of a multicenter SEOR-GICOR nonrandomized prospective trial (IPACOVID trial). Strahlenther. Onkol. 2021, 197, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Acosta, J.C.; Torres-Royo, L.; de Febrer, G.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Castañé, H.; Jiménez, A.; Vasco, C.; Araguas, P.; Gómez, J.; et al. Effect of Low-Dose Radiotherapy on the Circulating Levels of Paraoxonase-1-Related Variables and Markers of Inflammation in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.B.; Nasti, T.H.; Dhere, V.R.; Kleber, T.J.; Switchenko, J.M.; Buchwald, Z.S.; Stokes, W.A.; Weinberg, B.D.; Rouphael, N.; Steinberg, J.P.; et al. Immunomodulatory Low-Dose Whole-Lung Radiation for Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Pneumonia. Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Olmedo, E.; Suárez-Gironzini, V.; Pérez, M.; Filigheddu, T.; Mínguez, C.; Sanjuan-Sanjuan, A.; González, J.A.; Rivas, D.; Gorospe, L.; Larrea, L.; et al. COVID-19 pneumonia treated with ultra-low doses of radiotherapy (ULTRA-COVID study): A single institution report of two cases. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2021, 197, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautmann, M.G.; Beyer, L.P.; Süss, C.; Neumaier, U.; Steger, F.; Putz, F.J.; Kölbl, O.; Pohl, F. Radiotherapy of epicondylitis humeri. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2019, 195, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.; Winter, P.J.; Grahame, R. Radiotherapy in the treatment of osteoarthrosis of the knee. Rheumatology 1973, 12, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, K.R. Therapeutic effects of low radiation doses. Strahlenther. Onkolog. 1994, 170, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, A.; Ameri, P.; Rahnama, N.; Mokhtari, M.; Sedaghat, M.; Hadavand, F.; Bozorgmehr, R.; Haghighi, M.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Low-Dose Whole-Lung Irradiation for COVID-19 Pneumonia: Final Results of a Pilot Study. Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, G.; Ponniah, S.; Sundaram, V.; Marimuthu, P.K.; Pitchaikannu, V.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Thangarasu, J.; Kannupaiyan, G.; Ramamoorthy, P.; Thangaraj, B.; et al. Whole lung irradiation as a novel treatment for COVID-19: Interim results of an ongoing phase 2 trial in India. Radiother. Oncolog. 2021, 163, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mandal, A.; Singh, D.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Rakesh, A.; Ranjan, R.; Verma, M.; Rai, D.K.; Bhushan, D.; et al. Interim Analysis of Impact of Adding Low Dose Pulmonary Radiotherapy to Moderate COVID-19 Pneumonia Patients: IMpaCt-RT Study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 822902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.S.; Hernández, D.; Trujillo, C.; Calderón, D.; Esqueda, P.; Calva, F.; Betancourt, A.; Ramírez, M.; Cervantes, G.; Souto, M.A.; et al. The clinical efficacy of low-dose whole-lung irradiation in moderate-to-severe COVID-19 pneumonia: RTMX-20 trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 166, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Shams, S.F.; Mohammadi, S.; Mortazavi, S.A.R.; Sihver, L. Low-Dose Radiation Therapy for COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Radiation 2021, 1, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; González-Rivera, M.; Almansa, R.; Micheloud, D.; Tedim, A.P.; Domínguez-Gil, M.; Resino, S.; Martín-Fernández, M.; Ryan Murua, P.; Pérez-García, F.; et al. Viral RNA load in plasma is associated with critical illness and a dysregulated host response in COVID-19. J. