Intracranial Efficacy of Systemic Therapy in Patients with Asymptomatic Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics
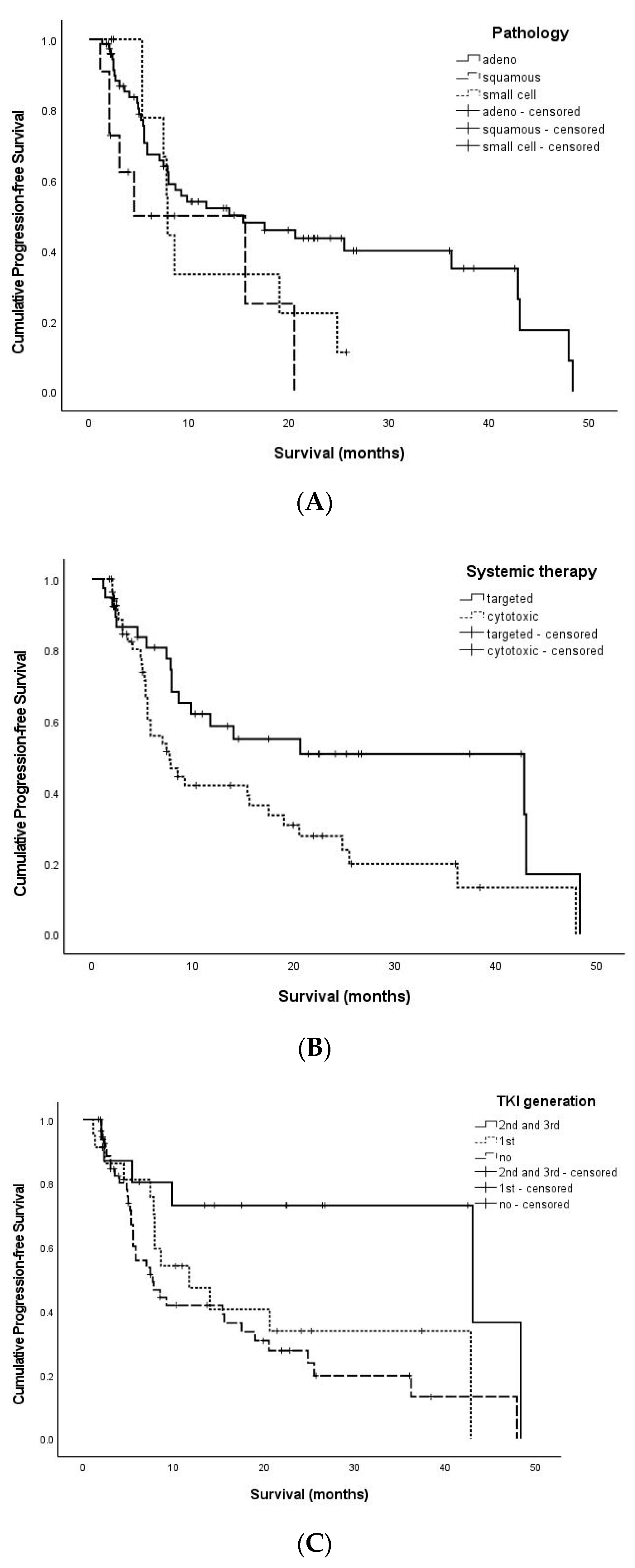
3.2. PFS-Related Factors
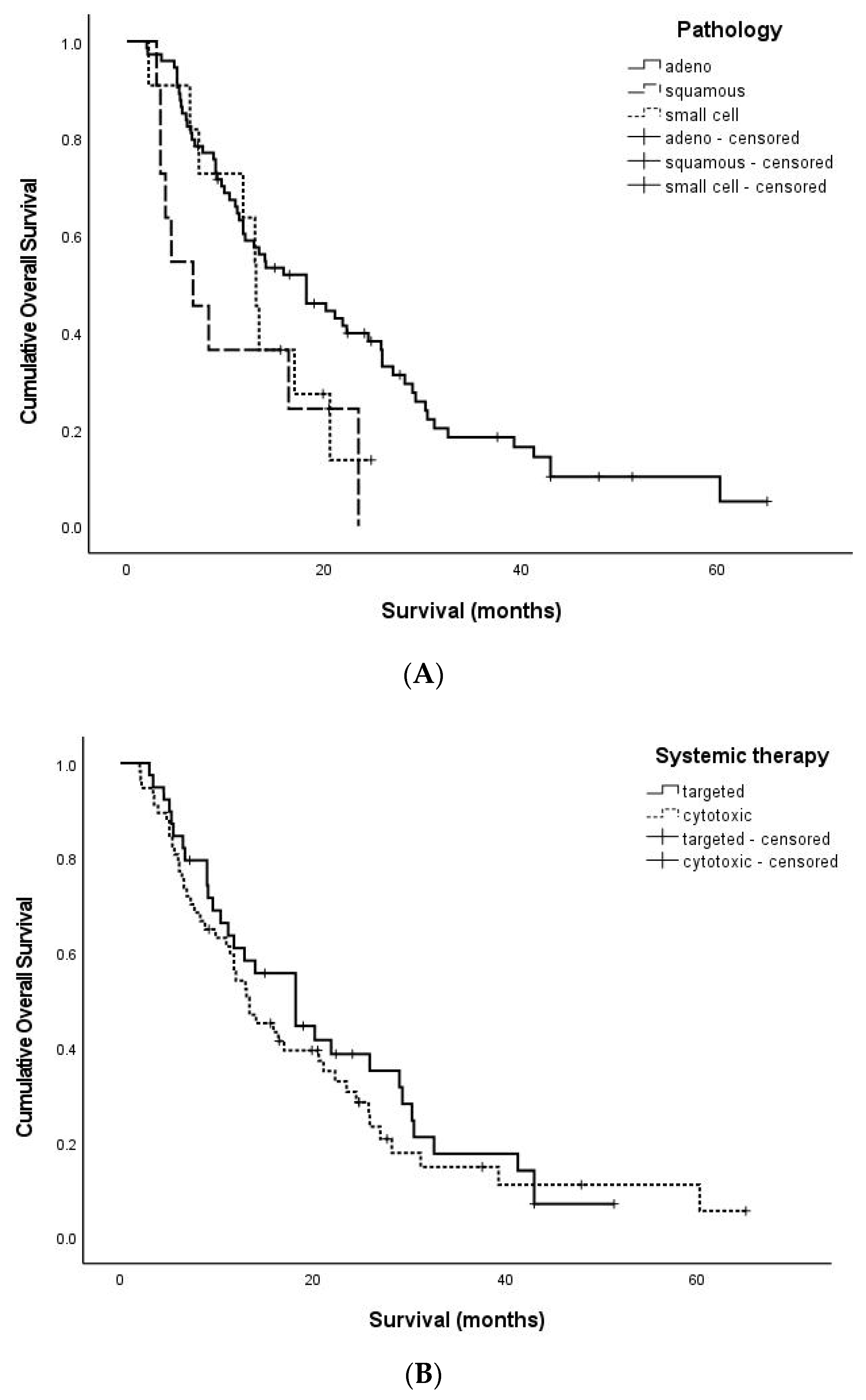
3.3. OS-Related Factors
3.4. Management of Recurrent Brain Metastases
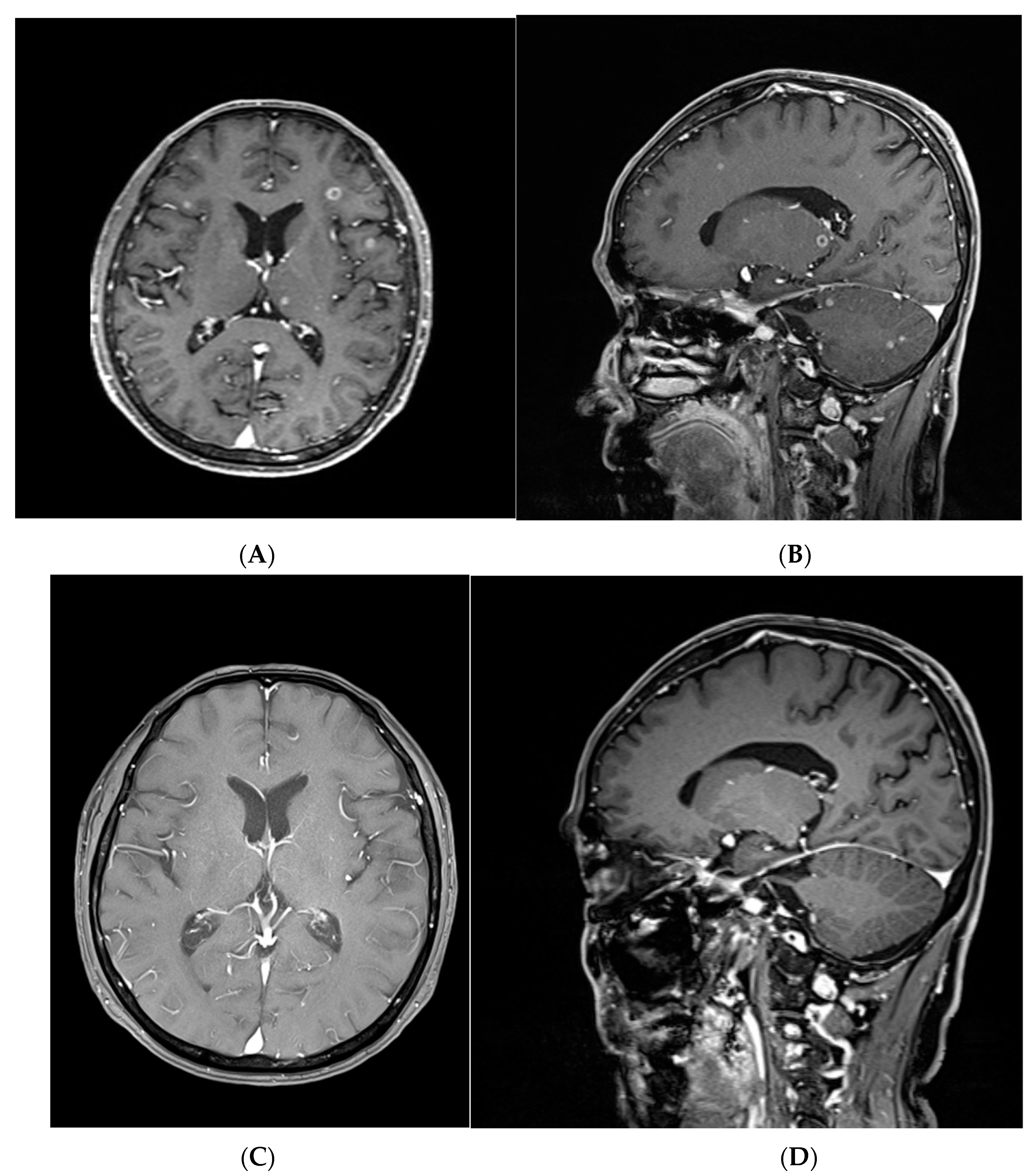
3.5. A Representative Case Treated with Targeted Therapy without Local Brain Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pellerino, A.; Bruno, F.; Ruda, R.; Soffietti, R. Systemic Therapy for Lung Cancer Brain Metastases. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2021, 22, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singer, L.; Kumthekar, P. Updates on Molecular Targeted Therapies for Intraparenchymal CNS Metastases. Cancers 2021, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Goffin, J.R.; Arnold, A.; Ellis, P.M. Survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer after a diagnosis of brain metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2013, 20, e300–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.K.; Kwon, H.J.; Kubica, P.A.; Huff, W.X.; O’Regan, R.; Dey, M. Brain metastases: An update on the multi-disciplinary approach of clinical management. Neurochirurgie 2022, 68, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J., Jr.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, S.; Milner-Watts, C.; Perna, M.; Janzic, U.; Vidal, N.; Kaudeer, N.; Ahmed, M.; McDonald, F.; Locke, I.; Minchom, A.; et al. Systemic treatment of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 132, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Brown, P.D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Burri, S.; Cahill, D.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gatson, N.T.N.; Gondi, V.; et al. Treatment for Brain Metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlesi, F.; Gervais, R.; Lena, H.; Hureaux, J.; Berard, H.; Paillotin, D.; Bota, S.; Monnet, I.; Chajara, A.; Robinet, G. Pemetrexed and cisplatin as first-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with asymptomatic inoperable brain metastases: A multicenter phase II trial (GFPC 07-01). Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2466–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailon, O.; Chouahnia, K.; Augier, A.; Bouillet, T.; Billot, S.; Coman, I.; Ursu, R.; Belin, C.; Zelek, L.; Des Guetz, G.; et al. Upfront association of carboplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with brain metastases of lung adenocarcinoma. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Arrieta, O.; Prabhash, K.; Syrigos, K.N.; Goksel, T.; Park, K.; Gorbunova, V.; Kowalyszyn, R.D.; Pikiel, J.; et al. Ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel for second-line treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer after disease progression on platinum-based therapy (REVEL): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.Y.; Na, I.I.; Kim, C.H.; Park, S.; Baek, H.; Yang, S.H. EGFR mutation and brain metastasis in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallet, V.; Cadranel, J.; Doubre, H.; Toper, C.; Monnet, I.; Chinet, T.; Oliviero, G.; Foulon, G.; De Cremoux, H.; Vieira, T.; et al. Prospective screening for ALK: Clinical features and outcome according to ALK status. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuson, W.J.; Lester-Coll, N.H.; Wu, A.J.; Yang, T.J.; Lockney, N.A.; Gerber, N.K.; Beal, K.; Amini, A.; Patil, T.; Kavanagh, B.D.; et al. Management of Brain Metastases in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Naive Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Multi-Institutional Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.J.; Myall, N.J.; Sun, F.; Patil, T.; Mushtaq, R.; Yu, C.; Sinha, S.; Pollom, E.L.; Nagpal, S.; Camidge, D.R.; et al. Brain Metastases in EGFR- and ALK-Positive NSCLC: Outcomes of Central Nervous System-Penetrant Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Alone Versus in Combination With Radiation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Wu, Y.L.; Hirsh, V.; O’Byrne, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Mok, T.; Popat, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Massey, D.; Zazulina, V.; et al. First-Line Afatinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Common Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutations and Brain Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Hirsh, V.; Boyer, M.; Yang, J.C.; Mok, T.