Office-Based Intraosseous Infiltrations of PRGF as an Effective Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Observational Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. PRGF Preparation
2.3. PRGF Infiltration Procedure
2.4. Patient Evaluation and Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
3.3. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| KOA | Knee osteoarthritis |
| GFs | Growth factors |
| KOOS | Knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome score |
| MCII | Minimally clinically important improvement |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| PRGF | Plasma rich in growth factors |
| PRP | Platelet-rich plasma |
| SCB | Subchondral bone |
| SM | Synovial membrane |
| WALANT | Wide-awake local anesthesia no tourniquet |
References
- Brandt, K.D.; Radin, E.L.; Dieppe, P.A.; van de Putte, L. Yet more evidence that osteoarthritis is not a cartilage disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, E.L.; Rose, R.M. Role of subchondral bone in the initiation and progression of cartilage damage. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1986, 213, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, S.R. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone 2012, 51, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, S.; Walsh, D.A. Osteochondral alterations in osteoarthritis. Bone 2012, 51, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radin, E.L. The physiology and degeneration of joints. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1972, 2, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhen, G.; Hu, Y.; An, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wan, M.; et al. Subchondral bone osteoclasts induce sensory innervation and osteoarthritis pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1076–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Li, G.; Liu, D.; Xie, W.; Xiao, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, M. Peripheral nerves in the tibial subchondral bone: The role of pain and homeostasis in osteoarthritis. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.; Thai, J.; Nazemian, V.; Song, R.; Ivanusic, J.J. Changes to the activity and sensitivity of nerves innervating subchondral bone contribute to pain in late-stage osteoarthritis. Pain 2022, 163, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, T.; Huh, Y.; Maixner, W.; Cheng, J.; Ji, R.R. Neuroimmune modulation of pain and regenerative pain medicine. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Fiz, N.; Guadilla, J.; Padilla, S.; Anitua, E.; Sanchez, P.; Delgado, D. Intraosseous infiltration of platelet-rich plasma for severe knee osteoarthritis. Arthrosc. Tech. 2014, 3, e713–e717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Delgado, D.; Sanchez, P.; Muinos-Lopez, E.; Paiva, B.; Granero-Molto, F.; Prosper, F.; Pompei, O.; Perez, J.C.; Azofra, J.; et al. Combination of Intra-Articular and Intraosseous Injections of Platelet Rich Plasma for Severe Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4868613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Padilla, S.; Prado, R.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Platelet-rich plasma: Are the obtaining methods, classification and clinical outcome always connected? Regen. Med. 2022, 17, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Nurden, P.; Prado, R.; Nurden, A.T.; Padilla, S. Autologous fibrin scaffolds: When platelet- and plasma-derived biomolecules meet fibrin. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buul, G.M.; Koevoet, W.L.; Kops, N.; Bos, P.K.; Verhaar, J.A.; Weinans, H.; Bernsen, M.R.; van Osch, G.J. Platelet-rich plasma releasate inhibits inflammatory processes in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendinelli, P.; Matteucci, E.; Dogliotti, G.; Corsi, M.M.; Banfi, G.; Maroni, P.; Desiderio, M.A. Molecular basis of anti-inflammatory action of platelet-rich plasma on human chondrocytes: Mechanisms of NF-kappaB inhibition via HGF. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 225, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaseri, A.; Busch, F.; Mobasheri, A.; Buhrmann, C.; Aldinger, C.; Rad, J.S.; Shakibaei, M. IGF-1 and PDGF-bb suppress IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation through down-regulation of NF-κB signaling: Involvement of Src/PI-3K/AKT pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, C. Comparative evaluation of leukocyte- and platelet-rich plasma and pure platelet-rich plasma for cartilage regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Xu, H.; Sheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Xie, X.; Zhang, C. Comparative evaluation of the effects of platelet-rich plasma formulations on extracellular matrix formation and the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human articular chondrocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 2940–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arra, M.; Abu-Amer, Y. Cross-talk of inflammation and chondrocyte intracellular metabolism in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Arra, M.; Swarnkar, G.; Alippe, Y.; Mbalaviele, G.; Abu-Amer, Y. IκB-ζ signaling promotes chondrocyte inflammatory phenotype, senescence, and erosive joint pathology. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Delgado, D.; Pompei, O.; Perez, J.C.; Sanchez, P.; Garate, A.; Bilbao, A.M.; Fiz, N.; Padilla, S. Treating Severe Knee Osteoarthritis with Combination of Intra-Osseous and Intra-Articular Infiltrations of Platelet-Rich Plasma: An Observational Study. Cartilage 2019, 10, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Jorquera, C.; Sanchez, P.; Beitia, M.; Garcia-Cano, B.; Guadilla, J.; Delgado, D. Platelet-rich plasma injections delay the need for knee arthroplasty: A retrospective study and survival analysis. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Jorquera, C.; de Dicastillo, L.L.; Fiz, N.; Knorr, J.; Beitia, M.; Aizpurua, B.; Azofra, J.; Delgado, D. Real-world evidence to assess the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee degenerative pathology: A prospective observational study. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X221100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Ma, S. Comparison of hyaluronic acid and PRP intra-articular injection with combined intra-articular and intraosseous PRP injections to treat patients with knee osteoarthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Luna, A.; Fahandezh-Saddi Diaz, H.; Villanueva Martinez, M.; Prado, R.; Padilla, S.; Anitua, E. Office-Based Intraosseous Infiltrations of PRGF in Knee Osteoarthritis: Description of Technique. Arthrosc. Tech. 2022, 11, e917–e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, W.M. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Kon, E.; Di Matteo, B.; Delgado, D.; Cole, B.J.; Dorotei, A.; Dragoo, J.L.; Filardo, G.; Fortier, L.A.; Giuffrida, A.; Jo, C.H.; et al. Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: An expert opinion and proposal for a novel classification and coding system. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 1447–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, E.M.; Roos, H.P.; Lohmander, L.S.; Ekdahl, C.; Beynnon, B.D. Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS)--development of a self-administered outcome measure. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1998, 28, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Visualizing samples with box plots. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquerizo, V.; Padilla, S.; Aguirre, J.J.; Begona, L.; Orive, G.; Anitua, E. Two cycles of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) intra-articular injections improve stiffness and activities of daily living but not pain compared to one cycle on patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquerizo, V.; Plasencia, M.A.; Arribas, I.; Seijas, R.; Padilla, S.; Orive, G.; Anitua, E. Comparison of Intra-Articular Injections of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF-Endoret) Versus Durolane Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Patients With Symptomatic Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthroscopy 2013, 29, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Fiz, N.; Azofra, J.; Usabiaga, J.; Aduriz Recalde, E.; Garcia Gutierrez, A.; Albillos, J.; Garate, R.; Aguirre, J.J.; Padilla, S.; et al. A randomized clinical trial evaluating plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) versus hyaluronic acid in the short-term treatment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy 2012, 28, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang-Saegusa, A.; Cugat, R.; Ares, O.; Seijas, R.; Cusco, X.; Garcia-Balletbo, M. Infiltration of plasma rich in growth factors for osteoarthritis of the knee short-term effects on function and quality of life. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2011, 131, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychagin, A.; Lipina, M.; Garkavi, A.; Islaieh, O.; Timashev, P.; Ashmore, K.; Kon, E. Intraosseous injections of platelet rich plasma for knee bone marrow lesions treatment: One year follow-up. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, K.; Vargas-Hernandez, J.S.; Sanchez, T.R.; Moreu, N.M.; Mont, M.A.; Higuera, C.A.; Piuzzi, N.S. Are Subchondral Intraosseous Injections Effective and Safe for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review. J. Knee Surg. 2019, 32, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belk, J.W.; Kraeutler, M.J.; Houck, D.A.; Goodrich, J.A.; Dragoo, J.L.; McCarty, E.C. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belk, J.W.; Lim, J.J.; Keeter, C.; McCulloch, P.C.; Houck, D.A.; McCarty, E.C.; Frank, R.M.; Kraeutler, M.J. Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis Who Receive Platelet-Rich Plasma or Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate Injections Have Better Outcomes Than Patients Who Receive Hyaluronic Acid: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arthroscopy 2023, 39, 1714–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.H.; Kraus, V.B.; Setton, L.A. Progress in intra-articular therapy. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.L.; Im, G.I. Drug delivery systems for intra-articular treatment of osteoarthritis. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Zalduendo, M.M.; Prado, R.; Alkhraisat, M.H.; Orive, G. Morphogen and proinflammatory cytokine release kinetics from PRGF-Endoret fibrin scaffolds: Evaluation of the effect of leukocyte inclusion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, M.M.; Briquez, P.S.; Guc, E.; Tortelli, F.; Kilarski, W.W.; Metzger, S.; Rice, J.J.; Kuhn, G.A.; Muller, R.; Swartz, M.A.; et al. Growth factors engineered for super-affinity to the extracellular matrix enhance tissue healing. Science 2014, 343, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Anitua, E.; Delgado, D.; Sanchez, P.; Prado, R.; Goiriena, J.J.; Prosper, F.; Orive, G.; Padilla, S. A new strategy to tackle severe knee osteoarthritis: Combination of intra-articular and intraosseous injections of Platelet Rich Plasma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsdal, M.A.