Massive Transfusion Increases Serum Magnesium Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
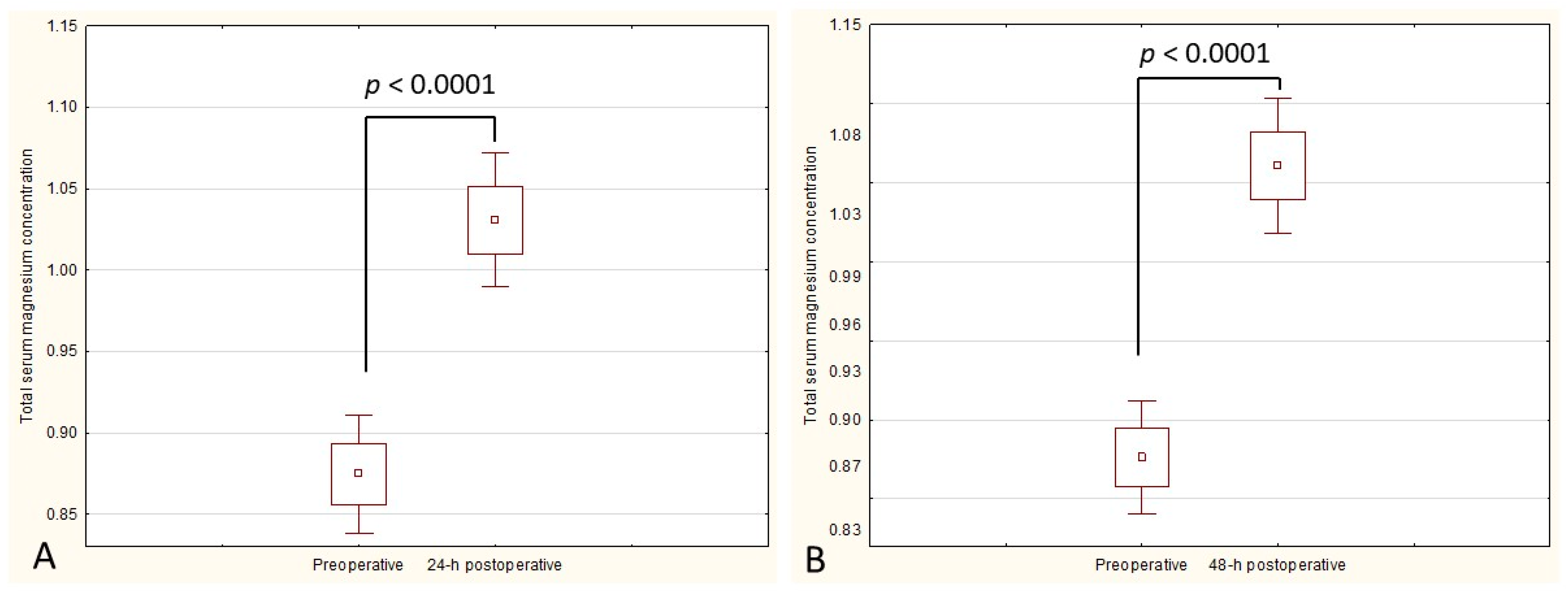
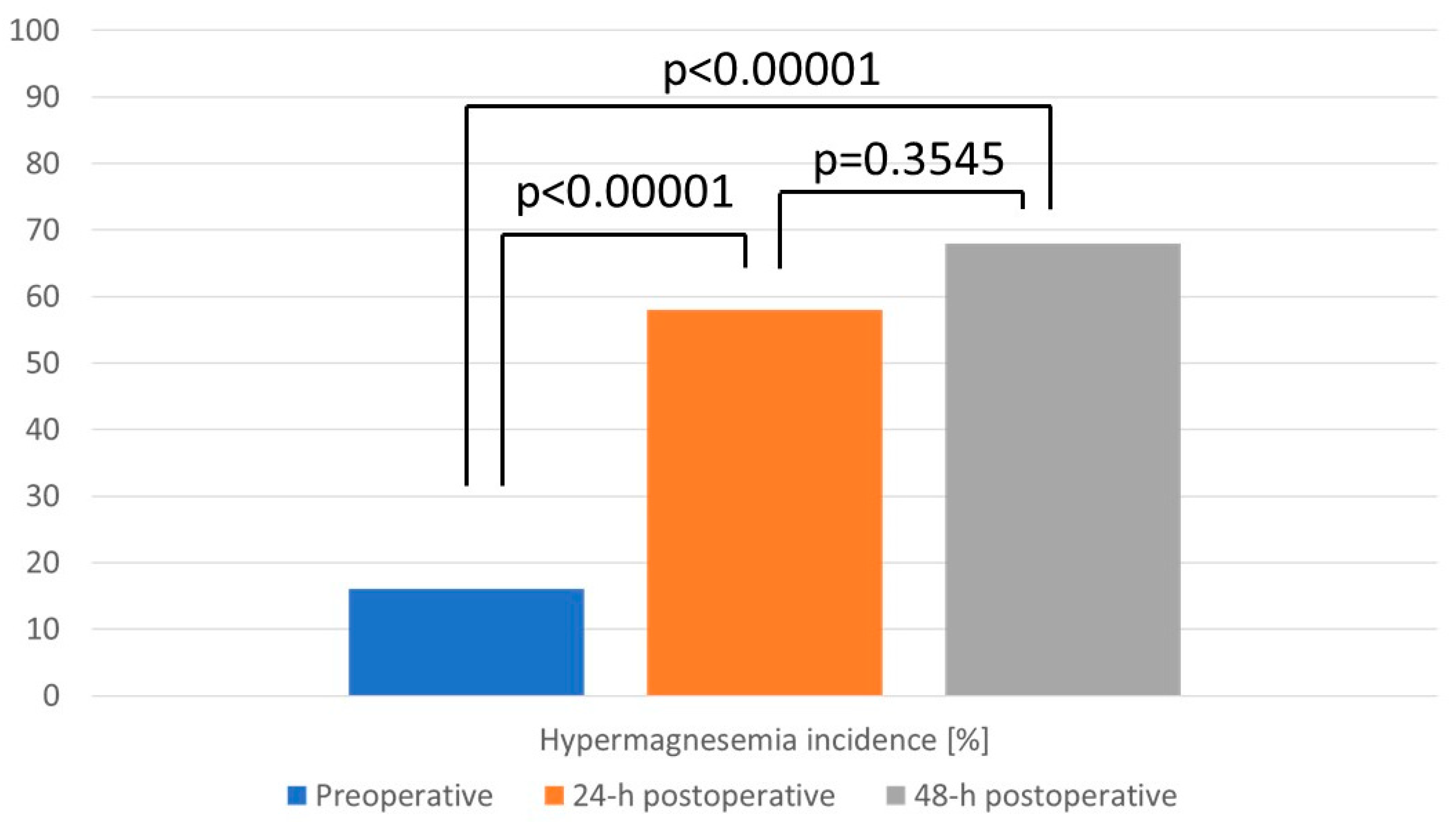
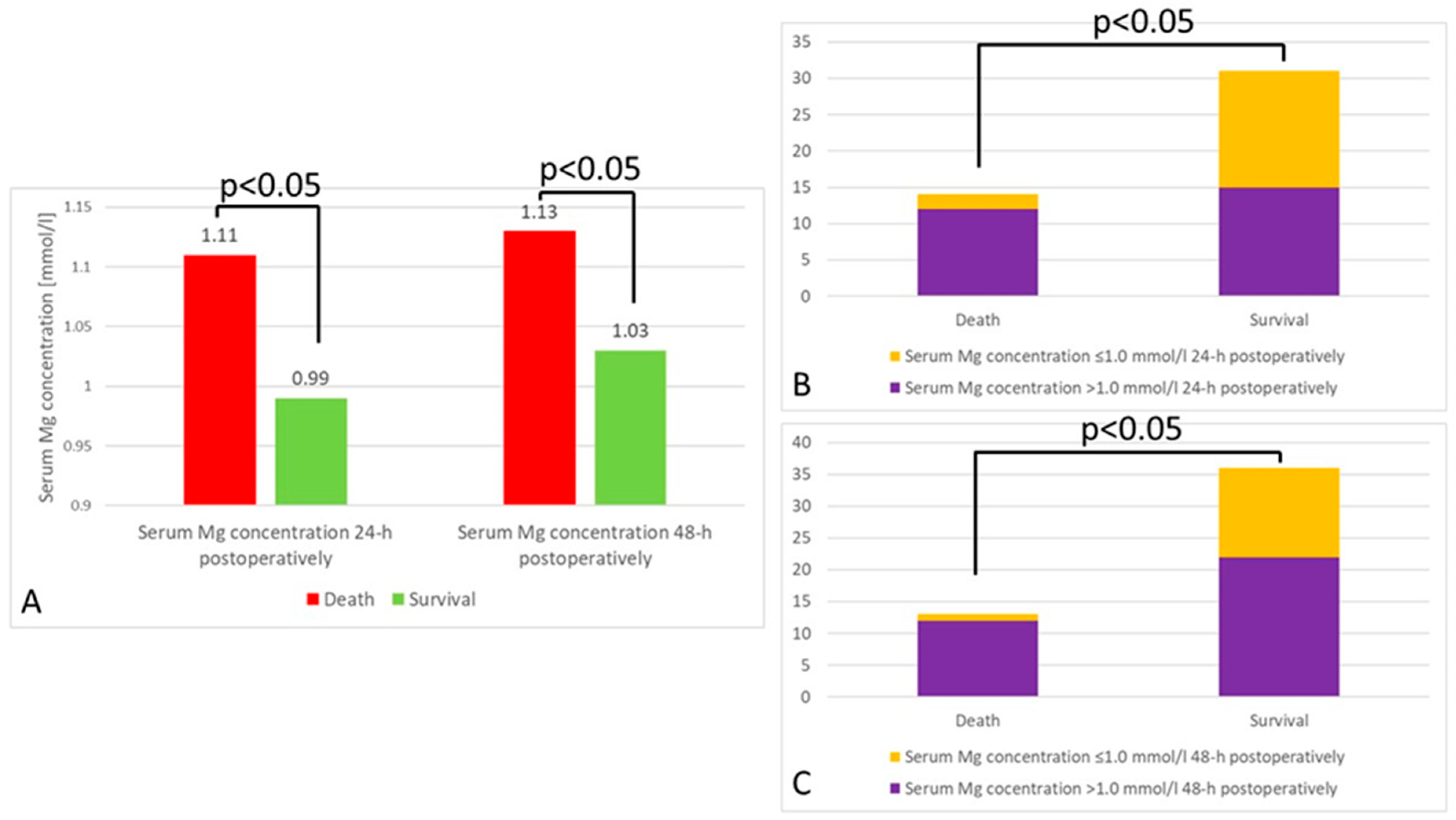
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abuzeid, A.M.; O’keeffe, T. Review of massive transfusion protocols in the injured, bleeding patient. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihler, K.C.; Napolitano, L.M. Complications of Massive Transfusion. Chest 2010, 137, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayter, M.A.; Pavenski, K.; Baker, J. Massive transfusion in the trauma patient: Continuing Professional Development. Can. J. Anaesth. 2012, 59, 1130–1145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Mohammed, A. Magnesium: The Forgotten Electrolyte—A Review on Hypomagnesemia. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Xiong, L.Z. Perioperative Red Blood Cell Transfusion: What We Do Not Know. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 2383–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.R. Additives and Anticoagulants. Available online: https://www.lifeblood.com.au/health-professionals/products/additives-anticoagulants (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Bazzano, G.; Galazzi, A.; Giusti, G.D.; Panigada, M.; Laquintana, D. The Order of Draw during Blood Collection: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.-A.; Bruserud, Ø. Hypomagnesemia in critically ill patients. J. Intensiv. Care 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaine, J.; Chonchol, M.; Levi, M. Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wal-Visscher, E.R.; Kooman, J.P.; van der Sande, F.M. Magnesium in Chronic Kidney Disease: Should We Care? Blood Purif. 2018, 45, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Shi, R. High-Normal Serum Magnesium and Hypermagnesemia Are Associated with Increased 30-Day In-Hospital Mortality: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 625133. [Google Scholar]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5 (Suppl. S1), i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairley, J.; Glassford, N.J.; Zhang, L.; Bellomo, R. Magnesium status and magnesium therapy in critically ill patients: A systematic review. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, R.; Märtensson, J.; Eastwood, G.M. Metabolic and electrolyte disturbance after cardiac arrest: How to deal with it. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 29, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Umehara, K.; Shirozu, K.; Sumie, M.; Karashima, Y.; Higashi, M.; Yamaura, K. Association between ionized magnesium and postoperative shivering. J. Anesth. 