Digital versus Conventional Dentures: A Prospective, Randomized Cross-Over Study on Clinical Efficiency and Patient Satisfaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Randomization
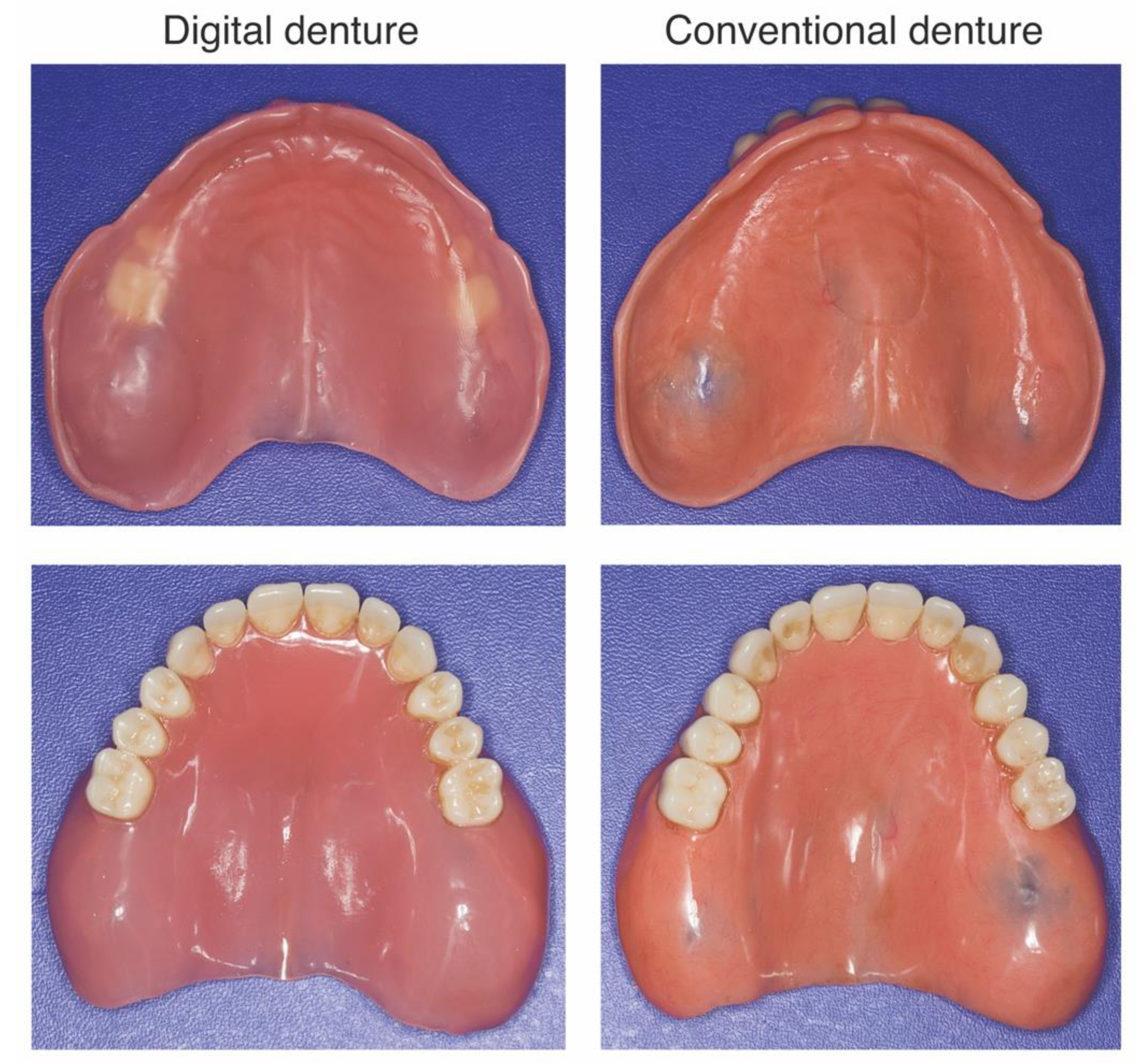
2.2. Conventional and Digital Dentures
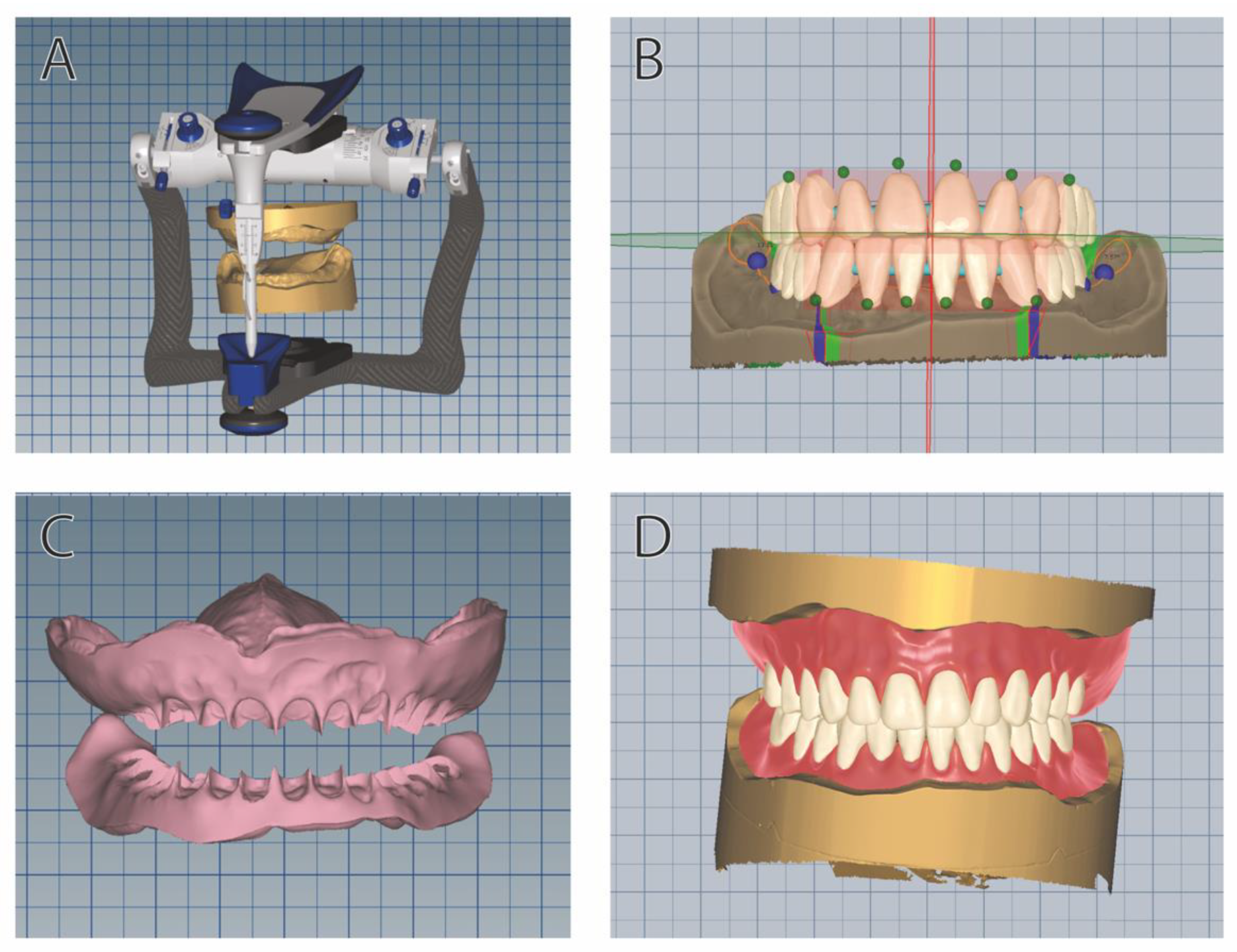
2.3. Clinical Workflow
2.4. Clinical Evaluation Based on the Sato-Score
2.5. Oral Health-Related Quality of Life
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Evaluation and Appointments
3.2. Oral Health-Related Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerritsen, A.E.; Allen, P.F.; Witter, D.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Creugers, N.H. Tooth loss and oral health-related quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos Sugio, C.Y.; Mosquim, V.; Jacomine, J.C.; Zabeu, G.S.; de Espindola, G.G.; Bonjardim, L.R.; Bonfante, E.A.; Wang, L. Impact of rehabilitation with removable complete or partial dentures on masticatory efficiency and quality of life: A cross-sectional mapping study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 128, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.S.; Pelekis, N.D.; Thomason, J.M. Conventional rehabilitation of edentulous patients: The impact on oral health-related quality of life and patient satisfaction. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 16, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, M.R.; Alves, L.R.; Gurgel, B.C.; Calderon, P.S. Simplified versus traditional techniques for complete denture fabrication: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.J.; Lin, J.R.; Hsu, J.F. Patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes and oral health-related quality of life after treatment with traditional and modified protocols for complete dentures. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.P.; Taylor, T.D. Simplified complete dentures. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 48, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, T.R.; Della Vecchia, M.P.; Regis, R.R.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Muglia, V.A.; Mestriner, W., Jr.; de Souza, R.F. A randomised trial on simplified and conventional methods for complete denture fabrication: Masticatory performance and ability. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regis, R.R.; Cunha, T.R.; Della Vecchia, M.P.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Silva-Lovato, C.H.; de Souza, R.F. A randomised trial of a simplified method for complete denture fabrication: Patient perception and quality. J. Oral Rehabil. 