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.D.; Adams, V.R.; Beardslee, T.; Medina, P. Afatinib for the treatment of EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC: A review of clinical findings. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colclough, N.; Chen, K.; Johnstrom, P.; Strittmatter, N.; Yan, Y.; Wrigley, G.L.; Schou, M.; Goodwin, R.; Varnas, K.; Adua, S.J.; et al. Preclinical Comparison of the Blood-brain barrier Permeability of Osimertinib with Other EGFR TKIs. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebele, R.C.; Pilling, A.B.; Aisner, D.L.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Le, A.T.; Weickhardt, A.J.; Kondo, K.L.; Linderman, D.J.; Heasley, L.E.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.S.; Felip, E.; Chow, L.Q.; Camidge, D.R.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; De Pas, T.; et al. Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Cappuzzo, F.; Felip, E.; Blackhall, F.H.; Costa, D.B.; Kim, D.W.; Nakagawa, K.; Wu, Y.L.; Mekhail, T.; Paolini, J.; et al. Intracranial Efficacy of Crizotinib Versus Chemotherapy in Patients With Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From PROFILE 1014. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novello, S.; Mazieres, J.; Oh, I.J.; de Castro, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; Helland, A.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus chemotherapy in crizotinib-pretreated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from the phase III ALUR study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venur, V.A.; Chukwueke, U.N.; Lee, E.Q. Advances in Management of Brain and Leptomeningeal Metastases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Variable | No. Patients (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ≥70 | 55 (57.2%) |
| <70 | 41 (43.8%) | |
| Pathology | Adenocarcinoma | 74 (77%) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 11 (11.5%) | |
| Small cell carcinoma | 11 (11.5%) | |
| Other organ metastases | Yes | 90 (93.7%) |
| No | 6 (6.3%) | |
| Location | Supratentorial | 66 (68.7%) |
| Infratentorial | 8 (8.3%) | |
| Both | 22 (23%) | |
| Number of tumors | 1 | 47 (48.9%) |
| 2 to 5 | 24 (25%) | |
| Over 5 | 25 (26%) | |
