Diagnosis and Treatment in Unilateral Condylar Hyperplasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olate, S.; Netto, H.D.; Rodriguez-Chessa, J.; Alister, J.P.; de Albergaria-Barbosa, J.; de Moraes, M. Mandible condylar hyperplasia: A review of diagnosis and treatment protocol. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 6, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nolte, J.W.; Schreurs, R.; Karssemakers, L.H.E.; Tuinzing, D.B.; Becking, A.G. Demographic features in Unilateral Condylar Hyperplasia: An overview of 309 asymmetric cases and presentation of an algorithm. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Alcojol, L.; Monje, F.; González-García, R. Hyperplasia of the mandibular condyle: Clinical, histopathologic, and treatment considerations in a series of 36 patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Granizo, R.; Garcia-Rielo, J.M.; De la Sen, O.; Maniegas, L.; Berguer, A.; De Pedro, M. Correlation between single photon emission computed tomography and histopathologic findings in condylar hyperplasia of the temporomandibular joint. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.H.; Leung, Y.Y. SPECT bone scintigraphy for the assessment of condylar growth activity in mandibular asymmetry: Is it accurate? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obwegeser, H.L.; Makek, M.S. Hemimandibular hyperplasia—Hemimandibular elongation. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 1986, 14, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolford, L.M.; Movahed, R.; Perez, D.E. A classification system for conditions causing condylar hyperplasia. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 567–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniskas, S.; Ly, C.L.; Parsaei, Y.; Bruckman, K.C.; Steinbacher, D.M. Facial asymmetry in unilateral condylar hyperplasia: Comparing treatment for active versus burnt-out disease. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 439e–445e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higginson, J.A.; Bartram, A.C.; Banks, R.J.; Keith, D.J.W. Condylar hyperplasia: Current thinking. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olate, S.; Almeida, A.; Alister, J.P.; Navarro, P.; Netto, H.D.; de Moraes, M. Facial asymmetry and condylar hyperplasia: Considerations for diagnosis in 27 consecutives patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 6, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zapata, S.; Medina, H.; Saravia, D.; Navarro, P.; Olate, S. Morphometric analysis of the mandible in patients with facial asymmetry associated to condylar hyperplasia. A panoramic radiography study. Int. J. Morphol. 2014, 32, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, D.R.; Muñoz, P.; Cantín López, M.G.; de Moraes, M.; Olate, S. Comparative evaluation of condylar volume between patients with unilateral condylar hyperplasia and class III dentofacial deformity. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karssemakers, L.H.E.; Nolte, J.W.; Tuinzing, D.B.; Langenbach, G.E.J.; Becking, A.G.; Raijmakers, P.G. Impact of bone volume upon condylar activity in patients with unilateral condylar hyperplasia. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, D.R.; Muñoz, P.; Olate, S.; de Moraes, M.; Fariña, R. No differences in morphological characteristics between hyperplastic condyle and class III condyle. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteson, S.R.; Proffit, W.R.; Terry, B.C.; Staab, E.V.; Burkes, E.J., Jr. Bone scanning with 99mtechnetium phosphate to assess condylar hyperplasia. Report of two cases. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1985, 60, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippold, C.; Kruse-Losler, B.; Danesh, G.; Joos, U.; Meyer, U. Treatment of hemimandibular hyperplasia: The biological basis of condylectomy. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 45, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karssemakers, L.H.; Nolte, J.W.; Tuinzing, D.B.; Langenbach, G.E.; Raijmakers, P.G.; Becking, A.G. Microcomputed tomographic analysis of human condyles in unilateral condylar hyperplasia: Increased cortical porosity and trabecular bone volume fraction with reduced mineralisation. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 52, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fariña, R.A.; Becar, M.; Plaza, C.; Espinoza, I.; Franco, M.E. Correlation between single photon emission computed tomography, AgNOR count, and histomorphologic features in patients with active mandibular condylar hyperplasia. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saridin, C.P.; Raijmakers, P.G.; Al Shamma, S.; Tuinzing, D.B.; Becking, A.G. Comparison of different analytical methods used for analyzing SPECT scans of patients with unilateral condylar hyperactivity. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintaku, W.H.; Venturin, J.S.; Langlais, R.P.; Clark, G.T. Imaging modalities to access bony tumors and hyperplasic reactions of the temporomandibular joint. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg 2010, 68, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shi, J. Is single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography superior to single-photon emission computed tomography in assessing unilateral condylar hyperplasia? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Buitrago, D.F.; Muñoz Acosta, J.M.; Cárdenas-Perilla, R.A. Comparison of four methods for quantitative assessment of 99mTc-MDP SPECT in patients with suspected condylar hyperplasia. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. Imagen. Mol. 2019, 38, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, D.F.; Ríos Borrás, V.; Muñoz, J.M.; Cardenas-Perilla, R.; Almeida, L.E. SPECT/CT Correlation in the diagnosis of unilateral condilar hyperplasia. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saridin, C.P.; Raijmakers, P.G.; Slootweg, P.J.; Tuinzing, D.B.; Becking, A.G.; van der Waal, I. Unilateral condylar hyperactivity: A histopathologic analysis of 47 patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez, B.; Olate, S.; Cantín, M.; Sandoval, C.; Del Sol, M.; de Moraes, M. Histomorphometric analysis of unilateral condylar hyperplasia in the temporomandibular joint: The value of the condylar layer and cartilage island. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, B.; Olate, S.; Cantín, M.; Sandoval, C.; Fariña, R.; Del Sol, M. Histopathological analysis of unilateral condylar hyperplasia: Difficulties in diagnosis and characterization of the disease. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzan, D.W.; Katsnelson, A.; Bermanis, I.; Brin, I.; Casap, N. The clinical characteristics of condylar hyperplasia: Experience with 61 patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschang, P.H.; Gandini Júnior, L.G. Mandibular skeletal growth and modelling between 10 and 15 years of age. Eur. J. Orthod. 2002, 24, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olate, S.; Cantín, M.; Alister, J.P.; Uribe, F.; Navarro, P.; Olate, G.; de Moraes, M. Relación entre el tamaño condilar y la asimetría facial transversal en individuos con hiperplasia condilar [Relationship between condylar size and transverse facial asymmetry in subject with condylar hyperplasia]. Int. J. Morphol. 2013, 31, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, G.; Olate, S.; Cantín, M.; Vásquez, B.; Del Sol, M. TMJ in facial class III deformity. Condylar morphology relations. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 15, 3113–3117. [Google Scholar]
- Rabie, A.B.; Dai, J.; Xu, R. Recombinant AAV-mediated VEGF gene therapy induces mandibular condylar growth. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Guddadararangiah, S. Case report: Unilateral condylar hyperplasia. F1000Research 2021, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

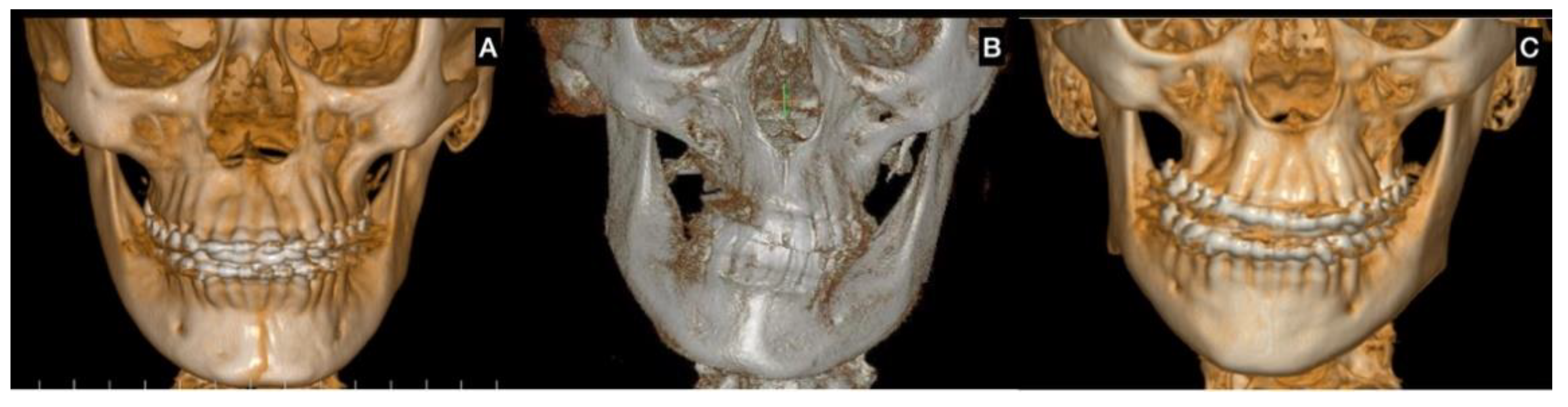
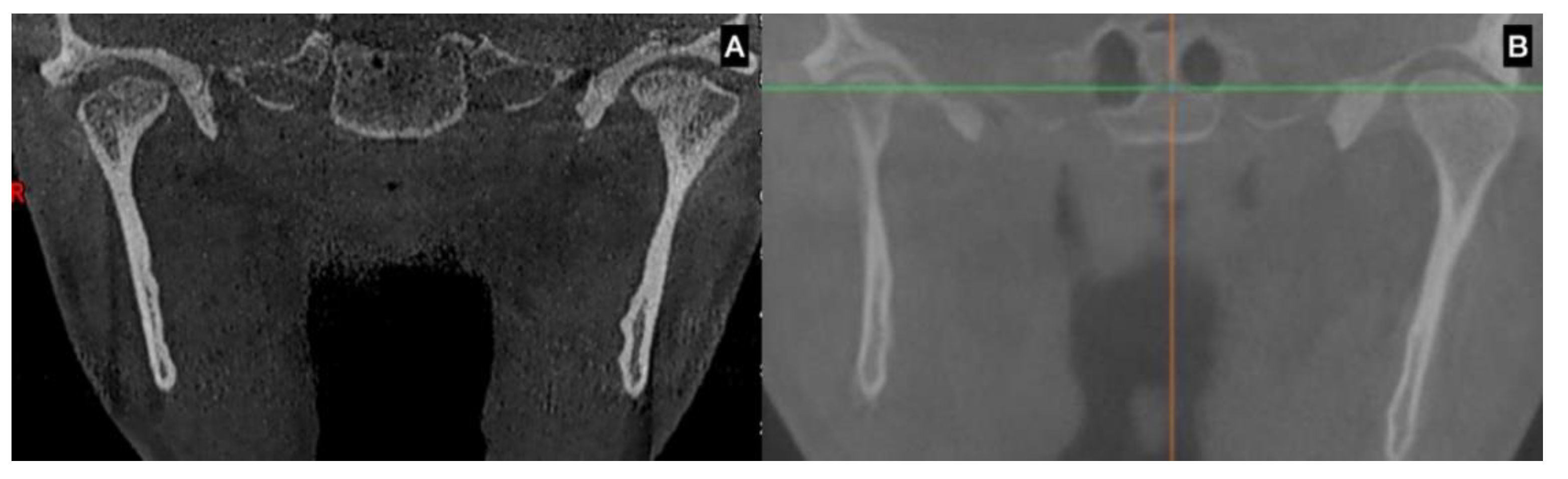
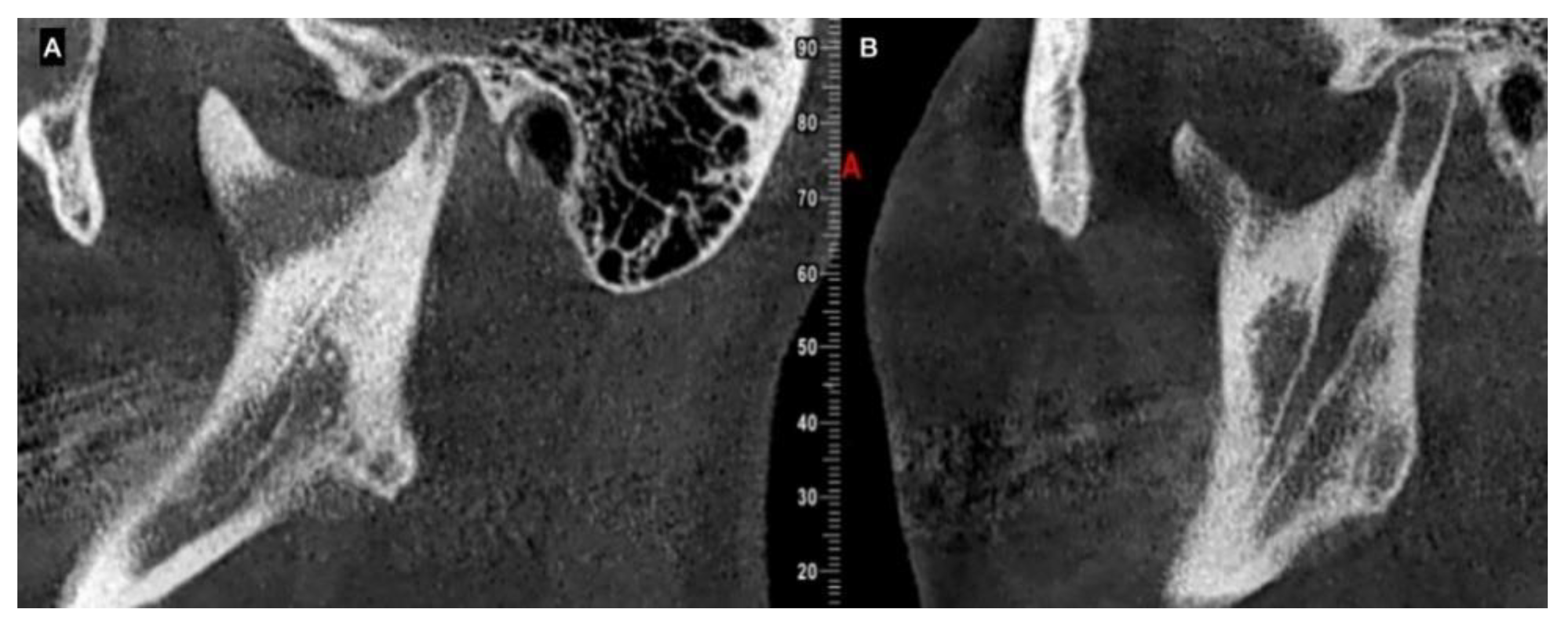
| Test | Characteristics and Definition |
|---|---|
| Family medical record | Family or patient describes a progressive facial asymmetry, occurring in the last time |
| With or without any family with facial deformity or facial asymmetry | |
| Pain or noise in the affected condyle could be reported | |
| Facial analysis | Chin midline deviation with the facial midline |
| Asymmetry in mandibular angles (vertical or horizontal differences) | |