2013, 40, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruti, P.; Mobilio, N.; Bellia, E.; Borracchini, A.; Catapano, S.; Gassino, G. Simplified edentulous treatment: A multicenter randomized controlled trial to evaluate the timing and clinical outcomes of the technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattadiyil, M.T.; AlHelal, A. An update on computer-engineered complete dentures: A systematic review on clinical outcomes. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlRumaih, H.S. Clinical Applications of Intraoral Scanning in Removable Prosthodontics: A Literature Review. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, H. Digital Removable Complete Dentures (DRCD). In Digital Restorative Dentistry; Faleh Tamimi, H.H., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 115–136. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin, M.S.; Baytaroglu, E.N.; Erdem, A.; Dilber, E. A review of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacture techniques for removable denture fabrication. Eur. J. Dent. 2016, 10, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubaraki, M.Q.; Moaleem, M.M.A.; Alzahrani, A.H.; Shariff, M.; Alqahtani, S.M.; Porwal, A.; Al-Sanabani, F.A.; Bhandi, S.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Heboyan, A.; et al. Assessment of Conventionally and Digitally Fabricated Complete Dentures: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2022, 15, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, N.Z.; Goodacre, B.J.; Goodacre, C.J.; Muller, F.; Wagner, S. CAD/CAM Complete Denture Systems and Physical Properties: A Review of the Literature. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Kamnoedboon, P.; McKenna, G.; Angst, L.; Schimmel, M.; Ozcan, M.; Muller, F. CAD-CAM removable complete dentures: A systematic review and meta-analysis of trueness of fit, biocompatibility, mechanical properties, surface characteristics, color stability, time-cost analysis, clinical and patient-reported outcomes. J. Dent. 2021, 113, 103777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadioti, E.; Musharbash, L.; Blatz, M.B.; Papavasiliou, G.; Kamposiora, P. 3D printed complete removable dental prostheses: A narrative review. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Russo, L.; Zhurakivska, K.; Guida, L.; Chochlidakis, K.; Troiano, G.; Ercoli, C. Comparative cost-analysis for removable complete dentures fabricated with conventional, partial, and complete digital workflows. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Schimmel, M.; Naharro, M.; Neill, C.O.; McKenna, G.; Muller, F. CAD/CAM milled removable complete dentures: Time and cost estimation study. J. Dent. 2019, 80, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; Lund, J.P.; Shapiro, S.H.; Locker, D.; Klemetti, E.; Chehade, A.; Savard, A.; Feine, J.S. Oral health status and treatment satisfaction with mandibular implant overdentures and conventional dentures: A randomized clinical trial in a senior population. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2003, 16, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Heydecke, G.; Tedesco, L.A.; Kowalski, C.; Inglehart, M.R. Complete dentures and oral health-related quality of life—Do coping styles matter? Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2004, 32, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.F. Assessment of oral health related quality of life. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2003, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroz, S.; Peroz, I.; Beuer, F.; Sterzenbach, G.; von Stein-Lausnitz, M. Digital versus conventional complete dentures: A randomized, controlled, blinded study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 128, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Azak, A.N.; Alp, G.; Eksi, H. Use of CAD-CAM technology for the fabrication of complete dentures: An alternative technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol. Bull. 1968, 70, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Tsuga, K.; Akagawa, Y.; Tenma, H. A method for quantifying complete denture quality. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1998, 80, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F.; Locker, D. A modified short version of the oral health impact profile for assessing health-related quality of life in edentulous adults. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 15, 446–450. [Google Scholar]
- Likert, R. A Technique for the Measurement of Attitudes; APA Psycnet: New York, NY, USA, 1932; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- de Grandmont, P.; Feine, J.S.; Tache, R.; Boudrias, P.; Donohue, W.B.; Tanguay, R.; Lund, J.P. Within-subject comparisons of implant-supported mandibular prostheses: Psychometric evaluation. J. Dent. Res. 1994, 73, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydecke, G.; Boudrias, P.; Awad, M.A.; De Albuquerque, R.F.; Lund, J.P.; Feine, J.S. Within-subject comparisons of maxillary fixed and removable implant prostheses: Patient satisfaction and choice of prosthesis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroz, S.; Peroz, I.; Beuer, F.; von Stein-Lausnitz, M.; Sterzenbach, G. Digital versus conventional complete dentures: A randomized, controlled, double-blinded crossover trial. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattadiyil, M.T.; Jekki, R.; Goodacre, C.J.; Baba, N.Z. Comparison of treatment outcomes in digital and conventional complete removable dental prosthesis fabrications in a predoctoral setting. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 114, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidra, A.S.; Farrell, K.; Burnham, D.; Dhingra, A.; Taylor, T.D.; Kuo, C.L. Prospective cohort pilot study of 2-visit CAD/CAM monolithic complete dentures and implant-retained overdentures: Clinical and patient-centered outcomes. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 578–586 e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwindling, F.S.; Stober, T. A comparison of two digital techniques for the fabrication of complete removable dental prostheses: A pilot clinical study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHelal, A.; AlRumaih, H.S.; Kattadiyil, M.T.; Baba, N.Z.; Goodacre, C.J. Comparison of retention between maxillary milled and conventional denture bases: A clinical study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stability of maxillary/mandibular denture under pressure and functional movements |
| 2: Within tissue displacement of a denture base under rotational/horizontal forces |
| 1: Displacement beyond normal tissue pattern |
| 0: Sliding of a denture base under rotational/horizontal forces |
| Retention of maxillary/mandibular denture |
| 2: Very good resistance to vertical pulling and lateral force on central incisors |
| 1: Moderate resistance to vertical pulling and little resistance to lateral force on central incisors |
| 0: Poor resistance to vertical pulling and no resistance to lateral force on central incisors |
| Border extension of maxillary/mandibular denture |
| 2: All satisfactory anatomical points |
| 1: max. three negative findings |
| 0: Overall flange overextension/sub-extension |
| Denture polish |
| 2: no negative findings |
| 1: one negative finding |
| 0: two or more negative findings |
| Aesthetics (teeth selection, arrangement of anterior teeth, smile line, lip support) |
| 2: no negative findings |
| 1: one negative finding |
| 0: two or more negative findings |
| Phonetics |
| 2: proper pronunciation (“S”, “F”, “TH”) |
| 1: discreet lisping and/or mumbling |
| 0: pronounced lisping and/or mumbling |
| Static occlusion |
| 2: continuously firm intermaxillary contacts in the posterior segment/soft contacts in the anterior segment |
| 1: incorrect intercuspation—up to two premature contacts |
| 0: incorrect intercuspation—three or more contacts to adjust |
| Dynamic occlusion |
| 2: canine guidance on the working side |
| 1: balance contact in the posterior segment |
| 0: hyper-balanced articulation |
| Vertical dimension |
| 2: interocclusal rest space 2 to 5 mm |
| 1: interocclusal rest space 1 or 6 mm |
| 0: interocclusal rest space < 1 mm or >6 mm |
| CD Type | Conventional Dentures | Digital Dentures | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grades | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | p Value | |
| Upper stability | 0 (0%) | 8 (80%) | 2 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (30%) | 7 (70%) | 0.025 |