2021, 35, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, E.; Lavee, J.; Shechter, M.; Kogan, A.; Maor, E.; Asher, E.; Freimark, D.; Klempfner, R.; Peled, Y. Relation of Low Serum Magnesium to Mortality and Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy Following Heart Transplantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 125, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameris, A.L.; Monnens, L.A.; Bindels, R.J.; Hoenderop, J.G.J. Drug-induced alterations in Mg2+ homoeostasis. Clin. Sci. 2012, 123, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liamis, G.; Hoorn, E.J.; Florentin, M.; Milionis, H. An overview of diagnosis and management of drug-induced hypomagnesemia. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, M.; Anderson, M.; Parkes, S.; Fowler, P. Magnesium flux during continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration with heparin and citrate anticoagulation. Crit. Care Resusc. J. Australas. Acad. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 14, 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kośka, A.; Kowalik, M.M.; Lango-Maziarz, A.; Karolak, W.; Jagielak, D.; Lango, R. Ionic homeostasis, acid-base balance and the risk of citrate accumulation in patients after cardiovascular surgery treated with continuous veno-venous haemofiltration with post-dilution regional citrate anticoagulation—An observational case-control study. Acta. Biochim. Pol. 2021, 68, 695–704. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.A.A.; Ismail, Y.; Ismail, A.A. Chronic magnesium deficiency and human disease; time for reappraisal? Qjm 2018, 111, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in Prevention and Therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaque, M.S. Magnesium: Are We Consuming Enough? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chrun, L.R.; João, P.R.D. Hypomagnesemia after spinal fusion. J. Pediatr. 2012, 88, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzinger, M.J.; Moretti, E.W.; Wilderman, R.F.; El-Moalem, E.H.; Toffaletti, J.G.; Moon, E.R. The relationship between ionized and total serum magnesium concentrations during abdominal surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 2003, 15, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Moren, A.M.; Hamptom, D.M.; Diggs, B.; Kiraly, L.; Fox, E.E.; Holcomb, J.B.; Rahbar, M.H.; Brasel, K.J.; Cohen, M.J.; Bulger, E.M.; et al. Recursive partitioning identifies greater than 4 U of packed red blood cells per hour as an improved massive transfusion definition. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015, 79, 920–924. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, V.S.; Sun, E.; Yau, S.; Abeyakoon, C.; Seamer, G.; Bhopal, S.; Tucker, H.; Doree, C.; Brunskill, S.J.; McQuilten, Z.K.; et al. Definitions of massive transfusion in adults with critical bleeding: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, R.B.; Nielsen, F. Interpreting magnesium status to enhance clinical care: Key indicators. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Cavalier, E.; Pottel, H. Serum Creatinine: Not So Simple! Nephron 2017, 136, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, A.; Bellone, F.; Chilà, D.; Loddo, S.; Morabito, N.; Basile, G.; Benvenga, S.; Corica, F. Rates of hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia in medical settings. Magnes. Res. 2021, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Chewcharat, A.; Petnak, T.; Mao, M.A.; Davis, P.W.; Bathini, T.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Qureshi, F.; Erickson, S.B. Hospital-Acquired Dysmagnesemia and In-Hospital Mortality. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, M.; Hansson, F.; Klarin, B. Analysis of hypo- and hypermagnesemia in an intensive care unit cohort. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2018, 62, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, J.L.; Matuschak, G.M. Magnesium in critical illness: Metabolism, assessment, and treatment. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahr, J.; Vender, J.; Gilbert, H.C.; Spiess, B.; Horrow, J.C.; Maddi, R. Effect of propofol with and without EDTA on haemodynamics and calcium and magnesium homeostasis during and after cardiac surgery. Intensiv. Care Med. 2000, 26 (Suppl. S4), S443–S451. [Google Scholar]
- Herr, D.L.; Kelly, K.; Hall, J.B.; Ulatowski, J.; Fulda, G.J.; Cason, B.; Hickey, R.; Nejman, A.M.; Zaloga, G.P.; Teres, D. Safety and Efficacy of Propofol with EDTA When Used for Sedation of Surgical Intensive Care Unit Patients. Intensiv. Care Med. 2000, 26 (Suppl. S4), S452–S462. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, J.; Zaloga, G.P.; Haupt, M.T.; Weinmann, M.; Murray, M.J.; Bandi, V.; Teres, D. Cation metabolism during propofol sedation with and without EDTA in patients with impaired renal function. Intensiv. Care Med. 2000, 26 (Suppl. S4), S433–S442. [Google Scholar]
- Kieboom, B.C.; Zietse, R.; Ikram, M.A.; Hoorn, E.J.; Stricker, B.H. Thiazide but not loop diuretics is associated with hypomagnesaemia in the general population. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2018, 27, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasala, S.; Carmody, J.B. How to use… serum creatinine, cystatin C and GFR. Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 2017, 102, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld, A.J.; Levine, B.S.; Rodriguez, M. Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphorus, and Magnesium Dysregulation in Chronic Kidney Disease. Semin. Dial. 2015, 28, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, J.W.; Popovtzer, M.M.; Massry, S.G.; Kleeman, C.R. The physicochemical state and renal handling of divalent ions in chronic renal failure. Arch. Intern. Med. 1969, 124, 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Laupland, K.B.; Tabah, A.; Jacobs, N.; Ramanan, M. Determinants of serum magnesium abnormalities and outcome among admissions to the intensive care unit. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2020, 39, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowska, J.; Małecka, M.; Ciepiela, O. Variations in Magnesium Concentration Are Associated with Increased Mortality: Study in an Unselected Population of Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1836. [Google Scholar]
