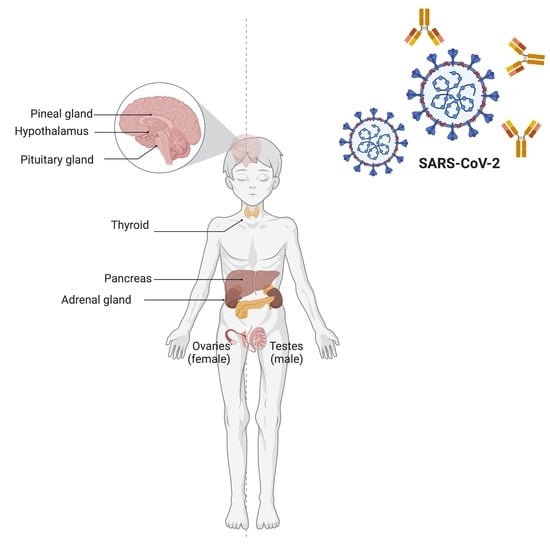
Endocrinological Involvement in Children and Adolescents Affected by COVID-19: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Thyroid
4. Adrenal Glands
5. Hypothalamic–Pituitary Involvement
5.1. Pituitary Gland Involvement of SARS-CoV-2 Virus
5.2. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children with Pre-Existing Hypothalamic–Pituitary Axis Dysfunction
5.3. Growth Hormone (GH) Release and Precocious Puberty during SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic
6. Diabetes
7. Limits in the Scope of the Study
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19 Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Brodin, P. SARS-CoV-2 infections in children: Understanding diverse outcomes. Immunity 2022, 55, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, M.D.; Escobar, G.J.; Lu, Y.; Schlessinger, D.; Steinman, J.B.; Steinman, L.; Lee, C.; Liu, V.X. Risk of severe COVID-19 infection among adults with prior exposure to children. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204141119. [Google Scholar]
- Mallapaty, S. Kids and covid: Why young immune systems are still on top. Nature 2021, 597, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, A.B.; Gilani, Z.; Godfred-Cato, S.; Belay, E.D.; Feldstein, L.R.; Patel, M.M.; Randolph, A.G.; Newhams, M.; Thomas, D.; Magleby, R.; et al. MIS-C Incidence Authorship Group. Incidence of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children among US persons infected with SARS-CoV-2. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2116420. [Google Scholar]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Porritt, R.A.; Cheng, M.H.; Bahar, I.; Arditi, M. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and long covid: The SARS-CoV-2 viral superantigen hypothesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 941009. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V.; WHO Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Ayuzo Del Valle, N.C.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. Long-COVID in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9950. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, U.M.; Abokor, A.A.; Edwards, J.M.; Waigi, E.W.; Royfman, R.S.; Hasan, S.A.; Smedlund, K.B.; Hardy, A.M.G.; Chakravarti, R.; Koch, L.G. SARS-CoV-2, ACE2 expression, and systemic organ invasion. Physiol. Genom. 2021, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Rotondi, M.; Coperchini, F.; Ricci, G.; Denegri, M.; Croce, L.; Ngnitejeu, S.T.; Villani, L.; Magri, F.; Latrofa, F.; Chiovato, L. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE-2 mRNA in thyroid cells: A clue for COVID-19-related subacute thyroiditis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Lazartigues, E.; Qadir, M.M.F.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Endocrine significance of SARS-CoV-2’s reliance on ACE2. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa108. [Google Scholar]
- Gnocchi, M.; D’Alvano, T.; Lattanzi, C.; Messina, G.; Petraroli, M.; Patianna, V.D.; Esposito, S.; Street, M.E. Current evidence on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on paediatric endocrine conditions. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 913334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCowan, R.; Wild, E.; Lucas-Herald, A.K.; McNeilly, J.; Mason, A.; Wong, S.C.; Ahmed, S.F.; Shaikh, M.G. The effect of COVID-19 on the presentation of thyroid disease in children. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1014533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y. Pediatric Endocrinology of Post-Pandemic Era. Chonnam Med. J. 2021, 57, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Shidid, S.; Kohlhoff, S.; Smith-Norowitz, T.A. Thyroid stimulating hormone levels in children before and during the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic. Health Sci. Rep. 2022, 5, e579. [Google Scholar]
- Dabas, A.; Singh, H.; Goswami, B.; Kumar, K.; Dubey, A.; Jhamb, U.; Yadav, S.; Garg, S. Thyroid Dysfunction in COVID-19. Indian. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 25, 198–201. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, D.T.W.; Lee, C.H.; Chow, W.S.; Lee, A.C.H.; Tam, A.R.; Fong, C.H.Y.; Law, C.Y.; Leung, E.K.H.; To, K.K.W.; Tan, K.C.B.; et al. Thyroid dysfunction in relation to immune profile, disease status, and outcome in 191 patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e926–e935. [Google Scholar]
- Calcaterra, V.; Biganzoli, G.; Dilillo, D.; Mannarino, S.; Fiori, L.; Pelizzo, G.; Zoia, E.; Fabiano, V.; Carlucci, P.; Camporesi, A.; et al. Non-thyroidal illness syndrome and SARS-CoV-2-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Calcaterra, V.; Zuccotti, G. Letter to the Editor: Changes in Thyroid Function in Children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Related to COVID-19 Observed over a 1-Year Follow-Up Period. Thyroid 2023, 33, 650–652. [Google Scholar]
- Elvan-Tüz, A.; Ayrancı, I.; Ekemen-Keleş, Y.; Karakoyun, I.; Çatlı, G.; Kara-Aksay, A.; Karadağ-Öncel, E.; Dündar, B.N.; Yılmaz, D. Are Thyroid Functions Affected in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children? J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 14, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Hikmet, F.; Méar, L.; Edvinsson, Å.; Micke, P.; Uhlén, M.; Lindskog, C. The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, M.M.; El-Zawawy, H.T.; Ahmed, S.M.; Aly Abdelhamid, M. Thyroid disease and covid-19 infection: Case series. Clin. Case. Rep. 2021, 9, e04225. [Google Scholar]
- Bogusławska, J.; Godlewska, M.; Gajda, E.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. Cellular and molecular basis of thyroid autoimmunity. Eur. Thyr. J. 2022, 11, R1–R16. [Google Scholar]
- Lania, A.; Sandri, M.T.; Cellini, M.; Mirani, M.; Lavezzi, E.; Mazziotti, G. Thyrotoxicosis in patients with COVID-19: The THYRCOV study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Ganie, M.A.; Charoo, B.A.; Sahar, T.; Bhat, M.H.; Ali, S.A.; Niyaz, M.; Sidana, S.; Yaseen, A. Thyroid Function, Urinary Iodine, and Thyroid Antibody Status Among the Tribal Population of Kashmir Valley: Data from Endemic Zone of a Sub-Himalayan Region. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 555840. [Google Scholar]
- Haller-Kikkatalo, K.; Alnek, K.; Metspalu, A.; Mihailov, E.; Metsküla, K.; Kisand, K.; Pisarev, H.; Salumets, A.; Uibo, R. Demographic associations for autoantibodies in disease-free individuals of a European population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44846. [Google Scholar]
- Flokas, M.E.; Bustamante, V.H.; Kanakatti Shankar, R. New-Onset Primary Adrenal Insufficiency and Autoimmune Hypothyroidism in a Pediatric Patient Presenting with MIS-C. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2022, 95, 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wei, T.; Lei, J. Potential interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and thyroid: A Review. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab004. [Google Scholar]
