Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Diagnosis of AE-IPF
2.3. HRCT Findings at AE-IPF Diagnosis
2.4. AE-IPF Treatment
2.5. Collection of Clinical Data
2.6. NLR Calculation
2.7. Oxygenation Deterioration on Days 4 and 8
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
3.2. Outcomes
3.3. Peripheral Blood Findings
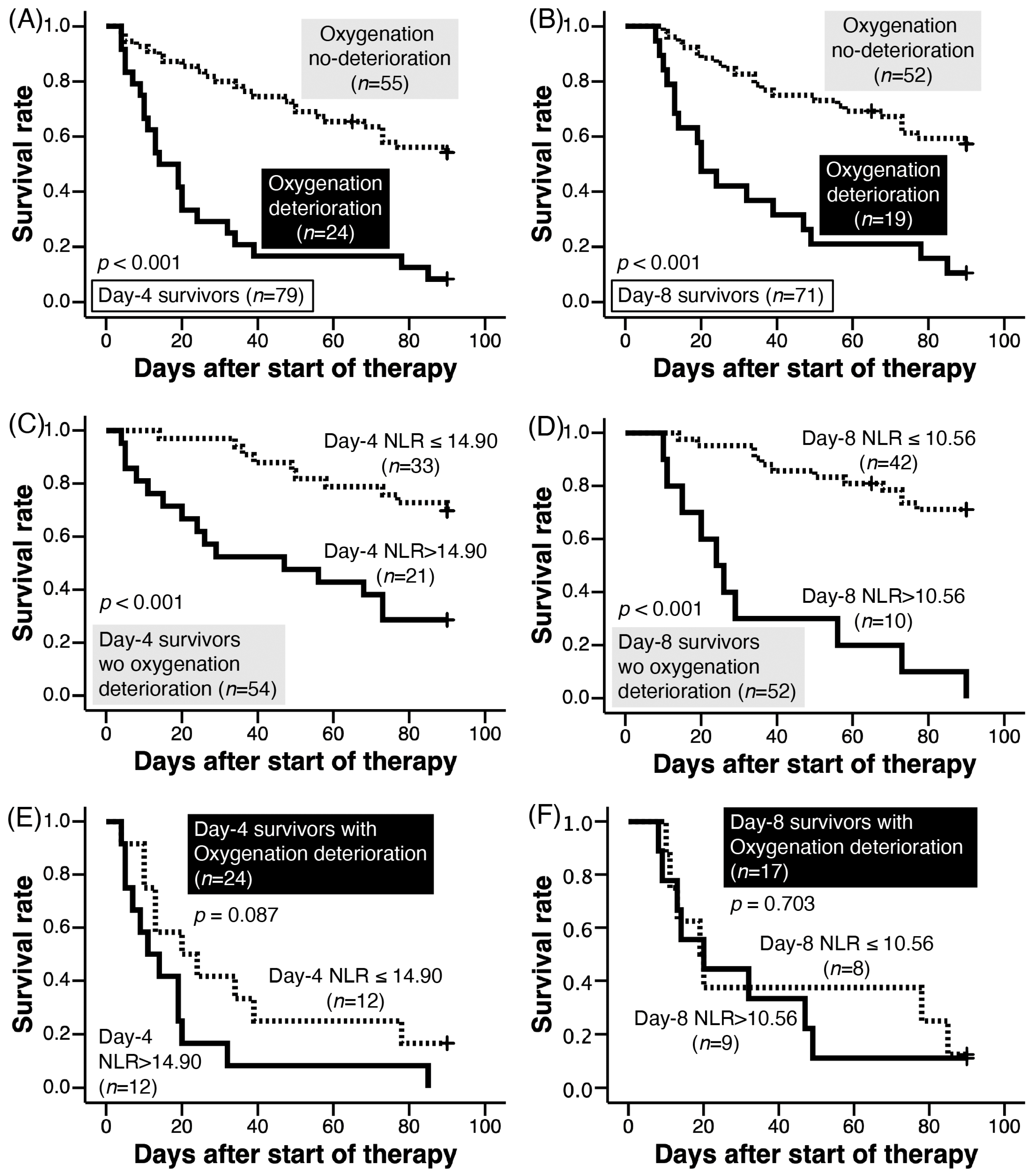
3.4. Oxygen Deterioration on Days 4 and 8
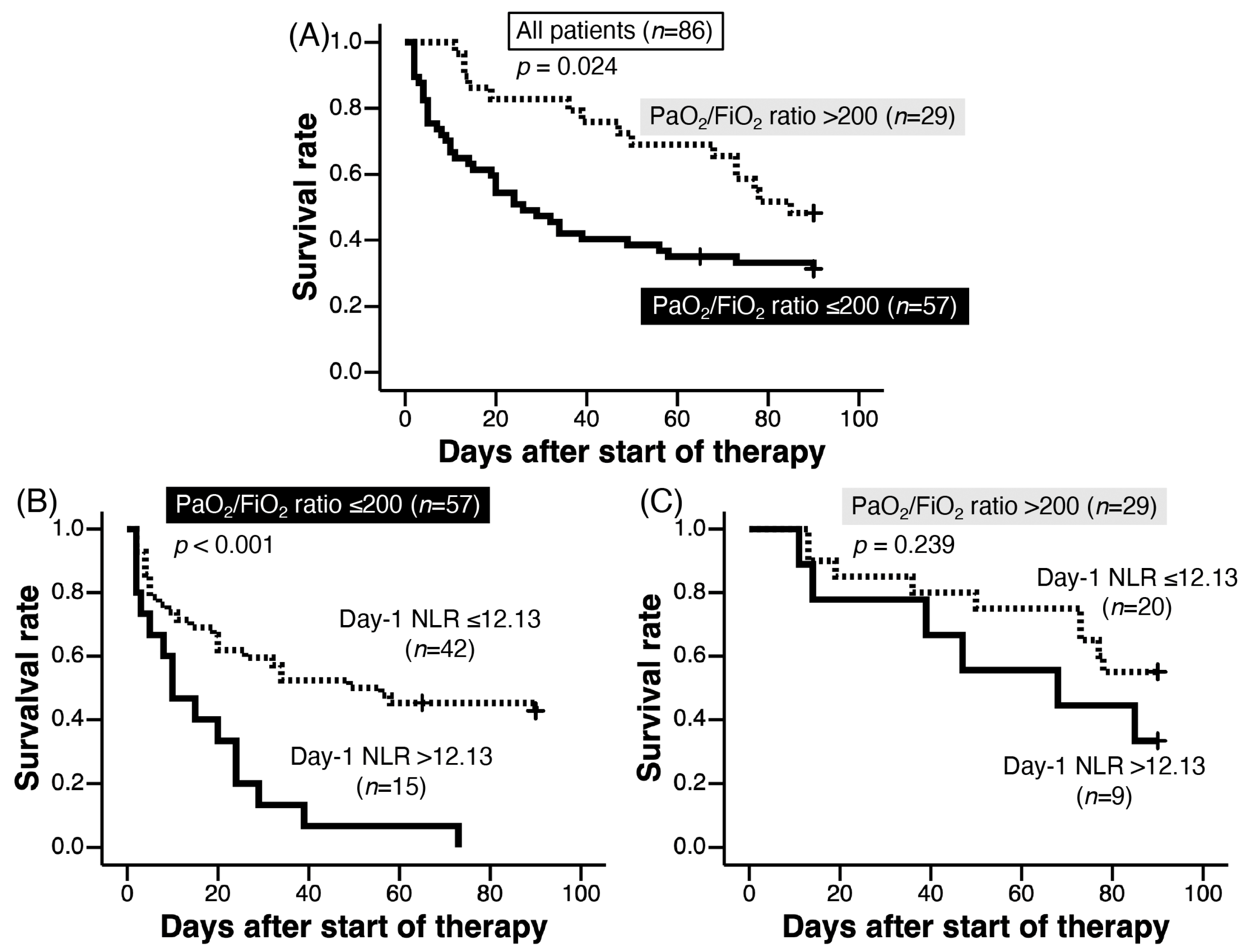
3.5. Correlations between the NLR and Other Parameters on Day 1
3.6. Cut-Off Values of NLR on Day 1, Day 4, and Day 8 for Predicting 90-Day Survival
3.7. Prognostic Factors of AE-IPF on Day 1 Examined by Cox Proportional Hazard Regression Analysis
3.8. Prognostic Factors of AE-IPF Survivors on Day 4 and Day 8 Examined by Cox Proportional Hazard Regression Analysis
3.9. NLR and Survival of Patients without Oxygenation Deterioration on Days 4 and 8
3.10. NLR and Survival of Patients with Oxygenation Deterioration on Days 4 and 8
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, M.; Kozuka, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakatani, M. Computed tomography findings in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An international working group report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Kondoh, Y.; Brown, K.K.; Johkoh, T.; Kataoka, K.; Fukuoka, J.; Kimura, T.; Matsuda, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Fukihara, J.; et al. Acute exacerbations of fibrotic interstitial lung diseases. Respirology 2020, 25, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Shimizu, H.; Isshiki, T.; Kurosaki, A.; Homma, S. Pharmacological treatment of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective study of 88 patients. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2019, 36, 176–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kishaba, T.; Tamaki, H.; Shimaoka, Y.; Fukuyama, H.; Yamashiro, S. Staging of acute exacerbation in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lung 2014, 192, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Qiu, X.; Xie, M.; Tian, Y.; Min, C.; Huang, M.; Hongyan, W.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Prognostic Value of Serum Osteopontin in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3424208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts—Rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; He, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. Diagnostic Value of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Predicting the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 9731854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Tang, Z.; Tao, W.; Wang, N. Prognostic value of neutrophils to lymphocytes and platelets ratio for 28-day mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. The association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte count ratio and mortality in septic patients: A retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-III database. