Differences between Hepatic and Cerebral Regional Tissue Oxygen Saturation at the Onset of Intradialytic Hypotension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Design and Participants
2.3. Collection of Clinical Information
2.4. Measurement of rSO2
2.5. Definition of IDH
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
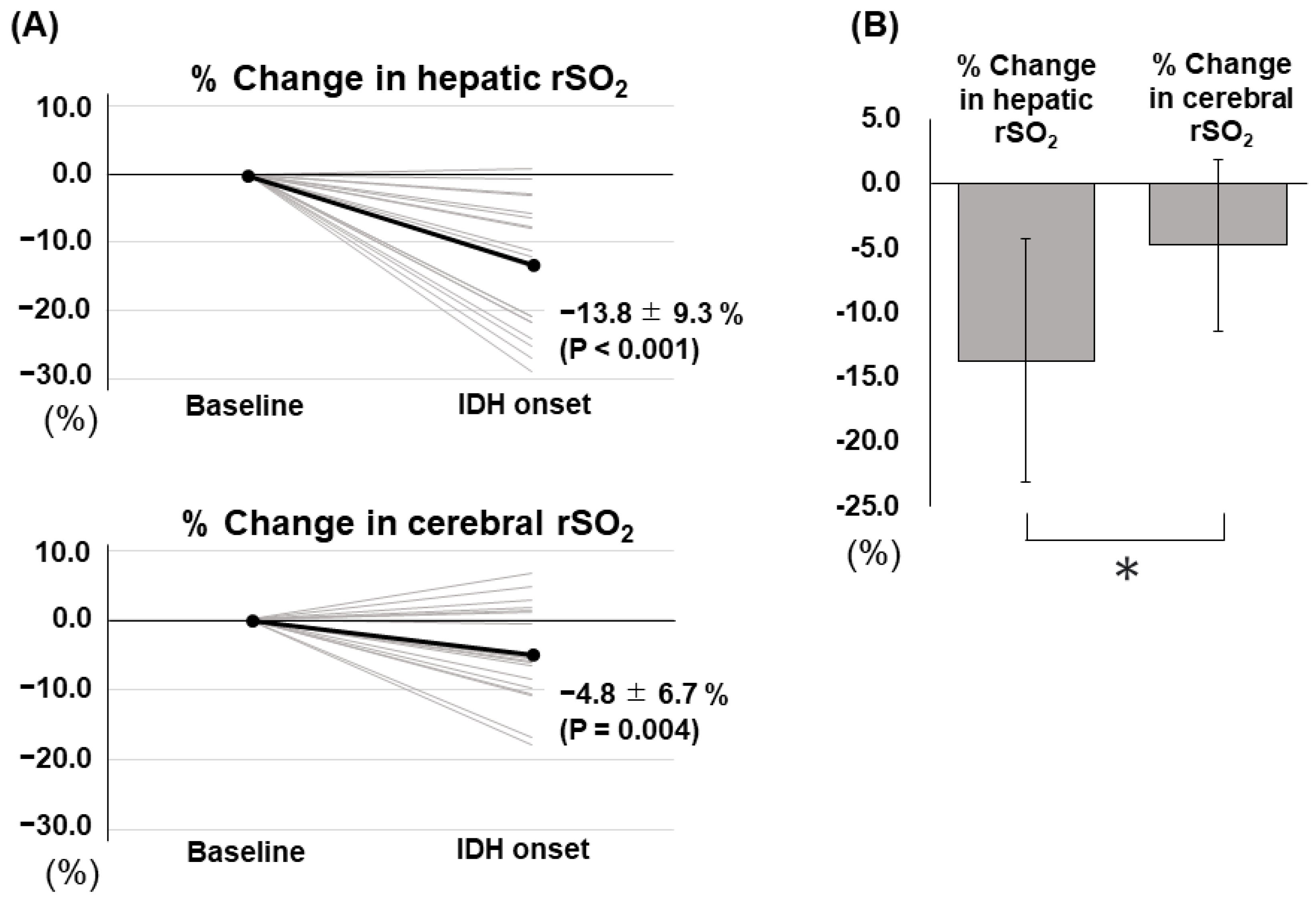
3.2. IDH-Related Changes in Hepatic and Cerebral rSO2
3.3. Factors Associated with the Difference between the Two rSO2 Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skonieczny, P.; Heleniak, Z.; Karowiec, M.; Zajączkowski, S.; Tylicki, L.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Rutkowski, P. Blood Pressure Control and Antihypertensive Treatment among Hemodialysis Patients-Retrospective Single Center Experience. Medicina 2021, 57, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, C.V.; Fenves, A.Z. Management of hypertension in hemodialysis patients. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2009, 11, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sars, B.; van der Sande, F.M.; Kooman, J.P. Intradialytic Hypotension: Mechanisms and Outcome. Blood Purif. 2020, 49, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.B.; Mc Causland, F.R. Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Treatment of Intradialytic Hypotension. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polinder-Bos, H.A.; Elting, J.W.J.; Aries, M.J.; García, D.V.; Willemsen, A.T.; van Laar, P.J.; Kuipers, J.; Krijnen, W.P.; Slart, R.H.; Luurtsema, G.; et al. Changes in cerebral oxygenation and cerebral blood flow during hemodialysis—A simultaneous near-infrared spectroscopy and positron emission tomography study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderliesten, T.; De Vis, J.B.; Lemmers, P.M.; van Bel, F.; Benders, M.J.; Hendrikse, J.; Petersen, E.T. Simultaneous quantitative assessment of cerebral physiology using respiratory-calibrated MRI and near-infrared spectroscopy in healthy adults. Neuroimage 2014, 85 Pt 1, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantini, S.; Sassaroli, A.; Tgavalekos, K.T.; Kornbluth, J. Cerebral blood flow and autoregulation: Current measurement techniques and prospects for noninvasive optical methods. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 031411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohovnik, I.; Post, J.; Uribarri, J.; Lee, H.; Sandu, O.; Langhoff, E. Cerebrovascular effects of hemodialysis in chronic kidney disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, T.; Ito, K.; Ookawara, S.; Shindo, M.; Uchida, T.; Kofuji, M.; Hayasaka, H.; Miyazawa, H.; Ueda, Y.; Hirai, K.; et al. Changes in tissue oxygenation in response to sudden intradialytic hypotension. J. Artif. Organs. 2020, 23, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarova, L.; Valerianova, A.; Kmentova, T.; Lachmanova, J.; Hladinova, Z.; Malik, J. Low cerebral oxygenation is associated with cognitive impairment in chronic hemodialysis patients. Nephron 2018, 139, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.; Kudlicka, J.; Lachmanova, J.; Valerianova, A.; Rocinova, K.; Bartkova, M.; Tesar, V. Tissue ischemia worsens during hemodialysis in end-stage renal disease patients. J. Vasc. Access. 