Multi-Stage Treatment for Spetzler–Martin Grades III, IV, and V Arteriovenous Malformations: Preoperative Embolization and Microsurgical Resection in a Consecutive Series of 250 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Endovascular Treatment
2.4. Microsurgical Resection
2.5. Follow-Up and Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Treatment and Follow-Up
3.3. Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Risk Factors
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stapf, C.; Mast, H.; Sciacca, R.R.; Choi, J.H.; Khaw, A.V.; Connolly, E.S.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Mohr, J.P. Predictors of hemorrhage in patients with untreated brain arteriovenous malformation. Neurology 2006, 66, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, J.; Huang, J. Updates in arteriovenous malformation management: The post-ARUBA era. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2020, 5, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, J.; Schaller, K.; Esche, J.; Bostrom, A. Microsurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: Subgroup outcomes in a consecutive series of 288 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Slomovic, A.; Ibrahim, G.; Radovanovic, I.; Tymianski, M. Microsurgery for ARUBA Trial (A Randomized Trial of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation)-Eligible Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Stroke 2017, 48, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, J.P.; Parides, M.K.; Stapf, C.; Moquete, E.; Moy, C.S.; Overbey, J.R.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Vicaut, E.; Young, W.L.; Houdart, E.; et al. Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): A multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicpinigaitis, A.J.; Ogulnick, J.V.; Mayer, S.A.; Gandhi, C.D.; Al-Mufti, F. Increase in Ruptured Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations and Mortality in the United States: Unintended Consequences of the ARUBA Trial? Stroke Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2023, 3, e000442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Mohr, J.P. Brain arteriovenous malformations in adults. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, M.V.; Marcellus, M.L.; Do, H.M.; Chang, S.D.; Rosenberg, J.K.; Steinberg, G.K.; Marks, M.P. Hemorrhage rate in patients with Spetzler-Martin grades IV and V arteriovenous malformations: Is treatment justified? Stroke 2007, 38, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, M.A.; Porter, P.J.; terBrugge, K.G.; Montanera, W.; Willinsky, R.A.; Wallace, M.C. Large and deep brain arteriovenous malformations are associated with risk of future hemorrhage. Stroke 2002, 33, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spetzler, R.F.; Martin, N.A. A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Zipfel, G.J.; Albuquerque, F.C.; Cooke, D.L.; Feldmann, E.; Sheehan, J.P.; Torner, J.C.; American Heart Association Stroke, C. Management of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2017, 48, e200–e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetzler, R.F.; Ponce, F.A. A 3-tier classification of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.T.; Kim, H.; McCulloch, C.E.; Mikhak, B.; Young, W.L. A supplementary grading scale for selecting patients with brain arteriovenous malformations for surgery. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafar, J.J.; Davis, A.J.; Berenstein, A.; Choi, I.S.; Kupersmith, M.J. The effect of embolization with N-butyl cyanoacrylate prior to surgical resection of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1993, 78, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viñuela, F.; Duckwiler, G.; Guglielmi, G. Contribution of interventional neuroradiology in the therapeutic management of brain arteriovenous malformations. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1997, 6, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualin, A.; Zampieri, P.; Nicolato, A.; Meneghelli, P.; Cozzi, F.; Beltramello, A. Surgery after embolization of cerebral arterio-venous malformation: Experience of 123 cases. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2014, 119, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Boto, G.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, R.; Gil, A.; Serna, C.; Lopez-Ibor, L. Combined staged therapy of complex arteriovenous malformations: Initial experience. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 127, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocer, N.; Kandemirli, S.G.; Dashti, R.; Kizilkilic, O.; Hanimoglu, H.; Sanus, G.Z.; Tunali, Y.; Tureci, E.; Islak, C.; Kaynar, M.Y. Single-stage planning for total cure of grade III-V brain arteriovenous malformations by embolization alone or in combination with microsurgical resection. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.T.; Essibayi, M.A.; Srinivasan, V.M.; Catapano, J.S.; Graffeo, C.S.; Lawton, M.T. Surgical management outcomes of intracranial arteriovenous malformations after preoperative embolization: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 2022, 45, 3499–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.K.; Heller, G.Z. The role of embolization before surgery for Spetzler-Ponce Class B and C brain AVMs: A prospective cohort series. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2018, 62, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.; Kis, B.; Siekmann, R.; Jans, P.; Laumer, R.; Kuhne, D. Preoperative embolization of intracranial arteriovenous malformations with Onyx. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Swieten, J.C.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Visser, M.C.; Schouten, H.J.; van Gijn, J. Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 1988, 19, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Stapf, C.; Hofmeister, C.; Mohr, J.P.; Sciacca, R.R.; Stein, B.M.; Faulstich, A.; Mast, H. Determinants of neurological outcome after surgery for brain arteriovenous malformation. Stroke 2000, 31, 2361–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.T.; Project, U.B.A.M.S. Spetzler-Martin Grade III arteriovenous malformations: Surgical results and a modification of the grading scale. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 740–748; discussion 748–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yan, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, R.; Han, H.; Meng, X.; Jin, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Long-term outcomes of Spetzler-Martin grade IV and V arteriovenous malformations: A single-center experience. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 53, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Nagata, I.; Nozaki, K.; Morimoto, M.; Taki, W.; Kikuchi, H. Posttreatment sequelae of palliatively treated cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2000, 46, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanis, A.; Yaşargil, M.G. The endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations. Adv. Tech. Stand. Neurosurg. 1998, 24, 131–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Starke, R.M.; Kano, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Mathieu, D.; Pierce, J.; Huang, P.P.; Feliciano, C.; Rodriguez-Mercado, R.; Almodovar, L.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for Spetzler-Martin Grade III arteriovenous malformations: An international multicenter study. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patibandla, M.R.; Ding, D.; Kano, H.; Xu, Z.; Lee, J.Y.K.; Mathieu, D.; Whitesell, J.; Pierce, J.T.; Huang, P.P.; Kondziolka, D.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for Spetzler-Martin Grade IV and V arteriovenous malformations: An international multicenter study. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luksik, A.S.; Law, J.; Yang, W.; Garzon-Muvdi, T.; Caplan, J.M.; Colby, G.; Coon, A.L.; Tamargo, R.J.; Huang, J. Assessing the Role of Preoperative Embolization in the Surgical Management of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzi, S.; Del Maestro, M.; Galzio, R. The Preoperative Functional Downgrading of Brain AVMs. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2021, 132, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Maestro, M.; Luzzi, S.; Gallieni, M.; Trovarelli, D.; Giordano, A.V.; Gallucci, M.; Ricci, A.; Galzio, R. Surgical Treatment of Arteriovenous Malformations: Role of Preoperative Staged Embolization. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2018, 129, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsenousi, A.; Aletich, V.A.; Alaraj, A. Neurological outcomes and cure rates of embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations with n-butyl cyanoacrylate or Onyx: A meta-analysis. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016, 8, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, C.M.; Zerris, V.; Malek, A.M. Electrocautery-induced ignition of spark showers and self-sustained combustion of onyx ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, ONS–E413–ONS–E418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, C.; Lin, F.; He, Q.; Yang, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Tu, W.; et al. Multimodal treatments of brain arteriovenous malformations: A comparison of microsurgical timings after endovascular embolization. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, Y.; Arakawa, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Kawamura, D.; Ebara, M.; Irie, K.; Takao, H.; Ikeuchi, S.; Ogawa, T.; Kato, M.; et al. Combined surgical and endovascular treatment of complex cerebrovascular diseases in the hybrid operating room. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2013, 5, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzelli, G.F.; Nelson, J.; McCoy, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hetts, S.W.; Amans, M.R.; Dowd, C.F.; Halbach, V.V.; Higashida, R.T.; Lawton, M.T.; et al. The effect of preoperative embolization and flow dynamics on resection of brain arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Mast, H.; Mohr, J.P.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Connolly, E.S.; Sciacca, R.R.; Khaw, A.; Stapf, C. Determinants of staged endovascular and surgical treatment outcome of brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 2005, 36, 2431–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, A.X.; Johnston, S.C.; Singh, V.; McCulloch, C.E.; Bennett, J.P.; Achrol, A.S.; Sidney, S.; Young, W.L. Longitudinal risk of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with arteriovenous malformation of the brain within a defined population. Stroke 2004, 35, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernesniemi, J.A.; Dashti, R.; Juvela, S.; Vaart, K.; Niemela, M.; Laakso, A. Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: A long-term follow-up study of risk of hemorrhage in 238 patients. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulasvirta, E.; Koroknay-Pal, P.; Hafez, A.; Elseoud, A.A.; Lehto, H.; Laakso, A. Characteristics and Long-Term Outcome of 127 Children With Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Starke, R.M.; Kano, H.; Mathieu, D.; Huang, P.P.; Feliciano, C.; Rodriguez-Mercado, R.; Almodovar, L.; Grills, I.S.; Silva, D.; et al. International multicenter cohort study of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations. Part 1: Predictors of hemorrhagic presentation. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 19, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, A.; Hernesniemi, J. Arteriovenous malformations: Epidemiology and clinical presentation. Neurosurg. Clin. 2012, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, D.J.; Lasner, T.M.; Hurst, R.W.; Flamm, E.S.; Zager, E.L.; King, J.T., Jr. Hypertension, small size, and deep venous drainage are associated with risk of hemorrhagic presentation of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 1998, 42, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, D.H.; Young, W.L.; Vang, M.C.; Sciacca, R.R.; Mast, H.; Koennecke, H.C.; Hartmann, A.; Joshi, S.; Mohr, J.P.; Pile-Spellman, J. Feeding artery pressure and venous drainage pattern are primary determinants of hemorrhage from cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 1998, 29, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataf, F.; Meder, J.F.; Roux, F.X.; Blustajn, J.; Merienne, L.; Merland, J.J.; Schlienger, M.; Chodkiewicz, J.P. Angioarchitecture associated with haemorrhage in cerebral arteriovenous malformations: A prognostic statistical model. Neuroradiology 1997, 39, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.; Salgado, H.; Polaina, M.; Trujillo, F.; Ponce de León, A.; Durand, F. A study on the venous drainage of 150 cerebral arteriovenous malformations as related to haemorrhagic risks and size of the lesion. Acta Neurochir. 1990, 103, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleetwood, I.G.; Marcellus, M.L.; Levy, R.P.; Marks, M.P.; Steinberg, G.K. Deep arteriovenous malformations of the basal ganglia and thalamus: Natural history. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, A.V.; Mohr, J.P.; Sciacca, R.R.; Schumacher, H.C.; Hartmann, A.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Mast, H.; Stapf, C. Association of infratentorial brain arteriovenous malformations with hemorrhage at initial presentation. Stroke 2004, 35, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turjman, F.; Massoud, T.F.; Vinuela, F.; Sayre, J.W.; Guglielmi, G.; Duckwiler, G. Correlation of the angioarchitectural features of cerebral arteriovenous malformations with clinical presentation of hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 1995, 37, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.D., Jr.; Wiebers, D.O.; Forbes, G.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Piepgras, D.G.; Marsh, W.R.; Maciunas, R.J. The natural history of unruptured intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1988, 68, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.D., Jr.; Wiebers, D.O.; Torner, J.C.; O’Fallon, W.M. Frequency of intracranial hemorrhage as a presenting symptom and subtype analysis: A population-based study of intracranial vascular malformations in Olmsted Country, Minnesota. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 85, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ApSimon, H.T.; Reef, H.; Phadke, R.V.; Popovic, E.A. A population-based study of brain arteriovenous malformation: Long-term treatment outcomes. Stroke 2002, 33, 2794–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapf, C.; Khaw, A.V.; Sciacca, R.R.; Hofmeister, C.; Schumacher, H.C.