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Mao, Z.; Xiao, M.; Wang, L.; Qi, S.; Zhou, F. Predictive values of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Antoniou, K.M.; Brown, K.K.; Cadranel, J.; Corte, T.J.; du Bois, R.M.; Lee, J.S.; Leslie, K.O.; Lynch, D.A.; Matteson, E.L.; et al. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society research statement: Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Tachibana, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Inoue, Y.; Tokura, S.; Okuma, T.; Akira, M.; Kitaichi, M.; Hayashi, S.; Inoue, Y. High-dose prednisolone after intravenous methyl prednisolone improves prognosis of acute exacerbation in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Respirology 2017, 22, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Sugimoto, C.; Matsumuro, A.; Hirose, M.; Kitaichi, M.; Akira, M.; Arai, T.; Hayashi, S.; Inoue, Y. Polymyxin-B hemoperfusion for acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Serum IL-7 as a prognostic marker. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2011, 28, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, T.; Kida, H.; Ogata, Y.; Marumo, S.; Matsuoka, H.; Gohma, I.; Yamamoto, S.; Mori, M.; Sugimoto, C.; Tachibana, K.; et al. Recombinant thrombomodulin for acute exacerbation in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Respirology 2019, 24, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Inoue, Y.; Sugimoto, C.; Inoue, Y.; Nakao, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Matsumuro, A.; Hirose, M.; Nakata, K.; Hayashi, S. CYFRA 21-1 as a disease severity marker for autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Respirology 2014, 19, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.R.; Artigas, A.; Brigham, K.L.; Carlet, J.; Falke, K.; Hudson, L.; Lamy, M.; Legall, J.R.; Morris, A.; Spragg, R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149 Pt 1, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Blancal, V.; Freynet, O.; Nunes, H.; Bouvry, D.; Naggara, N.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Denis, D.; Cohen, Y.; Vincent, F.; Valeyre, D.; et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Outcome and prognostic factors. Respiration 2012, 83, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Akira, M.; Sugimoto, C.; Tachibana, K.; Inoue, Y.; Shintani, S.; Okuma, T.; Kasai, T.; Hayashi, S.; Inoue, Y. Seroradiologic prognostic evaluation of acute exacerbation in patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: A retrospective observational study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 4132–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-C.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Pan, Y.-L.; Hwang, T.-L. Understanding the role of neutrophils in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, J.D. The complete blood count to diagnose septic shock. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12 (Suppl. S1), S16–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, Y.; Wilson, D.P.; Taylor, J.M.; Bannon, P.G.; Geczy, C.; Davenport, M.P.; Kritharides, L. A kinetic model of bone marrow neutrophil production that characterizes late phenotypic maturation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R1707–R1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lai, Y.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Nyunoya, T.; Chen, K.; Kitsios, G.; Nouraie, M.; Zhang, Y.; McVerry, B.J.; et al. Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 4 (PRMT4) contributes to lymphopenia in experimental sepsis. Thorax 2023, 78, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilloniz, C.; Peroni, H.J.; Gabarrús, A.; García-Vidal, C.; Pericàs, J.M.; Bermejo-Martin, J.; Torres, A. Lymphopenia Is Associated with Poor Outcomes of Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia and Sepsis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ju, M.; Chen, C.; Yang, D.; Hou, D.; Tang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Ji, S.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients: A retrospective study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achaiah, A.; Rathnapala, A.; Pereira, A.; Bothwell, H.; Dwivedi, K.; Barker, R.; Iotchkova, V.; Benamore, R.; Hoyles, R.K.; Ho, L.-P. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio as an indicator for disease progression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2022, 9, e001202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, M.; Yan, X. Prognostic Role of NLR, PLR and MHR in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 882217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishler, J.M.; Emerson, P.M. Development of Neutrophilia by serially increasing doses of dexamethasone. Br. J. Haematol. 1977, 36, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeklova, E.; Leva, L.; Jaglic, Z.; Faldyna, M. Dexamethasone-induced immunosuppression: A rabbit model. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 122, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzey, B.D.; Griffith, T.S.; Herndon, J.M.; Barreiro, R.; Tschopp, J.; Ferguson, T.A. Regulation of Fas Ligand-induced apoptosis by TNF. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3049–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozumi, H.; Hasegawa, H.; Miyashita, K.; Yasui, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kono, M.; Karayama, M.; Furuhashi, K.; Hashimoto, D.; Enomoto, N.; et al. Efficacy of corticosteroid and intravenous cyclophosphamide in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A propensity score-matched analysis. Respirology 2019, 24, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Nishiyama, O.; Kimura, T.; Matsuda, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Ando, M. Recombinant Human Thrombomodulin in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2015, 148, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Tanigami, H.; Suzuki, K.; Shimaoka, M. Thrombomodulin: A bifunctional modulator of inflammation and coagulation in sepsis. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 614545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccache, J.-M.; Jouneau, S.; Didier, M.; Borie, R.; Cachanado, M.; Bourdin, A.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Bonniaud, P.; Israël-Biet, D.; Prévot, G.; et al. Cyclophosphamide added to glucocorticoids in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (EXAFIP): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, Y.; Azuma, A.; Inoue, Y.; Ogura, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Tsushima, K.; Johkoh, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Ichikado, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; et al. Thrombomodulin alfa for acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A randomized double-blind placebo controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Azuma, A.; Cottin, V.; Hesslinger, C.; Stowasser, S.; Valenzuela, C.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Zoz, D.F.; Voss, F.; Maher, T.M. Trial of a Preferential Phosphodiesterase 4B Inhibitor for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.E.; Hesslinger, C.; Wollin, L.; Nickolaus, P. BI 1015550 is a PDE4B Inhibitor and a Clinical Drug Candidate for the Oral Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 838449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, F.; Ivanescu, A.D.; Fodor, P.; Moldovan, L.; Bataga, T. Correlation between Inflammatory Systemic Biomarkers and Surgical Trauma in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Total Cases (n = 86) |
|---|---|
| Before AE | |
| Age, years | 72 (66.0–75.25) |
| Sex, male/female | 72/14 |
| Smoking, NS/CS or Ex | 18/68 |
| IPF, histologically diagnosed/clinical | 27 */59 |
| Autoantibody, yes/no | 14/72 |
| PSL before AE, yes/no | 20/66 |
| Immunosuppressants, yes/no | 14/72 |
| Initial immunosuppressants, AZP/CyA/CPA | 9/3/2 |
| Pirfenidone, yes/no | 4/82 |
| Nintedanib, yes/no | 1/85 |
| LTOT, yes/no | 28/58 |
| At the onset of AE (day 1) | |
| Triggered, yes/no | 11 **/75 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, Torr | 155.4 (85.0–227.0) |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, ≤200/>200 | 57/29 |
| KL-6, ×100 U/mL | 15.40 (9.24–21.62) |
| WBC, ×109/L | 10.15 (8.10–13.22) |
| Neutrophils, ×109/L | 8.61 (6.08–11.60) |
| Lymphocytes, ×109/L | 1.10 (0.70–1.60) |
| NLR | 7.56 (4.61–12.90) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 11.57 (4.55–16.80) |
| LDH, U/L | 355.0 (296.5–423.5) |
| HRCT, diffuse/non-diffuse | 26/60 |
| HRCT, diffuse/multifocal/peripheral | 26/40/20 |
| Treatment for AE | |
| Intravenous high-dose methylprednisolone, yes/no | 86/0 |
| Initial dose of PSL, mg/kg | 0.933 (0.796–1.000) |
| Immunosuppressant, yes/no | 43/43 |
| CPA pulse, yes/no | 18/68 |
| AZP/CyA | 16/12 |
| Recombinant soluble thrombomodulin, yes/no | 8/78 |
| PPV within a month from the start of treatment, yes/no | 34/52 |
