Lactate-Based Difference as a Determinant of Outcomes following Surgery for Type A Acute Aortic Dissection: A Multi-Centre Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Extraction and Cleaning
2.2. Study Endpoints
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
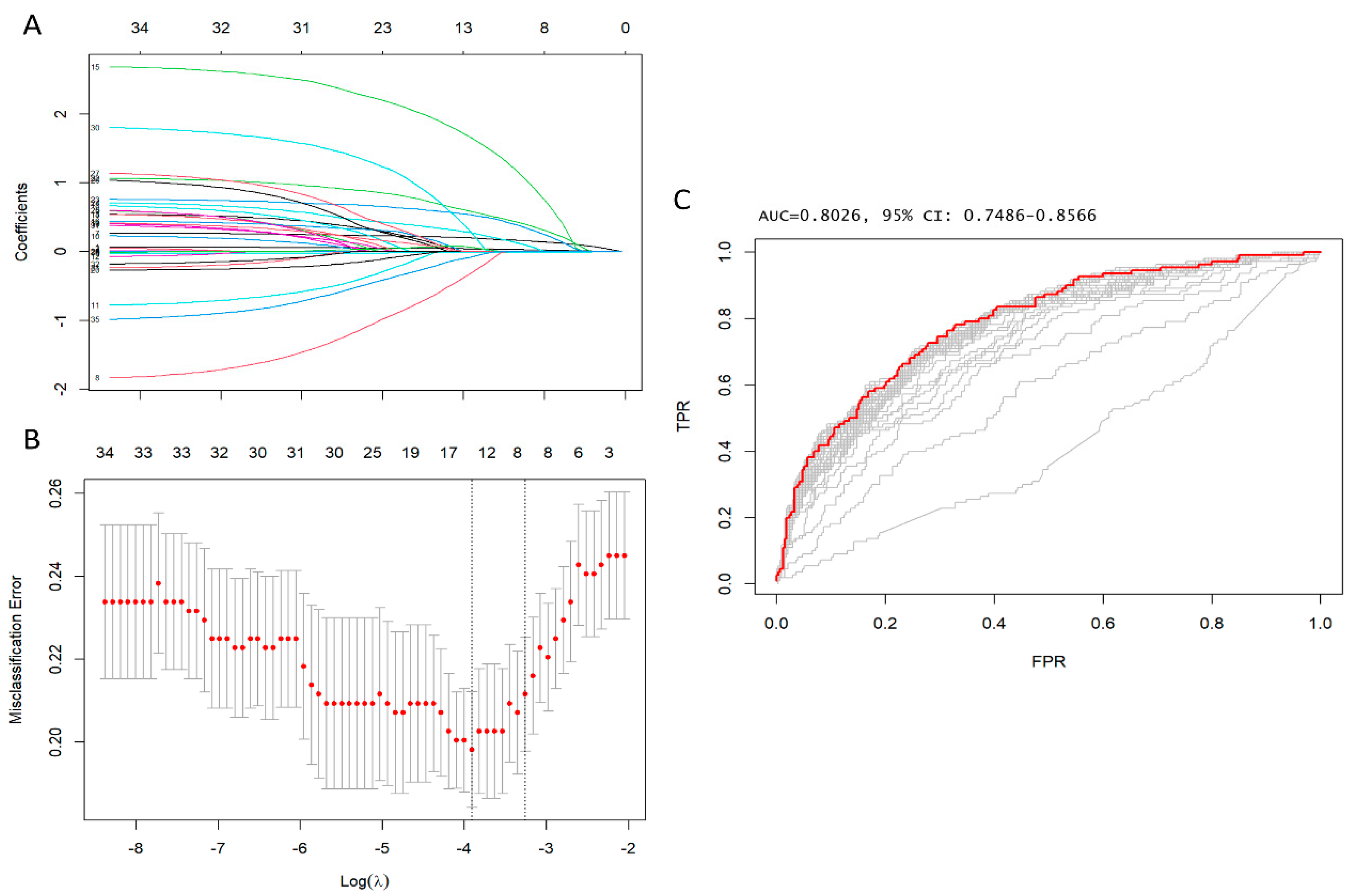
3.1. Predictors of Early Postoperative Mortality
3.2. Early Postoperative Outcomes
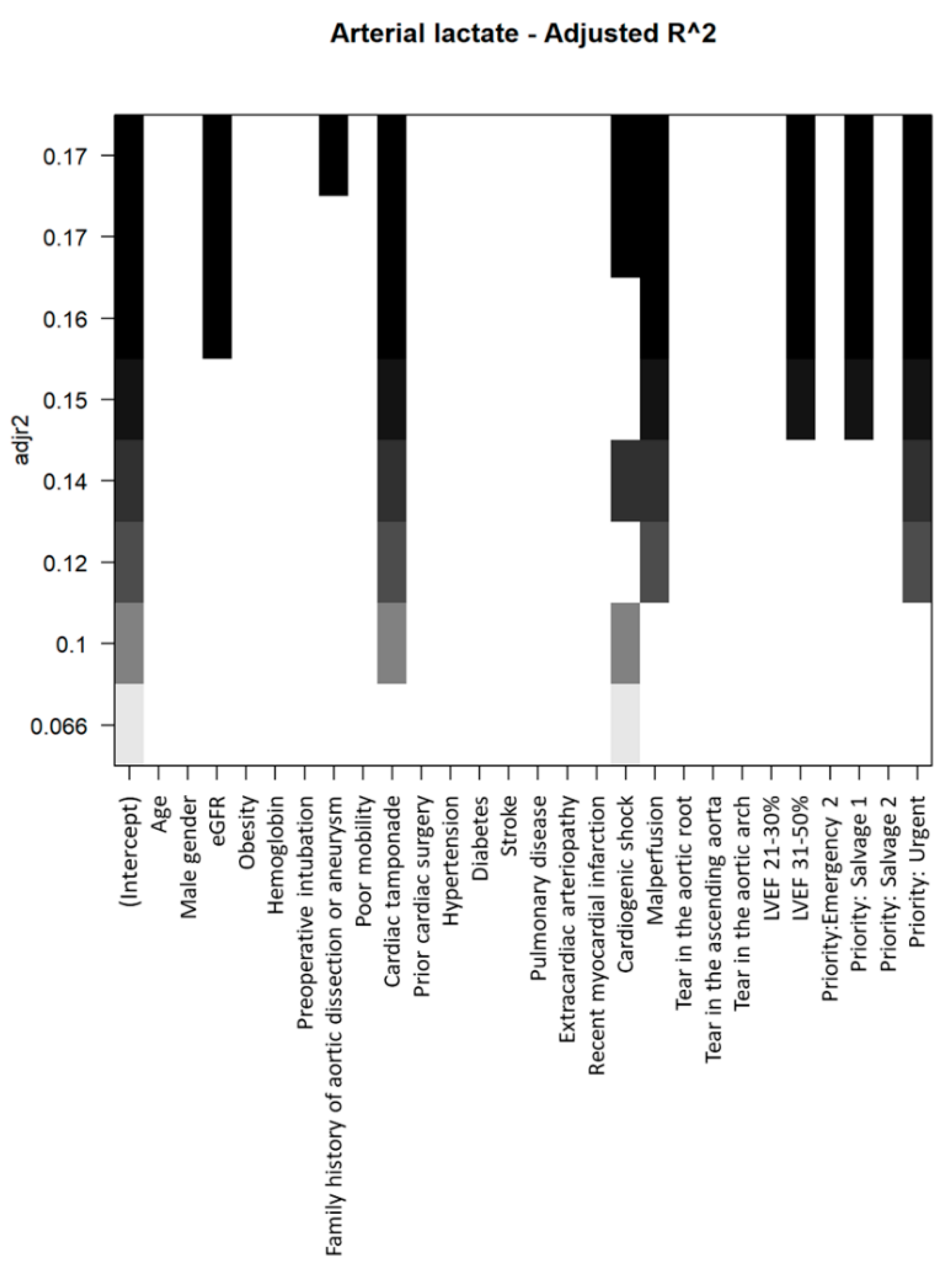
3.3. Predictors of Increased Preoperative Arterial Lactates
4. Discussion
4.1. Malperfusion Management Subgroup
4.2. Surgical Repair in Patients with Higher Lactate
4.3. Tailored Surgery
4.4. Processes of Care and Aortic Centres
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biancari, F.; Juvonen, T.; Fiore, A.; Perrotti, A.; Hervé, A.; Touma, J.; Pettinari, M.; Peterss, S.; Buech, J.; Dell’Aquila, A.M.; et al. Current outcome after surgery for type A aortic dissection. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, e885–e892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F.; Petiot, S.; Salsano, A.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Berger, J.; Kostantinou, M.; Bonnet, S.; Gambardella, I.; Biancari, F.; Almazil, A.; et al. Sex-based difference in aortic dissection outcomes: A multicenter study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, A.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Bossone, E.; Gleason, T.G.; Eusanio, M.D.; Sechtem, U.; Ehrlich, M.P.; Trimarchi, S.; Braverman, A.C.; Myrmel, T.; et al. Insights from the international registry of acute aortic dissection: A 20-year experience of collaborative clinical research. Circulation 2018, 137, 1846–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braverman, A.C. Acute aortic dissection: Clinician update. Circulation 2010, 122, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahase, E. Half of patients with acute aortic dissection in England die before reaching a specialist centre. BMJ 2020, 368, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.P.; Banerjee, A.; Fairhead, J.F.; Perkins, J.; Silver, L.E.; Rothwell, P.M. Oxford Vascular Study. Population-based study of incidence and outcome of acute aortic dissection and premorbid risk factor control: 10-year results from the Oxford vascular study. Circulation 2013, 127, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Gambardella, I.; Alzamil, A.; Salsano, A.; Santini, F.; Biancari, F.; Schoell, T.; Bonnet, N.; Folliguet, T.; et al. Surgical strategy for the repair of acute type A aortic dissection: A multicenter study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, U.; Dimagli, A.; Kaura, A.; Sinha, S.; Mariscalco, G.; Krasopoulos, G.; Moorjani, N.; Field, M.; Uday, T.; Kendal, S.; et al. Determinants of outcomes following surgery for type A acute aortic dissection: The UK national adult cardiac surgical audit. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 43, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossone, E.; Gorla, R.; LaBounty, T.M.; Suzuki, T.; Gilon, D.; Strauss, C.; Ballotta, A.; Patel, H.J.; Evangelista, A.; Ehrlich, M.P. Presenting systolic blood pressure and outcomes in patients with acute aortic dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzelmann, L.O.; Weigang, E.; Mehlhorn, U.; Abugameh, A.; Hoffmann, I.; Blettner, M.; Etz, C.D.; Czerny, M.; Vahl, C.F.; GERAADA Investigators. Mortality in patients with acute aortic dissection type A: Analysis of pre- and intraoperative risk factors from the German Registry for Acute Aortic Dissection Type A (GERAADA). Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 49, e44–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirsson, A.; Shioda, K.; Olsson, C.; Ahlsson, A.; Gunn, J.; Hansson, E.C.; Hjortdal, V.; Jeppsson, A.; Mennander, A.; Wickbom, A.; et al. Differential outcomes of open and clamp-on distal anastomosis techniques in acute type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 157, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, D.; McLarty, A.; Sun, E.; Itagaki, S.; Tannous, H.; Chu, D.; Egorova, N.; Chikwe, J. Type-A Aortic Dissection and Cerebral Perfusion: The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Database Analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 110, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbel, R.; Aboyans, V.; Boileau, C.; Bossone, E.; Bartolomeo, R.D.; Eggebrecht, H.; Evangelista, A.; Falk, V.; Frank, H.; Gaemperli, O.; et al. ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2873–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, W.C.; Green, S.Y.; Orozco-Sevilla, V.; Preventza, O.; Coselli, J.S. Contemporary Surgical Strategies for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 32, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Robinson, N.B.; Farrington, W.J.; Rahouma, M.; Gambardella, I.; Gaudino, M.; Girardi, L.N. A tailored strategy for repair of acute type A aortic dissection J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 164, 1698–1707.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Norton, E.L.; Hobbs, R.; Farhat, L.; Wu, X.; Hornsby, W.E.; Kim, K.M.; Patel, H.J.; Deeb, G.M. Short- and long-term outcomes of aortic root repair and replacement in patients undergoing acute type A aortic dissection repair: Twenty-year experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 157, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, A.; Miyahara, S.; Yamanaka, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Matsumori, M.; Okada, K.; Okita, Y. Early and late outcomes of repaired acute DeBakey type I aortic dissection after graft replacement. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 151, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Qi, R.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J. Total arch replacement combined with stented elephant trunk implantation: A new “standard” therapy for type a dissection involving repair of the aortic arch? Circulation 2011, 123, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylski, B.; Milewski, R.K.; Bavaria, J.E.