Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Is a Predictor for Future Changes of Diabetogenic Factors in Aged Chinese—A Four-Year Follow-Up Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
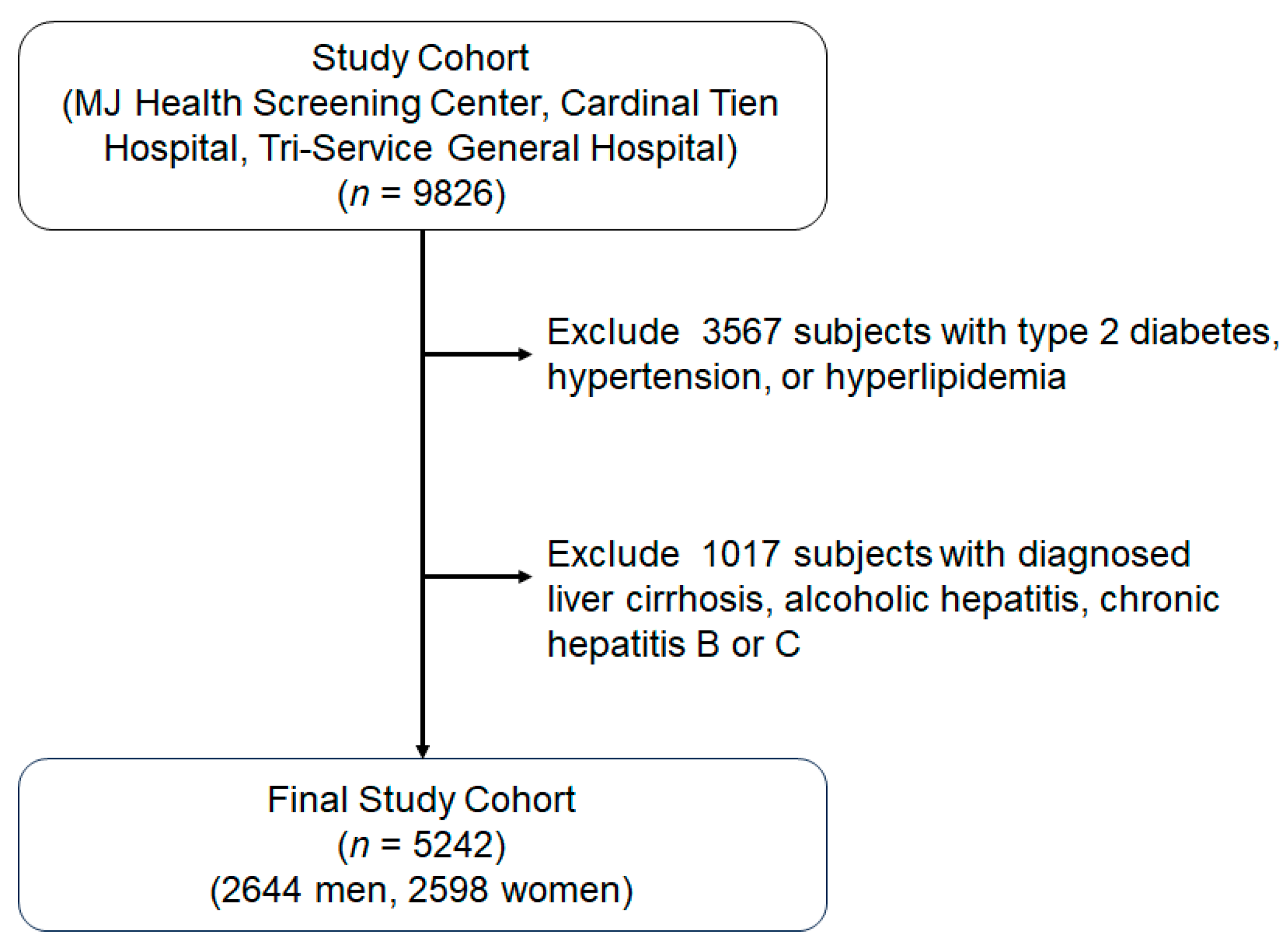
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Anthropometry and Laboratory Assessments
- (1)
- IR: There were 327 subjects without T2D enrolled. IR was measured by an insulin suppression test. The r value between the measured and calculated values was 0.581 (p < 0.001). The IR data were derived using a formula applied to subjects with normal glucose tolerance in Model 1.