- Piticchio, T.; Le Moli, R.; Tumino, D.; Frasca, F. Relationship between betacoronaviruses and the endocrine system: A new key to understand the COVID-19 pandemic—A comprehensive review. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1553–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Croce, L.; Gangemi, D.; Ancona, G.; Liboà, F.; Bendotti, G.; Minelli, L.; Chiovato, L. The cytokine storm and thyroid hormone changes in COVID-19. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 891–904. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, K.; Chainy, G.B.N.; Subudhi, U. Prospective role of thyroid disorders in monitoring COVID-19 pandemic. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05712. [Google Scholar]
- Medas, F.; Dobrinja, C.; Al-Suhaimi, E.A.; Altmeier, J.; Anajar, S.; Arikan, A.E.; Azaryan, I.; Bains, L.; Basili, G.; Bolukbasi, H.; et al. Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on surgery for indeterminate thyroid nodules (THYCOVID): A retrospective, international, multicentre, cross-sectional study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, S.; McLelland, B.; Bryce, N. 1651 the impact of covid-19 on thyroid surveillance offered to children with down syndrome. Abstracts 2021, 106, A444. [Google Scholar]
- McGlacken-Byrne, S.M.; Johnson, M.; Penner, J.; du Pré, P.; Katugampola, H. Characterising approaches to steroid therapy in paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2023, 59, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilci, F.; Yetimakman, A.F.; Jones, J.H.; Çizmecioğlu, F.M. A case of adrenal insufficiency during multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 31, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Arlt, W.; Baldeweg, S.E.; Pearce, S.H.S.; Simpson, H.L. Endocrinology in the time of COVID-19: Management of adrenal insufficiency. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, G25–G32. [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny, H.F.; Bryce, J.; Ali, S.R.; Giordano, R.; Baronio, F.; Chifu, I.; Tschaidse, L.; Cools, M.; van den Akker, E.L.; Falhammar, H.; et al. Outcome of COVID-19 infections in patients with adrenal insufficiency and excess. Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e220416. [Google Scholar]
- Banull, N.R.; Reich, P.J.; Anka, C.; May, J.; Wharton, K.; Kallogjeri, D.; Shimony, H.; Arbeláez, A.M. Association between Endocrine Disorders and Severe COVID-19 Disease in Pediatric Patients. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2022, 95, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, T.C.; Chien, M.M.; Liu, T.L.; Chang, H.; Tsai, M.L.; Tseng, S.H.; Ho, W.L.; Su, Y.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Lu, J.H.; et al. Adrenal Crisis Mimicking COVID-19 Encephalopathy in a Teenager with Craniopharyngioma. Children 2022, 9, 1238. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudino, R.; Orlandi, V.; Cavarzere, P.; Chinello, M.; Antoniazzi, F.; Cesaro, S.; Piacentini, G. Case Report: SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Child With Suprasellar Tumor and Hypothalamic-Pituitary Failure. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 596654. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.; Kang, J.; Li, G.; Ge, J.; Gu, J. Analysis of 2019-nCoV receptor ACE2 expression in different tissues and its significance study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1077. [Google Scholar]
- Finsterer, J.; Scorza, F.A. The pituitary gland in SARS-CoV-2 infections, vaccinations, and post-COVID syndrome. Clinics 2022, 78, 100157. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R. COVID-19, hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and clinical implications. Endocrine 2020, 68, 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Siejka, A.; Barabutis, N. Adrenal insufficiency in the COVID-19 era. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E784–E785. [Google Scholar]
- Leow, M.K.S.; Kwek, D.S.K.; Ng, A.W.K.; Ong, K.C.; Kaw, G.J.L.; Lee, L.S.U. Hypocortisolism in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 63, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wheatland, R. Molecular mimicry of ACTH in SARS—Implications for corticosteroid treatment and prophylaxis. Med. Hypotheses 2004, 63, 855–862. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, A.; Singh, A.; Kral, T.; Solomon, S. The immune-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Endocr. Rev. 1989, 10, 92–112. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, A.; Pepper, G.M.; Wyrwinski, P.M.; Ramirez, N.E.; Simon, R.; Pina, T.; Gruenspan, H.; Vaca, C.E. Adrenal insufficiency occurring during septic shock: Incidence, outcome, and relationship to peripheral cytokine levels. Am. J. Med. 1995, 98, 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Guarner, J.; Paddock, C.D.; Bartlett, J.; Zaki, S.R. Adrenal gland hemorrhage in patients with fatal bacterial infections. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Artamonova, I.N.; Petrova, N.A.; Lyubimova, N.A.; Kolbina, N.Y.; Bryzzhin, A.V.; Borodin, A.V.; Levko, T.A.; Mamaeva, E.A.; Pervunina, T.M.; Vasichkina, E.S.; et al. Case Report: COVID-19-Associated ROHHAD-Like Syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 854367. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, M.; Gunawardena, S.; Goenka, A.; Ey, E.; Kumar, G. Post COVID-19 Lymphocytic Hypophysitis: A Rare Presentation. Child. Neurol. Open 2022, 9, 2329048X221103051. [Google Scholar]
- Improving the Clinical Care of Children and Adolescents with Endocrine Conditions, including Diabetes, through Research and Education ESPE Patient Leaflet Information on COVID-19 and Pediatric Endocrine Diseases. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications- (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Peinkhofer, M.; Bossini, B.; Penco, A.; Giangreco, M.; Pellegrin, M.C.; Vidonis, V.; Vittori, G.; Grassi, N.; Faleschini, E.; Barbi, E.; et al. Reduction in pediatric growth hormone deficiency and increase in central precocious puberty diagnoses during COVID 19 pandemics. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Arcari, A.J.; Rodríguez Azrak, M.S.; Boulgourdjian, E.M.; Costanzo, M.; Guercio, G.V.; Gryngarten, M.G. Precocious puberty in relation to the COVID-19 pandemic. A survey among Argentine pediatric endocrinologists. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2023, 121, e202202767. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Weng, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Difference of Precocious Puberty Between Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Shanghai School-Aged Girls. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 349. [Google Scholar]
- Elbarbary, N.S.; dos Santos, T.J.; de Beaufort, C.; Wiltshire, E.; Pulungan, A.; Scaramuzza, A.E. The Challenges of Managing Pediatric Diabetes and Other Endocrine Disorders During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Results from an International Cross-Sectional Electronic Survey. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 1447. [Google Scholar]
