High Myopia and Thickness of Extraocular and Masticatory Muscles—7T MRI, Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
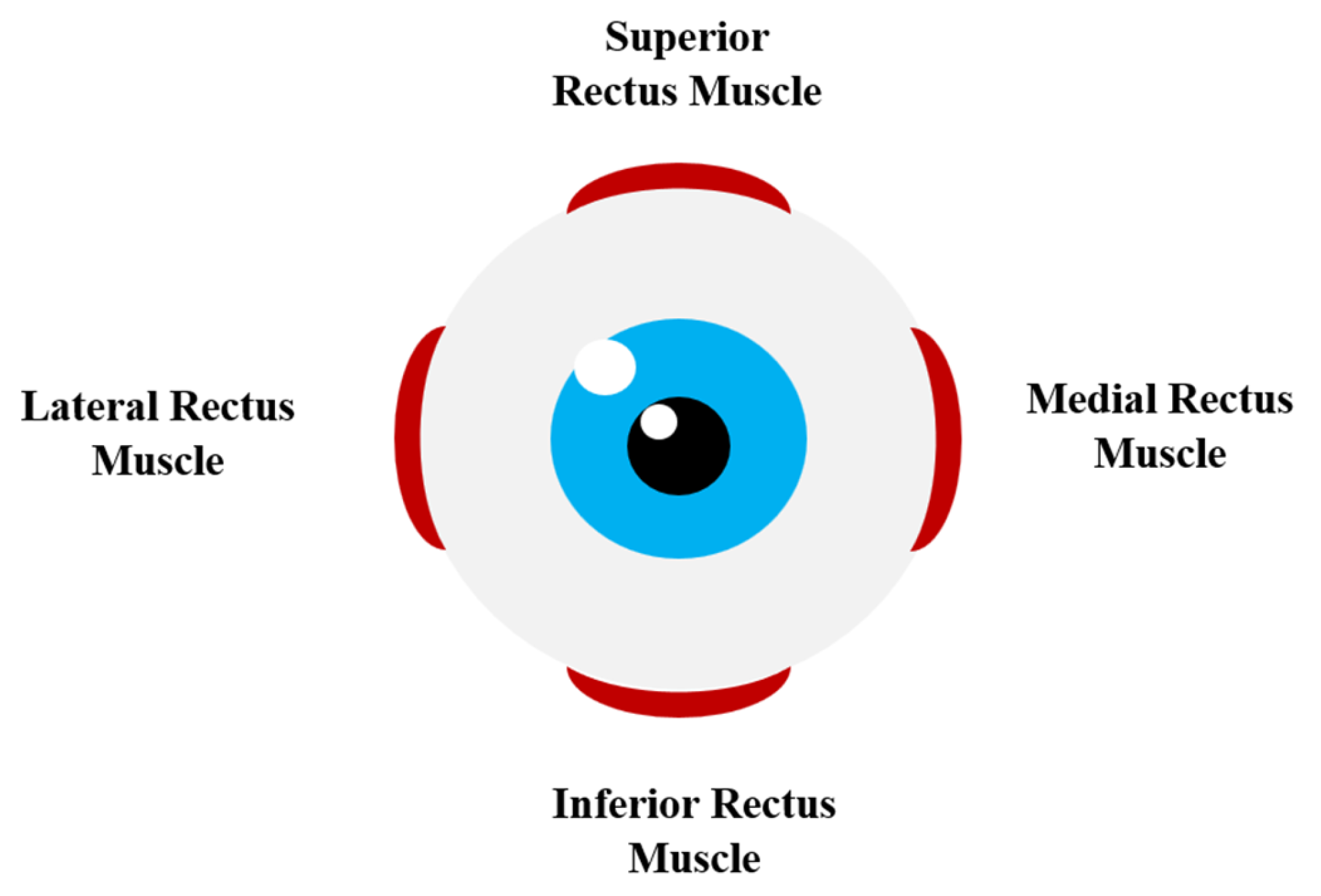
- Superior rectus (primary action: elevation; secondary action: incyclotorsion; tertiary action: adduction);
- Inferior rectus (primary action: depression; secondary action: excyclotorsion; tertiary action: adduction);
- Medial rectus (primary action: adduction);
- Lateral rectus (primary action: abduction) (Figure 1);
- Superior oblique (primary action: incyclotorsion; secondary action: depression; tertiary action: abduction);
- Inferior oblique (primary action: excyclotorsion; secondary action: elevation; tertiary action: abduction) [12].