| Dental conditions | Can be present with unilateral crossbite in the canine and/or molar area or unilateral open bite mainly in the posterior area |
| Progressive deviation of the dental midline with more than 4 mm. | |
| Trend to class III dental occlusion | |
| CBCT | Augmentation in condylar size in comparison to the non-hyperplastic condyle |
| Lack in upper cortical line of the affected condyle in the upper area showing an active metabolism | |
| Augmentation in radiolucency in the affected condyle with an image related to poor density in some cases | |
| SPECT | Differences 10% in caption of the radioisotope between the hyperplastic and the non-hyperplastic condyle |
| Sex | Age | Affected Side | SPECT Differences | Secondary Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 17 | R | 12 | NO |
| F | 19 | L | 6 | YES |
| F | 14 | L | 10 | NO |
| F | 22 | L | 16 | NO |
| F | 17 | L | 10 | NO |
| M | 22 | L | 14 | NO |
| F | 22 | R | 10 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 18 | NO |
| F | 22 | L | 6 | NO |
| F | 12 | R | 48 | NO |
| F | 15 | R | 10 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 14 | NO |
| F | 17 | L | 22 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 10 | NO |
| F | 17 | L | 14 | NO |
| F | 22 | R | 18 | NO |
| M | 15 | R | 12 | NO |
| F | 10 | L | 12 | NO |
| M | 16 | L | 26 | NO |
| F | 18 | R | 24 | NO |
| F | 13 | R | 18 | NO |
| M | 18 | R | 16 | NO |
| Average | 16.81 | 15.72 | ||
| Standard Deviation | 3.55 | 8.92 |
| Sex | Age | Affected Side | SPECT Differences | Secondary Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 15 | R | 16 | NO |
| F | 23 | R | 18 | YES |
| F | 21 | L | 16 | YES |
| F | 13 | L | 22 | NO |
| F | 45 | L | 28 | YES |
| F | 14 | L | 26 | NO |
| F | 41 | L | 10 | YES |
| F | 16 | L | 26 | YES |
| F | 20 | R | 24 | NO |
| M | 19 | L | 20 | NO |
| Average | 22.7 | 20.6 | ||
| Standard Deviation | 11.2 | 5.66 |
| Sex | Age | Affected Side | SPECT Differences | Secondary Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 18 | L | 10 | YES |
| F | 14 | L | 16 | NO |
| F | 21 | L | 10 | NO |
| F | 16 | R | 20 | YES |
| F | 22 | L | 16 | YES |
| F | 14 | L | 22 | NO |
| F | 22 | R | 23 | YES |
| F | 18 | R | 24 | YES |
| F | 35 | R | 10 | YES |
| F | 14 | R | 26 | NO |
| F | 16 | R | 40 | NO |
| F | 17 | R | 14 | YES |
| F | 14 | R | 12 | NO |
| F | 16 | R | 12 | NO |
| F | 17 | R | 16 | NO |
| M | 22 | L | 28 | NO |
| M | 43 | L | 22 | YES |
| Average | 19.94 | 18.88 | ||
| Standard Deviation | 7.84 | 7.99 |
| Sex | Age | Affected Side | SPECT (R/L) | SPECT Differences | Clinical Type | Secondary Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 10 | L | 44/56 | 12 | 1 | NO |
| F | 12 | R | 74/26 | 48 | 1 | NO |
| F | 13 | L | 39/61 | 22 | 2 | NO |