- Goffredo, M.; Pilotta, A.; Parissenti, I.; Forino, C.; Tomasi, C.; Goffredo, P.; Buzi, F.; Badolato, R. Early onset of puberty during COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: Experience from two Pediatric Endocrinology Italian Centers. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 36, 290–298. [Google Scholar]
- Yesiltepe Mutlu, G.; Eviz, E.; Haliloglu, B.; Kirmizibekmez, H.; Dursun, F.; Ozalkak, S.; Cayir, A.; Sacli, B.Y.; Ozbek, M.N.; Demirbilek, H.; et al. The effects of the covid-19 pandemic on puberty: A cross-sectional, multicenter study from Turkey. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira Neto, C.P.; Azulay, R.S.; Almeida, A.G.F.P.; Tavares, M.; Vaz, L.H.G.; Leal, I.R.L.; Gama, M.E.A.; Ribeiro, M.R.C.; Nascimento, G.C.; Magalhães, M.; et al. Differences in Puberty of Girls before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4733. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Qian, Y.; Wan, N.; Liu, L. Differential diagnosis of precocious puberty in girls during the COVID-19 pandemic: A pilot study. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Chioma, L.; Bizzarri, C.; Verzani, M.; Fava, D.; Salerno, M.; Capalbo, D.; Guzzetti, C.; Penta, L.; Di Luigi, L.; Di Iorgi, N.; et al. Sedentary lifestyle and precocious puberty in girls during the COVID-19 pandemic: An Italian experience. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e210650. [Google Scholar]
- Acar, S.; Özkan, B. Increased frequency of idiopathic central precocious puberty in girls during the COVID-19 pandemic: Preliminary results of a tertiary center study. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 35, 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Acinikli, K.Y.; Erbaş, İ.M.; Besci, Ö.; Demir, K.; Abacı, A.; Böber, E. Has the Frequency of Precocious Puberty and Rapidly Progressive Early Puberty Increased in Girls During the COVID-19 Pandemic? J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 14, 302. [Google Scholar]
- Baby, M.; Ilkowitz, J.; Cheema Brar, P. Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the diagnosis of idiopathic central precocious puberty in pediatric females in New York City. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 36, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberi, C.; Di Natale, V.; Assirelli, V.; Bernardini, L.; Candela, E.; Cassio, A. Implicating factors in the increase in cases of central precocious puberty (CPP) during the COVID-19 pandemic: Experience of a tertiary centre of pediatric endocrinology and review of the literature. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 3064. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetto, M.; Riveros, V.; Eymann, A.; Terrasa, S.; Alonso, G. Analysis of the incidence of central precocious puberty treated with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2023, 121, e202202849. [Google Scholar]
- Chioma, L.; Chiarito, M.; Bottaro, G.; Paone, L.; Todisco, T.; Bizzarri, C.; Cappa, M. COVID-19 pandemic phases and female precocious puberty: The experience of the past 4 years (2019 through 2022) in an Italian tertiary center. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 533. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.H.; Park, S.C. An increasing tendency of precocious puberty among Korean children from the perspective of COVID-19 pandemic effect. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1451. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, B.; Wei, H. Analysis of the Incidence and Risk Factors of Precocious Puberty in Girls during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 9229153. [Google Scholar]
- Geniuk, N.; De Jesús Suárez Mozo, M.; Pose, M.N.; Vidaurreta, S. Rapidly progressive precocious puberty during the COVID-19 lockdown. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2023, 121, e202202840. [Google Scholar]
- Ariza Jimenez, A.B.; Aguilar Gomez-Cardenas, F.J.; de la Camara Moraño, C. Likely impact of COVID-19 on referrals to pediatric endocrinology: Increased incidence of precocious puberty in a third-level hospital. Endocrinol. Diabetes. Nutr. 2022, 69, 542–544. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, S.; Matsubara, K.; Higuchi, S.; Matsubara, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Kitayama, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yorifuji, T. Clinical Pediatric Endocrinology Increased frequency of central precocious puberty during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic at a single center in the Osaka Metropolitan Area of Japan. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2023, 32, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mondkar, S.A.; Oza, C.; Khadilkar, V.; Shah, N.; Gondhalekar, K.; Kajale, N.; Khadilkar, A. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on idiopathic central precocious puberty—Experience from an Indian centre. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 35, 895–900. [Google Scholar]
- Orman, B.; Esen, S.; Keskin, M.; Şahin, N.M.; Savaş-Erdeve, Ş.; Çetinkaya, S. Status of Central Precocious Puberty Cases at the Onset of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: A Single-Center Experience. Turkish. Arch. Pediatr. 2022, 57, 349. [Google Scholar]
- Stagi, S.; De Masi, S.; Bencini, E.; Losi, S.; Paci, S.; Parpagnoli, M.; Ricci, F.; Ciofi, D.; Azzari, C. Increased incidence of precocious and accelerated puberty in females during and after the Italian lockdown for the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo, M.V.; Rungvivatjarus, T.; Klein, K.O. Incidence of central precocious puberty more than doubled during COVID-19 pandemic: Single-center retrospective review in the United States. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1007730. [Google Scholar]
- Turrizzani Colonna, A.; Curatola, A.; Sodero, G.; Lazzareschi, I.; Cammisa, I.; Cipolla, C. Central precocious puberty in children after COVID-19 outbreak: A single-center retrospective study. Minerva Pediatr. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzani, M.; Bizzarri, C.; Chioma, L.; Bottaro, G.; Pedicelli, S.; Cappa, M. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic lockdown on early onset of puberty: Experience of an Italian tertiary center. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Umano, G.R.; Maddaluno, I.; Riccio, S.; Lanzaro, F.; Antignani, R.; Giuliano, M.; Luongo, C.; Festa, A.; Miraglia del Giudice, E.; Grandone, A. Central precocious puberty during COVID-19 pandemic and sleep disturbance: An exploratory study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Prosperi, S.; Chiarelli, F. Early and precocious puberty during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 3537. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.S.; Aoki, C.; Shen, H. Puberty, steroids and GABAA receptor plasticity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, S91–S103. [Google Scholar]