| Lower stability a | 1 (10%) | 8 (80%) | 1 (10%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (60%) | 4 (40%) | 0.102 |
| Upper retention | 0 (0%) | 3 (30%) | 7 (70%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) | 9 (90%) | 0.157 |
| Lower retention a | 2 (20%) | 6 (60%) | 2 (20%) | 1 (10%) | 7 (70%) | 2 (20%) | 0.705 |
| Upper border extension | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) | 9 (90%) | 0.317 |
| Lower bd. extension a | 0 (0%) | 2 (20%) | 8 (80%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) | 9 (90%) | 0.317 |
| Denture polish | 0 (0%) | 2 (20%) | 8 (80%) | 0 (0%) | 8 (80%) | 2 (20%) | 0.034 |
| Aesthetics a | 0 (0%) | 5 (50%) | 5 (50%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (30%) | 7 (70%) | 0.414 |
| Phonetics | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (20%) | 8 (80%) | 0.157 |
| Static occlusion a | 0 (0%) | 9 (90%) | 1 (10%) | 1 (10%) | 6 (60%) | 3 (30%) | 0.564 |
| Dynamic occlusion a | 1 (10%) | 4 (40%) | 5 (50%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (50%) | 5 (50%) | 0.564 |
| Vertical dimension a | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (100%) | 1.000 |
| Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | p value | |||
| Sato-score | 67.4 ± 11.8 | 68.0 (66.0–75.3) | 73.2 ± 12.3 | 74.0 (66.0–85.0) | 0.160 | ||
| CD Type | OLD (O) | Conventional (C) | Digital (D) | p Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OHIP-Items | Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | O–D/C | C–D |
| Chewing difficulties | 3.5 ± 1.8 | 4.0 (1.8–4.8) | 4.2 ± 1.5 | 5.0 (4.0–5.0) | 3.7 ± 1.8 | 4.5 (2.3–5.0) | 0.530 | 0.363 |
| Food debris accumulation | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 2.5 (2.0–3.8) | 4.4 ± 1.4 | 4.5 (4.0–5.0) | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 4.5 (4.0–5.0) | 0.008 | 0.591 |
| Fit of the prosthesis | 3.4 ± 1.9 | 3.5 (1.5–5.0) | 4.7 ± 1.5 | 5.0 (4.3–5.8) | 4.1 ± 1.9 | 4.5 (3.3–5.8) | 0.206 | 0.425 |
| Pain in the mouth | 4.4 ± 1.5 | 5.0 (4.0–5.0) | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 4.0 (4.0–5.0) | 4.3 ± 1.9 | 5.0 (3.0–6.0) | 0.879 | 1.000 |
| Chewing efficiency | 3.3 ± 1.7 | 4.0 (2.0–4.0) | 4.5 ± 1.4 | 5.0 (4.3–5.0) | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 5.0 (3.3–5.0) | 0.107 | 0.678 |
| Wounds in the mouth | 4.2 ± 1.8 | 4.0 (3.3–6.0) | 4.2 ± 1.5 | 4.0 (4.0–5.5) | 3.9 ± 1.9 | 4.0 (3.0–5.8) | 0.831 | 0.604 |
| Discomfort | 4.2 ± 1.9 | 5.0 (3.3–5.8) | 5.1 ± 0.9 | 5.0 (4.3–6.0) | 4.6 ± 1.8 | 5.0 (4.3–6.0) | 0.399 | 0.427 |
| Concerns | 4.6 ± 1.9 | 5.5 (3.5–6.0) | 5.5 ± 0.5 | 5.5 (5.0–6.0) | 5.0 ± 1.2 | 5.0 (5.0–5.8) | 0.301 | 0.138 |