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, K.B.; Riu, F.; Gumà, J.; Guilarte, C.; Pique, B.; Hernandez, A.; Àvila, A.; Parra, S.; Castro, A.; Rovira, C.; et al. Study of the Plasma and Buffy Coat in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection—A Preliminary Report. Pathogens 2021, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidpoor, J.; Mortezaee, K. Interleukin-6 in SARS-CoV-2 induced disease: Interactions and therapeutic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Lv, T.; Li, S.; Liu, P.; et al. CURB-65 may serve as a useful prognostic marker in COVID-19 patients within Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa Cruz, A.; Mendes-Frias, A.; Oliveira, A.I.; Dias, L.; Matos, A.R.; Carvalho, A.; Capela, C.; Pedrosa, J.; Castro, A.G.; Silvestre, R. Interleukin-6 Is a Biomarker for the Development of Fatal Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 613422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Starke, K.; Reissig, D.; Petereit-Haack, G.; Schmauder, S.; Nienhaus, A.; Seidler, A. The isolated effect of age on the risk of COVID-19 severe outcomes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mu, S.; Wei, W.; Jin, C.; Tong, C.; Song, Z.; Zha, Y.; Xue, Y.; Gu, G. Lactate dehydrogenase, an independent risk factor of severe COVID-19 patients: A retrospective and observational study. Aging 2020, 12, 11245–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilowitz, N.R.; Kunichoff, D.; Garshick, M.; Shah, B.; Pillinger, M.; Hochman, J.S.; Berger, J.S. C-reactive protein and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.; Corre, F.; Honsel, V.; Curac, S.; Zarrouk, V.; Fantin, B.; Galy, A. Applicability of the CURB-65 pneumonia severity score for outpatient treatment of COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e96–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wei, Y.; Lyu, X.; Zhao, B.; Feng, Y.; Li, T.; Cao, H.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; et al. High aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase ratio on admission as risk factor for poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhou, F.; Qin, J.J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.J.; Cai, J.; Lin, L.; Ouyang, S.; et