- Abou El Ella, S.S.; Barseem, N.F.; Tawfik, M.A.; Ahmed, A.F. BMI relationship to the onset of puberty: Assessment of growth parameters and sexual maturity changes in Egyptian children and adolescents of both sexes. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Nokoff, N.; Thurston, J.; Hilkin, A.; Pyle, L.; Zeitler, P.S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Santoro, N.; Kelsey, M.M. Sex Differences in Effects of Obesity on Reproductive Hormones and Glucose Metabolism in Early Puberty. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4390. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, D.; Cui, W. The association between vitamin D levels and precocious puberty: A meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 427–429. [Google Scholar]
- Street, M.E.; Sartori, C.; Catellani, C.; Righi, B. Precocious Puberty and Covid-19 Into Perspective: Potential Increased Frequency, Possible Causes, and a Potential Emergency to Be Addressed. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 978. [Google Scholar]
- Zucchini, S.; Scozzarella, A.; Maltoni, G. Multiple influences of the COVID-19 pandemic on children with diabetes: Changes in epidemiology, metabolic control and medical care. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 198–208. [Google Scholar]
- Karavanaki, K.; Rodolaki, K.; Soldatou, A.; Karanasios, S.; Kakleas, K. Covid-19 infection in children and adolescents and its association with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1d) presentation and management. Endocrine 2023, 80, 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.; Joseph, S.; Badran, A.; Umpaichitra, V.; Bargman, R.; Chin, V.L. Increased Rates of Hospitalized Children with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Central Brooklyn during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Pediatr. 2023, 2023, 4580809. [Google Scholar]
- Farakla, I.; Lagousi, T.; Miligkos, M.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Vasilakis, I.A.; Mpinou, M.; Dolianiti, M.; Katechaki, E.; Taliou, A.; Spoulou, V.; et al. Stress hyperglycemia, Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 infection: The impact on newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2022, 3, 818945. [Google Scholar]
- Knip, M.; Parviainen, A.; Turtinen, M.; But, A.; Härkönen, T.; Hepojoki, J.; Sironen, T.; Iheozor-Ejiofor, R.; Uğurlu, H.; Saksela, K.; et al. Finnish Pediatric Diabetes Register. SARS-CoV-2 and type 1 diabetes in children in Finland: An observational study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Gesuita, R.; Rabbone, I.; Marconi, V.; De Sanctis, L.; Marino, M.; Tiberi, V.; Iannilli, A.; Tinti, D.; Favella, L.; Giorda, C. Trends and cyclic variation in the incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in two Italian regions over 33 years and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Baechle, C.; Eckert, A.; Kamrath, C.; Neu, A.; Manuwald, U.; Thiele-Schmitz, S.; Weidler, O.; Knauer-Fischer, S.; Rosenbauer, J.; Holl, R.W. Incidence and presentation of new-onset type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents from Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic 2020 and 2021: Current data from the DPV Registry. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 197, 110559. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández Herrero, M.; Terradas Mercader, P.; Latorre Martinez, E.; Feliu Rovira, A.; Rodríguez Zaragoza, N.; Parada Ricart, E. New diagnoses of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children during the COVID-19 pandemic Regional multicenter study in Spain. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2022, 69, 709–714. [Google Scholar]
- van den Boom, L.; Kostev, K.; Kuss, O.; Rathmann, W.; Rosenbauer, J. Type 1 diabetes incidence in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Diabetes Res Clin. Pract. 2022, 193, 110146. [Google Scholar]
- Ansar, A.; Livett, T.; Beaton, W.; Carrel, A.L.; Bekx, M.T. Sharp Rise in New-Onset Pediatric Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic. WMJ 2022, 121, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Raicevic, M.; Samardzic, M.; Soldatovic, I.; Curovic Popovic, N.; Vukovic, R. Trends in nationwide incidence of pediatric type 1 diabetes in Montenegro during the last 30 years. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 991533. [Google Scholar]
- Vorgučin, I.; Savin, M.; Stanković, Đ.; Miljković, D.; Ilić, T.; Simić, D.; Vrebalov, M.; Milanović, B.; Barišić, N.; Stojanović, V.; et al. Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Characteristics of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and Adolescents during the First Two Years of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Vojvodina. Medicina 2022, 58, 1013. [Google Scholar]
- Cinek, O.; Slavenko, M.; Pomahačová, R.; Venháčová, P.; Petruželková, L.; Škvor, J.; Neumann, D.; Vosáhlo, J.; Konečná, P.; Kocourková, K.; et al. Type 1 diabetes incidence increased during the COVID-19 pandemic years 2020-2021 in Czechia: Results from a large population-based pediatric register. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 956–960. [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffini, R.; Deodati, A.; Rapini, N.; Pampanini, V.; Cianfarani, S. Increased incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Figures from an Italian tertiary care center. J. Diabetes 2022, 14, 562–563. [Google Scholar]
- McKeigue, P.M.; McGurnaghan, S.; Blackbourn, L.; Bath, L.E.; McAllister, D.A.; Caparrotta, T.M.; Wild, S.H.; Wood, S.N.; Stockton, D.; Colhoun, H.M. Relation of Incident Type 1 Diabetes to Recent COVID-19 Infection: Cohort Study Using e-Health Record Linkage in Scotland. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 921–928. [Google Scholar]
- Lah Tomulić, K.; Matko, L.; Verbić, A.; Milardović, A.; Severinski, S.; Kolić, I.; Baraba Dekanić, K.; Šerifi, S.; Butorac Ahel, I. Epidemiologic Characteristics of Children with Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treated in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in a 10-Year-Period: Single Centre Experience in Croatia. Medicina 2022, 58, 638. [Google Scholar]
- Passanisi, S.; Salzano, G.; Aloe, M.; Bombaci, B.; Citriniti, F.; De Berardinis, F.; De Marco, R.; Lazzaro, N.; Lia, M.C.; Lia, R.; et al. Increasing trend of type 1 diabetes incidence in the pediatric population of the Calabria region in 2019–2021. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, K. Increase in Type 1 Diabetes Incidence in Children During COVID-19. Am. J. Nurs. 2022, 122, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Donbaloğlu, Z.; Tuhan, H.; Tural Kara, T.; Bedel, A.; Barsal Çetiner, E.; Singin, B.; Parlak, M. The Examination of the Relationship Between COVID-19 and New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Children. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2022, 57, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Abdou, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Hassanein, S.A.; Elsebaie, E.H.; Shamma, R.A. Presentations, Complications, and Challenges Encountered During Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Egyptian Children During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Single-Center Experience. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 814991. [Google Scholar]