| Feeling of uneasiness | 3.7 ± 1.6 | 4.0 (3.3–4.8) | 5.4 ± 0.7 | 5.5 (5.0–6.0) | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 5.5 (5.0–6.0) | 0.007 | 0.591 |
| Omitting certain foods | 3.3 ± 1.6 | 3.0 (2.0–4.8) | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 4.5 (4.0–5.0) | 4.3 ± 1.2 | 4.5 (4.0–5.0) | 0.084 | 0.678 |
| Impaired dietary habits | 4.5 ± 1.7 | 5.0 (3.3–6.0) | 5.0 ± 1.4 | 5.5 (5.0–6.0) | 4.8 ± 1.0 | 5.0 (4.0–5.8) | 0.438 | 0.662 |
| Inability to eat | 4.6 ± 1.6 | 5.0 (3.5–6.0) | 5.4 ± 1.0 | 6.0 (5.0–6.0) | 5.2 ± 0.9 | 5.5 (4.3–6.0) | 0.234 | 0.509 |
| Interruption of meals | 4.5 ± 1.4 | 4.5 (4.0–5.8) | 5.1 ± 0.7 | 5.0 (5.0–5.8) | 4.7 ± 1.7 | 5.5 (4.0–6.0) | 0.405 | 0.309 |
| Anger | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 4.0 (3.0–5.0) | 5.1 ± 0.7 | 5.0 (5.0–5.8) | 4.6 ± 1.6 | 5.0 (4.0–6.0) | 0.054 | 0.343 |
| Embarrassment | 4.5 ± 1.6 | 5.0 (3.3–6.0) | 5.4 ± 0.7 | 5.5 (5.0–6.0) | 5.0 ± 1.5 | 5.0 (5.0–6.0) | 0.163 | 0.269 |
| Averse to go out | 4.8 ± 1.8 | 6.0 (3.5–6.0) | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 5.5 ± 1.6 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 0.121 | 0.343 |
| Social intolerance | 4.9 ± 1.2 | 5.0 (4.3–6.0) | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 5.5 ± 1.3 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 0.053 | 0.435 |
| Irritability | 5.0 ± 1.2 | 5.0 (5.0–6.0) | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 6.0 (5.3–6.0) | 5.4 ± 1.3 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 0.093 | 0.468 |
| Inability to enjoy company | 4.9 ± 1.4 | 5.0 (5.0–6.0) | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 5.6 ± 1.3 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 0.052 | 0.496 |
| Life less satisfying | 4.4 ± 1.8 | 5.0 (3.5–5.8) | 5.5 ± 0.8 | 6.0 (5.3–6.0) | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 6.0 (6.0–6.0) | 0.068 | 1.000 |
| OHIP-20 TOTAL SCORE | 83.1 ± 27.1 | 95.5 (63.0–99.5) | 101.7 ± 12.0 | 106.0 (93.8–109.3) | 95.6 ± 24.2 | 105.0 (87.8–110.8) | 0.116 | 0.332 |
| CD Type | Old (O) | Conventional | Digital | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satisfaction Factors | Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | Mean ± SD | Md (IQR) | O–D/C | C–D |
| Ease of cleaning | 8.9 ± 2.1 | 9.7 (9.4–9.8) | 8.8 ± 1.9 | 9.6 (9.4–9.9) | 9.8 ± 0.2 | 9.8 (9.7–9.9) | 0.631 | 0.140 |
| Satisfaction with dentures | 5.1 ± 3.7 | 6.1 (2.0–8.1) | 8.0 ± 1.9 | 8.7 (6.3–9.4) | 8.3 ± 1.8 | 9.2 (6.6–9.7) | 0.048 | 0.592 |
| Ability to speak | 7.3 ± 3.6 | 9.6 (4.9–9.8) | 9.3 ± 0.5 | 9.6 (8.8–9.7) | 8.6 ± 1.7 | 9.5 (8.0–9.7) | 0.232 | 0.112 |
| Comfort | 5.2 ± 3.8 | 6.0 (2.0–7.9) | 7.8 ± 2.3 | 8.4 (5.9–9.6) | 8.6 ± 1.7 | 9.5 (7.0–9.8) | 0.053 | 0.294 |
| Aesthetics | 6.4 ± 4.0 | 8.3 (3.9–9.5) | 9.4 ± 0.6 | 9.7 (9.2–9.9) | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 9.9 (9.6–9.9) | 0.031 | 0.121 |