al. Longitudinal Association Between Markers of Liver Injury and Mortality in COVID-19 in China. Hepatology 2020, 72, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosch, S.F.; Mahajan, S.D.; Collins, A.R. SARS Coronavirus Spike Protein-Induced Innate Immune Response Occurs via Activation of the NF-kappaB Pathway in Human Monocyte Macrophages in Vitro. Virus Res. 2009, 142, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yan, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Tang, X.; Temperton, N.J.; Weiss, R.A.; Brenchley, J.M.; Douek, D.C.; et al. T Cell Responses to Whole SARS Coronavirus in Humans. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5490–5500. [Google Scholar]
- Sinderewicz, E.; Czelejewska, W.; Jezierska-Wozniak, K.; Staszkiewicz-Chodor, J.; Maksymowicz, W. Immune Response to COVID-19: Can We Benefit from the SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV Pandemic Experience? Pathogens 2020, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhan, Y.; Wu, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Ye, L.; Xu, S.; Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Analysis of Serum Cytokines in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 4410–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
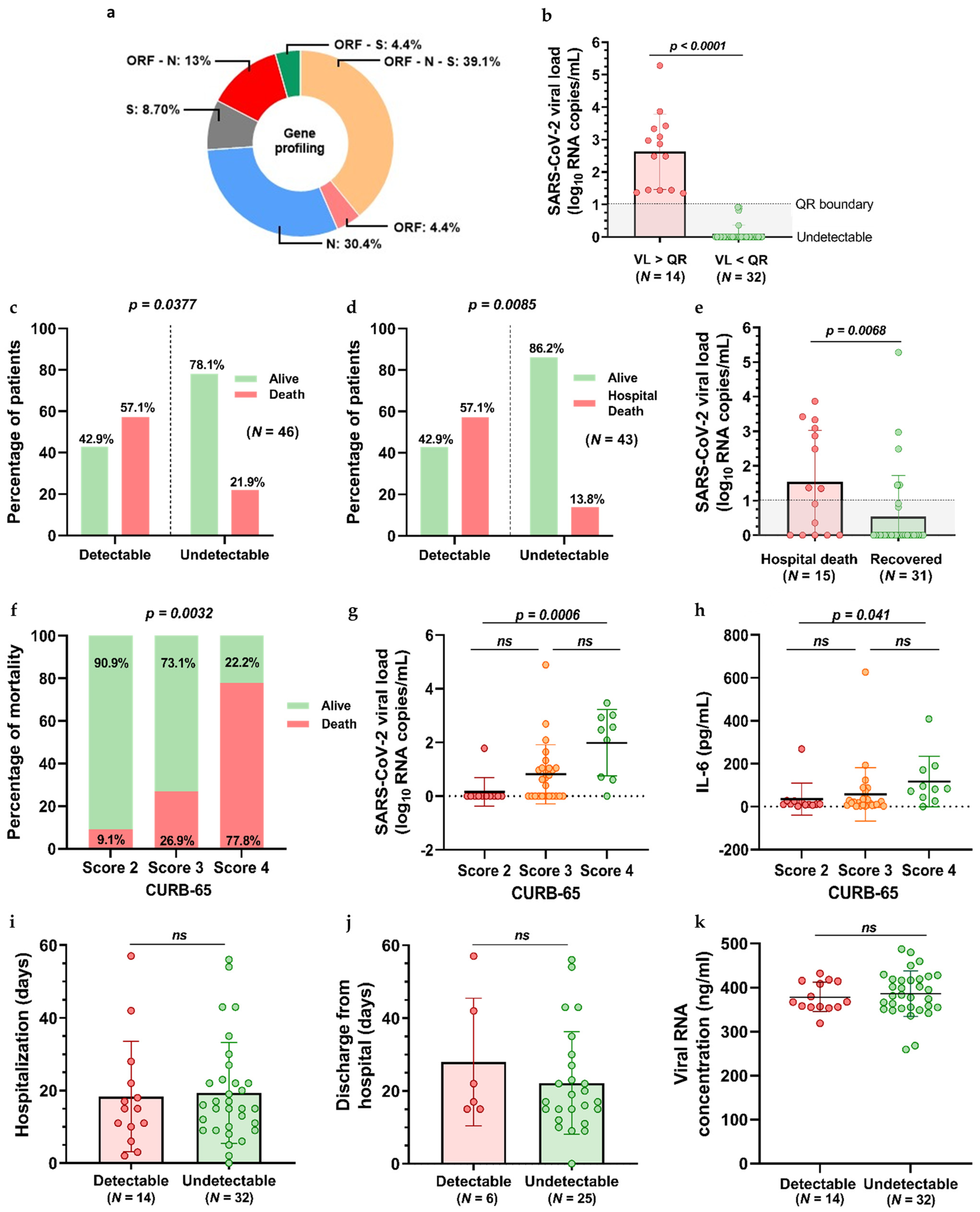
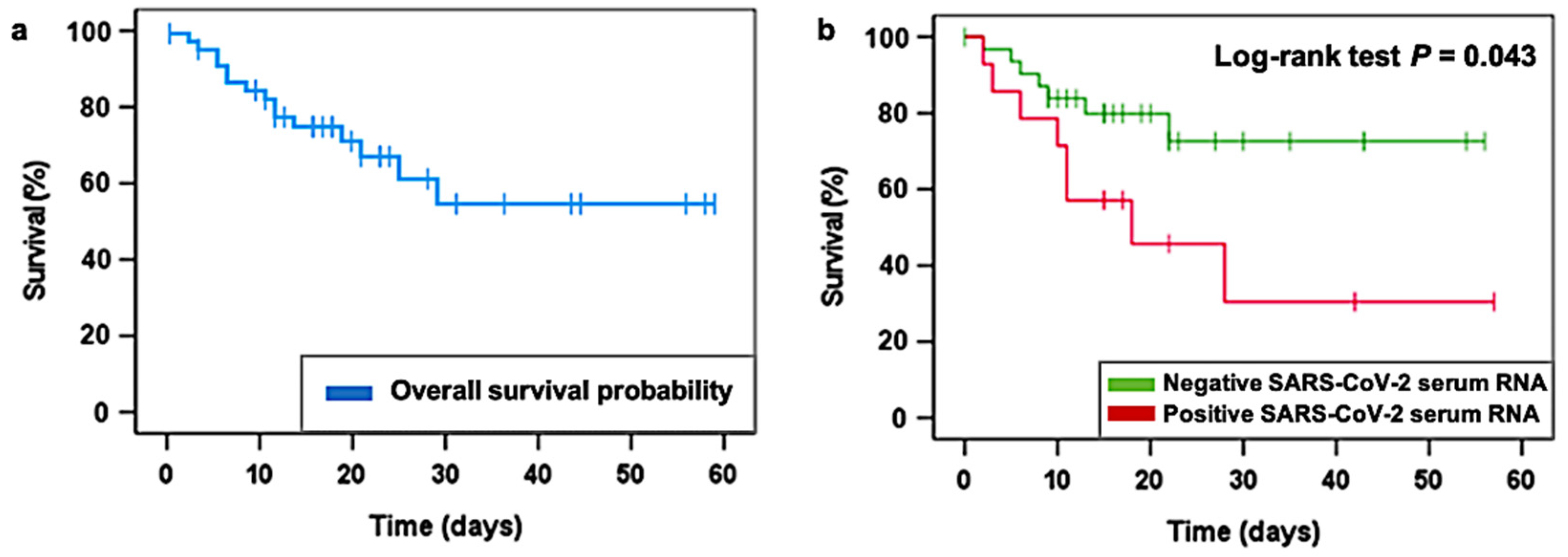

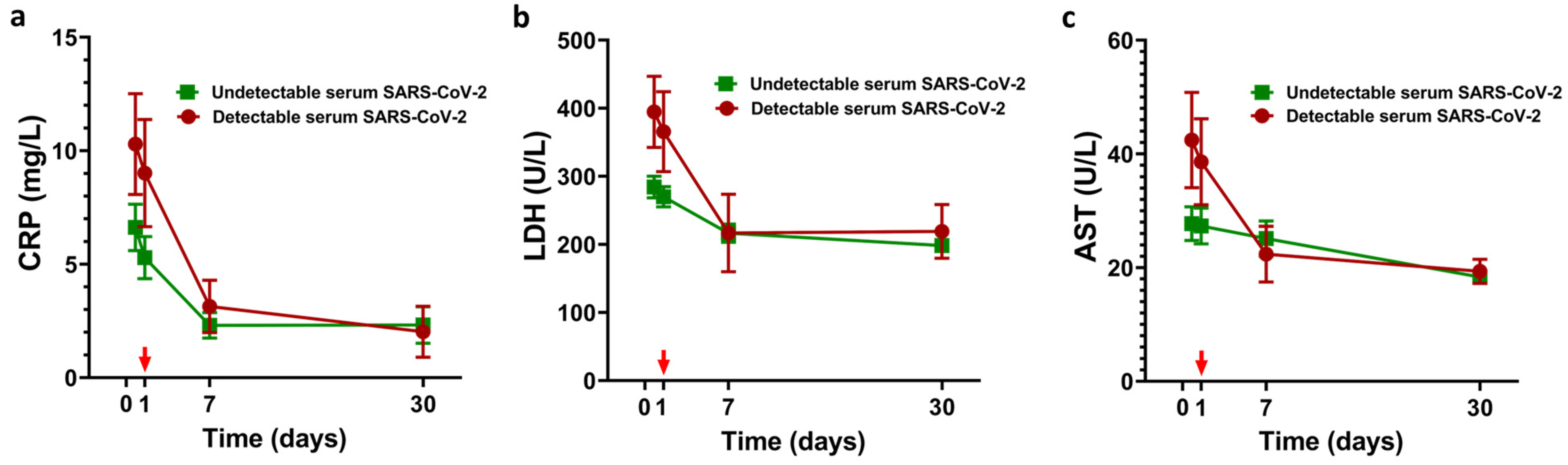
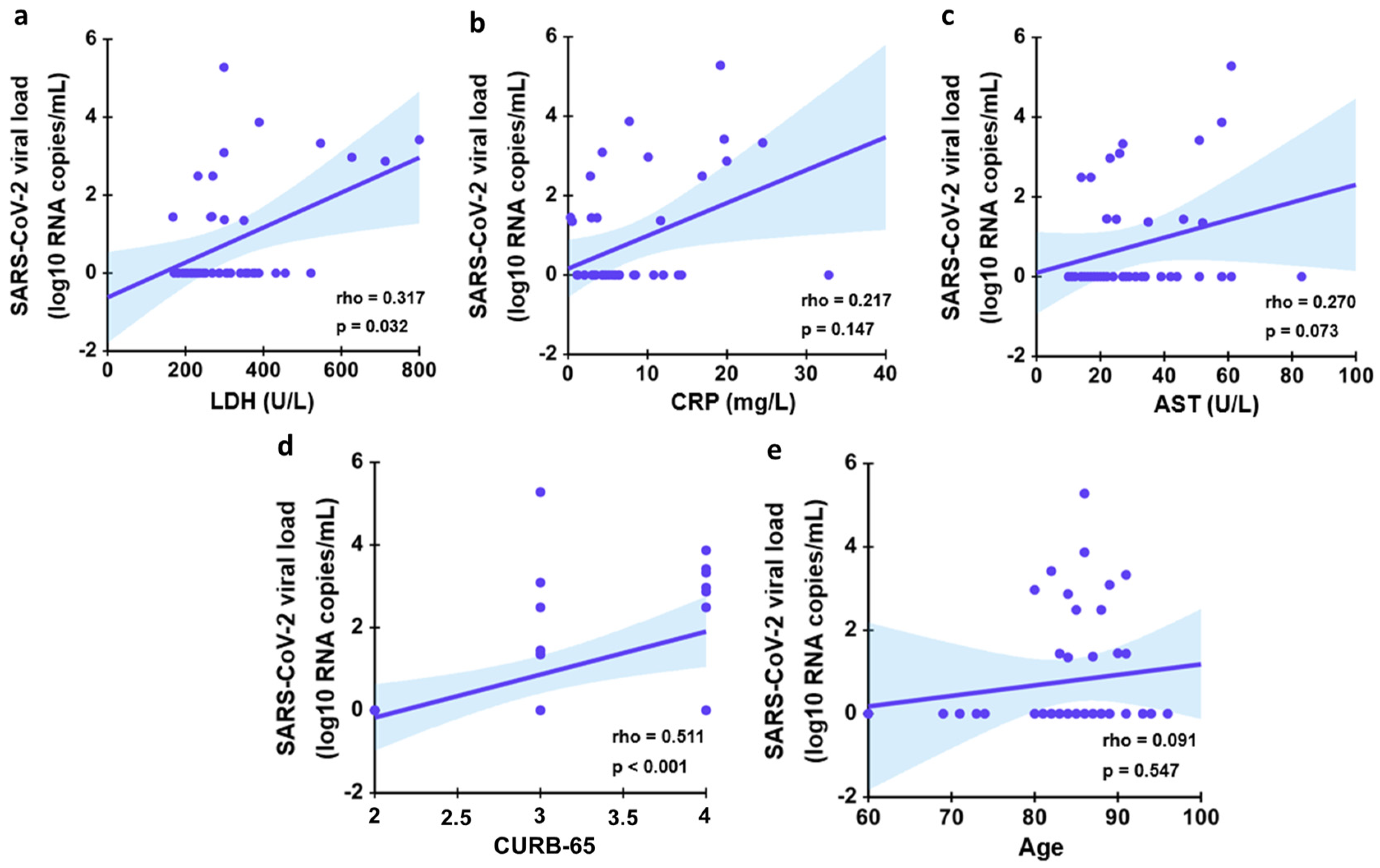
| Characteristic | Entire Cohort (N = 46) | Recovered (N = 31) | Deceased (N = 15) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 21 (45.65) b | 15 (48.39) b | 6 (40) b |
| Male | 25 (54.35) b | 16 (51.61) b | 9 (60) b |
| Age | 84.61 ± 6.611 a | 84.97 ± 5.351 a | 83.87 ± 8.847 a |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Neurological diseases | 13 (28.26) b | 7 (22.58) b | 6 (40) b |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 37 (80.43) | 25 (80.65) | 12 (80) |