- Angkananard, T.; Anothaisintawee, T.; Eursiriwan, S.; Gorelik, O.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J.; Thakkinstian, A. The association of serum magnesium and mortality outcomes in heart failure patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Tyler, L.N. Transfusion of blood and blood products: Indications and complications. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 83, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lichtiger, B.; Perry-Thornton, E. Hemolytic transfusion reactions in oncology patients: Experience in a large cancer center. J. Clin. Oncol. 1984, 2, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poder, T.G.; Nonkani, W.G.; Leponkouo, É.T. Blood Warming and Hemolysis: A Systematic Review with Me-ta-Analysis. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.M.; Scarpa, A. Regulation of cellular magnesium. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, d720-34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Watering, L.M. Age of blood: Does older blood yield poorer outcomes? Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2013, 20, 526–532. [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer, P.F.; Cancelas, J.A.; Cardigan, R.; Devine, D.V.; Gulliksson, H.; Sparrow, R.L.; Vassallo, R.R.; de Wildt-Eggen, J.; Baumann-Baretti, B.; Hess, J.R. Evaluation of overnight hold of whole blood at room temperature before component processing: Effect of red blood cell (RBC) additive solutions on in vitro RBC measures. Transfusion 2011, 51 (Suppl. S1), 15s–24s. [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow, R.L. Time to revisit red blood cell additive solutions and storage conditions: A role for “omics” analyses. Blood Transfus. 2012, 10 (Suppl. S2), s7–s11. [Google Scholar]
- Dopsaj, V.; Martinovic, J.; Dopsaj, M.; Stevuljevic, J.K.; Bogavac-Stanojevic, N. Gender-Specific Oxidative Stress Parameters. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 32, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maturu, P.; Varadacharyulu, N. Adaptive changes in fatty acid profile of erythrocyte membrane in relation to plasma and red cell metabolic changes in chronic alcoholic men. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmavathi, P.; Reddy, V.D.; Kavitha, G.; Paramahamsa, M.; Varadacharyulu, N. Chronic cigarette smoking alters erythrocyte membrane lipid composition and properties in male human volunteers. Nitric Oxide 2010, 23, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, J.S.; Waters, J.H.; Seltsam, A.; Scharberg, E.A.; Richter, E.; Kameneva, M.V.; Yazer, M.H. Menopausal status affects the susceptibility of stored RBCs to mechanical stress. Vox Sang. 2011, 100, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.R. Measures of stored red blood cell quality. Vox Sang. 2014, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, D.; Cappadone, C.; Farruggia, G.; Prata, C. Magnesium: Biochemistry, Nutrition, Detection, and Social Impact of Diseases Linked to Its Deficiency. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, G.; Mazur, A.; Trousselard, M.; Bienkowski, P.; Yaltsewa, N.; Amessou, M.; Noah, L.; Pouteau, E. Magnesium Status and Stress: The Vicious Circle Concept Revisited. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, L. Magnesium, stress and neuropsychiatric disorders. Magnes. Trace Elem. 1991, 10, 287–301. [Google Scholar]
| No. | Reason for Hospitalization | Drugs Administered Intravenously during Hospitalization | Dialysis | Chronic Diseases | Survival | Preoperative Mg Concentration | 24 h Postoperative Mg Concentration | 48 h Postoperative Mg Concentration | RBCs Approximate Volume [mL] | The Mean Intracellular Concentration in Transfused RBCs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Multi-site trauma | Propofol, sufentanil, tazocin | No | Alcohol dependence syndrome | Yes | 0.83 | 1.07 | 1.04 | 2600 | 1.325 |
| 2 | Tight aortic stenosis | Biotraxon, lenovor, amiodarone, furosemide | No | Hypertension | Yes | 0.88 | 1.08 | 1.11 | 2350 | 0.85 |
| 3 | Severe vitamin B12 deficiency anemia | - | Yes | p-ANCA systemic vasculitis, hypertension, chronic kidney disease | Yes | 0.95 | 1.01 | 1.1 | 2950 | 1.424 |
| 4 | Hemorrhage of the digestive tract | Midanium, norepinephrine, adrenalin | Yes | Alcohol dependence syndrome | No | 0.96 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 2600 | 1.34 |
| 5 | Laparotomy due to disseminated cancer | Levonor, morphine, furosemide, meronem | No | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy, t2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity | Yes | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.94 | 2350 | 0.62 |
| 6 | Liver transplant | No data | No data | Inflammatory bowel disease, hypothyroidism | Yes | 0.81 | 0.99 | 0.82 | 2950 | 1.028 |
| 7 | Liver retransplantation | Metronidazole | Yes | Renal failure, recurrent cholangitis | Yes | 0.71 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 2600 | 0.55 |
| 8 | Severe aortic stenosis | Furosemide, insulin, tramadol, propofol, sufentanil | No | No | Yes | 0.77 | 1.08 | 1.14 | 2350 | 1.705 |
| 9 | Ascending aortic aneurysm | Biofazolin, propofol, sulfentanyl, furosemide | No | Hypertension | Yes | 1.15 | 1.42 | 1.4 | 2950 | 1.59333 |
| 10 | Insufficiency of the main artery valve | Adrenaline, norepinephrine, dobutamine, levosimendan, propofol, midazolam, sufentanil, morphine, furosemide, heparin, coradrone, lignocaine, biotraxone, antithrombin III, PPI | No | Heart failure, ascending aortic aneurysm, permanent atrial fibrillation, hypertension | No | 0.99 | 1.09 | 1.12 | 2350 | 1.525 |