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Moser, W.; Szeto, W.Y.; Desai, N.D. Long-term results of aggressive hemiarch replacement in 534 patients with type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 2981–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, H.H.; Richardt, D.; Diwoky, M.; Auer, C.; Bucsky, B.; Nasseri, B.; Klotz, S. Survival and reoperation after valve-sparing root replacement and root repair in acute type A dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 156, 2076–2082.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.D.; Ganapathi, A.M.; Hanna, J.M.; Williams, J.B.; Gaca, J.G.; Hughes, G.C. Outcomes of acute type a dissection repair before and after implementation of a multidisciplinary thoracic aortic surgery program. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, J.S.; Liu, J.; Kulshrestha, K.; Moon, M.R.; Damiano RJJr Maniar, H.; Pasque, M.K. The impact of surgical strategy on survival after repair of type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 150, 294–301.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvonen, T.; Jormalainen, M.; Mustonen, C.; Demal, T.; Fiore, A.; Perrotti, A.; Hervé, A.; Mazzaro, E.; Gatti, G.; Pettinari, M.; et al. Direct Aortic Versus Supra-Aortic Arterial Cannulation During Surgery for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. World J. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancari, F.; Dell'Aquila, A.M.; Gatti, G.; Perrotti, A.; Hervé, A.; Touma, J.; Pettinari, M.; Peterss, S.; Buech, J.; Wisniewski, K.; et al. Interinstitutional analysis of the outcome after surgery for type A aortic dissection. Eur. J. Trauma. Emerg. Surg. 2023, 49, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancari, F.; Pettinari, M.; Mariscalco, G.; Mustonen, C.; Nappi, F.; Buech, J.; Hagl, C.; Fiore, A.; Touma, J.; Dell'Aquila, A.M.; et al. Outcome after Surgery for Iatrogenic Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grembi, J.A.; Rogawski McQuade, E.T. Introducing risk Communicator: An R package to obtain interpretable effect estimates for public health. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Variable selection with stepwise and best subset approaches. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancari, F.; Mariscalco, G.; Yusuff, H.; Tsang, G.; Luthra, S.; Onorati, F.; Francica, A.; Rossetti, C.; Perrotti, A.; Chocron, S.L.; et al. European registry of type A aortic dissection (ERTAAD)—Rationale, design and definition criteria. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 16, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratzka, L.F.; Bakris, G.L.; Beckman, J.A.; Bersin, R.M.; Carr, V.F.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Eagle, K.A.; Hermann, L.K.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Kazerooni, E.A.; et al. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with thoracic aortic disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, e27–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonser, R.S.; Ranasinghe, A.M.; Loubani, M.; Evans, J.D.; Thalji, N.M.; Bachet, J.E.; Carrel, T.P.; Czerny, M.; Di Bartolomeo, R.; Grabenwöger, M.; et al. Evidence, lack of evidence, controversy, and debate in the provision and performance of the surgery of acute type A aortic dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2455–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassar, A.S.; Sundt, T.M., 3rd. How should we manage type A aortic dissection? Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 67, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, A.E., Jr.; Johns, V.J., Jr.; Kime, S.W., Jr. Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: A review of 505 cases. Medicine 1958, 37, 217–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.; Thordsen, S.; Thomas, T.; Mackey-Bojack, S.M.; Duncanson, E.R.; Nwuado, D.; Garberich, R.F.; Harris, K.M. Clinical and pathologic findings of aortic dissection at autopsy: Review of 336 cases over nearly 6 decades. Am. Heart J. 2019, 209, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.M.; Nienaber, C.A.; Peterson, M.D.; Woznicki, E.M.; Braverman, A.C.; Trimarchi, S.; Myrmel, T.; Pyeritz, R.; Hutchison, S.; Strauss, C.; et al. Early Mortality in Type A Acute Aortic Dissection: Insights From the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pape, L.A.; Awais, M.; Woznicki, E.M.; Suzuki, T.; Trimarchi, S.; Evangelista, A.; Myrmel, T.; Larsen, M.; Harris, K.M.; Greason, K.; et al. Presentation, Diagnosis, and Outcomes of Acute Aortic Dissection: 17-Year Trends From the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Montgomery, D.; Brinster, D.R.; Gilon, D.; Upchurch, G.R., Jr.; Gleason, T.G.; Estrera, A.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Eagle, K.A.; Hughes, G.C. Predicting In-Hospital Survival in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Medically Treated. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1360–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampoldi, V.; Trimarchi, S.; Eagle, K.A.; Nienaber, C.A.; Oh, J.K.; Bossone, E.; Myrmel, T.; Sangiorgi, G.M.; De Vincentiis, C.; Cooper, J.V.; et al. Simple risk models to predict surgical mortality in acute type A aortic dissection: The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection score. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 83, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T.C.; Beaulieu, R.J.; Ehlert, B.A.; Ratchford, E.V.; Black, J.H., 3rd. Malperfusion syndromes in aortic dissections. Vasc. Med. 2016, 21, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimarchi, S.; Eagle, K.A.; Nienaber, C.A.; Rampoldi, V.; Jonker, F.H.; De Vincentiis, C.; Frigiola, A.; Menicanti, L.; Tsai, T.; Froehlich, J.; et al. Role of age in acute type A aortic dissection outcome: Report from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 40, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helder, M.R.K.; Schaff, H.V.; Day, C.N.; Pochettino, A.; Bagameri, G.; Greason, K.L.; Lansman, S.L.; Girardi, L.N.; Storlie, C.B.; Habermann, E.B. Regional and Temporal Trends in the Outcomes of Repairs for Acute Type A Aortic Dissections. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 109, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylski, B.; Beyersdorf, F.; Kari, F.A.; Schlosser, J.; Blanke, P.; Siepe, M. Acute type A aortic dissection extending beyond ascending aorta: Limited or extensive distal repair. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; Chung, C.H.; Moon, D.H.; Ha, G.