| Stability | 4.6 ± 3.8 | 5.1 (1.2–8.0) | 8.0 ± 2.9 | 9.6 (5.9–9.9) | 8.4 ± 2.8 | 9.8 (8.7–9.9) | 0.021 | 0.300 |
| Overall chewing efficiency | 4.4 ± 2.9 | 4.8 (2.1–5.1) | 7.6 ± 1.9 | 8.4 (6.0–8.8) | 7.5 ± 2.7 | 8.5 (5.7–9.5) | 0.009 | 0.855 |
| Ability to chew white bread | 7.8 ± 2.3 | 8.5 (6.9–9.4) | 9.0 ± 1.5 | 9.5 (8.8–9.9) | 8.6 ± 2.4 | 9.7 (8.9–9.9) | 0.277 | 0.664 |
| Ability to chew cheese | 5.0 ± 3.7 | 4.2 (3.2–8.5) | 7.2 ± 3.3 | 9.0 (4.9–9.8) | 7.1 ± 3.3 | 8.2 (6.4–9.3) | 0.067 | 0.891 |
| Ability to chew beets | 3.1 ± 2.7 | 2.4 (1.4–4.6) | 5.9 ± 3.3 | 7.5 (3.2–8.4) | 5.8 ± 3.2 | 6.9 (3.0–7.8) | 0.029 | 0.786 |
| Ability to chew sausages | 3.4 ± 3.1 | 2.3 (1.5–4.6) | 6.0 ± 3.0 | 7.4 (3.1–8.0) | 7.1 ± 2.9 | 7.9 (6.8–8.9) | 0.022 | 0.122 |
| Ability to chew steaks | 4.6 ± 4.1 | 3.6 (1.1–8.3) | 7.1 ± 3.5 | 8.7 (5.4–9.8) | 7.7 ± 3.1 | 8.9 (7.0–9.7) | 0.161 | 0.524 |
| Ability to chew apples | 4.0 ± 3.2 | 3.2 (1.3–6.4) | 7.1 ± 3.0 | 8.3 (5.6–9.2) | 6.8 ± 3.0 | 7.1 (5.3–9.2) | 0.016 | 0.734 |
| Ability to chew salad | 7.0 ± 3.0 | 7.8 (5.9–9.3) | 8.2 ± 2.9 | 9.4 (8.4–9.8) | 8.6 ± 2.0 | 9.6 (8.3–9.8) | 0.175 | 0.425 |
| Satisfaction with oral health | 6.1 ± 3.5 | 7.3 (4.2–8.8) | 7.7 ± 2.8 | 8.5 (7.4–9.4) | 7.7 ± 3.0 | 9.3 (6.3–9.7) | 0.147 | 0.925 |
| Health affection by oral health status | 20.0% | 10.0% | 10.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zupancic Cepic, L.; Gruber, R.; Eder, J.; Vaskovich, T.; Schmid-Schwap, M.; Kundi, M. Digital versus Conventional Dentures: A Prospective, Randomized Cross-Over Study on Clinical Efficiency and Patient Satisfaction. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020434
Zupancic Cepic L, Gruber R, Eder J, Vaskovich T, Schmid-Schwap M, Kundi M. Digital versus Conventional Dentures: A Prospective, Randomized Cross-Over Study on Clinical Efficiency and Patient Satisfaction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(2):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020434
Chicago/Turabian StyleZupancic Cepic, Lana, Reinhard Gruber, Jaryna Eder, Tom Vaskovich, Martina Schmid-Schwap, and Michael Kundi. 2023. "Digital versus Conventional Dentures: A Prospective, Randomized Cross-Over Study on Clinical Efficiency and Patient Satisfaction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 2: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020434
APA StyleZupancic Cepic, L., Gruber, R., Eder, J., Vaskovich, T., Schmid-Schwap, M., & Kundi, M. (2023). Digital versus Conventional Dentures: A Prospective, Randomized Cross-Over Study on Clinical Efficiency and Patient Satisfaction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(2), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020434