- (2)
- FPIS: There were 186 subjects, self-referred for diabetes screening, enrolled. The FPIS was measured by frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance tests. The r value between the measured and calculated values was 0.671 (p < 0.001).
- (3)
- SPIS: There were 82 participants, including those with normal glucose tolerance, pre-diabetes, and T2D without oral anti-diabetic agents in the out-patient clinic. The SPIS was measured by a modified low dose glucose infusion test. The r value between the measured and calculated values was 0.65 (p = 0.002).
- (4)
- GE: There were 227 participants, including individuals with normal glucose tolerance, pre-diabetes, and T2D who are not taking oral anti-diabetic medications. GE was measured by frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance tests. The r value between the measured and calculated values was 0.43 (p = 0.001).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
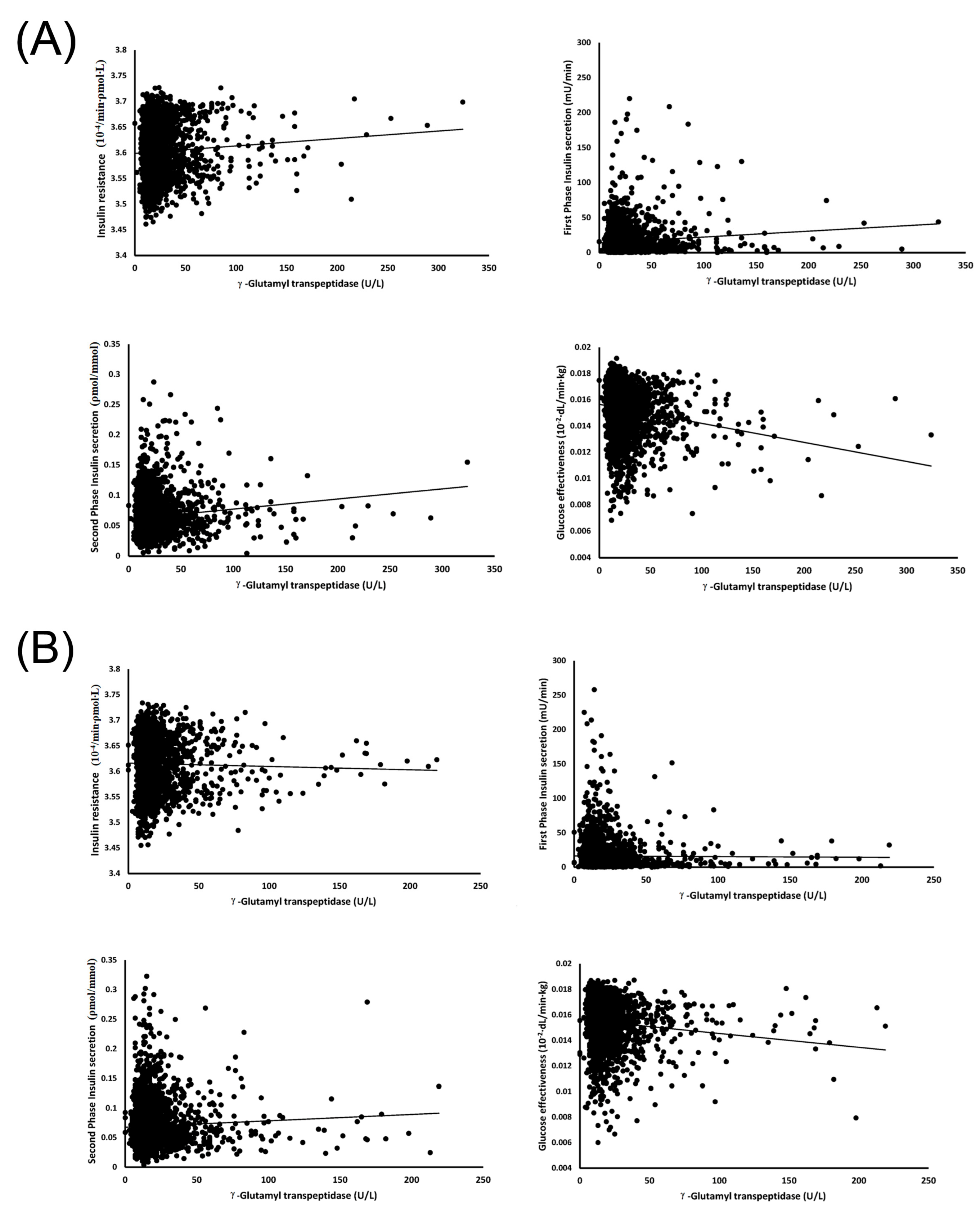
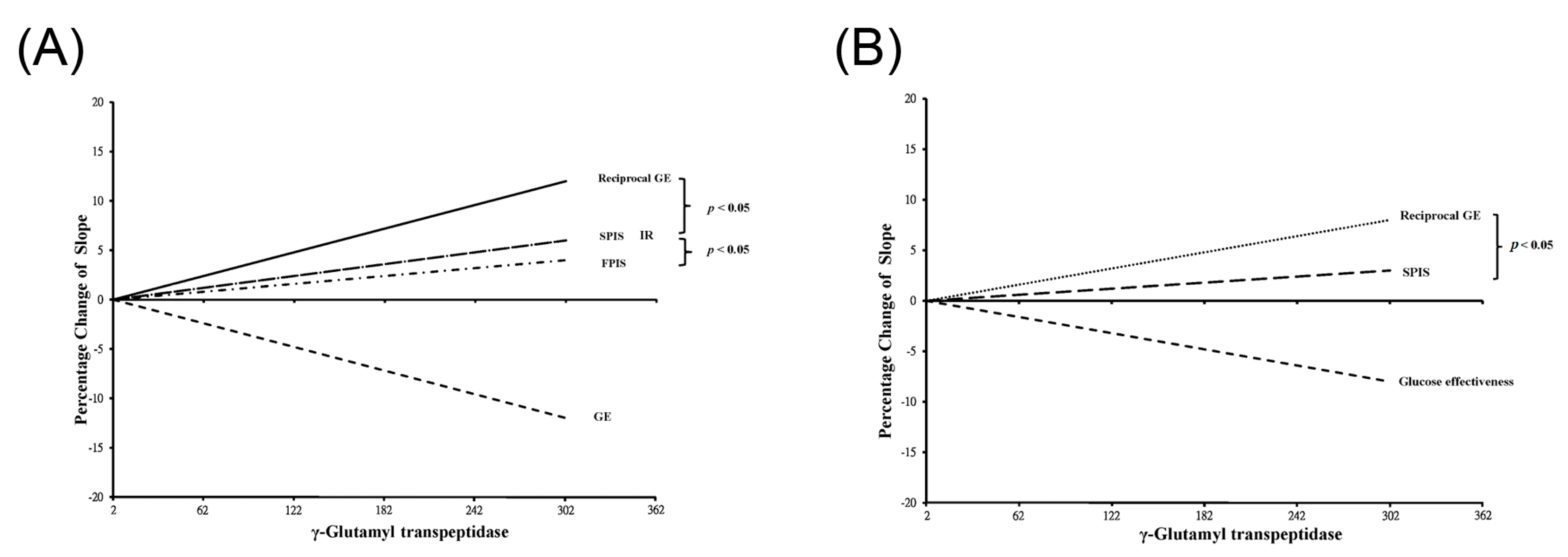
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheen, Y.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Jiang, Y.D.; Huang, C.N.; Liu, J.S.; Sheu, W.H. Trends in prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus from 2005 to 2014 in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118 (Suppl. 2), S66–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Andrikopoulos, S.; Gunton, J.E. First phase insulin secretion and type 2 diabetes. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, J.D.; Kahn, S.E.; Ader, M.; Watanabe, R.M.; Ni, T.C.; Bergman, R.N. Role of glucose effectiveness in the determination of glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, J.B. Gamma glutamyl transferase. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2001, 38, 263–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmela, P.I.; Sotaniemi, E.A.; Niemi, M.; Mäentausta, O. Liver function tests in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1984, 7, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Ha, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Christiani, D.C.; Gross, M.D.; Steffes, M.; Blomhoff, R.; Jacobs, D.R. Gamma-glutamyltransferase and diabetes—A 4 year follow-up study. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, A.O.; Lilja, M.; Kauma, H.; Savolainen, M.J.; Reunanen, A.; Kesäniemi, Y.A. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and the metabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 248, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Z.; Lin, J.D.; Hsia, T.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chang, J.B.; Chen, J.-S.; Pei, C.; Pei, D.; Chen, Y.-L. An accurate method to estimate insulin resistance from multiple regression model using data of metabolic syndrome and oral glucose tolerance test. J. Diabetes Invest. 2014, 5, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.D.; Hsu, C.H.; Liang, Y.J.; Lian, W.