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Lories, R.J.; Abramson, S.; Spector, T.; Pastoureau, P.; Christiansen, C.; Attur, M.; Henriksen, K.; Goldring, S.R.; et al. The coupling of bone and cartilage turnover in osteoarthritis: Opportunities for bone antiresorptives and anabolics as potential treatments? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Scherr, T.; Yang, Y.; Price, C.; Wang, L. Elevated cross-talk between subchondral bone and cartilage in osteoarthritic joints. Bone 2012, 51, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Yoshida, T.; Böker, K.O.; Foerster, R.H.; Jochim, L.; Flux, A.L.; Grosskopf, B.; Hawellek, T.; Lehmann, W.; Schilling, A.F. Changes of the subchondral bone microchannel network in early osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.M.; Churchman, S.M.; Gomez, A.; McGonagle, D.; Conaghan, P.G.; Ponchel, F.; Jones, E. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Alterations in Bone Marrow Lesions in Patients With Hip Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, O.H.; David, N.; Campisi, J.; Elisseeff, J.H. Senescent cells and osteoarthritis: A painful connection. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muinos-Lopez, E.; Delgado, D.; Sanchez, P.; Paiva, B.; Anitua, E.; Fiz, N.; Aizpurua, B.; Guadilla, J.; Padilla, S.; Granero-Molto, F.; et al. Modulation of Synovial Fluid-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Intra-Articular and Intraosseous Platelet Rich Plasma Administration. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1247950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Sanchez, M.; Aguirre, J.J.; Prado, R.; Padilla, S.; Orive, G. Efficacy and safety of plasma rich in growth factors intra-articular infiltrations in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy 2014, 30, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiz, N.; Delgado, D.; Garate, A.; Sanchez, P.; Oraa, J.; Bilbao, A.M.; Guadilla, J.; Sanchez, M. Intraosseous infiltrations of Platelet-Rich Plasma for severe hip osteoarthritis: A pilot study. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, S585–S590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilas, D.C.; Churchman, S.M.; McGonagle, D.; Jones, E. Targeting subchondral bone mesenchymal stem cell activities for intrinsic joint repair in osteoarthritis. Future Sci. OA 2017, 3, Fso228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, P.; Fiz, N.; Beitia, M.; Owston, H.E.; Delgado, D.; Jones, E.; Sanchez, M. Effect of Combined Intraosseous and Intraarticular Infiltrations of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma on Subchondral Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Patients with Hip Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Wu, A.T.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chou, K.R.; Zeng, R.; Wang, M.F.; Chang, W.C.; Hwang, S.M.; Su, C.H.; Deng, W.P. The balance between adipogenesis and osteogenesis in bone regeneration by platelet-rich plasma for age-related osteoporosis. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6773–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.; Cao, X. Targeting TGFbeta signaling in subchondral bone and articular cartilage homeostasis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chan, Y.T.; Yung, P.S.H.; Tuan, R.S.; Jiang, Y. Subchondral Bone Remodeling: A Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 607764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakin, S.G.; Coles, M.; Sherlock, J.P.; Powrie, F.; Carr, A.J.; Buckley, C.D. Pathogenic stromal cells as therapeutic targets in joint inflammation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Huang, C.F.; Lin, T.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Tina Chen, S.Y.; Liu, A.; Chen, W.H.; Wei, H.J.; Wang, M.F.; Williams, D.F.; et al. Delayed animal aging through the recovery of stem cell senescence by platelet rich plasma. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9767–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuz, P.C.; Kruger, J.P.; Metzlaff, S.; Freymann, U.; Endres, M.; Pruss, A.; Petersen, W.; Kaps, C. Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Types Show Impact on Chondrogenic Differentiation, Migration, and Proliferation of Human Subchondral Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells. Arthroscopy 2015, 31, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, J.P.; Hondke, S.; Endres, M.; Pruss, A.; Siclari, A.; Kaps, C. Human platelet-rich plasma stimulates migration and chondrogenic differentiation of human subchondral progenitor cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, J.P.; Ketzmar, A.K.; Endres, M.; Pruss, A.; Siclari, A.; Kaps, C. Human platelet-rich plasma induces chondrogenic differentiation of subchondral progenitor cells in polyglycolic acid-hyaluronan scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulawig, R.; Krüger, J.P.; Klein, O.; Konthur, Z.; Schütte, H.; Klose, J.; Kaps, C.; Endres, M. Identification of fibronectin as a major factor in human serum to recruit subchondral mesenchymal progenitor cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Pelacho, B.; Prado, R.; Aguirre, J.J.; Sanchez, M.; Padilla, S.; Aranguren, X.L.; Abizanda, G.; Collantes, M.; Hernandez, M.; et al. Infiltration of plasma rich in growth factors enhances in vivo angiogenesis and improves reperfusion and tissue remodeling after severe hind limb ischemia. J. Control. Release 2015, 202, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assirelli, E.; Filardo, G.; Mariani, E.; Kon, E.; Roffi, A.; Vaccaro, F.; Marcacci, M.; Facchini, A.; Pulsatelli, L. Effect of two different preparations of platelet-rich plasma on synoviocytes. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 2690–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Sanchez, M.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; De la Fuente, M.; Muruzabal, F.; Orive, G. Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) stimulates proliferation and migration of primary keratocytes and conjunctival fibroblasts and inhibits and reverts TGF-beta1-Induced myodifferentiation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6066–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.; Wen, C.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Crane, J.L.; Mears, S.C.; Askin, F.B.; Frassica, F.J.; Chang, W.; Yao, J.; et al. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan Tat, S.; Lajeunesse, D.; Pelletier, J.P.; Martel-Pelletier, J. Targeting subchondral bone for treating osteoarthritis: What is the evidence? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 24, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M.F.; Herguijuela, M.; Forkert, R.; Otten, U. Nerve growth factor in rheumatic diseases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 40, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, P.V.; Ng, M.K.; Klika, A.; Kamath, A.F.; Muschler, G.F.; Higuera, C.A.; Piuzzi, N.S. The Cost-Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Markov Decision Analysis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2020, 102, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Demark, R.E., Jr.; Becker, H.