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Choo, S.J.; Lee, J.W. Total arch repair versus hemiarch repair in the management of acute DeBakey type I aortic dissection. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011, 40, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolomeo, R.; Leone, A.; Di Marco, L.; Pacini, D. When and how to replace the aortic arch for type A dissection. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Eusanio, M.; Berretta, P.; Cefarelli, M.; Jacopo, A.; Murana, G.; Castrovinci, S.; Di Bartolomeo, R. Total Arch Replacement Versus More Conservative Management in Type A Acute Aortic Dissection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lang, X.; Lu, F.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Xu, Z. Acute type A dissection without intimal tear in arch: Proximal or extensive repair? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leshnower, B.G.; Chen, E.P. When and how to replace the aortic root in type A aortic dissection. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirsson, A.; Bavaria, J.E.; Swarr, D.; Keane, M.G.; Woo, Y.J.; Szeto, W.Y.; Pochettino, A. Fate of the residual distal and proximal aorta after acute type a dissection repair using a contemporary surgical reconstruction algorithm. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 84, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berretta, P.; Patel, H.J.; Gleason, T.G.; Sundt, T.M.; Myrmel, T.; Desai, N.; Korach, A.; Panza, A.; Bavaria, J.; Khoynezhad, A.; et al. IRAD experience on surgical type A acute dissection patients: Results and predictors of mortality. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.M.; Strauss, C.E.; Eagle, K.A.; Hirsch, A.T.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Tsai, T.T.; Shiran, H.; Fattori, R.; Evangelista, A.; Cooper, J.V.; et al. Correlates of delayed recognition and treatment of acute type A aortic dissection: The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Circulation. 2011, 124, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikwe, J.; Cavallaro, P.; Itagaki, S.; Seigerman, M.; Diluozzo, G.; Adams, D.H. National outcomes in acute aortic dissection: Influence of surgeon and institutional volume on operative mortality. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 95, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.D.; Benrashid, E.; Ross, A.K.; Pickett, L.C.; Smith, P.K.; Daneshmand, M.A.; Schroder, J.N.; Gaca, J.G.; Hughes, G.C. The utility of the aortic dissection team: Outcomes and insights after a decade of experience. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaja, R.; Talukder, S.; Norkunas, M.; Hoffman, R.; Nienaber, C.; Pepper, J.; Rosendahl, U.; Asimakopoulos, G.; Quarto, C. Impact of a streamlined rotational system for the management of acute aortic syndrome: Sharing is caring†. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstone, A.B.; Chiu, P.; Baiocchi, M.; Lingala, B.; Lee, J.; Rigdon, J.; Fischbein, M.P.; Woo, Y.J. Interfacility Transfer of Medicare Beneficiaries With Acute Type A Aortic Dissection and Regionalization of Care in the United States. Circulation 2019, 140, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helliker, K.; Burton, T. Medical ignorance contributes to toll from aortic illness. The Wall Street Journal, 4 November 2003. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | N = 449 |
