Ethanol Enhances Endothelial Rigidity by Targeting VE-Cadherin—Implications for Acute Aortic Dissection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Experimental Conditions
2.3. Cell Migration
2.4. Metabolic Viability
2.5. In Vitro Vascular Permeability Assay
2.6. Hanging Drop Assay
2.7. RT-PCR and Western Blotting
2.8. VE-Cadherin Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
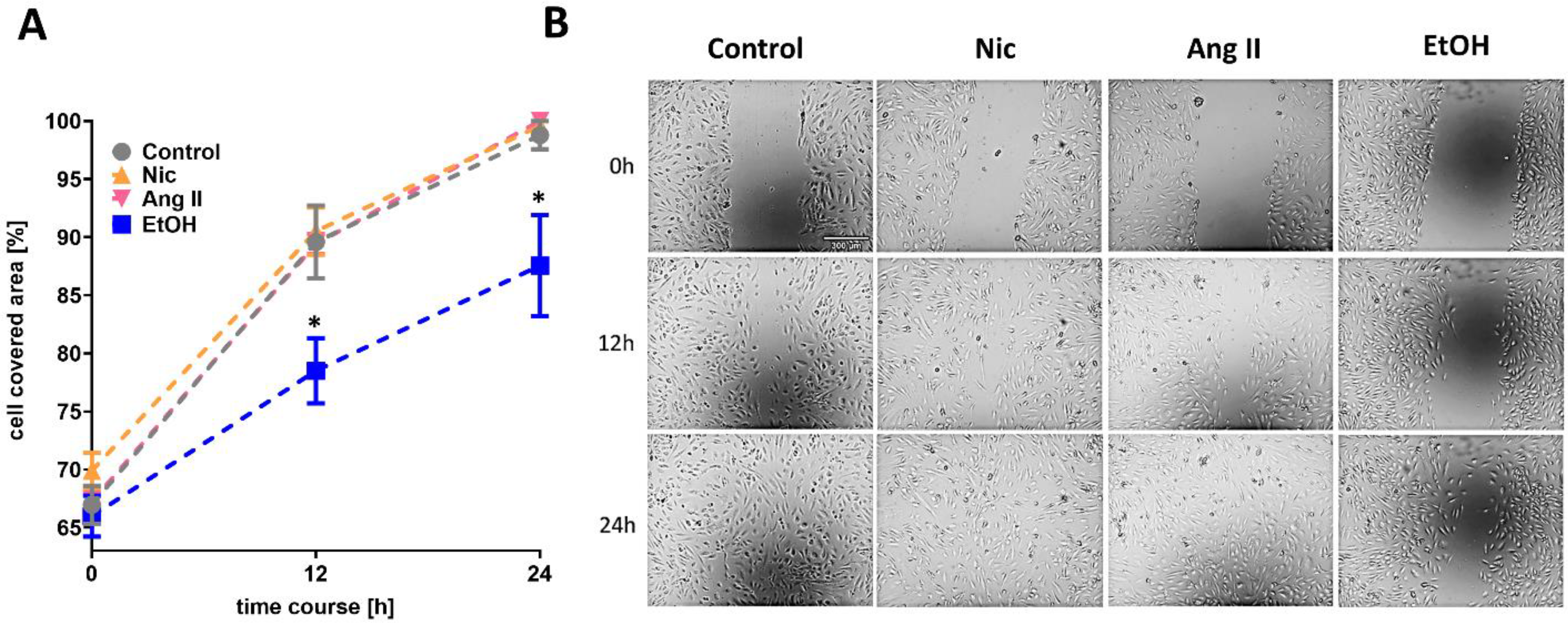
3.1. Cell Migration
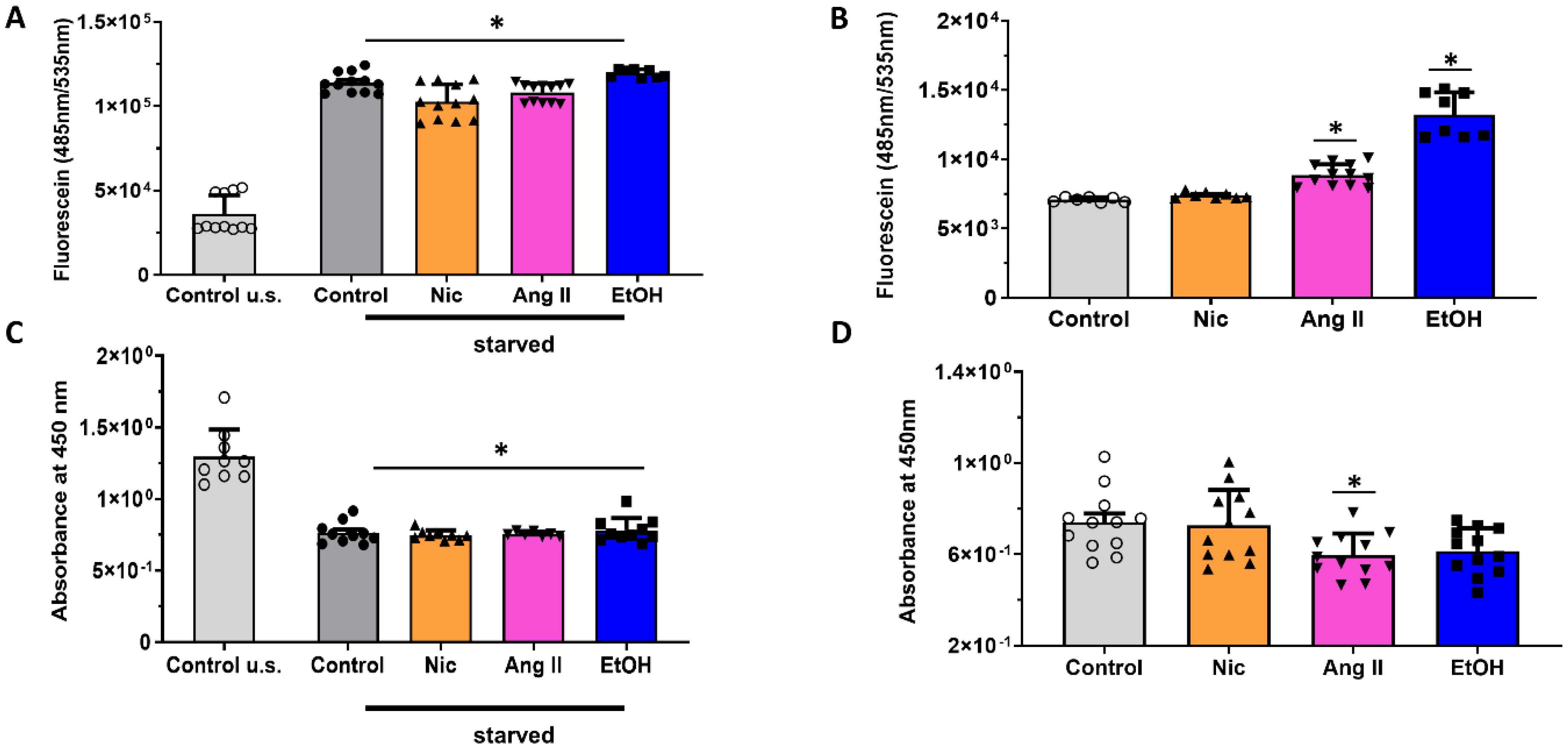
3.2. Permeability and Metabolic Activity
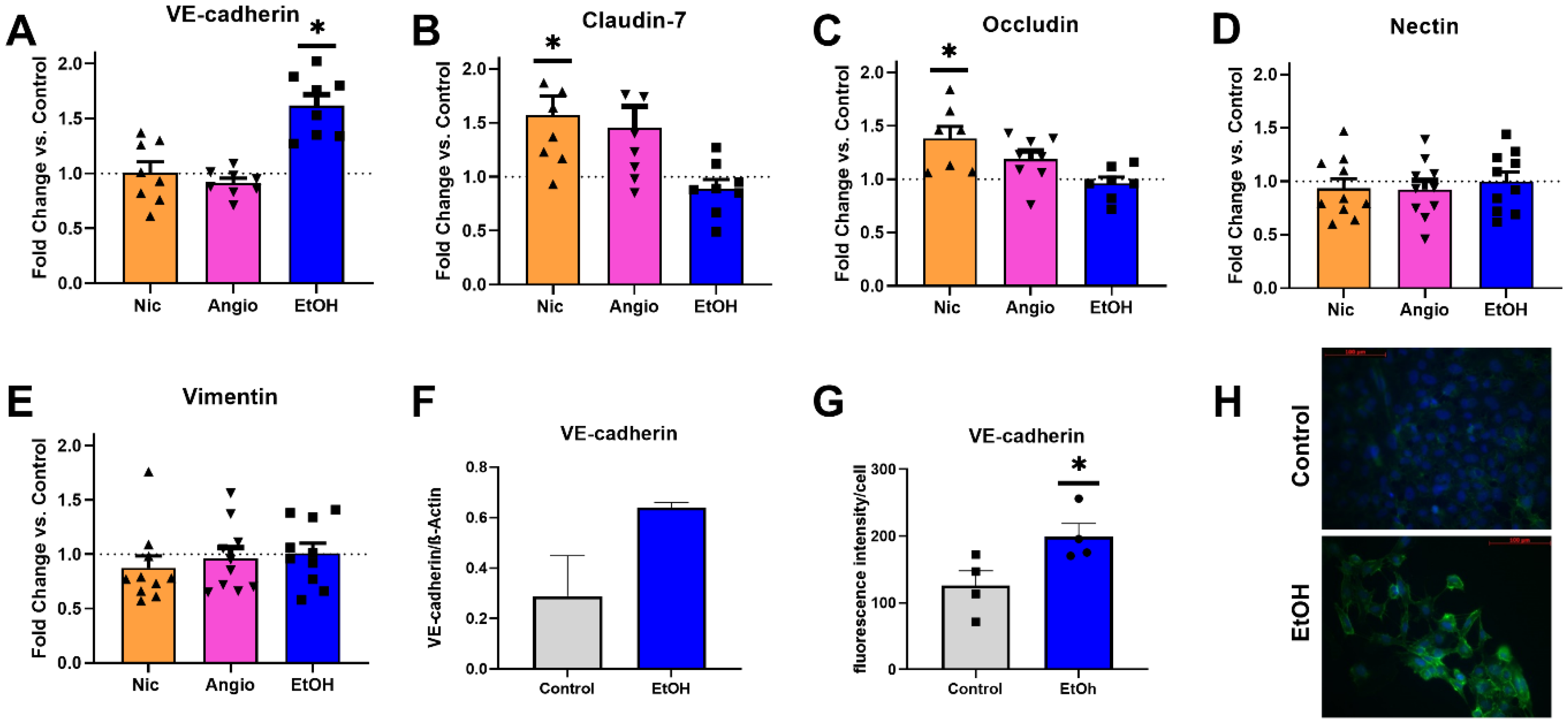
3.3. Mechanical Adherence
3.4. Transcriptional Expression
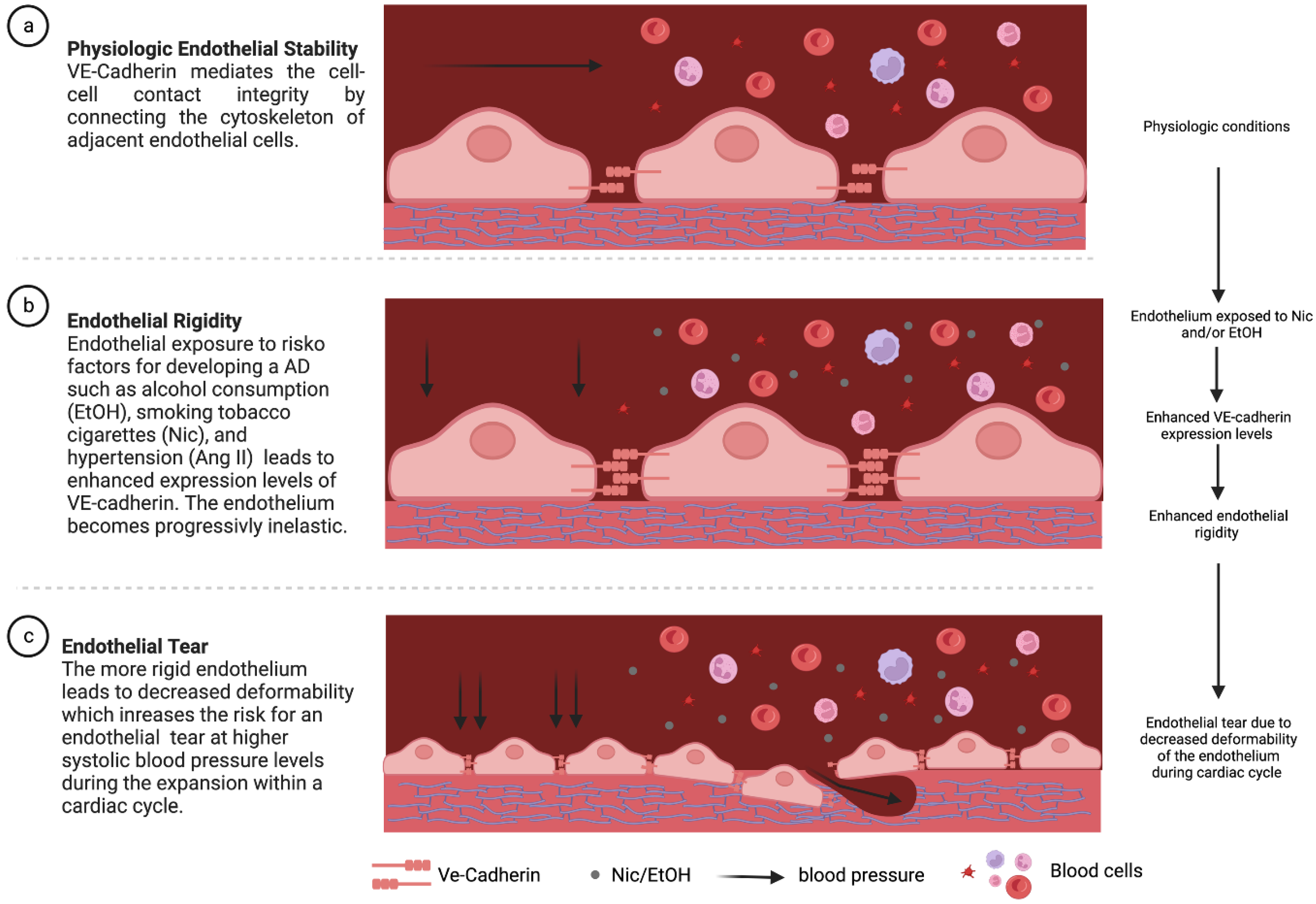
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melvinsdottir, I.H.; Lund, S.H.; Agnarsson, B.A.; Sigvaldason, K.; Gudbjartsson, T.; Geirsson, A. The incidence and mortality of acute thoracic aortic dissection: Results from a whole nation study. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhuber, A.; Raddatz, A.; Betge, S.; Ploenes, C.; Ito, W.; Janosi, R.A.; Ott, C.; Langheim, E.; Czerny, M.; Puls, R.; et al. Interdisciplinary German clinical practice guidelines on the management of type B aortic dissection. Gefasschirurgie 2023, 28, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, S.; Gandra, S.R.; Fox, K.M.; Mesterton, J.; Banefelt, J.; Johansson, G.; Levin, L.; Sobocki, P. Healthcare costs associated with cardiovascular events in patients with hyperlipidemia or prior cardiovascular events: Estimates from Swedish population-based register data. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2015, 17, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, P. Grey matter: Ageing in developing countries. Lancet 2012, 379, 1285–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criado, F.J. Aortic Dissection: A 250-Year Perspective. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2011, 38, 694–700. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3233335/ (accessed on 17 November 2020). [PubMed]