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Mast, H.; Mohr, J.P.; Hartmann, A. Effect of age on clinical and morphological characteristics in patients with brain arteriovenous malformation. Stroke 2003, 34, 2664–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, B.; Lindquist, C.; Johansson, A.; Steiner, L. Annual risk for the first hemorrhage from untreated cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1997, 40, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulasvirta, E.; Niini, T.; Hafez, A.; Koroknay-Pál, P.; Niemelä, M.; Luostarinen, T.; Laakso, A. Correlation between arteriovenous malformation nidus size and intraparenchymal hematoma volume in the event of rupture. Brain Spine 2022, 2, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spetzler, R.F.; Hargraves, R.W.; McCormick, P.W.; Zabramski, J.M.; Flom, R.A.; Zimmerman, R.S. Relationship of perfusion pressure and size to risk of hemorrhage from arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 76, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Kurata, A.; Irikura, K.; Endo, M.; Fujii, K.; Kitahara, T.; Ohwada, T. The factors influencing haematoma volume due to arteriovenous malformations. Acta Neurochir. 1999, 141, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nornes, H.; Grip, A. Hemodynamic aspects of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1980, 53, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.G.; Spetzler, R.F. The prospective application of a grading system for arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 1994, 34, 2–6; discussion 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Batjer, H.; Samson, D. Arteriovenous malformations of the posterior fossa. Clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, and surgical treatment. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 64, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, C.G.; Friedman, A.H.; Peerless, S.J. Posterior fossa arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symon, L.; Tacconi, L.; Mendoza, N.; Nakaji, P. Arteriovenous malformations of the posterior fossa: A report on 28 cases and review of the literature. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 9, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.; Kim, H.; Pourmohamad, T.; Young, W.L.; Lawton, M.T.; University of California, S.F.A.M.S.P. Cerebellar arteriovenous malformations: Anatomic subtypes, surgical results, and increased predictive accuracy of the supplementary grading system. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetts, S.W.; Cooke, D.L.; Nelson, J.; Gupta, N.; Fullerton, H.; Amans, M.R.; Narvid, J.A.; Moftakhar, P.; McSwain, H.; Dowd, C.F.; et al. Influence of patient age on angioarchitecture of brain arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlmann, E.; Whitfield, P.C. The changing face of neurosurgery for the older person. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzino, G.; Fergus, A.H.; Jensen, M.E.; Kongable, G.L.; Kassell, N.F. Long-term outcome after surgical excision of parenchymal arteriovenous malformations in patients over 60 years of age. Surg. Neurol. 1997, 47, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, J.K.; Winkler, E.A.; Catapano, J.S.; Spetzler, R.F.; Lawton, M.T. Surgical selection and outcomes among elderly patients with brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 49, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, B.A.; Du, R. Natural history of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: A meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammos, S.K.; Gardenghi, B.; Bortolotti, C.; Cloft, H.J.; Lanzino, G. Aneurysms Associated with Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1966–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redekop, G.; TerBrugge, K.; Montanera, W.; Willinsky, R. Arterial aneurysms associated with cerebral arteriovenous malformations: Classification, incidence, and risk of hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aliberti, G.; Talamonti, G.; Cenzato, M.; La Camera, A.; Debernardi, A.; Valvassori, L.; Mariangela, P.; Nichelatti, M. Arterial and venous aneurysms associated with arteriovenous malformations. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Unruptured AVMs | Ruptured AVMs | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 163/250 (65.2) | 87/250 (34.8) | |
| Age in years ‡ | 55.12 (14.43) | 58.49 (19.15) | 0.001 * |
| Age (years) | 0.006 * | ||
| 0–19 | 1(0.6) | 0 | |
| 20–39 | 22 (13.5) | 16 (18.4) | |
| 40–59 | 77 (47.2) | 31 (35.6) | |
| 60–79 | 56 (34.4) | 25 (28.7) | |
| ≥80 | 7 (4.3) § | 15 (17.2) § | |
| Sex | 0.803 | ||
| Male | 91 (55.8) | 50 (57.5) | |
| Female | 72 (44.2) | 37 (42.5) | |
| AVM grade | |||
| SM III (Ponce B) | 95 (58.2) | 55 (63.2) | 0.743 |
| SM IV | 56 (34.4) | 26 (29.9) | |
| SM V | 12 (7.4) | 6 (6.9) | |
| Ponce C | 68 (41.7) | 32 (36.8) | 0.448 |
| Nidus size (cm) | 0.021 * | ||
| <3 | 19 (11.7) § | 22 (25.3) § | |
| 3–6 | 120 (73.6) | 54 (62.1) | |
| >6 | 24 (14.7) | 11 (12.6) | |
| Eloquent area | 127 (77.9) | 62 (71.3) | 0.244 |
| Deep venous drainage | 108 (66.3) | 72 (82.8) | 0.006 * |
| Location | |||
| Supratentorial | 151 (92.6) | 68 (78.2) | 0.001 * |
| Infratentorial | 12 (7.4) | 19 (21.8) | |
| AVM side | 0.001 * | ||
| Right | 81 (49.7) | 38 (43.7) | |
| Left | 81 (49.7) | 40 (46) | |
| Midline | 1 (0.6) § | 9 (10.3) § | |
| Presence of aneurysms | 26 (16) | 31 (35.6) | 0.001 * |
| Aneurysm type | 0.661 | ||
| Flow-related arterial | 25 (96.2) | 29 (93.5) | |
| Intranidal | 1 (3.8) | 2 (6.5) | |
| Presence of venous varix | 7 (4.3) | 5 (5.7) | 0.410 |
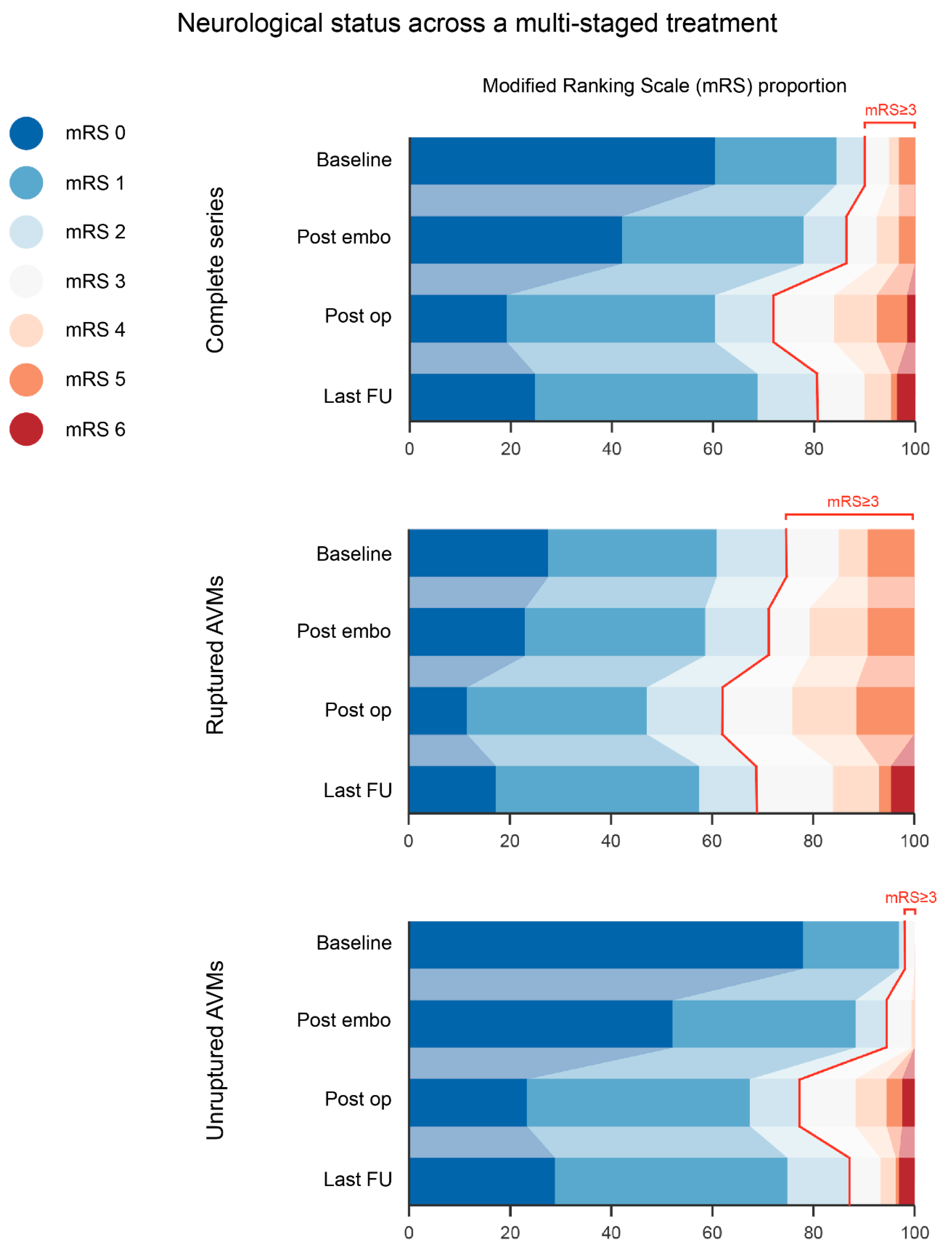
| mRS score ≥ 3 at presentation | 3 (1.8) | 22 (25.3) | 0.001 * |
| Number of embolizations ‡ | 5.9 (5.684) | 5.2 (5.133) | 0.338 |
| Percentage devascularization | 0.09 | ||
| <50 | 11 (6.7) | 13 (14.9) | |
| 50–80 | 39 (23.9) | 16 (18.4) | |
| >80 | 113 (69.4) | 58 (66.7) | |
| mRS score ≥ 3 after embolization | 9 (5.5) | 25 (28.7) | 0.001 * |
| Number of surgeries ‡ | 1.09 (0.281) | 1.15 (0.390) | 0.181 |
| mRS score ≥ 3 after surgery | 37 (22.7) | 33 (37.9) | 0.011 * |
| Total resection | 132 (81) | 58 (66.7) | 0.012 * |
| Preoperative SRS | 16 (9.8) | 10 (11.5) | 0.679 |
| mRS score ≥ 3 at last follow-up | 21 (12.9) | 27 (31) | 0.001 * |
| mRS score shift from ≤2 to ≥3 | 18 (11) | 11 (12.6) | 0.707 |
| Percentage Devascularization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | <50% | 50–80% | >80% | p Value |
| Number of patients | 24/250 (9.6) | 55/250 (22) | 171/250 (68.4) | |
| AVM grade | 0.003 * | |||
| III (Ponce B) | 13 (54.2) | 31 (56.4) | 106 (62) | |
| IV | 5 (20.8) | 23 (41.8) | 54 (31.6) | |
| V | 6 (25) § | 1 (1.8) | 11 (6.4) | |
| Ponce C | 11(45.8%) | 24 (43.6%) | 65 (38%) | 0.63 |
| Nidus size (cm) | 0.004 * | |||
| <3 | 6 (25) | 4 (7.2) | 31 (18.1) | |
| 3–6 | 10 (41.7) § | 42 (76.4) | 122 (71.4) | |
| >6 | 8 (33.3) § | 9 (16.4) | 18 (10.5) | |
| Brain eloquent area | 20 (83.3) | 42 (76.4) | 127 (74.3) | 0.619 |
| Deep venous drainage | 19 (79.2) | 33 (60) | 128 (74.9) | 0.073 |
| AVM status | 0.09 | |||
| Unruptured | 11 (45.8) | 39 (70.9) | 113 (66.1) | |
| Ruptured | 13 (54.2) | 16 (29.1) | 58 (33.9) | |
| Location | 0.032 * | |||
| Supratentorial | 17 (70.8) § | 49 (89.1) | 153 (89.5) | |
| Infratentorial | 7 (29.2) § | 6 (10.9) | 18(10.5) | |
| AVM side | 0.018 * | |||
| Right | 16 (66.7) | 22 (40) | 81 (47.4) | |