|---|---|
| Age (median [IQR]) | 65.00 [56.00, 75.00] |
| Male | 304 (67.7) |
| Weight, kg (median [IQR]) | 77.00 [69.00, 85.00] |
| Height, cm (median [IQR]) | 172.00 [165.00, 178.00] |
| Obesity (%) | 67 (14.9) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 (median [IQR]) | 72.00 [56.00, 87.75] |
| Haemoglobin, g/L (median [IQR]) | 122.00 [108.00, 136.00] |
| Arterial lactate, mmol/L (median [IQR]) | 1.40 [1.00, 2.80] |
| Family history of aortic dissection or aneurysm (%) | 31 (6.9) |
| Prior cardiac surgery (%) | 17 (3.8) |
| Hypertension (%) | 350 (78.0) |
| Diabetes (%) | 25 (5.6) |
| Stroke (%) | 6 (1.3) |
| Pulmonary disease (%) | 24 (5.3) |
| Extracardiac arteriopathy (%) | 21 (4.7) |
| Poor mobility (%) | 11 (2.4) |
| Recent myocardial infarction (%) | 17 (3.8) |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction (%) | |
| >50% | 278 (61.9) |
| 21–30% | 8 (1.8) |
| 31–50% | 163 (36.3) |
| Systolic pulmonary artery pressure (%) | |
| <30 mmHg | 365 (81.3) |
| <31 mmHg | 2 (0.4) |
| >55 mmHg | 8 (1.8) |
| 30–55 mmHg | 74 (16.5) |
| Bicuspid aortic valve (%) | 9 (2.0) |
| Cardiogenic shock requiring inotropes (%) | 61 (13.6) |
| Cardiac tamponade (%) | 65 (14.5) |
| Preoperative intubation (%) | 171 (38.1) |
| Any malperfusion excluding myocardial malperfusion (%) | 131 (29.2) |
| Tear in the aortic root (%) | 115 (25.6) |
| Tear in the ascending aorta (%) | 275 (63.0) |
| Tear in the aortic arch (%) | 59 (13.1) |
| CABG (%) | 40 (8.9) |
| Ascending aorta replacement | 238 (53) |
| Aortic root replacement (%) | 109 (24.3) |
| Total or partial aortic arch repair (%) | 102 (22.7) |
| Antegrade cerebral perfusion (%) | 107 (23.8) |
| Retrograde cerebral perfusion (%) | 203 (45.2) |
| Myocardial ischemic time, min (median [IQR]) | 118.00 [86.00, 166.00] |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass time, min (median [IQR]) | 205.00 [155.00, 273.00] |
| Hypothermic circulatory arrest duration, min (median [IQR]) | 39.00 [26.00, 54.75] |
| Urgency of the procedure * | |
| Emergency 1 | 100 (22.3) |
| Emergency 2 | 125 (27.8) |
| Salvage 1 | 19 (4.2) |
| Salvage 2 | 3 (0.7) |
| Urgent | 202 (45.0) |
| Variables | ODDS RATIO | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.0578 | 1.0321–1.0842 | <0.0001 |
| eGFR | 0.9784 | 0.99662–0.9908 | 0.0007 |
| Arterial lactate | 1.3781 | 1.1756–1.6156 | 0.0001 |
| Family history of aortic dissection or aneurysm | 0.2343 | 0.0534–1.0281 | 0.0545 |
| Poor mobility | 14.0323 | 2.6177–75.2198 | 0.0020 |
| Cardiac tamponade | 2.3044 | 1.2053–4.4056 | 0.0116 |
| Preoperative intubation | 2.3994 | 1.4174–4.0617 | 0.0011 |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass time | 1.0044 | 1.0017–1.0070 | 0.0011 |