| 11 | Aortic valve disease and coronary artery disease | Propofol, sulfentanyl, furosemide, ebrantil | No | Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, t2 diabetes mellitus, COPD, heart failure | Yes | 0.88 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 2350 | 1.16 |
| 12 | Liver transplantation | Unfractionated heparin | No | No data | Yes | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 2600 | 1.74 |
| 13 | Replacement of the aortic valve with the ascending aorta | Propofol, sulfentanyl, levonor, dobutamine | No | Aortic regurgitation, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, hypertension, thyroid nodular goiter | No | 0.82 | 1.06 | 1.14 | 2350 | 0.86 |
| 14 | Bleeding from esophageal varices | Terlipressin, PPI, K supplementation, insulin | No | Liver failure, pancreatic head tumor infiltrating the bile ducts | Yes | 0.83 | 1.1 | 1.04 | 2350 | 1.475 |
| 15 | Severe iron deficiency anemia | Clonazepam, furosemide | No | Severe microcytic anemia, hypertension, atherosclerosis | Yes | 1.03 | 1.11 | 1.08 | 2400 | 1.58 |
| 16 | Sideropenic anemia caused by recurrent bleeding from hemorrhoids | - | No | Hypothyroidism | Yes | 0.9 | 1.02 | 0.98 | 2350 | 1.72 |
| 17 | Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver | Norepinephrine, anti-encephalopathic drugs, antibiotic, propofol, sufentanil | No | Alcohol dependence syndrome, esophageal varices | No | 0.96 | 0.99 | 1.07 | 2350 | 1.38 |
| 18 | Abdominal pain after subtotal gastrectomy for gastric adenoma | Propofol, sufentanil, antibiotic, furosemide, norepinephrine | No | Hypothyroidism, diverticular disease | No | 0.76 | 1.31 | 1.2 | 2350 | 1.8 |
| 19 | Dissecting aneurysm of the main artery | Propofol, morphine, noradrenaline, epinephrine, glypressin, polfilin, meronem, vancomycin | Yes | Loeys–Dietz syndrome, hypertension, asthma | No | 0.81 | 1.04 | 1.1 | 2950 | 1.476 |
| 20 | Pancreatic cancer disseminated | Hydrocortisone, clemastine | No | No | Yes | 0.98 | - | 1.21 | 2350 | 0.585 |
| 21 | Dissection of the ascending aorta | Tramadol, trifas, biofazolin | No | Hypertension, aortic regurgitation, hypothyroidism | Yes | 1.04 | 1.18 | 1.32 | 2350 | 0.605 |
| 22 | Iron deficiency anemia | Venofer | No | Hypertension | Yes | 1.01 | - | 1.18 | 2400 | 1.04 |
| 23 | Decompensated liver cirrhosis | - | No | Ovarian cancer, portal vein thrombosis, hemorrhoids, depression | Yes | 0.68 | 0.88 | 0.72 | 2350 | 1.23 |
| 24 | Severe nosebleed after the completion of chemotherapy for sarcoma of the hip | - | No | Hypothyroidism | Yes | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.88 | 2350 | 1.425 |
| 25 | Mitral valve defect | Vancomycin, cordarone, concor cor amiodarone, trifas | No | Heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias, dyslipidemia, | Yes | 0.93 | 0.95 | 1.0 | 2350 | 0.97 |