| Left | 5 (20.8) § | 31 (56.4) | 85 (49.7) | |
| Midline | 3 (12.5) | 2 (3.6) | 5 (2.9) | |
| Presence of aneurysms | 7 (29.2) | 11 (20) | 39(22.8) | 0.671 |
| Presence of venous varix | 4 (16.7) § | 4 (7.3) | 4(2.3) § | 0.006 * |
| Logistic Regressions | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 0–19 | - | - | - | |||
| 20–39 | 0.449 | 0.151–1.333 | 0.149 | |||
| 40–59 | 0.279 | 0.132–0.591 | 0.001 * | 0.654 | 0.264–1.625 | 0.361 |
| 60–79 | 1.651 | 0.864–3.155 | 0.129 | |||
| ≥80 | 9.985 | 3.893–25.613 | 0.001 * | 9.398 | 2.689–32.843 | 0.001 * |
| Female sex | 0.907 | 0.479–1.716 | 0.764 | |||
| mRS score ≥ 3 at presentation | 21.402 | 7.895–58.017 | 0.001 * | 30.376 | 8.106–113.831 | 0.001 * |
| Location | ||||||
| Supratentorial | 0.370 | 0.163–0.836 | 0.017 * | 0.404 | 0.116–1.414 | 0.156 |
| Infratentorial | 2.705 | 1.196–6.119 | 0.017 * | 2.473 | 0.707–8.644 | 0.156 |
| Side | ||||||
| Left | 0.577 | 0.302–1.100 | 0.095 | |||
| Right | 1.126 | 0.600–2.114 | 0.711 | |||
| Midline | 7.071 | 1.911–26.162 | 0.003 * | 4.678 | 0.711–30.759 | 0.108 |
| AVM grade | ||||||
| SM III (Ponce B) | 0.743 | 0.394–1.402 | 0.360 | |||
| SM IV | 1.446 | 0.754–2.771 | 0.267 | |||
| SM V | 0.831 | 0.231–2.994 | 0.777 | |||
| Ponce C | 1.345 | 0.713–2.537 | 0.360 | |||
| Nidus size (cm) | ||||||
| <3 | 0.682 | 0.269–1.727 | 0.419 | |||
| 3–6 | 1.076 | 0.539–2.145 | 0.836 | |||
| >6 | 1.296 | 0.548–3.065 | 0.554 | |||
| Eloquent brain area | 0.961 | 0.464–1.990 | 0.914 | |||
| Deep venous drainage | 1.058 | 0.522–2.146 | 0.875 | |||
| Ruptured AVM | 3.043 | 1.596–5.801 | 0.001 * | 0.498 | 0.176–1.409 | 0.189 |
| Presence of aneurysms | 3.586 | 1.827–7.041 | 0.001 * | 2.028 | 0.846–4.862 | 0.113 |
| Presence of venous varix | 1.430 | 0.372–5.494 | 0.603 | |||
| Percentage devascularization | ||||||
| <50 | 1.460 | 0.547–3.902 | 0.450 | |||
| 50–80 | 1.068 | 0.504–2.263 | 0.865 | |||
| >80 | 0.808 | 0.416–1.567 | 0.527 | |||
| Preoperative SRS | 0.744 | 0.244–2.269 | 0.603 | |||
| Logistic Regressions | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 0–19 | - | |||||
| 20–39 | 0.634 | 0.298–1.350 | 0.238 | |||
| 40–59 | 1.086 | 0.603–1.955 | 0.783 | |||
| 60–79 | 2.598 | 1.268–5.324 | 0.009 * | 2.155 | 0.986–4.708 | 0.054 |
| ≥80 | 0.222 | 0.091–0.545 | 0.001 * | 0.255 | 0.093–0.703 | 0.008 * |
| Female sex | 0.928 | 0.517–1.664 | 0.802 | |||
| mRS score ≥ 3 at presentation | 0.429 | 0.181–1.012 | 0.053 | |||
| Location | ||||||
| Supratentorial | 0.716 | 0.281–1.826 | 0.485 | |||
| Infratentorial | 1.396 | 0.548–3.561 | 0.485 | |||
| Side | ||||||
| Left | 1.430 | 0.795–2.571 | 0.232 | |||
| Right | 0.677 | 0.378–1.212 | 0.189 | |||
| Midline | 0.784 | 0.162–3.799 | 0.763 | |||
| AVM grade | ||||||
| SM III (Ponce B) | 2.953 | 1.624–5.369 | 0.001 * | - | - | - |
| SM IV | 0.414 | 0.228–0.752 | 0.004 * | - | - | - |
| SM V | 0.465 | 0.172–1.260 | 0.132 | - | - | - |
| Ponce C | 0.390 | 0.223–0.682 | 0.001 * | - | - | - |
| Nidus size (cm) | ||||||
| <3 | 1.650 | 0.691–3.943 | 0.260 | |||
| 3–6 | 1.607 | 0.874–2.955 | 0.127 | |||
| >6 | 0.306 | 0.145–0.642 | 0.002 * | 0.241 | 0.103–0.565 | 0.001 * |
| Eloquent brain area | 1.465 | 0.766–2.802 | 0.248 | |||
| Deep venous drainage | 0.373 | 0.173–0.807 | 0.012 * | 0.332 | 0.142–0.779 | 0.011 * |
| Ruptured AVM | 0.470 | 0.260–0.850 | 0.013 * | 0.680 | 0.345–1.342 | 0.266 |
| Presence of aneurysms | 0.851 | 0.432–1.676 | 0.641 | |||
| Presence of venous varix | 0.945 | 0.247–3.608 | 0.934 | |||
| Percentage devascularization | ||||||
| <50 | 0.327 | 0.138–0.776 | 0.011 * | 0.438 | 0.165–1.165 | 0.098 |
| 50–80 | 1.552 | 0.728–3.308 | 0.255 | |||
| >80 | 1.225 | 0.663–2.264 | 0.516 | |||
| Preoperative SRS | 1.367 | 0.492–3.797 | 0.549 | |||