| NPPV/IPPV § | 20/14 |
| PMX-DHP therapy †, yes/no | 20/66 |
| Pirfenidone, yes/no | 3/83 |
| Nintedanib, yes/no | 0/86 |
| Outcomes | |
| Day-4 survivors (3-day survivors), yes/no | 79/7 |
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 4, yes/no | 24/55 |
| Day-8 survivors (7-day survivors), yes/no | 71/15 |
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 8, yes/no | 19/52 |
| Day-91 survivors (90-day survivors) #, yes/no/unknown | 31/54/1 |
| Median survival time, days | 49 |
| Neutrophils, ×109/L | Lymphocytes, ×109/μL | NLR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day-4 survivors (n = 78 §) | |||
| Day 1 | 8.61 (6.03–11.62) | 1.14 (0.73–1.60) | 7.36 (4.53–12.17) |
| Day 4 | 10.15 (8.20–14.12) | 0.90 (0.50–1.30) | 12.10 (7.17–21.26) |
| p-value * | |||
| Day 1 vs. Day 4 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Day-8 survivors (n = 68 †) | |||
| Day 1 | 8.47 (6.06–11.47) | 1.14 (0.75–1.67) | 7.12 (4.19–12.15) |
| Day 4 | 10.10 (7.60–13.15) | 0.90 (0.50–1.33) | 11.94 (6.40–18.24) |
| Day 8 | 10.03 (7.80–12.00) | 1.60 (0.90–2.17) | 5.21 (3.48–11.23) |
| p-value * | |||
| Day 1 vs. Day 8 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.521 |
| Day 4 vs. Day 8 | 0.290 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Deterioration | Non-Deterioration | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| On day 4 (n = 78 *) | n = 24 | n = 54 ** | |
| Day-4 NLR | 15.25 (8.48–24.75) | 11.94 (6.48–19.43) | 0.443 |
| NLR increase on day 4 from day 1 | 6.42 (−5.11–14.69) | 4.01 (−0.22–8.89) | 0.779 |
| NLR increase on day 4 from day 1, >0/≤0 | 15/9 | 40/14 | 0.420 |
| Neutrophils on day 4, ×109/L | 10.30 (8.90–13.57) | 9.80 (8.05–14.28) | 0.753 |
| Lymphocytes on day 4, ×109/L | 0.88 (0.45–1.13) | 0.90 (0.50–1.36) | 0.528 |
| LDH on day 4, U/L | 385 (352–510) # | 306 (264–375) | <0.001 |
| CRP on day 4, mg/dL | 4.36 (2.49–8.88) | 2.60 (1.13–7.50) | 0.295 |
| On day 8 (n = 69 †) | n = 17 ‡ | n = 52 | |
| Day-8 NLR | 10.94 (6.33–21.50) | 4.82 (3.25–9.07) | 0.002 |
| NLR increase on day 8 from day 1 | 2.19 (−8.19–13.95) | −0.89 (−3.56–1.93) | 0.303 |
| NLR increase on day 8 from day 1, >0/≤0 | 10/7 | 20/32 | 0.167 |
| Neutrophils on day 8, ×109/L | 10.36 (8.05–12.60) | 9.75 (7.34–12.00) | 0.456 |
| Lymphocytes on day 8, ×109/L | 0.929 (0.650–1.38) | 1.91 (1.20–2.46) | 0.001 |
| LDH on day 8, U/L | 388 (326–477) | 278 (237–355) | <0.001 |
| CRP on day 8, mg/dL | 4.61 (1.00–11.14) | 1.33 (0.55–3.51) | 0.012 |
| Rho | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Before AE | ||
| Age, years | 0.288 | 0.007 |
| Sex, male/female | 0.199 | 0.066 |
| Smoking, CS or Ex/NS | −0.079 | 0.467 |
| SLB or autopsy for underlying IPF, yes/no | 0.022 | 0.839 |
| Autoantibody, yes/no | 0.060 | 0.581 |
| PSL before AE, yes/no | 0.208 | 0.054 |
| LTOT, yes/no | 0.076 | 0.487 |
| At the onset of AE | ||
| Triggered, yes/no | −0.090 | 0.407 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, Torr | 0.231 | 0.033 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, ≤200/>200 | 0.182 | 0.093 |