- Kamrath, C.; Rosenbauer, J.; Eckert, A.J.; Siedler, K.; Bartelt, H.; Klose, D.; Sindichakis, M.; Herrlinger, S.; Lahn, V.; Holl, R.W. Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Germany: Results from the DPV Registry. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Nóvoa-Medina, Y.; Pavlovic-Nesic, S.; González-Martín, J.M.; Hernández-Betancor, A.; López, S.; Domínguez-García, A.; Quinteiro-Domínguez, S.; Cabrera, M.; De La Cuesta, A.; Caballero-Fernández, E.; et al. Role of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the appearance of new onset type 1 diabetes mellitus in children in Gran Canaria, Spain. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 35, 393–397. [Google Scholar]
- Vlad, A.; Serban, V.; Timar, R.; Sima, A.; Botea, V.; Albai, O.; Timar, B.; Vlad, M. Increased Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Romanian Children. Medicina 2021, 57, 973. [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth, R.; Wallace, S.; Oliver, N.S.; Yeung, S.; Kshirsagar, A.; Naidu, H.; Kwong, R.M.W.; Kumar, P.; Logan, K.M. New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes in Children During COVID-19: Multicenter Regional Findings in the U.K. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, e170–e171. [Google Scholar]
- Nri-Ezedi, C.A.; Ulasi, T.O.; Okeke, K.N.; Okonkwo, I.T.; Echendu, S.T.; Agu, N.V.; Nwaneli, E.I. A surge of type 1 diabetes mellitus among Nigerian children during the Covid-19 pandemic. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2022, 20, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Herczeg, V.; Luczay, A.; Ténai, N.; Czine, G.; Tóth-Heyn, P. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Children with Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. Indian Pediatr. 2022, 59, 809–810. [Google Scholar]
- Denina, M.; Trada, M.; Tinti, D.; Funiciello, E.; Novara, C.; Moretto, M.; Rosati, S.; Garazzino, S.; Bondone, C.; De Sanctis, L. Increase in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes and serological evidence of recent SARS-CoV-2 infection: Is there a connection? Front. Med. 2022, 9, 927099. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati, M.; Keshvari, M.; Mirnasuri, S.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Il Shin, J.; Smith, L. The global impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the incidence of pediatric new-onset type 1 diabetes and ketoacidosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5112–5127. [Google Scholar]
- Lavik, A.R.; Ebekozien, O.; Noor, N.; Alonso, G.T.; Polsky, S.; Blackman, S.M.; Chen, J.; Corathers, S.D.; Demeterco-Berggren, C.; Gallagher, M.P.; et al. Trends in Type 1 Diabetic Ketoacidosis During COVID-19 Surges at 7 US Centers: Highest Burden on non-Hispanic Black Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Gesualdo, P.; Geno Rasmussen, C.; Alkanani, A.A.; He, L.; Dong, F.; Rewers, M.J.; Michels, A.W.; Yu, L. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children and Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes. Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 517–521. [Google Scholar]
- Messaaoui, A.; Hajselova, L.; Tenoutasse, S. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in new-onset type 1 diabetes in children during pandemic in Belgium. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 34, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Kompaniyets, L.; Bull-Otterson, L.; Boehmer, T.K.; Baca, S.; Alvarez, P.; Hong, K.; Hsu, J.; Harris, A.M.; Gundlapalli, A.V.; Saydah, S. Post-COVID-19 Symptoms and Conditions Among Children and Adolescents—United States, March 1, 2020–January 31, 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 993–999. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, C.E.; Koyama, A.K.; Alvarez, P.; Chow, W.; Lundeen, E.A.; Perrine, C.G.; Pavkov, M.E.; Rolka, D.B.; Wiltz, J.L.; Bull-Otterson, L.; et al. Risk for newly diagnosed diabetes >30 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection among persons aged <18 years—United states, March 1, 2020–June 28, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Noorzae, R.; Junker, T.G.; Hviid, A.P.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Olsen, S.F. Risk of Type 1 Diabetes in Children Is Not Increased After SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Nationwide Prospective Study in Denmark. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, F.; Itonaga, T.; Maeda, M.; Ihara, K. Long-term trends of pediatric type 1 diabetes incidence in Japan before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5803. [Google Scholar]
- Reschke, F.; Lanzinger, S.; Herczeg, V.; Prahalad, P.; Schiaffini, R.; Mul, D.; Clapin, H.; Zabeen, B.; Pelicand, J.; Phillip, M.; et al. The COVID-19 Pandemic Affects Seasonality, With Increasing Cases of New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes in Children, From the Worldwide SWEET Registry. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2594–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Ata, A.; Jalilova, A.; Kırkgöz, T.; Işıklar, H.; Demir, G.; Altınok, Y.A.; Özkan, B.; Zeytinlioğlu, A.; Darcan, Ş.; Özen, S.; et al. Does COVID-19 predispose patients to type 1 diabetes mellitus? Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 31, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tittel, S.R.; Rosenbauer, J.; Kamrath, C.; Ziegler, J.; Reschke, F.; Hammersen, J.; Mönkemöller, K.; Pappa, A.; Kapellen, T.; Holl, R.W. Did the COVID-19 lockdown affect the incidence of pediatric type 1 diabetes in Germany? Diabetes Care 2020, 43, e172–e173. [Google Scholar]
- Pitocco, D.; Tartaglione, L.; Viti, L.; Di Leo, M.; Manto, A.; Caputo, S.; Pontecorvi, A. Lack of type 1 diabetes involvement in SARS-COV-2 population: Only a particular coincidence? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 164, 108220. [Google Scholar]
- Alassaf, A.; Gharaibeh, L.; Ibrahim, S.; Daher, A.; Irsheid, A.; Albaramki, J.; Odeh, R. Effect of COVID-19 pandemic on presentation and referral patterns of newly diagnosed children with type 1 diabetes in a developing country. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 35, 859–866. [Google Scholar]
- Bombaci, B.; Passanisi, S.; Sorrenti, L.; Salzano, G.; Lombardo, F. Examining the associations between COVID-19 infection and pediatric type 1 diabetes. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 489–497. [Google Scholar]
- d’Annunzio, G.; Bassi, M.; De Rose, E.L.; Lezzi, M.; Minuto, N.; Calevo, M.G.; Gaiero, A.; Fichera, G.; Borea, R.; Maghnie, M. Increased Frequency of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: The Link With COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2022, 3, 846827. [Google Scholar]