| F | 13 | R | 59/41 | 18 | 1 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 42/58 | 16 | 3 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 45/55 | 10 | 1 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 41/59 | 18 | 1 | NO |
| M | 14 | L | 39/61 | 22 | 3 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 43/57 | 14 | 1 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 37/63 | 26 | 2 | NO |
| F | 14 | L | 45/55 | 10 | 1 | NO |
| F | 14 | R | 63/37 | 26 | 3 | NO |
| F | 14 | R | 56/44 | 12 | 3 | NO |
| F | 15 | R | 58/42 | 16 | 2 | NO |
| F | 15 | R | 55/45 | 10 | 1 | NO |
| M | 15 | R | 56/44 | 12 | 1 | NO |
| F | 16 | R | 60/40 | 20 | 3 | YES |
| F | 16 | R | 30/70 | 40 | 3 | NO |
| F | 16 | L | 37/63 | 26 | 2 | YES |
| M | 16 | L | 37/63 | 26 | 1 | NO |
| F | 16 | R | 56/44 | 12 | 3 | NO |
| Average | 14.23 | 19.8 | ||||
| Standard Deviation | 1.48 | 9.9 |
| Sex | Age | Affected Side | SPECT (R/L) | SPECT Differences | Clinical Type | Secondary Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 17 | R | 56/44 | 12 | 1 | NO |
| F | 17 | L | 55/45 | 10 | 1 | NO |
| F | 17 | L | 39/61 | 22 | 1 | NO |
| F | 17 | R | 57/43 | 14 | 3 | YES |
| F | 17 | L | 43/57 | 14 | 1 | NO |
| F | 17 | R | 58/42 | 16 | 3 | NO |
| F | 18 | L | 45/55 | 10 | 3 | YES |
| F | 18 | R | 62/38 | 24 | 3 | YES |
| F | 18 | R | 62/38 | 24 | 1 | NO |
| M | 18 | R | 58/42 | 16 | 1 | NO |
| F | 19 | L | 47/53 | 6 | 1 | YES |
| M | 19 | L | 40/60 | 20 | 2 | NO |
| F | 20 | R | 62/38 | 24 | 2 | NO |
| F | 21 | L | 45/55 | 10 | 3 | NO |
| F | 21 | L | 58/42 | 16 | 2 | YES |
| F | 22 | L | 42/58 | 16 | 1 | NO |
| M | 22 | L | 43/57 | 14 | 1 | NO |
| F | 22 | R | 55/45 | 10 | 1 | NO |
| F | 22 | L | 42/58 | 16 | 3 | YES |
| F | 22 | L | 47/53 | 6 | 1 | NO |
| F | 22 | R | 61/39 | 23 | 3 | YES |
| F | 22 | R | 59/41 | 18 | 1 | NO |
| M | 22 | L | 36/64 | 28 | 3 | NO |
| F | 23 | R | 59/41 | 18 | 2 | YES |
| F | 35 | R | 55/45 | 10 | 3 | YES |
| F | 41 | L | 45/55 | 10 | 2 | YES |
| M | 43 | L | 39/61 | 22 | 3 | YES |
| F | 45 | L | 36/64 | 28 | 2 | YES |
| Average | 22.75 | 16.32 | ||||
| Standard Deviation | 7.98 | 6.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltran, J.; Zaror, C.; Moya, M.P.; Netto, H.D.; Olate, S. Diagnosis and Treatment in Unilateral Condylar Hyperplasia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031017
Beltran J, Zaror C, Moya MP, Netto HD, Olate S. Diagnosis and Treatment in Unilateral Condylar Hyperplasia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltran, Jorge, Carlos Zaror, María Paz Moya, Henrique Duque Netto, and Sergio Olate. 2023. "Diagnosis and Treatment in Unilateral Condylar Hyperplasia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031017
APA StyleBeltran, J., Zaror, C., Moya, M. P., Netto, H. D., & Olate, S. (2023). Diagnosis and Treatment in Unilateral Condylar Hyperplasia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031017