| Systemic therapy | Targeted therapy | 39 (40.6%) |
| Cytotoxic chemotherapy | 57 (59.3%) | |
| TKI generation | 1st generation | 23 (23.9%) |
| 2nd and 3rd generation | 16 (16.6%) | |
| No targeted therapy | 57 (59.3%) | |
| Recurrence pattern | No recurrence | 44 (45.8%) |
| Local | 8 (8.3%) | |
| Distant and Local | 41 (42.7%) | |
| Dissemination | 3 (3.1%) |
| PFS-Related Factors | |||
| Clinical Factors | Median PFS (Min-Max) | PFS p-Value | |
| Age | ≥70 | 7.7 (1.9–48.3) | 0.861 |
| <70 | 6.2 (1.1–47.9) | ||
| Pathology | Adenocarcinoma | 7.9 (1.3–48.3) | 0.069 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 3.9 (1.1–20.5) | ||
| Small cell carcinoma | 7.7 (2.2–25.7) | ||
| Location | Supratentorial | 7.4 (1.1–48.3) | 0.614 |
| Infratentorial | 8.2 (2.0–10.9) | ||
| Both | 6.8 (1.9–47.9) | ||
| Number | 1 | 7.4 (1.3–48.3) | 0.857 |
| 2 to 5 | 6.6 (1.1–47.9) | ||
| Over 5 | 7.9 (1.9–36.2) | ||
| Other organ metastases | Yes | 7.2 (1.1–48.3) | 0.399 |
| No | 16.5 (3.4–47.9) | ||
| Systemic therapy | Targeted therapy | 10.2 (1.1–48.3) | 0.020 |
| Cytotoxic chemotherapy | 5.5 (1.7–47.9) | ||
| TKI generation | 1st generation | 7.9 (1.1–42.8) | 0.016 |
| 2nd and 3rd generation | 16.0 (2.0–48.3) | ||
| No targeted therapy | 5.5 (1.7–47.9) | ||
| OS-related factors | |||
| Clinical factors | median OS (min-max) | OS p-value | |
| Age | ≥70 | 13.0 (2.0–65.0) | 0.972 |
| <70 | 16.4 (3.4–60.2) | ||
| Pathology | Adenocarcinoma | 15.4 (2.0–65.0) | 0.032 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 6.7 (3.0–23.5) | ||
| Small cell carcinoma | 13.1 (2.2–24.8) | ||
| Location | Supratentorial | 16.1 (2.2–65.0) | 0.240 |
| Infratentorial | 12.4 (5.1–25.9) | ||
| Both | 12.4 (2.0–47.9) | ||
| Number | 1 | 18.2 (3.0–65.0) | 0.124 |
| 2 to 5 | 12.1 (2.0–47.9) | ||
| Over 5 | 11.8 (2.1–39.3) | ||
| Other organ metastases | Yes | 13.4 (2.0–60.2) | 0.010 |
| No | 20.2 (4.8–65.0) | ||
| Systemic therapy | Targeted therapy | 18.2 (3.0–51.3) | 0.445 |
| Cytotoxic chemotherapy | 13.1 (2.0–65.0) | ||
| TKI generation | 1st generation | 14.0 (3.0–43.0) | 0.401 |
| 2nd and 3rd generation | 18.2 (5.3–51.3) | ||
| No targeted therapy | 13.1 (2.0–65.0) | ||
| Recurrence pattern | No recurrence | 15.7 (2.0–60.2) | 0.208 |
| Local | 15.8 (5.5–65.0) | ||
