PNI as a Potential Add-On Biomarker to Improve the IMDC Intermediate Prognostic Score
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Patients
3.2. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis for Progression-Free Survival
3.3. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis for Overall Survival
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibovich, B.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Crispen, P.L.; Boorjian, S.A.; Thompson, R.H.; Blute, M.L.; Cheville, J.C. Histological subtype is an independent predictor of outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.N.A.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; Chen, H.S.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics, Review, Based on November 2016 SEER Data Submission, Posted to the SEER Web Site aNCI, Bethesda MAahscgc. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2014/ (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Motzer, R.J.; Bacik, J.; Murphy, B.A.; Russo, P.; Mazumdar, M. Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: Results from a large, multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Jonasch, E.; Boyle, S.; Carlo, M.I.; Manley, B.; Agarwal, N.; Alva, A.; Beckermann, K.; Choueiri, T.K.; Costello, B.A.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Kidney Cancer, Version 1.2021. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2020, 18, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T. Recent eUpdate to the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines on renal cell carcinoma on cabozantinib and nivolumab for first-line clear cell renal cancer: Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2021, 32, 422–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Motzer, R.J. Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Royle, K.L.; Gregory, W.; Ralph, C.; Maraveyas, A.; Din, O.; Eisen, T.; Nathan, P.; Powles, T.; Griffiths, R.; et al. Temporary treatment cessation versus continuation of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (STAR): An open-label, non-inferiority, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manneh, R.; Lema, M.; Carril-Ajuria, L.; Ibatá, L.; Martínez, S.; Castellano, D.; de Velasco, G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Combination Therapy versus Sunitinib as First-Line Treatment for Favorable-IMDC-Risk Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sella, A.; Michaelson, M.D.; Matczak, E.; Simantov, R.; Lin, X.; Figlin, R.A. Heterogeneity of Patients With Intermediate-Prognosis Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Sunitinib. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2017, 15, 291–299.e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, R.; Ozguven, S.; Telli, T.A.; Isik, S.; Demircan, N.C.; Basoglu, T.; Yasar, A.; Celebi, A.; Filizoglu, N.; Ustun, H.S.; et al. Prognostic significance of 18F-FDG PET/CT indices in metastatic renal cell cancer and evaluation of revised IMDC risk model by including 18F-FDG PET-CT parameters. Acta Radiol. 2023, 64, 2040–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, S.R.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, D.S. Prognostic nutritional index as a prognostic factor for renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Mackenzie, M.; Wood, L.; Donskov, F.; Tan, M.H.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Albiges, L.; Staehler, M.; Bensalah, K.; Dabestani, S.; Giles, R.H.; Hofmann, F.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Lam, T.B.; et al. Updated European Association of Urology Guidelines: Recommendations for the Treatment of First-line Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, N.; Obara, W.; Tatsugami, K.; Naito, S.; Kamba, T.; Takahashi, M.; Murai, S.; Abe, T.; Oba, K.; Naito, S. Prognosis of Japanese patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the era of molecular-targeted therapy. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.I.; Cho, D.S. Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Prognostic Nutritional Index in Patients Undergoing Nephrectomy for Nonmetastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 43, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuzzi, S.E.; Signori, A.; Buti, S.; Banna, G.L.; Murianni, V.; Damassi, A.; Maruzzo, M.; Giannarelli, D.; Tortora, G.; Galli, L.; et al. Validation of the Meet-URO score in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving first-line nivolumab and ipilimumab in the Italian Expanded Access Program. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunt, B. Advances and controversies in grading and staging of renal cell carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22 (Suppl. S2), S24–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Cheng, C.; Ficarra, V.; Murai, M.; Oudard, S.; Pantuck, A.J.; Zigeuner, R.; Karakiewicz, P.I. Prognostic factors and predictive models in renal cell carcinoma: A contemporary review. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskawi, M.; Sun, M.; Trinh, Q.D.; Bianchi, M.; Hansen, J.; Tian, Z.; Rink, M.; Ismail, S.; Shariat, S.F.; Montorsi, F.; et al. A review of integrated staging systems for renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Mazumdar, M.; Bacik, J.; Berg, W.; Amsterdam, A.; Ferrara, J. Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, P.J.; Witte, R.S.; Trump, D.L. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with recurrent or metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 7310–7313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bacik, J.; Mariani, T.; Russo, P.; Mazumdar, M.; Reuter, V. Treatment outcome and survival associated with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of non-clear-cell histology. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekhail, T.M.; Abou-Jawde, R.M.; Boumerhi, G.; Malhi, S.; Wood, L.; Elson, P.; Bukowski, R. Validation and extension of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering prognostic factors model for survival in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studentova, H.; Rusarova, N.; Ondruskova, A.; Zemankova, A.; Student, V., Jr.; Skanderova, D.; Melichar, B. The Role of Cytoreductive Nephrectomy in Renal Cell Carcinoma with Sarcomatoid Histology: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5475–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Porta, C.; Schmidinger, M.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Bex, A.; Khoo, V.; Grünwald, V.; Gillessen, S.; Horwich, A. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köstek, O.; Yılmaz, E.; Hacıoğlu, M.B.; Demircan, N.C.; Gökyer, A.; Uzunoğlu, S.; Tunçbilek, N.; Çiçin, İ.; Erdoğan, B. Changes in skeletal muscle area and lean body mass during pazopanib vs. sunitinib therapy for metastatic renal cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 83, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaliya, M.; Surati, D.; Surati, R.; Padmani, S.; Boussios, S. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Pazopanib Therapy. Diseases 2023, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
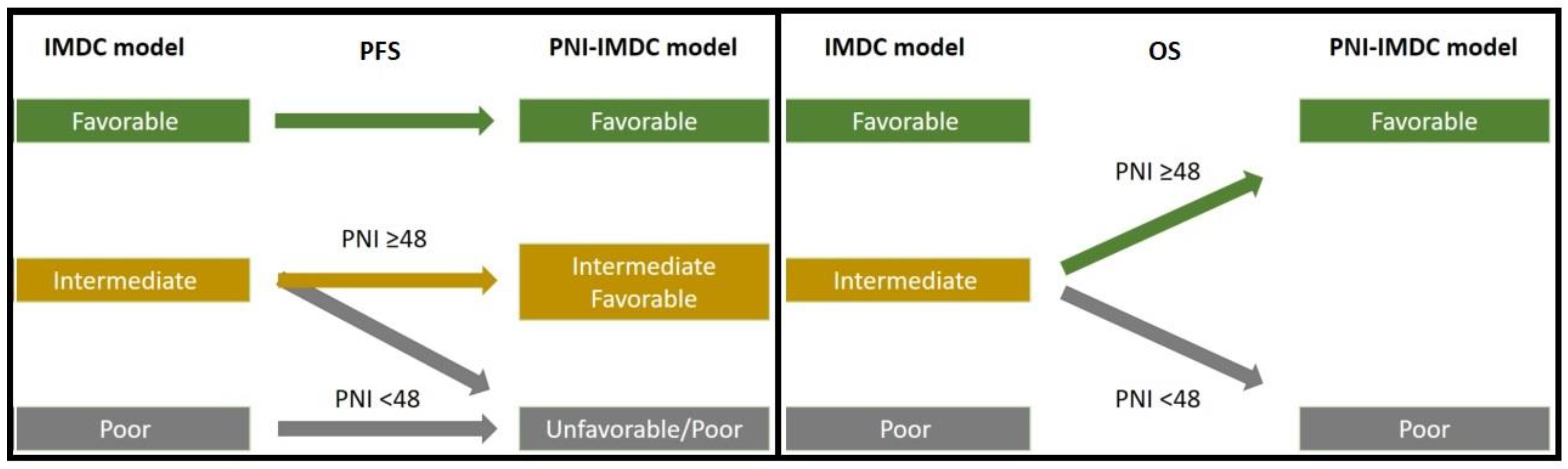


| Progression-Free Survival | Overall Survival | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (95%CI) | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Median (95%CI) | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age | ||||||
| <60 | 6.4 (3.6–9.2) | Ref. | 0.92 | 21.9 (2.1–40.2) | Ref. | 0.3 |
| ≥60 | 7.7 (4.6–10.8) | 1.023 (0.633–1.652) | 22.3 (12.2–32.5) | 1.264 (0.811–1.970) | ||
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 6.4 (2.8–9.9) | Ref. | 0.41 | 17.5 (9.1–25.9) | Ref. | 0.12 |
| Male | 6.9 (5.1–8.6) | 0.826 (0.523–1.305) | 25.4 (17.7–33.1) | 0.684 (0.423–1.107) | ||
| ECOG performance score | ||||||
| 0–1 | 7.2 (5.6–8.7) | Ref. | 0.11 | 25.4 (19.1–31.7) | Ref. | <0.001 |
| ≥2 | 3.5 (2.8–4.2) | 2.096 (0.844–5.206) | 4.1 (3.1–5.1) | 7.657 (3.529–16.612) | ||
| Histopathology | ||||||