| Respiratory diseases | 17 (36.96) | 12 (38.71) | 5 (33.33) |
| Other comorbidities | 40 (86.96) | 26 (83.87) | 14 (93.33) |
| Pharmacological treatment | |||
| Corticosteroids (dexamethasone) | 46 (100) b | 31 (100) | 15 (100) |
| Functional Status (Barthel Index) | |||
| Independent | 8 (17.39) b | 7 (22.58) b | 1 (6.67) b |
| Minimally dependent | 19 (41.30) | 14 (45.16) | 5 (33.33) |
| Partially dependent | 9 (19.57) | 4 (12.90) | 5 (33.33) |
| Very dependent | 7 (15.22) | 5 (16.13) | 2 (13.33) |
| Total dependent | 3 (6.52) | 1 (3.23) | 2 (13.33) |
| Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) | |||
| No cognitive decline | 23 (50) b | 19 (61.29) b | 4 (26.67) |
| Very mild cognitive decline | 8 (17.39) | 4 (12.90) | 4 (26.67) |
| Mild cognitive decline | 9 (19.57) | 5 (16.13) | 4 (26.67) |
| Moderate cognitive decline | 1 (2.17) | 1 (3.23) | 0 (0) |
| Moderately severe cognitive decline | 2 (4.35) | 2 (6.45) | 0 (0) |
| Severe cognitive decline | 3 (6.52) | 0 (0) | 3 (20) |
| Very severe cognitive decline | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Basal SpO2 | 93.43 ± 2.713 a | 94.03 ± 2.627 a | 92.20 ± 2.541 a |
| Basal SaFi | 283 ± 94.720 a | 305 ± 80.870 a | 237.40 ± 107.400 a |
| Mild | 37 (80.43) b | 28 (90.32) b | 9 (60) b |
| Moderate | 4 (8.70) | 2 (6.45) | 2 (13.33) |
| Severe | 5 (10.87) | 1 (3.23) | 4 (26.67) |
| CURB-65 Score | |||
| Score 1 | - | - | - |
| Score 2 | 12 (26.09) b | 10 (32.26) b | 2 (13.33) |
| Score 3 | 25 (54.35) | 19 (61.29) | 6 (40) |
| Score 4 | 9 (19.56) | 2 (6.45) | 7 (46.67) |
| Score 5 | - | - | - |
| First radiological findings | |||
| CT lung involvement <5% | - | - | - |
| CT lung involvement 5−25% | 1 (2.17) b | − | 1 (6.67) |
| CT lung involvement 26−49% | 7 (15.22) | 6 (19.35) | 1 (6.67) |
| CT lung involvement 50−75% | 22 (47.83) | 17 (54.84) | 5 (33.33) |
| CT lung involvement >75% | 16 (34.78) | 8 (25.81) | 8 (53.33) |