| Variables | Arterial Lactate <2.6 mmol/L (N = 337) | Arterial Lactate ≥2.6 mmol/L (N = 112) | p Value | Risk Difference (95% CI) * | Risk Ratio (95% CI) * | Odds Ratio (95% CI) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early mortality | 60 (17.8%) | 50 (44.6%) | <0.001 | 23.4% (13.8%, 32.9%) | 2.264 (1.660, 3.082) | 4.069 (2.430, 7.783) |
| Stroke | 31 (9.2%) | 16 (14.3%) | 0.179 | 4.3% (−4.2%, 11.3%) | 1.465 (0.620, 2.466) | 1.557 (0.581, 3.051) |
| Paraplegia | 10 (3.0%) | 3 (2.7%) | 1.000 | 0.3% (−2.3%, 5.6%) | 1.115 (0.000, 3.593) | 1.121 (0.000, 4.322) |
| Mesenteric ischemia | 13 (3.9%) | 11 (9.8%) | 0.029 | 5.0% (−1.3%, 9.2%) | 2.235 (0.747, 4.984) | 2.547 (0.702, 6.886) |
| Sepsis | 72 (21.4%) | 38 (33.9%) | 0.011 | 8.2% (−3.1%, 18.8%) | 1.367 (0.872, 2.028) | 1.560 (0.824, 2.903) |
| Dialysis | 40 (11.9%) | 27 (24.1%) | 0.003 | 9.3% (2.0%, 16.7%) | 1.743 (1.157, 2.576) | 2.077 (1.228, 3.460) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 81 (24.0%) | 24 (21.4%) | 0.663 | −4.7% (−12.6%, 3.9%) | 0.808 (0.507, 1.185) | 0.752 (0.403, 1.260) |
| Reoperation for bleeding | 38 (11.3%) | 10 (8.9%) | 0.603 | −2.8% (−9.9%, 5.3%) | 0.753 (0.244, 1.641) | 0.713 (0.189, 1.960) |
| Deep sternal wound infection—mediastinitis | 11 (3.3%) | 8 (7.1%) | 0.135 | 1.0% (−2.2%,5.2%) | 1.250 (0.479, 2.925) | 1.287 (0.453, 3.870) |
| VA ECMO | 9 (2.7%) | 14 (12.5%) | <0.001 | 7.0% (1.3%, 14.3%) | 3.360 (1.343, 10.164) | 3.949 (1.428, 17.172) |
| Independent Variables | Beta | t | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | −0.0101 | −2.611 | 0.009 |
| Cardiac tamponade | 1.0516 | 4.240 | <0.0001 |
| Cardiogenic shock | 0.6409 | 1.968 | 0.05 |
| LVEF 31–50% | 0.4499 | 2.451 | 0.014 |
| Priority: Salvage 1 | 1.1128 | 1.968 | 0.05 |
| Priority: Urgent | 0.8814 | 3.892 | 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nappi, F.; Alzamil, A.; Salsano, A.; Avtaar Singh, S.S.; Gambardella, I.; Santini, F.; Fiore, A.; Perocchio, G.; Demondion, P.; Mesnildrey, P.; et al. Lactate-Based Difference as a Determinant of Outcomes following Surgery for Type A Acute Aortic Dissection: A Multi-Centre Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196177
Nappi F, Alzamil A, Salsano A, Avtaar Singh SS, Gambardella I, Santini F, Fiore A, Perocchio G, Demondion P, Mesnildrey P, et al. Lactate-Based Difference as a Determinant of Outcomes following Surgery for Type A Acute Aortic Dissection: A Multi-Centre Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196177
Chicago/Turabian StyleNappi, Francesco, Almothana Alzamil, Antonio Salsano, Sanjeet Singh Avtaar Singh, Ivancarmine Gambardella, Francesco Santini, Antonio Fiore, Giacomo Perocchio, Pierre Demondion, Patrick Mesnildrey, and et al. 2023. "Lactate-Based Difference as a Determinant of Outcomes following Surgery for Type A Acute Aortic Dissection: A Multi-Centre Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196177
APA StyleNappi, F., Alzamil, A., Salsano, A., Avtaar Singh, S. S., Gambardella, I., Santini, F., Fiore, A., Perocchio, G., Demondion, P., Mesnildrey, P., Schoell, T., Bonnet, N., & Leprince, P. (2023). Lactate-Based Difference as a Determinant of Outcomes following Surgery for Type A Acute Aortic Dissection: A Multi-Centre Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196177