| 26 | Cerebellar tumor | Tazocin, vancomycin, ceftriaxone, amikacin, analgesics | No | Hypertension, gastroesophageal reflux | No | 1.04 | 1.08 | - | 2400 | 1.265 |
| 27 | Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver | Vancomycin, analgesics, anti-encephalopathic drugs, anti-coagulants | No | CKD | Yes | 0.75 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 2350 | 0.985 |
| 28 | Progressive liver damage | Propofol, norepinephrine, fluconazole | Yes | No | No | 0.71 | 1.05 | 0.98 | 2950 | 1.46 |
| 29 | Iron and vitamin B12 deficiency anemia | - | No | Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, impaired fasting glucose | Yes | 0.85 | 1.01 | 0.92 | 2350 | 0.855 |
| 30 | Hepatic failure in the course of PBC | Diuretics, norepinephrine | No | Pancreatic tail cyst, kidney cysts | Yes | 0.87 | 1.21 | 1.21 | 2950 | 0.828 |
| 31 | Liver transplant for secondary biliary cirrhosis | Diuretics, norepinephrine | No | No data | Yes | 1.08 | 1.19 | 1.33 | 2950 | 0.872 |
| 32 | Multiple myeloma, kappa light chain disease, ISS 3, D-S IIIB | - | Yes | Hypertension, CDK | Yes | 0.88 | 1.04 | 0.87 | 2950 | 0.724 |
| 33 | Inflammation of the bile ducts | Morphine, midanium, norepinephrine | No | Ulcerative colitis in remission | Yes | 0.91 | 1.17 | 1.08 | 2950 | 0.888 |
| 34 | Liver transplantation due to HCV infection | Sufentanil | No | Hypertension | Yes | 0.85 | 0.98 | 1.07 | 2600 | 0.825 |
| 35 | Severe symptoms of cholestasis | Proton-pump inhibitors | No | Heart failure, hepatic steatosis and failure, hypertension | Yes | 0.63 | 0.71 | 1.05 | 2950 | 0.83667 |
| 36 | Liver transplantation | No data | No data | No data | Yes | 0.64 | 0.88 | 1.1 | 2600 | 0.9 |
| 37 | Liver transplantation | Prograph, Augmentin MFF, prednisolone | No | T2 diabetes mellitus, thrombosis of the portal system | Yes | 0.79 | 0.84 | 1.03 | 2600 | 0.928 |
| 38 | Left lung nodule biopsy | - | No | Hypertension, diverticular disease, nephrolithiasis, atherosclerosis, | Yes | 1.03 | 0.98 | 1.09 | 2350 | 0.908 |
| 39 | Liver transplantation | Vancomycin, analgesics, anti-encephalopathic drugs, anti-coagulants | No | Renal failure, ascites, hemorrhagic diathesis | Yes | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 2600 | 0.772 |
| 40 | Progressive liver damage | Propofol, norepinephrine, fluconazole | Yes | No | No | 0.97 | 0.91 | 1.04 | 2950 | 0.9075 |
| 41 | Pulmonary embolism | - | No | Extensive ulceration of the duodenal bulb, gastric hernia, liver cyst, diverticular disease | No | 0.98 | 1.07 | 1.11 | 2350 | 0.744 |
| 42 | Liver transplantation due to toxic damage | Sufentanil, midazolam, norepinephrine, colistin, | Yes | No data | No | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.15 | 2600 | 0.76 |