- Rivero-Martín, M.J.; Rivas-Mercado, C.M.; Ceñal-González-Fierro, M.J.; López-Barrena, N.; Lara-Orejas, E.; Alonso-Martín, D.; Alfaro-Iznaola, C.; Alcázar-Villar, M.J.; Sánchez-Escudero, V.; González-Vergaz, A. Severity of new-onset type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents during the coronavirus-19 disease pandemic. Endocrinol. Diabetes. Nutr. 2022, 69, 810–815. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, F.; Ozyilmaz, L.G.B.; Sahin, E.G.; Can, Y.Y.; Altas, U.; Cam, H. Does the severity of diabetic ketoacidosis in children with type 1 diabetes change during the COVID-19 pandemic? A single-center experience from a pediatric intensive care unit. N. Clin. Istanb. 2022, 9, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Leiva-Gea, I.; Fernández, C.A.; Cardona-Hernandez, R.; Lozano, M.F.; Bahíllo-Curieses, P.; Arroyo-Díez, J.; León, M.C.; Martín-Frías, M.; Barreiro, S.C.; Delgado, A.M.; et al. Increased Presentation of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Changes in Age and Month of Type 1 Diabetes at Onset during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Spain. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4338. [Google Scholar]
- Kiral, E.; Kirel, B.; Havan, M.; Keskin, M.; Karaoglan, M.; Yildirim, A.; Kangin, M.; Talay, M.N.; Urun, T.; Altug, U.; et al. Increased Severe Cases and New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Among Children Presenting with Diabetic Ketoacidosis During First Year of COVID-19 Pandemic in Turkey. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 926013. [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini, V.; Marino, M.; Scaramuzza, A.E.; Tiberi, V.; Bobbio, A.; Delvecchio, M.; Piccinno, E.; Ortolani, F.; Innaurato, S.; Felappi, B.; et al. The Silent Epidemic of Diabetic Ketoacidosis at Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents in Italy During the COVID-19 Pandemic in 2020. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 878634. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrzak, I.; Michalak, A.; Seget, S.; Bednarska, M.; Beń-Skowronek, I.; Bossowski, A.; Chobot, A.; Dżygało, K.; Głowińska-Olszewska, B.; Górnicka, M.; et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis incidence among children with new-onset type 1 diabetes in Poland and its association with COVID-19 outbreak-Two-year cross-sectional national observation by PolPeDiab Study Group. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Oh, K.; Kang, E.; Rhie, Y.-J.; Lee, J.; Hong, Y.H.; Shin, Y.-L.; Kim, J.H. Comparison of Initial Presentation of Pediatric Diabetes Before and During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Era. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2022, 37, e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamrath, C.; Rosenbauer, J.; Eckert, A.J.; Ohlenschläger, U.; Sydlik, C.; Nellen-Hellmuth, N.; Holl, R.W. Glycated hemoglobin at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and at follow-up in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 749–753. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, G.; Cimbek, E.A.; Yeşilbaş, O.; Bostan, Y.E.; Karagüzel, G. A Long-Term Comparison of Presenting Characteristics of Children with Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 14, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Nagl, K.; Waldhör, T.; Hofer, S.E.; Fritsch, M.; Meraner, D.; Prchla, C.; Rami-Merhar, B.; Fröhlich-Reiterer, E. Alarming Increase of Ketoacidosis Prevalence at Type 1 Diabetes-Onset in Austria-Results from a Nationwide Registry. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 820156. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, M.A.; Mecham, C.; Arreola, E.V.; Sinha, M. Increase in the Number of Pediatric New-Onset Diabetes and Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cases During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 479–485. [Google Scholar]
- Mastromauro, C.; Blasetti, A.; Primavera, M.; Ceglie, L.; Mohn, A.; Chiarelli, F.; Giannini, C. Peculiar characteristics of new-onset Type 1 Diabetes during COVID-19 pandemic. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman, B.L.; Yu, J.; Tanaka, C.; Longhurst, C.A.; Kim, J.J. Incidence of New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Among US Children During the COVID-19 Global Pandemic. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 414–415. [Google Scholar]
- Luciano, T.M.; Halah, M.P.; Sarti, M.T.A.; Floriano, V.G.; da Fonseca, B.A.L.; Del Roio Liberatore, R., Jr.; Antonini, S.R. DKA and new-onset type 1 diabetes in Brazilian children and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 66, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, S.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Weinberg, A.; Auerbach, A.; German, A.; Haim, A.; Zung, A.; Brener, A.; Strich, D.; Azoulay, E.; et al. Alarming increase in ketoacidosis in children and adolescents with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Israel. Pediatr Diabetes 2022, 23, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Abdulrazzaq, D.; Alkandari, A.; Alhusaini, F.; Alenazi, N.; Gujral, U.P.; Narayan, K.M.V.; Al-Kandari, H.; CODeR Group. Higher rates of diabetic ketoacidosis and admission to the paediatric intensive care unit among newly diagnosed children with type 1 diabetes in Kuwait during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2022, 38, e3506. [Google Scholar]
- Kostopoulou, E.; Eliopoulou, M.I.; Rojas Gil, A.P.; Chrysis, D. Impact of COVID-19 on new-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus—A one-year prospective study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 5928–5935. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Lee, R.; Ko, C.W.; Moon, J.E. Increase in blood glucose level and incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus in the Daegu-Gyeongbuk area during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A retrospective cross-sectional study. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2022, 39, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mameli, C.; Scaramuzza, A.; Macedoni, M.; Marano, G.; Frontino, G.; Luconi, E.; Pelliccia, C.; Felappi, B.; Guerraggio, L.P.; Spiri, D.; et al. Type 1 diabetes onset in Lombardy region, Italy, during the COVID-19 pandemic: The double-wave occurrence. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 39, 101067. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandre, M.I.; Henriques, A.R.; Cavaco, D.; Rodrigues, L.; Costa, S.; Robalo, B.; Pereira, C.; Sampaio, M.L. New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes in Children and COVID-19. Acta. Med. Port. 2021, 34, 642–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, S.Ö.; Gürbüz, F.; Turan, İ.; Celiloğlu, C.; Yüksel, B. Changes in the presentation of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes in children during the COVID-19 pandemic in a tertiary center in Southern Turkey. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 34, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Bogale, K.T.; Urban, V.; Schaefer, E.; Bangalore Krishna, K. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Prevalence of Diabetic Ketoacidosis at Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes: A Single-Centre Study in Central Pennsylvania. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 4, e00235. [Google Scholar]