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Wu, C.Z.; Pei, D.; Chen, Y.-L. The estimation of first-phase insulin secretion by using components of the metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 675245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Wu, C.Z.; Lian, W.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Pei, D.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, J.-D. Measuring second phase of insulin secretion by components of metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Diabetes. Clin. Diagn. 2015, 2, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Lee, S.F.; Pei, C.; Pei, D.; Lee, C.H.; He, C.T.; Liang, Y.-J.; Lin, J.-D. Predicting glucose effectiveness in Chinese participants using routine measurements. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2016, 14, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.psychometrica.de/correlation.html (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- André, P.; Balkau, B.; Vol, S.; Charles, M.A.; Eschwège, E.; DESIR Study Group. Gamma-glutamyltransferase activity and development of the metabolic syndrome (International Diabetes Federation Definition) in middle-aged men and women: Data from the Epidemiological Study on the Insulin Resistance Syndrome (DESIR) cohort. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, J.H.; Oh, C.M.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.K.; Choi, J.M. Clinical association between serum γ-glutamyltransferase levels and the development of insulin resistance in Korean men: A 5-year follow-up study. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, J.; Tomiyama, H.; Yambe, M.; Koji, Y.; Motobe, K.; Shiina, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamashina, A. Elevated serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and gamma glutamyltransferase are markers of inflammation and oxidative stress independent of the metabolic syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2006, 189, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meigs, J.B.; Larson, M.G.; Fox, C.S.; Keaney, J.F., Jr.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J. Association of oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and diabetes risk phenotypes: The Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, A.; Kawai, D.; Yamamoto, K. Multiple hits, including oxidative stress, as pathogenesis and treatment target in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20704–20728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Succurro, E.; Arturi, F.; Grembiale, A.; Iorio, F.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Andreozzi, F.; Sciacqua, A.; Hribal, M.