2017, 18, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEwen, C.; Sutherland, S.; Daly, J.; Pugh, C.; Tarassenko, L. Relationship between Hypotension and Cerebral Ischemia during Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2511–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsuyoshi, Y.; Ito, K.; Ookawara, S.; Uchida, T.; Morishita, Y. Difference in Cerebral and Hepatic Oxygenation in Response to Ultrafiltration in a Hemodialysis Patient with Congestive Heart Failure. Cureus 2021, 13, e13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minato, S.; Ookawara, S.; Ito, K.; Miyazawa, H.; Hayasaka, H.; Kofuji, M.; Uchida, T.; Morino, J.; Kaneko, S.; Yanai, K.; et al. Differences in cerebral and hepatic oxygenation in response to intradialytic blood transfusion in patients undergoing hemodialysis. J. Artif. Organs. 2019, 22, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, S.; Ito, K.; Ookawara, S.; Kiryu, S.; Iguchi, M.; Sanayama, H.; Kakei, M.; Tabei, K.; Morishita, Y. Does food ingestion during hemodialysis lead to change in hepatic oxygenation? Nefrologia 2022, 43, 383–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirakata, H.; Nitta, K.; Inaba, M.; Shoji, T.; Fujii, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Tabei, K.; Joki, N.; Hase, H.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy guidelines for management of cardiovascular diseases in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2012, 16, 387–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Mottola, L.; Quaresima, V. Principles, techniques, and limitations of near infrared spectroscopy. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 29, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.D. Cerebral oxygenation monitoring: Near-infrared spectroscopy. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2006, 3, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslehaty, H.; Krause-Titz, U.; Petridis, A.K.; Barth, H.; Mehdorn, H.M. Continuous measurement of cerebral oxygenation with near-infrared spectroscopy after spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. ISRN Neurol. 2012, 2012, 907187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongo, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Okudera, H.; Hokama, M.; Nakagawa, F. Noninvasive cerebral optical spectroscopy: Depth-resolved measurements of cerebral haemodynamics using indocyanine green. Neurol. Res. 1995, 17, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, S1–S153. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, D.; Chandler, B. Splanchnic circulation. BJA Educ. 2015, 16, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstead, W.M. Cerebral Blood Flow Autoregulation and Dysautoregulation. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, O.B.; Strandgaard, S.; Edvinsson, L. Cerebral autoregulation. Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 1990, 2, 161–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kanbay, M.; Ertuglu, L.A.; Afsar, B.; Ozdogan, E.; Siriopol, D.; Covic, A.; Basile, C.; Ortiz, A. An update review of intradialytic hypotension: Concept, risk factors, clinical implications and management. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Levin, N.W.; Twardowski, Z.J.; Wizemann, V.; Saito, A.; Kimata, N.; Gillespie, B.W.; Combe, C.; Bommer, J.; et al. Longer treatment time and slower ultrafiltration in hemodialysis: Associations with reduced mortality in the DOPPS. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movilli, E.; Gaggia, P.; Zubani, R.; Camerini, C.; Vizzardi, V.; Parrinello, G.; Savoldi, S.; Fischer, M.S.; Londrino, F.; Cancarini, G. Association between high ultrafiltration rates and mortality in uraemic patients on regular haemodialysis. A 5-year prospective observational multicentre study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 3547–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flythe, J.E.; Kimmel, S.E.; Brunelli, S.M. Rapid fluid removal during dialysis is associated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age (years) | 70.0 (63.0–76.0) |