| Deficit | Post-Embolization | Post-Surgery | Last Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disabling deficit mRS score ≥ 3 | 15 (6.7) | 49 (21.8) | 29 (12.8) |
| Non-disabling deficit mRS score ≤2 | 54 (24) | 88 (39.1) | 91 (40.4) |
| Total | 69 (27.6) | 137 (60.9) | 120 (53.3) |
| Logistic Regressions | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 0–19 | - | - | - | |||
| 20–39 | 0.202 | 0.027–1.539 | 0.123 | |||
| 40–59 | 0.359 | 0.139–0.927 | 0.034 * | 0.597 | 0.211–1.685 | 0.330 |
| 60–79 | 1.925 | 0.847–4.379 | 0.118 | |||
| ≥80 | 5.133 | 1.865–14.131 | 0.002 * | 4.061 | 1.269–12.995 | 0.018 * |
| Female sex | 0.789 | 0.343–1.815 | 0.577 | |||
| mRS score ≥ 3 at presentation | - | - | - | |||
| Location | ||||||
| Supratentorial | 0.257 | 0.101–0.658 | 0.005 * | 0.271 | 0.098–0.753 | 0.012 * |
| Infratentorial | 3.884 | 1.520–9.923 | 0.005 * | 3.689 | 1.328–10.247 | 0.012 * |
| Side | ||||||
| Left | 0.437 | 0.182–1.045 | 0.063 | |||
| Right | 1.573 | 0.692–3.577 | 0.279 | |||
| Midline | 4.043 | 0.978–16.714 | 0.054 | |||
| AVM grade | ||||||
| SM III (Ponce B) | 0.448 | 0.197–1.022 | 0.056 | |||
| SM IV | 2.246 | 0.990–5.097 | 0.053 | |||
| SM V | 1.083 | 0.235–5.000 | 0.918 | |||
| Ponce C | 2.230 | 0.979–5.081 | 0.056 | |||
| Nidus size (cm) | ||||||
| <3 | 0.184 | 0.024–1.398 | 0.102 | |||
| 3–6 | 1.515 | 0.583–3.938 | 0.394 | |||
| >6 | 1.540 | 0.540–4.393 | 0.420 | |||
| Eloquent brain area | 1.085 | 0.415–2.838 | 0.868 | |||
| Deep venous drainage | 1.062 | 0.426–2.650 | 0.897 | |||
| Ruptured AVM | 1.193 | 0.517–2.755 | 0.679 | |||
| Presence of aneurysms | 2.838 | 1.222–6.592 | 0.015 * | 1.728 | 0.683–4.369 | 0.248 |
| Presence of venous varix | 0.775 | 0.096–6.254 | 0.811 | |||
| Percentage devascularization | ||||||
| <50 | 0.350 | 0.045–2.701 | 0.314 | |||
| 50–80 | 0.829 | 0.297–2.309 | 0.719 | |||
| >80 | 1.611 | 0.621–4.184 | 0.327 | |||
| Preoperative SRS | 0.318 | 0.041–2.453 | 0.272 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfter, M.; Albiña-Palmarola, P.; Cimpoca, A.; Díaz-Peregrino, R.; Jans, P.; Ganslandt, O.; Kühne, D.; Henkes, H. Multi-Stage Treatment for Spetzler–Martin Grades III, IV, and V Arteriovenous Malformations: Preoperative Embolization and Microsurgical Resection in a Consecutive Series of 250 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185990
Alfter M, Albiña-Palmarola P, Cimpoca A, Díaz-Peregrino R, Jans P, Ganslandt O, Kühne D, Henkes H. Multi-Stage Treatment for Spetzler–Martin Grades III, IV, and V Arteriovenous Malformations: Preoperative Embolization and Microsurgical Resection in a Consecutive Series of 250 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):5990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185990
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfter, Marcel, Pablo Albiña-Palmarola, Alexandru Cimpoca, Roberto Díaz-Peregrino, Paul Jans, Oliver Ganslandt, Dietmar Kühne, and Hans Henkes. 2023. "Multi-Stage Treatment for Spetzler–Martin Grades III, IV, and V Arteriovenous Malformations: Preoperative Embolization and Microsurgical Resection in a Consecutive Series of 250 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 5990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185990
APA StyleAlfter, M., Albiña-Palmarola, P., Cimpoca, A., Díaz-Peregrino, R., Jans, P., Ganslandt, O., Kühne, D., & Henkes, H. (2023). Multi-Stage Treatment for Spetzler–Martin Grades III, IV, and V Arteriovenous Malformations: Preoperative Embolization and Microsurgical Resection in a Consecutive Series of 250 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 5990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185990