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holden, B.A.; Fricke, T.R.; Wilson, D.A.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Wong, T.Y.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Resnikoff, S. Global Prevalence of Myopia and High Myopia and Temporal Trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subudhi, P.; Agarwal, P. Myopia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Flitcroft, D.I.; He, M.; Jonas, J.B.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Rahi, J.; Resnikoff, S.; Vitale, S.; Yannuzzi, L. IMI—Defining and Classifying Myopia: A Proposed Set of Standards for Clinical and Epidemiologic Studies. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, M20–M30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theophanous, C.; Modjtahedi, B.S.; Batech, M.; Marlin, D.S.; Luong, T.Q.; Fong, D.S. Myopia Prevalence and Risk Factors in Children. Clin. Ophthalmol. Auckl. NZ 2018, 12, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooper, J.; Tkatchenko, A.V. A Review of Current Concepts of the Etiology and Treatment of Myopia. Eye Contact Lens 2018, 44, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Insight into the Molecular Genetics of Myopia. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 1048–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Mrugacz, M.; Gajecka, M.; Mrukwa-Kominek, E.; Witkowska, K.J. Myopia: Risk Factors, Disease Mechanisms, Diagnostic Modalities, and Therapeutic Options. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2018, e7942379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, E.; Jacobsen, N. Genetic and Environmental Effects on Myopia Development and Progression. Eye 2014, 28, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose, K.A.; French, A.N.; Morgan, I.G. Environmental Factors and Myopia: Paradoxes and Prospects for Prevention. Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 5, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.S. Factors Associated with Axial Length Elongation in High Myopia in Adults. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.; Hammond, C. High Myopia and Its Risks. Community Eye Health 2019, 32, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shumway, C.L.; Motlagh, M.; Wade, M. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Eye Extraocular Muscles. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Demer, J.L.; Clark, R.A. Functional Anatomy of Human Extraocular Muscles during Fusional Divergence. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 120, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchili, N.; Ortu, E.; Pietropaoli, D.; Cattaneo, R.; Monaco, A. Dental Occlusion and Ophthalmology: A Literature Review. Open Dent. J. 2016, 10, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zieliński, G.; Filipiak, Z.; Ginszt, M.; Matysik-Woźniak, A.; Rejdak, R.; Gawda, P. The Organ of Vision and the Stomatognathic System—Review of Association Studies and Evidence-Based Discussion. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Nakano, T.; Asamoto, K.; Ikeda, H.; Ichinose, A.; Iwaki, M.; Selva, D.; Leibovitch, I. Anatomy of Tenons Capsule. Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol. 2012, 40, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, Z.B.; Jain, M.; Jozsa, F.; Zito, P.M. Anatomy, Skin, Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System (SMAS) Fascia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zieliński, G.; Wójcicki, M.; Rapa, M.; Matysik-Woźniak, A.; Baszczowski, M.; Ginszt, M.; Litko-Rola, M.; Szkutnik, J.; Różyło-Kalinowska, I.; Rejdak, R.; et al. Masticatory Muscle Thickness and Activity Correlates to Eyeball Length, Intraocular Pressure, Retinal and Choroidal Thickness in Healthy Women versus Women with Myopia. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, G.; Baszczowski, M.; Rapa, M.; Matysik-Woźniak, A.; Zawadka, M.; Szkutnik, J.; Gawda, P.; Rejdak, R.; Majcher, P.; Ginszt, M. The Axial Length of the Eyeball and Bioelectrical Activity of Masticatory and Neck Muscles: A Preliminary Report. Pain Res. Manag. 2022, 2022, 6115782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Butterworth, J.; Malecaze, F.; Calvas, P. Axial Length of Myopia: A Review of Current Research. Ophthalmologica 2010, 225, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.S.; Hess, J.R. Understanding Tests of the Association of Categorical Variables: The Pearson Chi-Square Test and Fisher’s Exact Test. Transfusion 2017, 57, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y. Statistical Notes for Clinical Researchers: Chi-Squared Test and Fisher’s Exact Test. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2017, 42, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, N.; Sadeghi, R.; Momeni-Moghaddam, H.; Zarifmahmoudi, L.; Ehsaei, A. Comparison of Cyclopentolate versus Tropicamide Cycloplegia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Optom. 2018, 11, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPM—Statistical Parametric Mapping. Available online: https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/ (accessed on 29 March 2023).
- FreeSurfer. Available online: https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu (accessed on 29 March 2023).