| KL-6, ×100 U/mL (n = 82) | −0.088 | 0.433 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.210 | 0.053 |
| LDH, U/L | 0.176 | 0.104 |
| HRCT, diffuse/non-diffuse | 0.332 | 0.002 |
| Parameters | n | Cutoff | AUC | 95% CI | p-Value | Sensitivity § | Specificity # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day-1 NLR | 85 * | 12.13 | 0.712 | 0.602–0.823 | 0.001 | 38.9% | 90.3% |
| Day-4 NLR | 78 ** | 14.90 | 0.684 | 0.567–0.801 | 0.006 | 57.4% | 80.6% |
| Day-8 NLR | 69 ¶ | 10.56 | 0.774 | 0.666–0.883 | <0.001 | 48.6% | 96.8% |
| Parameter | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | |||
| Before AE | |||
| Age, years | 0.987 | 0.953–1.022 | 0.472 |
| Sex, male/female | 1.241 | 0.585–2.631 | 0.573 |
| Smoking, CS or Ex/NS | 1.478 | 0.722–3.027 | 0.285 |
| Autoantibody, yes/no | 0.993 | 0.485–2.033 | 0.986 |
| PSL before AE, yes/no | 1.571 | 0.884–2.795 | 0.124 |
| LTOT, yes/no | 1.562 | 0.898–2.719 | 0.114 |
| At the onset of AE (day 1) | |||
| Triggered, yes/no | 0.776 | 0.332–1.813 | 0.558 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, Torr | 0.997 | 0.994–1.001 | 0.130 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, ≤200/>200 | 1.956 | 1.075–3.556 | 0.028 |
| KL-6, ×100 U/mL (n = 82) | 1.006 | 0.983–1.030 | 0.590 |
| WBC, ×108/L | 1.001 | 0.994–1.008 | 0.710 |
| Neutrophils, ×108/L | 1.004 | 0.997–1.010 | 0.292 |
| Lymphocytes, ×108/L | 0.921 | 0.875–0.968 | 0.001 |
| NLR | 1.034 | 1.016–1.053 | <0.001 |
| NLR >12.13/≤12.13 | 3.075 | 1.712–5.521 | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 1.001 | 0.971–1.033 | 0.933 |
| LDH, U/L | 1.002 | 0.999–1.004 | 0.216 |
| HRCT, diffuse/non-diffuse | 1.858 | 1.068–3.233 | 0.028 |
| Multivariate * | |||
| Model 1 | |||
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, ≤200/>200 | 2.226 | 1.195–4.147 | 0.012 |
| NLR | 1.041 | 1.021–1.061 | <0.001 |
| Model 2 | |||
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio, ≤200/>200 | 2.387 | 1.290–4.417 | 0.006 |
| NLR >12.13/≤12.13 | 2.906 | 1.635–5.166 | <0.001 |
| Parameter | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| On day 4 (n = 79 *) | |||
| Univariate analysis | |||
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 4, yes/no | 4.393 | 2.428–7.948 | <0.001 |
| Day-4 NLR | 1.026 | 1.011–1.041 | <0.001 |
| Day-4 NLR, >14.90/≤14.90 | 3.075 | 1.712–5.521 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils on day 4, ×108/L | 1.003 | 0.997–1.010 | 0.286 |
| Lymphocytes on day 4, ×108/L | 0.924 | 0.870–0.981 | 0.009 |
| LDH on day 4, U/L | 1.003 | 1.001–1.005 | <0.001 |
| CRP on day 4, mg/dL | 1.012 | 0.965–1.061 | 0.628 |
| Multivariate analysis ** | |||
| Model 1 | |||
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 4, yes/no | 3.949 | 2.138–7.293 | <0.001 |
| Day-4 NLR | 1.024 | 1.009–1.040 | 0.002 |
| LDH on day 4, U/L | 1.003 | 1.001–1.005 | 0.008 |
| Model 2 | |||
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 4, yes/no | 3.553 | 1.920–6574 | <0.001 |