| Risk Factors | Univariate Cox Regression Analysis | Multivariate Cox Regression Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age | 1.125 (0.990–1.279) | 0.071 | 1.463 (1.062–2.014) | 0.020 |
| Sex (Female) | 0.897 (0.325–2.481) | 0.835 | - | - |
| Viral Load | 1.596 (1.166–2.184) | 0.004 | 1.738 (1.009–2.992) | 0.046 |
| RNA serum concentration | 1.005 (0.991–1.019) | 0.466 | - | - |
| Neurological disease | 1.542 (0.525–4.525) | 0.431 | - | - |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1.355 (0.378–4.865) | 0.641 | - | - |
| Respiratory disease | 1.111 (0.394–3.130) | 0.843 | - | - |
| Other comorbidities | 2.578 (0.338–19.648) | 0.361 | - | - |
| Days with symptoms | 1.075 (0.782–1.476) | 0.657 | - | - |
| IL-6 | 1.000 (0.995–1.005) | 0.927 | - | - |
| Ferritin | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.143 | - | - |
| C-reactive protein | 1.075 (1.017–1.138) | 0.011 | 0.979 (0.841–1.141) | 0.789 |
| LDH | 1.004 (1.001–1.007) | 0.005 | 1.007 (1.000–1.014) | 0.064 |
| Hemoglobin | 1.244 (0.953–1.625) | 0.108 | - | - |
| CD4 cells | 0.998 (0.994–1.003) | 0.486 | - | - |
| CD8 cells | 0.999 (0.994–1.004) | 0.708 | - | - |
| CD4/CD8 ratio | 0.961 (0.774–1.192) | 0.715 | - | - |
| D-dimer | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.278 | - | - |
| CURB-65 | 3.153 (1.348–7.373) | 0.008 | 1.795 (0.398–8.081) | 0.446 |
| Glucose | 1.002 (0.996–1.008) | 0.485 | - | - |
| Respiratory Frequency | 1.000 (0.981–1.019) | 0.986 | - | - |
| AST | 1.019 (1.005–1.034) | 0.009 | 0.996 (0.974–1.018) | 0.706 |
| ALT | 1.010 (0.992–1.029) | 0.255 | - | - |
| Leukocytes | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.951 | - | - |
| Lymphocytes | 0.999 (0.998–1.001) | 0.348 | - | - |
| Platelets | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.165 | - | - |
| Variable | AUC | p Value | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| Viral Load | 0.7460 | 0.0015 | 0.5352 | 0.8693 |
| CURB-65 | 0.7377 | 0.0019 | 0.5309 | 0.8616 |
| LDH | 0.7467 | 0.0018 | 0.5293 | 0.8720 |