- Cerutti, C.; Ridley, A.J. Endothelial cell-cell adhesion and signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejana, E.; Orsenigo, F.; Molendini, C.; Baluk, P.; McDonald, D.M. Organization and signaling of endothelial cell-to-cell junctions in various regions of the blood and lymphatic vascular trees. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 335, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Piao, H.; Li, B.; Xu, J.; Wei, S.; Liu, K. Poor management of hypertension is an important precipitating factor for the development of acute aortic dissection. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goran, K.P. Excessive alcohol consumption and aortic dissection: Probable but unexplored relation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 1163–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Peng, H.; Mastej, V.; Chen, W. MicroRNA Regulation of Endothelial Junction Proteins and Clinical Consequence. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.A.; Uppada, S.; Achkar, I.W.; Hashem, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Shanmugakonar, M.; Al-Naemi, H.A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S. Tight Junction Proteins and Signaling Pathways in Cancer and Inflammation: A Functional Crosstalk. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, S.; Tang, C.; Musini, V.M.; Wright, J.M. Effect of alcohol on blood pressure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 7, CD012787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laksitorini, M.D.; Yathindranath, V.; Xiong, W.; Parkinson, F.E.; Thliveris, J.A.; Miller, D.W. Impact of Wnt/β-catenin signaling on ethanol-induced changes in brain endothelial cell permeability. J. Neurochem. 