| Clear cell | 7.4 (5.8–9.0) | Ref. | 0.4 | 23.9 (14.4–33.4) | Ref. | 0.85 |
| Non-clear cell | 4.3 (2.4–6.1) | 1.233 (0.753–2.018) | 19.7 (9.0–30.4) | 1.051 (0.606–1.824) | ||
| IMDC score, n (%) | ||||||
| Favorable | 20.4 (16.6–24.2) | Ref. | <0.001 | 41.3 (0.5–82.1) | Ref. | 0.004 |
| Intermediate | 6.4 (4.8–8.0) | 3.698 (1.893–7.226) | <0.001 | 20.1 (10.4–29.7) | 1.717 (0.959–3.074) | 0.07 |
| Poor | 3.8 (2.9–4.7) | 6.201 (2.824–13.615) | <0.001 | 12.4 (1.2–23.7) | 3.411 (1.641–7.089) | 0.001 |
| PNI | ||||||
| <48 | 3.8 (3.3–4.2) | Ref. | <0.001 | 12.5 (5.5–19.5) | Ref. | 0.001 |
| ≥48 | 10.9 (7.7–14.0) | 0.444 (0.298–0.662) | 32.3 (17.2–47.5) | 0.460 (0.291–0.726) | ||
| Adjusted IMDCC and PNI model | ||||||
| Favorable | 20.4 (16.6–24.2) | Ref. | <0.001 | 41.3 (0.5–82.1) | Ref. | 0.001 |
| Intermediate (PNI-High) | 10.8 (8.8–12.8) | 2.648 (1.302–5.386) | 0.007 | 30.3 (18.0–42.6) | 1.219 (0622–2.390) | 0.564 |
| Intermediate (PNI-Low) | 3.8 (3.6–3.9) | 5.497 (2.722–11.103) | <0.001 | 12.5 (5.6–19.4) | 2.315 (1.223–4.382) | 0.01 |
| Poor | 3.8 (2.9–4.7) | 6.108 (2.803–13.311) | <0.001 | 12.4 (1.2–23.7) | 3.510 (1.685–7.312) | 0.001 |
| Primary nephrectomy, n (%) | ||||||
| Absent | 3.7 (2.6–4.7) | Ref. | 0.85 | 7.8 (4.5–11.1) | Ref. | <0.001 |
| Present | 7.7 (6.2–9.1) | 0.955 (0.571–1.595) | 30.3 (21.0–39.6) | 0.366 (0.228–0.588) | ||
| Sarcomatoid differentiation, n (%) | ||||||
| Absent | 7.1 (4.0–10.3) | Ref. | 0.59 | 37.0 (26.8–47.2) | Ref. | 0.08 |
| Present | 7.5 (6.5–8.5) | 0.849 (0.465–1.550) | 15.1 (11.1–19.1) | 2.097 (0.913–4.815) | ||
| Metastasectomy, present | 11.6 (4.5–18.8) | 0.616 (0.398–0.952) | 0.03 | 27.5 (15.4–39.6) | 0.728 (0.446–1.187) | 0.2 |
| Lung, present | 11.7 (3.0–20.5) | 0.707 (0.325–1.540) | 0.38 | 34.5 (25.3–43.7) | 0.570 (0.224–1.451) | 0.23 |
| Bone, present | 6.4 (2.8–10.0) | 1.912 (0.828–4.418) | 0.12 | 20.0 (2.7–37.3) | 1.496 (0.552–4.056) | 0.42 |
| Metastatic site | ||||||
| Bone, present | 4.3 (2.1–6.4) | 1.01 (0.677–1.481) | 0.99 | 15.1 (12.0–18.3) | 1.865 (1.190–2.923) | 0.007 |
| Visceral, present | 6.4 (4.4–8.4) | 1.192 (0.599–2.368) | 0.61 | 20.1 (12.2–27.9) | 1.597 (0.768–3.320) | 0.21 |
| Visceral metastasis | ||||||
| Lung, present | 6.8 (5.1–8.5) | 0.934 (0.548–1.593) | 0.8 | 22.3 (12.1–32.6) | 1.183 (0.663–2.109) | 0.56 |
| Liver, present | 4.3 (1.8–6.7) | 1.725 (1.069–2.784) | 0.02 | 13.2 (10.0–16.4) | 1.710 (1.032–2.831) | 0.03 |
| Brain, present | 12.4 (6.9–17.9) | 0.632 (0.318–1.258) | 0.19 | 16.0 (6.6–25.4) | 1.184 (0.569–2.466) | 0.65 |
| Metastasis site number | ||||||
| <3 | 7.4 (5.4–9.4) | Ref. | 0.36 | 32.3 (16.0–48.6) | Ref. | 0.007 |
| ≥3 | 4.2 (1.3–7.2) | 1.208 (0.801–1.819) | 15.1 (7.1–23.2) | 1.831 (1.177–2.851) | ||