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. One-hour post-load plasma glucose levels are associated with elevated liver enzymes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, D.L.; Bennett, L.L.; Grodsky, G.M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology 1968, 83, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.Y.; Pan, X.Y.; Song, K.X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Li, F.; Cheng, X.Y.; Qu, S. Differential patterns of insulin secretion and sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease versus patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus alone. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranges, S.; Trevisan, M.; Dorn, J.M.; Dmochowski, J.; Donahue, R.P. Body fat distribution, liver enzymes, and risk of hypertension: Evidence from the Western New York Study. Hypertension 2005, 46, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.; Hong, Y.; Lu, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y. Association between serum free fatty acid levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, M.; Tonelli, J.; Kishore, P.; Stein, D.; Ragucci, E.; Gitig, A.; Reddy, K. Contribution of elevated free fatty acid levels to the lack of glucose effectiveness in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2748–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, P.; Tonelli, J.; Koppaka, S.; Fratila, C.; Bose, A.; Lee, D.E.; Reddy, K.; Hawkins, M. Time-dependent effects of free fatty acids on glucose effectiveness in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macit, M.S.; Acar-Tek, N. Evaluation of Nutritional Status and Allostatic Load in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2020, 44, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longpré-Poirier, C.; Ach, T.; Romain, A.J. Commentary: “Considerations to ensure that nutrition information improves the allostatic load model”, correspondence on “The association between mediterranean diet adherence and allostatic load in older adults” by Obomsawin et al. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 144, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billon, M.C.; Dupre, G.; Hanoune, J. In vivo modulation of rat hepatic gamma-glutamyltransferase activity by glucocorticoids. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1980, 18, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Men | Women | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 2644 | 2598 |
| Age (year) *** | 65 ± 5.1 | 63 ± 4.0 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) * | 23.0 ± 2.58 | 23.2 ± 2.83 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) ** | 125.7 ± 17.54 | 126.9 ± 17.40 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) *** | 74.6 ± 10.5 | 72.4 ± 9.98 |
| Waist circumference (cm) *** | 99.8 ± 14.7 | 97.8 ± 13.8 |
| Glutamate oxaloacetic transaminase (µkat/L) | 0.43 ± 0.20 | 0.42 ± 0.27 |
| Glutamate pyruvate transaminase (µkat/L) *** | 0.43 ± 0.30 | 0.39 ± 0.35 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) *** | 1.1 ± 0.17 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) *** | 6.6 ± 1.4 | 5.4 ± 1.2 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.19 ± 0.55 | 1.20 ± 0.52 |