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Smith, V.J.S. Wide-Awake Anesthesia in the In-Office Procedure Room: Lessons Learned. Hand 2018, 13, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bismil, M.; Bismil, Q.; Harding, D.; Harris, P.; Lamyman, E.; Sansby, L. Transition to total one-stop wide-awake hand surgery service-audit: A retrospective review. JRSM Short Rep. 2012, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boffa, A.; Salerno, M.; Merli, G.; De Girolamo, L.; Laver, L.; Magalon, J.; Sanchez, M.; Tischer, T.; Filardo, G. Platelet-rich plasma injections induce disease-modifying effects in the treatment of osteoarthritis in animal models. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2021, 29, 4100–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.D.; Devji, T.; Bhandari, M.; Fierlinger, A.; Niazi, F.; Christensen, R. Clinical benefit of intra-articular saline as a comparator in clinical trials of knee osteoarthritis treatments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Knees (n) | 85 |
| Patients (n) | 79 |
| Gender | |
| Female (n, %) | 30 (38.0%) |
| Male (n, %) | 49 (62.0%) |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 60.9 ± 9.6 |
| Height (cm, mean ± SD) | 170.3 ± 9.0 |
| Weight (kg, mean ± SD) | 80.0 ± 17.6 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2, mean ± SD) | 27.5 ± 5.2 |
| Kellgren and Lawrence OA grade (n, %) | |
| Grade 3 | 38 (44.7%) |
| Grade 4 | 47 (55.3%) |
| Treatment side (n, %) | |
| Right (n, %) | 55 (64.7%) |
| Left (n, %) | 30 (35.3%) |
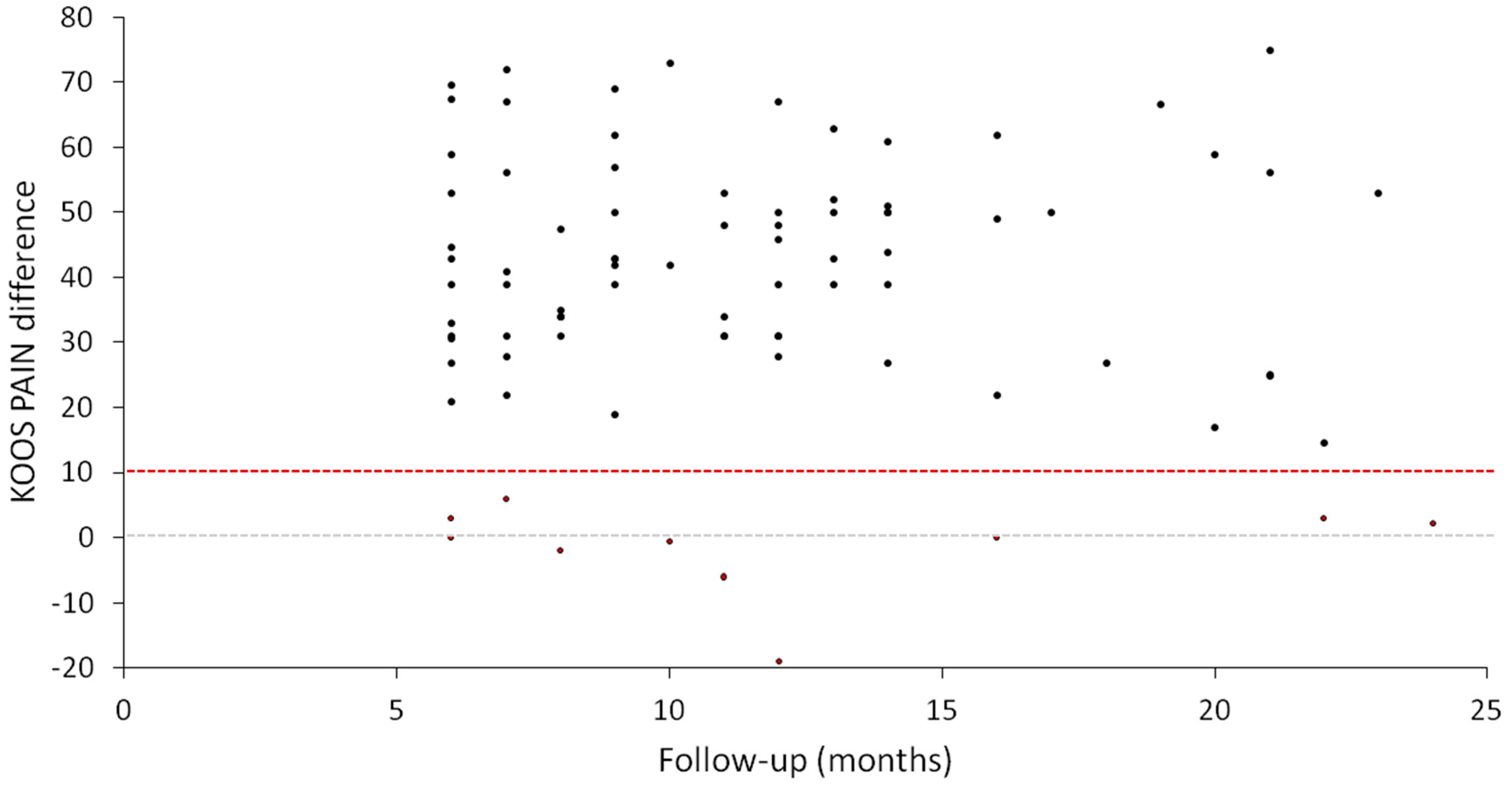
| Follow-up period (months, median (IQR *)) | 11 (7–14) |
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | p Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | |||
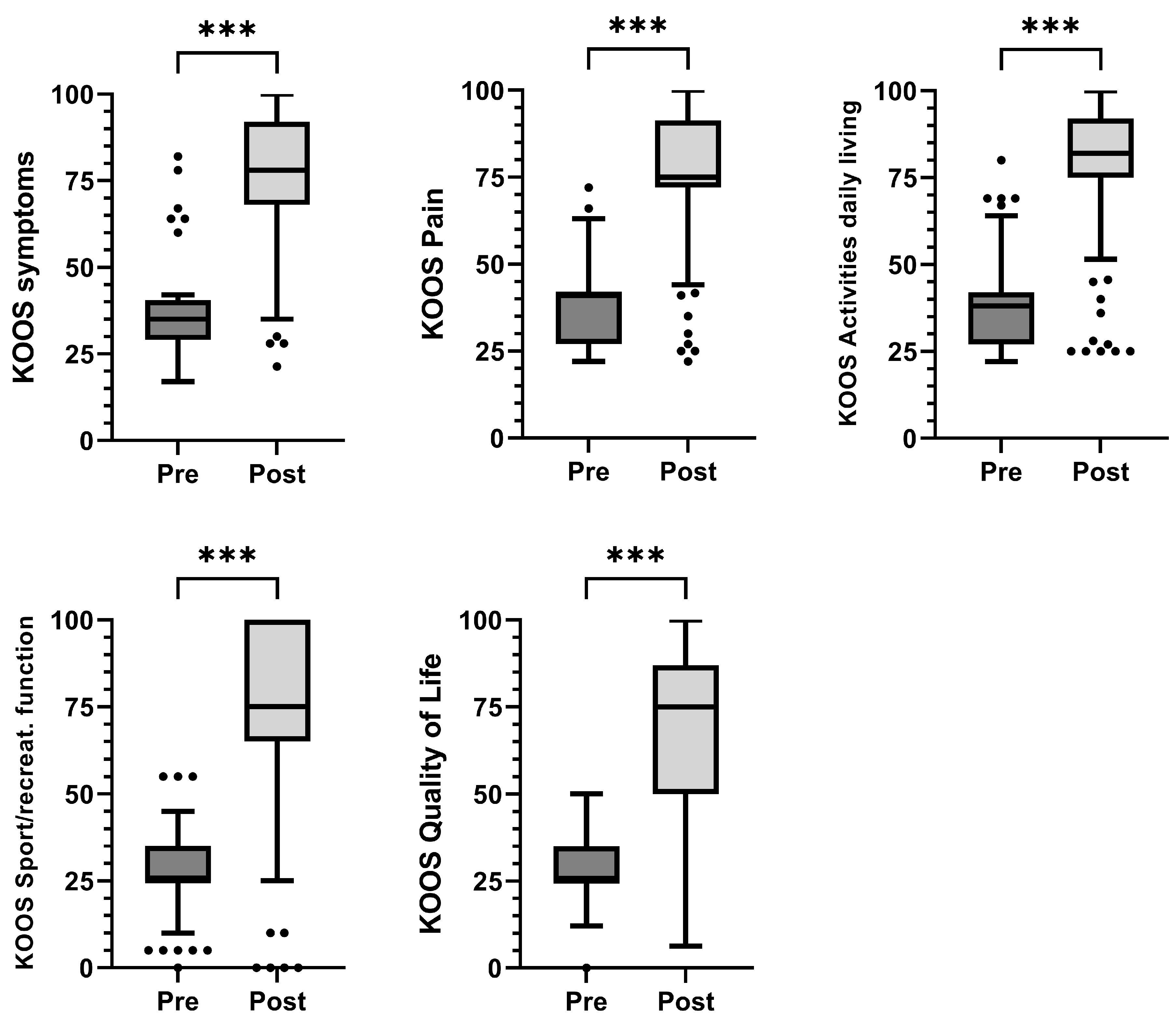
| Pain | 41 (27–42) | 75 (72–91.4) | <0.001 |
| Symptoms | 35 (29–40.5) | 78 (68–92) | <0.001 |
| Activities of Daily Living | 38 (27–42) | 82 (75–92) | <0.001 |
| Sports/recreation | 25 (25–35) | 75 (65–100) | <0.001 |
| Quality of life | 25 (25–35) | 75 (50–87) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ríos Luna, A.; Fahandezh-Saddi Díaz, H.; Villanueva Martínez, M.; Iglesias, R.; Prado, R.; Padilla, S.; Anitua, E. Office-Based Intraosseous Infiltrations of PRGF as an Effective Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Observational Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134512
Ríos Luna A, Fahandezh-Saddi Díaz H, Villanueva Martínez M, Iglesias R, Prado R, Padilla S, Anitua E. Office-Based Intraosseous Infiltrations of PRGF as an Effective Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Observational Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134512
Chicago/Turabian StyleRíos Luna, Antonio, Homid Fahandezh-Saddi Díaz, Manuel Villanueva Martínez, Roberto Iglesias, Roberto Prado, Sabino Padilla, and Eduardo Anitua. 2023. "Office-Based Intraosseous Infiltrations of PRGF as an Effective Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Observational Clinical Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134512
APA StyleRíos Luna, A., Fahandezh-Saddi Díaz, H., Villanueva Martínez, M., Iglesias, R., Prado, R., Padilla, S., & Anitua, E. (2023). Office-Based Intraosseous Infiltrations of PRGF as an Effective Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Observational Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134512