2020, 157, 1118–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Molina, P.; Souza-Smith, F.M. Ethanol-Induced Lymphatic Endothelial Cell Permeability via MAP-Kinase Regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2021, 321, C104–C116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; You, J.; Wang, P.; Feng, C.; Xu, G.; Zhao, R.; et al. Long-term exposure to ethanol downregulates tight junction proteins through the protein kinase Cα signaling pathway in human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4789–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavey, M.; Lecuit, T. Molecular Bases of Cell-Cell Junctions Stability and Dynamics. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a002998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowski, L.; Schröder-Heurich, B.; Kipke, B.; Schmidt, C.; Von Kaisenberg, C.S.; Von Versen-Höynck, F. Low Ethanol Concentrations Promote Endothelial Progenitor Cell Capacity and Reparative Function. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Chen, G.; Fu, W.; Liao, M.; Frank, J.A.; Bower, K.A.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Luo, J. Ethanol Disrupts Vascular Endothelial Barrier: Implication in Cancer Metastasis. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 127, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, K.; Hasegawa, H. Blood Vessels as a Key Mediator for Ethanol Toxicity: Implication for Neuronal Damage. Life 2022, 12, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulorz, J.; Spin, J.M.; Mulorz, P.; Wagenhäuser, M.U.; Deng, A.; Mattern, K.; Rhee, Y.H.; Toyama, K.; Adam, M.; Schelzig, H.; et al. E-cigarette exposure augments murine abdominal aortic aneurysm development: Role of Chil1. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 119, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Luo, J.; Fu, M.; Luo, L.; Cai, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Dong, R.; Yang, Y.; Tu, L.