| Day-4 NLR, >14.90/≤14.90 | 3.395 | 1.834–6.282 | <0.001 |
| LDH on day 4, U/L | 1.004 | 1002–1.006 | 0.008 |
| On day 8 (n = 71 §) | |||
| Univariate analysis | |||
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 8, yes/no | 4.131 | 2.165–7.883 | <0.001 |
| Day-8 NLR | 1.065 | 1.035–1.095 | <0.001 |
| Day-8 NLR, >10.56/≤10.56 | 5.451 | 2.784–10.671 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils on day 8, ×108/L | 1.010 | 1.001–1.019 | 0.022 |
| Lymphocytes on day 8, ×108/L | 0.927 | 0.889–0.968 | <0.001 |
| LDH on day 8, U/L | 1.002 | 1.001–1.004 | 0.012 |
| CRP on day 8, mg/dL | 1.079 | 1.022–1.139 | 0.006 |
| Multivariate # | |||
| Model 3 | |||
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 8, yes/no | 2.849 | 1.366–5.942 | 0.005 |
| Day-8 NLR | 1.046 | 1.014–1.080 | 0.005 |
| Model 4 | |||
| Oxygenation deterioration on day 8, yes/no | 2.318 | 1.105–4.863 | 0.026 |
| Day-8 NLR, >10.56/≤10.56 | 3.927 | 1.685–8.267 | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Higher NLR * | Lower NLR * | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 4 | n = 21 | n = 33 | |
| Initial dose of PSL, mg/kg | 0.909 (0.831–1.015) | 0.930 (0.565–0.987) | 0.950 |
| Immunosuppressant, yes/no | 8/13 | 21/12 | 0.095 |
| CPA pulse, yes/no | 3/18 | 5/28 | 1.000 |
| AZP/CyA | 3/3 | 9/8 | 1.000 |
| Days from AE to IMs onset | 7.5 (3.25–29.75) | 15.0 (2.5–45.5) | 0.756 |
| Days from AE to IMs onset, ≤3/3< | 2/6 | 7/14 | 1.000 |
| Recombinant soluble TM, yes/no | 2/19 | 4/29 | 1.000 |
| PMX-DHP therapy, yes/no | 3/18 | 9/24 | 0.329 |
| Pirfenidone after AE, yes/no | 0/21 | 2/31 | 0.516 |
| Day 8 | n = 10 | n = 42 | |
| Initial dose of PSL, mg/kg | 0.932 (0.802–1.111) | 0.918 (0.555–0.984) | 0.318 |
| IMs, yes/no | 3/7 | 24/18 | 0.167 |
| CPA pulse, yes/no | 2/8 | 4/38 | 0.324 |
| AZP/CyA | 1/1 | 11/11 | 1.000 |
| Days from AE to IMs onset | 7 (3–14) | 12.5 (1.25–41.75) | 0.546 |
| Days from AE to IMs onset, ≤7/7< | 2/1 | 10/14 | 0.569 |
| Recombinant soluble TM, yes/no | 0/10 | 5/37 | 0.569 |
| PMX-DHP therapy, yes/no | 3/7 | 7/35 | 0.382 |
| Pirfenidone after AE, yes/no | 0/10 | 2/40 | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arai, T.; Takimoto, T.; Takeuchi, N.; Minomo, S.; Kagawa, T.; Inoue, Y. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237446
Arai T, Takimoto T, Takeuchi N, Minomo S, Kagawa T, Inoue Y. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(23):7446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237446
Chicago/Turabian StyleArai, Toru, Takayuki Takimoto, Naoko Takeuchi, Shojiro Minomo, Tomoko Kagawa, and Yoshikazu Inoue. 2023. "Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 23: 7446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237446
APA StyleArai, T., Takimoto, T., Takeuchi, N., Minomo, S., Kagawa, T., & Inoue, Y. (2023). Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(23), 7446. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237446