| Male sex, n (%) | 69 (76) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.4 (19.9–25.0) |
| HD vintage (years) | 0.6 (0.1–6.2) |
| Cardiovascular diseases, n (%) | 35 (38) |
| Cerebrovascular diseases, n (%) | 15 (16) |
| Administration of antihypertensive drugs, n (%) | 84 (92) |
| Administration of vasopressor before HD, n (%) | 11 (12) |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 9.8 ± 1.6 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 137 ± 4 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.1 (2.8–3.6) |
| O2 saturation (%) | 96.0 (93.7–97.2) |
| Ultrafiltration rate (mL/kg/h) | 9.3 (5.4–11.4) |
| Development of IDH, n (%) | 20 (22) |
| Hepatic rSO2 before HD (%) | 55.8 ± 15.3 |
| Hepatic rSO2 at the lowest SBP (%) | 53.8 ± 14.9 |
| % Change in hepatic rSO2 (%) | −2.8 ± 11.3 |
| Cerebral rSO2 before HD (%) | 50.2 ± 10.1 |
| Cerebral rSO2 at the lowest SBP (%) | 49.3 ± 9.7 |
| % Change in cerebral rSO2 (%) | −1.5 ± 6.4 |
| SBP before HD (mmHg) | 147 ± 24 |
| Lowest SBP (mmHg) | 122 ± 24 |
| % Change in SBP (%) | −13.4 (−21.3–−7.6) |
| SBP after HD (mmHg) | 146 ± 24 |
| MBP before HD (mmHg) | 100 ± 17 |
| MBP at the lowest SBP (mmHg) | 86 ± 18 |
| % Change in MBP (%) | −9.0 (−20.4–−5.0) |
| MBP after HD (mmHg) | 99 ± 15 |
| Variables | |
|---|---|
| % Change in hepatic rSO2 (%) | −13.8 ± 9.3 |
| % Change in cerebral rSO2 (%) | −4.8 ± 6.7 |
| Difference between the two rSO2 changes (%) | 9.0 ± 9.9 |
| % Change in SBP (%) | −23.8 (−32.5–−10.6) |
| % Change in MBP (%) | −24.9 (−37.6–−20.6) |
| Simple Linear Regression | Multivariable Linear Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | r | p | Standardized Coefficient | p |
| Age | −0.045 # | 0.670 | ||
| Male sex | −0.148 | 0.161 | ||
| Body mass index | 0.014 # | 0.896 | ||
| HD vintage | 0.138 # | 0.191 | ||
| Cardiovascular diseases | 0.044 | 0.682 | ||
| Cerebrovascular diseases | −0.122 | 0.251 | ||
| Administration of hypertensive drugs | 0.136 | 0.199 | ||
| Administration of vasopressors before HD | 0.143 | 0.178 | ||
| Hemoglobin | 0.013 | 0.900 | ||
| Sodium | −0.118 | 0.265 | ||
| Albumin | 0.008 # | 0.938 | ||
| O2 saturation | 0.203 # | 0.054 | ||
| Ultrafiltration rate | 0.302 # | 0.004 * | 0.250 | 0.010 * |
| Development of IDH | 0.389 | <0.001 * | 0.356 | <0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaneko, S.; Ookawara, S.; Ito, K.; Minato, S.; Mutsuyoshi, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Hirai, K.; Morishita, Y. Differences between Hepatic and Cerebral Regional Tissue Oxygen Saturation at the Onset of Intradialytic Hypotension. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154904
Kaneko S, Ookawara S, Ito K, Minato S, Mutsuyoshi Y, Ueda Y, Hirai K, Morishita Y. Differences between Hepatic and Cerebral Regional Tissue Oxygen Saturation at the Onset of Intradialytic Hypotension. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(15):4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154904
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaneko, Shohei, Susumu Ookawara, Kiyonori Ito, Saori Minato, Yuko Mutsuyoshi, Yuichiro Ueda, Keiji Hirai, and Yoshiyuki Morishita. 2023. "Differences between Hepatic and Cerebral Regional Tissue Oxygen Saturation at the Onset of Intradialytic Hypotension" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 15: 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154904
APA StyleKaneko, S., Ookawara, S., Ito, K., Minato, S., Mutsuyoshi, Y., Ueda, Y., Hirai, K., & Morishita, Y. (2023). Differences between Hepatic and Cerebral Regional Tissue Oxygen Saturation at the Onset of Intradialytic Hypotension. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154904