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase deletion attenuated nicotine-induced arterial stiffness via limiting the loss of SIRT1. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2021, 321, H353–H368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenhäuser, M.U.; Schellinger, I.N.; Yoshino, T.; Toyama, K.; Kayama, Y.; Deng, A.; Guenther, S.P.; Petzold, A.; Mulorz, J.; Mulorz, P.; et al. Chronic Nicotine Exposure Induces Murine Aortic Remodeling and Stiffness Segmentation—Implications for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Susceptibility. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mokembo, J.N.; Monayo, S.M.; Jha, N.K.; Kopylov, P.; et al. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to nicotine-induced atherosclerosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5276–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagat, M.; Grzanka, D.; Izdebska, M.; Maczynska, E.; Grzanka, A. Nornicotine impairs endothelial cell-cell adherens junction complexes in EA.hy926 cell line via structural reorganization of F-actin. Folia Histochem. Et Cytobiol. 2013, 51, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kakafika, A.; Mikhailidis, D. Smoking and Aortic Diseases. Circ. J. 2007, 71, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.P.J.; Sideso, E.; Handa, A.; Rothwell, P.M. Incidence, risk factors, outcome and projected future burden of acute aortic dissection. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 3, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turu, G.; Balla, A.; Hunyady, L. The Role of β-Arrestin Proteins in Organization of Signaling and Regulation of the AT1 Angiotensin Receptor. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueyo, M.E.; Gonzalez, W.; Nicoletti, A.; Savoie, F.; Arnal, J.-F.; Michel, J.