| AST | 0.7552 | 0.0003 | 0.5670 | 0.8685 |
| CRP | 0.7313 | 0.0032 | 0.5184 | 0.8588 |
| Age | 0.6698 | 0.0201 | 0.4747 | 0.8022 |
| Viral Load + CRP | 0.7957 | 0.0001 | 0.5774 | 0.9078 |
| Viral Load + LDH | 0.8468 | 0.0000 | 0.6313 | 0.9409 |
| Viral Load + AST | 0.8589 | 0.0000 | 0.6894 | 0.9392 |
| Viral Load + Age | 0.8320 | 0.0000 | 0.6590 | 0.9214 |
| Viral Load + CURB-65 | 0.8196 | 0.0001 | 0.5790 | 0.9297 |
| AST + LDH | 0.7768 | 0.0001 | 0.5846 | 0.8864 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piqué, B.; Peña, K.; Riu, F.; Acosta, J.C.; Torres-Royo, L.; Malave, B.; Araguas, P.; Benavides, R.; de Febrer, G.; Camps, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Serum Viral Load and Prognostic Markers Proposal for COVID-19 Pneumonia in Low-Dose Radiation Therapy Treated Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030798
Piqué B, Peña K, Riu F, Acosta JC, Torres-Royo L, Malave B, Araguas P, Benavides R, de Febrer G, Camps J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Serum Viral Load and Prognostic Markers Proposal for COVID-19 Pneumonia in Low-Dose Radiation Therapy Treated Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030798
Chicago/Turabian StylePiqué, Berta, Karla Peña, Francesc Riu, Johana C. Acosta, Laura Torres-Royo, Barbara Malave, Pablo Araguas, Rocío Benavides, Gabriel de Febrer, Jordi Camps, and et al. 2023. "SARS-CoV-2 Serum Viral Load and Prognostic Markers Proposal for COVID-19 Pneumonia in Low-Dose Radiation Therapy Treated Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030798
APA StylePiqué, B., Peña, K., Riu, F., Acosta, J. C., Torres-Royo, L., Malave, B., Araguas, P., Benavides, R., de Febrer, G., Camps, J., Joven, J., Arenas, M., & Parada, D. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 Serum Viral Load and Prognostic Markers Proposal for COVID-19 Pneumonia in Low-Dose Radiation Therapy Treated Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030798