- McGlacken-Byrne, S.M.; Drew, S.E.V.; Turner, K.; Peters, C.; Amin, R. The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic is associated with increased severity of presentation of childhood onset type 1 diabetes mellitus: A multi-centre study of the first COVID-19 wave. Diabet Med. 2021, 38, e14640. [Google Scholar]
- Boboc, A.A.; Novac, C.N.; Ilie, M.T.; Ieșanu, M.I.; Galoș, F.; Bălgrădean, M.; Berghea, E.C.; Ionescu, M.D. The Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the New Cases of T1DM in Children. A Single-Centre Cohort Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 551. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, S.M.; Woodger, K.; Regan, F.; Soni, A.; Wright, N.; Agwu, J.C.; Williams, E.; Timmis, A.; Kershaw, M.; Moudiotis, C.; et al. Presentation of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes in children and young people during COVID-19: A national UK survey. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2020, 4, e000884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, E.A.C.; Pacaud, D. Diabetic ketoacidosis at presentation of type 1 diabetes in children in Canada during the COVID-19 pandemic. Paediatr. Child. Health 2021, 26, 208–209. [Google Scholar]
- Salmi, H.; Heinonen, S.; Hästbacka, J.; Lääperi, M.; Rautiainen, P.; Miettinen, P.J.; Vapalahti, O.; Hepojoki, J.; Knip, M. New-onset type 1 diabetes in Finnish children during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, E.M.; Elhenawy, Y.I.; Matter, R.M.; Aly, H.H.; Thabet, R.A.; Fereig, Y.A. Clinical characteristics and outcome of hospitalized children and adolescent patients with type 1 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic: Data from a single center surveillance study in Egypt. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 34, 925–936. [Google Scholar]
- Alaqeel, A.; Aljuraibah, F.; Alsuhaibani, M.; Huneif, M.; Alsaheel, A.; Al Dubayee, M.; Alsaedi, A.; Bakkar, A.; Alnahari, A.; Taha, A.; et al. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Incidence of New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes and Ketoacidosis Among Saudi Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 669302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Rosolowsky, E.; Pacaud, D.; Huang, C.; Lemay, J.; Brockman, N.; Rath, M.; Doulla, M. Diabetic ketoacidosis at type 1 diabetes diagnosis in children during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pediatr. Diabetes 2021, 22, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.; Weiser, G.; Krupik, D.; Takagi, D.; Peled, S.; Pines, N.; Hashavya, S.; Gur-Soferman, H.; Gamsu, S.; Kaplan, O.; et al. Diabetic Ketoacidosis at Emergency Department Presentation During the First Months of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic in Israel: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Dżygało, K.; Nowaczyk, J.; Szwilling, A.; Kowalska, A. Increased frequency of severe diabetic ketoacidosis at type 1 diabetes onset among children during COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: An observational cohort study. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 26, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Boddu, S.K.; Aurangabadkar, G.; Kuchay, M.S. New onset diabetes, type 1 diabetes and COVID-19. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Güemes, M.; Storch-de-Gracia, P.; Enriquez, S.V.; Martín-Rivada, Á.; Brabin, A.G.; Argente, J. Severity in pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus debut during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 1601–1603. [Google Scholar]
- Kamrath, C.; Mönkemöller, K.; Biester, T.; Rohrer, T.R.; Warncke, K.; Hammersen, J.; Holl, R.W. Ketoacidosis in Children and Adolescents with Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Germany. JAMA 2020, 324, 801–804. [Google Scholar]
- Elgenidy, A.; Awad, A.K.; Saad, K.; Atef, M.; El-Leithy, H.H.; Obiedallah, A.A.; Hammad, E.M.; Ahmad, F.A.; Ali, A.M.; Dailah, H.G.; et al. Incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID-19 pandemic: A meta-analysis of 124,597 children with diabetes. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Birkebaek, N.H.; Kamrath, C.; Grimsmann, J.M.; Aakesson, K.; Cherubini, V.; Dovc, K.; de Beaufort, C.; Alonso, G.T.; Gregory, J.W.; White, M.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on long-term trends in the prevalence of diabetic ketoacidosis at diagnosis of paediatric type 1 diabetes: An international multicentre study based on data from 13 national diabetes registries. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamrath, C.; Rosenbauer, J.; Eckert, A.J.; Pappa, A.; Reschke, F.; Rohrer, T.R.; Mönkemöller, K.; Wurm, M.; Hake, K.; Raile, K.; et al. Incidence of COVID-19 and Risk of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021050856. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, Z.; Gawlik, J.; Wędrychowicz, A.; Nazim, J.; Starzyk, J. The incidence and causes of acute hospitalizations and emergency room visits in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus prior to and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A single-centre experience. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2023, 29, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, H.; To, T.; Stein, R.; Fung, K.; Daneman, D. Is diabetic ketoacidosis at disease onset a result of missed diagnosis? J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Wersäll, J.H.; Adolfsson, P.; Forsander, G.; Ricksten, S.E.; Hanas, R. Delayed referral is common even when new-onset diabetes is suspected in children. A Swedish prospective observational study of diabetic ketoacidosis at onset of type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2021, 22, 900–908. [Google Scholar]
- Keiner, E.S.; Slaughter, J.C.; Datye, K.A.; Cherrington, A.D.; Moore, D.J.; Gregory, J.M. COVID-19 Exacerbates Insulin Resistance During Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2406–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Piccolo, G.; De Rose, E.L.; Bassi, M.; Napoli, F.; Minuto, N.; Maghnie, M.; Patti, G.; D’annunzio, G. Infectious diseases associated with pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus: A narrative review. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 966344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrosso, D.M.F.; Primavera, M.; Samvelyan, S.; Tagi, V.M.; Chiarelli, F. Stress and Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Clinical Outcome. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2023, 96, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zorena, K.; Michalska, M.; Kurpas, M.; Jaskulak, M.; Murawska, A.; Rostami, S. Environmental Factors and the Risk of Developing Type 1 Diabetes-Old Disease and New Data. Biology 2022, 11, 608. [Google Scholar]