-B. Angiotensin II Stimulates Endothelial Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 via Nuclear Factor-κB Activation Induced by Intracellular Oxidative Stress. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, I.A.; Xu, Y.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Davidge, S.T. Angiotensin II-induced MMP-2 release from endothelial cells is mediated by TNF-α. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2004, 286, C779–C784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueyo, M.E.; Arnal, J.-F.; Rami, J.; Michel, J.-B.; de Cavanagh, E.M.V.; Inserra, F.; Dautzenberg, M.; Just, A.; Ferder, M.; Manucha, W.; et al. Angiotensin II stimulates the production of NO and peroxynitrite in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1998, 274, C214–C220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitopoulou, I.; Orfanos, S.E.; Kotanidou, A.; Maltabe, V.; Manitsopoulos, N.; Karras, P.; Kouklis, P.; Armaganidis, A.; Maniatis, N.A. Vascular endothelial-cadherin downregulation as a feature of endothelial transdifferentiation in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2016, 311, L352–L363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Meng, L.; Zhang, P.; Lin, H.; Chi, J.; Peng, F.; Guo, H. Angiotensin II inhibits the protein expression of ZO-1 in vascular endothelial cells by downregulating VE-cadherin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, L.A.; Haven, A.K.; Bauer, N.N. Circulating microparticles in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension increase intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression selectively in pulmonary artery endothelium. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.F.; Carvalho, F.A.; Moreira, C.; Nogueira, J.B.; Santos, N.C. Essential arterial hypertension patients present higher cell adhesion forces, contributing to fibrinogen-dependent cardiovascular risk. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14897–14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drożdż, D.; Drożdż, M.; Wójcik, M. Endothelial dysfunction as a factor leading to arterial hypertension. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, D.C.; van der Vlag, J.; Nijenhuis, T. Laminar flow substantially affects the morphology and functional phenotype of glomerular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mulorz, J.; Ibing, W.; Cappallo, M.; Braß, S.M.; Takeuchi, K.; Raaz, U.; Schellinger, I.N.; Krott, K.J.; Schelzig, H.; Aubin, H.; et al. Ethanol Enhances Endothelial Rigidity by Targeting VE-Cadherin—Implications for Acute Aortic Dissection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154967
Mulorz J, Ibing W, Cappallo M, Braß SM, Takeuchi K, Raaz U, Schellinger IN, Krott KJ, Schelzig H, Aubin H, et al. Ethanol Enhances Endothelial Rigidity by Targeting VE-Cadherin—Implications for Acute Aortic Dissection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(15):4967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154967
Chicago/Turabian StyleMulorz, Joscha, Wiebke Ibing, Melanie Cappallo, Sönke Maximilian Braß, Kiku Takeuchi, Uwe Raaz, Isabel Nahal Schellinger, Kim Jürgen Krott, Hubert Schelzig, Hug Aubin, and et al. 2023. "Ethanol Enhances Endothelial Rigidity by Targeting VE-Cadherin—Implications for Acute Aortic Dissection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 15: 4967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154967
APA StyleMulorz, J., Ibing, W., Cappallo, M., Braß, S. M., Takeuchi, K., Raaz, U., Schellinger, I. N., Krott, K. J., Schelzig, H., Aubin, H., Oberhuber, A., Elvers, M., & Wagenhäuser, M. U. (2023). Ethanol Enhances Endothelial Rigidity by Targeting VE-Cadherin—Implications for Acute Aortic Dissection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 4967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154967