| Distant and Local | 13.4 (3.4–51.3) | ||
| Dissemination | 7.2 (3.9–10.4) | ||
| PFS-Related Factors | ||||
| Clinical Factors | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | 95% CI | |
| Other organ metastases | Absence Presence (reference) | 0.347 1 | 0.068 | 0.111–1.080 |
| Pathology | Adenocarcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Small cell carcinoma (reference) | 0.824 1.827 1 | 0.642 0.249 | 0.365–1.862 0.656–5.089 |
| TKI generation | 2nd and 3rd generation 1st generation No targeted therapy (reference) | 0.229 0.740 1 | 0.005 0.395 | 0.082–0.640 0.370–1.480 |
| OS-related factors | ||||
| Clinical factors | Hazard ratio | p-value | 95% CI | |
| Other organ metastases | Absence Presence (reference) | 0.094 1 | 0.020 | 0.013–0.689 |
| Pathology | Adenocarcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma small cell carcinoma (reference) | 0.608 1.479 1 | 0.205 0.412 | 0.281–1.313 0.580–3.772 |
| TKI generation | 2nd and 3rd generation 1st generation No targeted therapy (reference) | 0.555 0.974 1 | 0.123 0.927 | 0.263–1.173 0.558–1.702 |
| Recurrence pattern | No dissemination Dissemination | 0.279 1 | 0.098 | 0.062–1.266 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.-G.; Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Moon, K.-S.; Kim, I.-Y.; Jung, S.; Oh, H.-J.; Oh, I.-J.; Jung, T.-Y. Intracranial Efficacy of Systemic Therapy in Patients with Asymptomatic Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134307
Sun M-G, Park SJ, Kim YJ, Moon K-S, Kim I-Y, Jung S, Oh H-J, Oh I-J, Jung T-Y. Intracranial Efficacy of Systemic Therapy in Patients with Asymptomatic Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134307
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Min-Gwan, Sue Jee Park, Yeong Jin Kim, Kyung-Sub Moon, In-Young Kim, Shin Jung, Hyung-Joo Oh, In-Jae Oh, and Tae-Young Jung. 2023. "Intracranial Efficacy of Systemic Therapy in Patients with Asymptomatic Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134307
APA StyleSun, M.-G., Park, S. J., Kim, Y. J., Moon, K.-S., Kim, I.-Y., Jung, S., Oh, H.-J., Oh, I.-J., & Jung, T.-Y. (2023). Intracranial Efficacy of Systemic Therapy in Patients with Asymptomatic Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134307