| First-line tyrosine kinase option | ||||||
| Sunitinib | 6.0 (3.9–8.0) | Ref. | 0.78 | 25.4 (16.7–34.1) | Ref. | 0.21 |
| Pazopanib | 7.3 (3.6–11.1) | 0.944 (0.618–1.441) | 15.2 (12.5–18.0) | 1.325 (0.846–2.076) | ||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Histopathology, clear cell | 0.660 (0.380–1.145) | 0.13 | 0.652 (0.378–1.126) | 0.12 |
| IMDC score | 0.008 | |||
| Favorable | 0.308 (0.133–0.714) | 0.006 | ||
| Intermediate | 0.890 (0.508–1.561) | 0.68 | ||
| Poor | Ref. | |||
| PNI ≥ 48 | 0.503 (0.328–0.773) | 0.002 | ||
| Adjusted IMDCC and PNI model | <0.001 | |||
| Favorable | 0.226 (0.099–0.516) | <0.001 | ||
| Intermediate (PNI-High) | 0.484 (0.270–0.866) | 0.01 | ||
| Intermediate (PNI-Low) | 1.006 (0.556–1.822) | 0.98 | ||
| Poor | Ref. | |||
| Metastasectomy, present | 0.680 (0.433–1.068) | 0.09 | 0.683 (0.437–1.067) | 0.09 |
| Liver, present | 1.436 (0.859–2.401) | 0.16 | 1.518 (0.909–2.533) | 0.11 |
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Nephrectomy, present | 0.449 (0.270–0.748) | 0.002 |
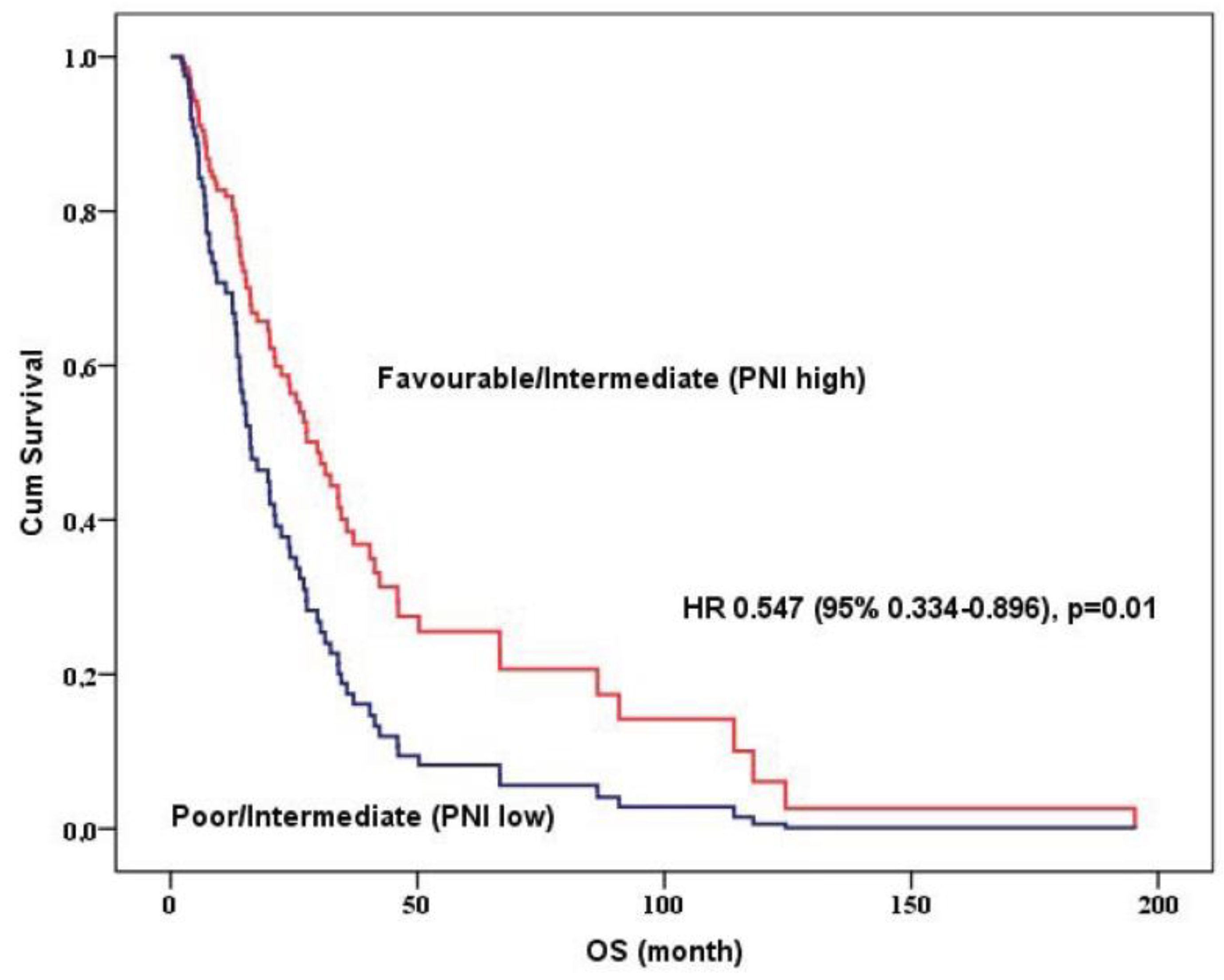
| Adjusted IMDCC and PNI model | 0.01 | |
| Favorable/Intermediate (PNI-High) | 0.547 (0.334–0.896) | |
| ECOG 2 and more, present | 4.220 (1.815–9.814) | 0.001 |
| Bone metastasis, present | 1.997 (1.252–3.185) | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayoğlu, İ.V.; Hüseynov, J.; Topal, A.; Sever, N.; Majidova, N.; Çelebi, A.; Yaşar, A.; Arıkan, R.; Işık, S.; Hacıoğlu, M.B.; et al. PNI as a Potential Add-On Biomarker to Improve the IMDC Intermediate Prognostic Score. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196420
Bayoğlu İV, Hüseynov J, Topal A, Sever N, Majidova N, Çelebi A, Yaşar A, Arıkan R, Işık S, Hacıoğlu MB, et al. PNI as a Potential Add-On Biomarker to Improve the IMDC Intermediate Prognostic Score. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196420
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayoğlu, İbrahim Vedat, Javid Hüseynov, Alper Topal, Nadiye Sever, Nargiz Majidova, Abdussamet Çelebi, Alper Yaşar, Rukiye Arıkan, Selver Işık, Muhammet Bekir Hacıoğlu, and et al. 2023. "PNI as a Potential Add-On Biomarker to Improve the IMDC Intermediate Prognostic Score" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196420
APA StyleBayoğlu, İ. V., Hüseynov, J., Topal, A., Sever, N., Majidova, N., Çelebi, A., Yaşar, A., Arıkan, R., Işık, S., Hacıoğlu, M. B., Ercelep, Ö., Sarı, M., Erdoğan, B., Hacıbekiroğlu, İ., Topaloğlu, S., Köstek, O., & Çiçin, İ. (2023). PNI as a Potential Add-On Biomarker to Improve the IMDC Intermediate Prognostic Score. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196420