- Lança, A.; Rodrigues, C.; Diamantino, C.; Fitas, A.L. COVID-19 in two children with new-onset diabetes: Case reports. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e247309. [Google Scholar]
- Prosperi, S.; Chiarelli, F. COVID-19 and diabetes in children. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 27, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Lammi, N.; Karvonen, M.; Tuomilehto, J. Do microbes have a causal role in type 1 diabetes? Med. Sci. Monit. 2005, 11, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, F.; Amiel, S.A.; Zimmet, P.; Alberti, G.; Bornstein, S.; Eckel, R.H.; Mingrone, G.; Boehm, B.; Cooper, M.E.; Chai, Z.; et al. New-Onset Diabetes in Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 789–790. [Google Scholar]
- Mine, K.; Nagafuchi, S.; Mori, H.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Pancreatic Cell Failure. Biology 2021, 11, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Zubkiewicz-Kucharska, A.; Seifert, M.; Stepkowski, M.; Noczyńska, A. Diagnosis of type 1 diabetes during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: Does lockdown affect the incidence and clinical status of patients? Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, G.; Zhai, J.; Du, B. COVID-19 as a Trigger for type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, dgad165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Wittschieber, D.; Sanft, J.; Kleemann, S.; Elschner, S.; Haupt, K.F.; Vau, V.; Haring, C.; Rödel, J.; Henke, A.; et al. Early postmortem mapping of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in patients with COVID-19 and the correlation with tissue damage. Elife 2021, 10, e60361. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Che, X.; Hou, J.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Qiu, L.; Li, Z.; et al. Organ distribution of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) in SARS patients: Implications for pathogenesis and virus transmission pathways. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 622–630. [Google Scholar]
- Suwanwongse, K.; Shabarek, N. Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus, DKA, and COVID-19: Causality or coincidence? A report of three cases. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M. Is type 1 diabetes related to coronavirus disease 2019 in children? Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2022, 65, 252–253. [Google Scholar]
- Rewers, M.; Bonifacio, E.; Ewald, D.; Geno Rasmussen, C.; Jia, X.; Pyle, L.; Ziegler, A.-G.; ASK Study Group; Fr1da Study Group. SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Presymptomatic Type 1 Diabetes Autoimmunity in Children and Adolescents from Colorado, USA, and Bavaria, Germany. JAMA 2022, 328, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, H.; Josefsen, K.; Krogvold, L.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Gerling, I.; Pociot, F.; Buschard, K. PDE12 in type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18149. [Google Scholar]
- Calcaterra, V.; Bosoni, P.; Dilillo, D.; Mannarino, S.; Fiori, L.; Fabiano, V.; Carlucci, P.; Di Profio, E.; Verduci, E.; Mameli, C.; et al. Impaired Glucose-Insulin Metabolism in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Related to SARS-CoV-2 in Children. Children 2021, 8, 384. [Google Scholar]
- Calcaterra, V.; Zuccotti, G. Persistent insulin resistance at one year follow-up in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Endocrine System or Organ | Keywords | Number of Suitable Articles (Total Number) | Type of Article |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid | “thyroid” OR “hyperthyroidism” OR “hypothyroidism” OR “thyroiditis” AND “coronavirus disease 2019” OR “COVID-19” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “MIS-C” OR “multisystem inflammatory syndrome” AND “children” OR “adolescents” | 12 (33) | 1 cross-sectional study 3 cohort studies 1 case control study 1 retrospective case note review 1 cross-sectional chart review 2 narrative reviews 3 case reports |
| Adrenal glands | “adrenal insufficiency” OR “hypercortisolism” AND “coronavirus disease 2019” OR “COVID-19” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “MIS-C” OR “multisystem inflammatory syndrome” AND “children” OR “adolescents” | 10 (10) | 2 narrative reviews 2 single-center or multicenter cohort studies 1 cross-sectional study 1 clinical practice guideline 4 case reports |
| Hypothalamus-pituitary system | “hypothalamus” OR “pituitary” OR “Hypopituitarism” OR “hypophysitis” OR “growth hormone” OR “central precocious puberty” AND “coronavirus disease 2019” OR “COVID-19” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “MIS-C” OR “multisystem inflammatory syndrome” AND “children” OR “adolescents” | 34 (96) | 4 cross-sectional studies 1 case control study 17 retrospective studies 9 reviews 3 case reports |
| Gonads | “puberty” OR “central precocious puberty” AND “coronavirus disease 2019” OR “COVID-19” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “MIS-C” OR “multisystem inflammatory syndrome” AND “children” OR “adolescents” | 32 (32) | 5 narrative reviews 1 cohort study 6 cross-sectional studies 20 case-control studies |
| Pancreas | “type 1 diabetes” OR “juvenile onset diabetes” OR “insulin-dependent diabetes” OR “T1D” AND “coronavirus disease 2019” OR “COVID-19” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “MIS-C” OR “multisystem inflammatory syndrome” AND “children” OR “adolescents” | 102 (253) | 2 meta-analyses 6 narrative reviews 72 cohort studies 9 cross-sectional studies 2 case-control studies 11 case reports or case series |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calcaterra, V.; Tagi, V.M.; De Santis, R.; Biuso, A.; Taranto, S.; D’Auria, E.; Zuccotti, G. Endocrinological Involvement in Children and Adolescents Affected by COVID-19: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165248
Calcaterra V, Tagi VM, De Santis R, Biuso A, Taranto S, D’Auria E, Zuccotti G. Endocrinological Involvement in Children and Adolescents Affected by COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(16):5248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165248
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalcaterra, Valeria, Veronica Maria Tagi, Raffaella De Santis, Andrea Biuso, Silvia Taranto, Enza D’Auria, and Gianvincenzo Zuccotti. 2023. "Endocrinological Involvement in Children and Adolescents Affected by COVID-19: A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 16: 5248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165248
APA StyleCalcaterra, V., Tagi, V. M., De Santis, R., Biuso, A., Taranto, S., D’Auria, E., & Zuccotti, G. (2023). Endocrinological Involvement in Children and Adolescents Affected by COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(16), 5248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165248