| 43 | Primary sclerosing cholangitis and chronic liver failure | Analgesics, norepinephrine | No | Kidney failure | No | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.24 | 2950 | 0.893 |
| 44 | Liver transplant | Analgesics | No | Esophageal varices, anemia, chronic pancreatitis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus | Yes | 0.82 | 1.07 | 1.14 | 2950 | 1.07 |
| 45 | Rectal perforation | Analgesics | No | Cirrhosis | Yes | 0.83 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 2950 | 0.793 |
| 46 | Acute kidney injury and tacrolimus poisoning | Diuretics, meropenem, diflucan | Yes | Depression, acute renal failure, hypertension, alcohol dependence syndrome | Yes | 0.8 | 0.98 | 1.15 | 2950 | 0.75 |
| 47 | Cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis | Pressor amines | Yes | Esophageal varices, Graves’ disease | Yes | 0.64 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 2950 | 0.723 |
| 48 | Inflammation and deterioration of kidney function | Tacrolimus, pressor amines, propofol | Yes | No | No | 0.88 | 1.28 | 1.31 | 2600 | 0.873 |
| 49 | Hepatic encephalopathy | - | No | Portal hypertension, splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, chronic pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus | Yes | 0.67 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 2350 | 0.572 |
| Factors Potentially Affecting Magnesium Homeostasis | Preoperatively | 24 h Postoperatively | 48 h Postoperatively |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | p = 0.29 | p = 0.88 | p = 0.09 |
| Comorbidities | p = 0.11 | p = 0.99 | p = 0.88 |
| Intravenous administration of sedatives | p = 0.55 | p < 0.05 | p < 0.05 |
| Intravenous administration of diuretics | p = 0.11 | p < 0.05 | p < 0.05 |
| Intravenous administration of antimicrobials | p = 0.57 | p = 0.6 | p = 0.43 |
| Dialysis | p = 0.13 | p = 0.65 | p = 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malinowska, J.; Małecka-Giełdowska, M.; Pietrucha, K.; Górska, G.; Kogut, D.; Ciepiela, O. Massive Transfusion Increases Serum Magnesium Concentration. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155157
Malinowska J, Małecka-Giełdowska M, Pietrucha K, Górska G, Kogut D, Ciepiela O. Massive Transfusion Increases Serum Magnesium Concentration. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(15):5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155157
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalinowska, Justyna, Milena Małecka-Giełdowska, Katarzyna Pietrucha, Gabriela Górska, Dagmara Kogut, and Olga Ciepiela. 2023. "Massive Transfusion Increases Serum Magnesium Concentration" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 15: 5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155157
APA StyleMalinowska, J., Małecka-Giełdowska, M., Pietrucha, K., Górska, G., Kogut, D., & Ciepiela, O. (2023). Massive Transfusion Increases Serum Magnesium Concentration. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12155157