| High density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) *** | 1.36 ± 0.33 | 1.62 ± 0.37 |
| Low density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) *** | 3.29 ± 0.81 | 3.37 ± 0.87 |
| γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase (U/L) *** | 24.3 ± 21.8 | 19.1 ± 17.9 |
| Men (n = 2644) | Women (n = 2598) | |
|---|---|---|
| First phase insulin secretion (μU/min) | 16.0 ± 19.3 | 16.1 ± 21.4 |
| Second phase insulin secretion (ρmol/mmol) *** | 0.064 ± 0.032 | 0.070 ± 0.039 |
| Insulin resistance (10−4/min∙ρmol∙L) *** | 3.602 ± 0.052 | 3.615 ± 0.052 |
| Glucose effectiveness (10−2∙dL/min∙kg) * | 0.0153 ± 0.0018 | 0.0154 ± 0.0017 |
| r | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Men (n = 2644) | ||
| First phase insulin secretion | 0.103 | <0.001 |
| Second phase insulin secretion | 0.119 | <0.001 |
| Insulin resistance | 0.068 | <0.001 |
| Glucose effectiveness | −0.177 | <0.001 |
| Women (n = 2598) | ||
| First phase insulin secretion | −0.008 | 0.696 |
| Second phase insulin secretion | 0.050 | 0.011 |
| Insulin resistance | −0.021 | 0.276 |
| Glucose effectiveness | −0.109 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, M.S.; Lo, C.Y.J.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chen, F.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, J.-S.; Pei, D.; Pitrone, P.; Wu, C.-Z. Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Is a Predictor for Future Changes of Diabetogenic Factors in Aged Chinese—A Four-Year Follow-Up Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5606. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175606
Wong MS, Lo CYJ, Chen Y-L, Chen F-Y, Kuo C-H, Chen J-S, Pei D, Pitrone P, Wu C-Z. Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Is a Predictor for Future Changes of Diabetogenic Factors in Aged Chinese—A Four-Year Follow-Up Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5606. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175606
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Man Sze, Chun Yen Jun Lo, Yen-Lin Chen, Fang-Yu Chen, Chun-Heng Kuo, Jin-Shuen Chen, Dee Pei, Pietro Pitrone, and Chung-Ze Wu. 2023. "Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Is a Predictor for Future Changes of Diabetogenic Factors in Aged Chinese—A Four-Year Follow-Up Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5606. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175606
APA StyleWong, M. S., Lo, C. Y. J., Chen, Y.-L., Chen, F.-Y., Kuo, C.-H., Chen, J.-S., Pei, D., Pitrone, P., & Wu, C.-Z. (2023). Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Is a Predictor for Future Changes of Diabetogenic Factors in Aged Chinese—A Four-Year Follow-Up Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5606. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175606