- Vasudeva, A.; Dhakal, R.; Vupparaboina, K.K.; Verkicharla, P.K. Do Rectus Muscle Parameters Vary between Emmetropes and Myopes? Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. J. Br. Coll. Ophthalmic Opt. Optom. 2021, 41, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exposto, F.G.; Renner, N.; Bendixen, K.H.; Svensson, P. Pain in the Temple? Headache, Muscle Pain or Both: A Retrospective Analysis. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2021, 41, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, R.; Dureja, G.P.; Tripathi, M.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Bijlani, R.L.; Mathur, R. Role of Temporalis Muscle over Activity in Chronic Tension Type Headache: Effect of Yoga Based Management. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 51, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lajmi, H.; Choura, R.; Ben Achour, B.; Doukh, M.; Amin, Z.; Hmaied, W. Headache Associated with Refractive Errors: Characteristics and Risk Factors. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harle, D.E.; Evans, B.J.W. The Correlation between Migraine Headache and Refractive Errors. Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 2006, 83, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size—Or Why the p Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and Reporting Effect Sizes to Facilitate Cumulative Science: A Practical Primer for t-Tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozgen, A.; Ariyurek, M. Normative Measurements of Orbital Structures Using CT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 170, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdlum, S.; Boonsirikamchai, P.; Setsakol, E. Normal Measurements of Extraocular Muscle Using Computed Tomography. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. Chotmaihet Thangphaet 2007, 90, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, P.; Sudhalkar, A.; Jalali, S.; Pesala, V.; Narayanan, R.; Sahu, C.; Chhablani, J. Echographic Study of Extraocular Muscle Thickness in Normal Indian Population. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 28, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierro, L.; Zaganelli, E.; Tavola, A.; Muraglia, M. Extraocular Muscle Size Comparison between Normal and Myopic Eyes Using Standardized A Scan Echography. Ophthalmol. J. Int. Ophtalmol. Int. J. Ophthalmol. Z. Augenheilkd. 1998, 212 (Suppl. 1), 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Fong, K.S.; Wong, H.B.; Looi, A.; Chan, L.L.; Rootman, J.; Seah, L.L. Normative Measurements of the Chinese Extraocular Musculature by High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, I.G.; Wu, P.-C.; Ostrin, L.A.; Tideman, J.W.L.; Yam, J.C.; Lan, W.; Baraas, R.C.; He, X.; Sankaridurg, P.; Saw, S.-M.; et al. IMI Risk Factors for Myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, T.Q.; Shu, Y.-H.; Modjtahedi, B.S.; Fong, D.S.; Choudry, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Nau, C.L. Racial and Ethnic Differences in Myopia Progression in a Large, Diverse Cohort of Pediatric Patients. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Emmetropic Subjects | High Myopic Subjects | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Test | p | ||
| n Eyeballs | 30 | 24 | |||||
| Age | 33.71 | 6.49 | 39.92 | 11.84 | Z | −2.08 | 0.04 |
| Visual Acuity Right | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | Z | −2.30 | 0.02 * | |
| Visual Acuity Left | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.3 | Z | −3.31 | 0.00 * | |
| Refractive Error Right | −9.75 | 5.25 | |||||
| Refractive Error Left | −11.50 | 6.25 | |||||
| Axial Length Eyeball | 23.58 | 0.36 | 27.14 | 2.31 | Z | −6.12 | 0.00 * |
| Emmetropic Subjects | High Myopic Subjects | Test | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mm) | SD | Mean (mm) | SD | ||||
| Medial Rectus Muscle | 3.50 | 0.50 | 5.09 | 0.57 | Z | −6.07 | 0.00 * ES = 0.98 |
| Lateral Rectus Muscle | 3.49 | 0.49 | 4.18 | 0.94 | Z | −2.88 | 0.00 * ES = 0.98 |
| Superior Rectus Muscle | 3.19 | 0.46 | 3.89 | 0.64 | Z | −3.98 | 0.00 * ES = 0.67 |
| Inferior Rectus Muscle | 3.20 | 0.51 | 3.72 | 0.75 | Z | −2.51 | 0.01 * ES = 0.45 |
| Temporalis Muscle | 8.99 | 1.77 | 15.20 | 2.78 | Z | −5.66 | 0.00 * ES = 0.92 |
| Masseter Muscle | 9.34 | 1.91 | 16.91 | 3.13 | Z | −5.86 | 0.00 * ES = 0.95 |
| Emmetropic Subjects | Axial Length Eyeball | Medial Rectus Muscle | Lateral Rectus Muscle | Superior Rectus Muscle | Inferior Rectus Muscle | Temporalis Muscle | Masseter Muscle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axial Length Eyeball | r | - | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.00 | −0.13 | −0.05 | 0.00 |
| p | 0.12 | 0.45 | 0.98 | 0.51 | 0.80 | 0.99 | ||
| Medial Rectus Muscle | r | - | 0.68 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.46 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.01 * | |||
| Lateral Rectus Muscle | r | - | 0.19 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.24 | ||
| p | 0.33 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.21 | ||||
| Superior Rectus Muscle | r | - | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.29 | |||
| p | 0.00 * | 0.02 * | 0.14 | |||||
| Inferior Rectus Muscle | r | - | 0.60 | 0.32 | ||||
| p | 0.00 * | 0.10 | ||||||
| Temporalis Muscle | r | - | 0.26 | |||||
| p | 0.17 | |||||||
| Masseter Muscle | r | - | ||||||
| p |
| High Myopic Subjects | Axial Length Eyeball | Medial Rectus Muscle | Lateral Rectus Muscle | Superior Rectus Muscle | Inferior Rectus Muscle | Temporalis Muscle | Masseter Muscle | Refractive Error | Visual Acuity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axial Length Eyeball | r | - | −0.09 | −0.43 | −0.25 | 0.14 | −0.26 | −0.14 | −0.80 | 0.12 |
| p | 0.68 | 0.04 * | 0.23 | 0.52 | 0.21 | 0.50 | 0.00 * | 0.67 | ||
| Medial Rectus Muscle | r | - | 0.58 | −0.14 | 0.10 | −0.12 | −0.16 | −0.16 | −0.17 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.59 | 0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | |||
| Lateral Rectus Muscle | r | - | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.06 | ||
| p | 0.68 | 0.79 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.90 | 0.84 | ||||
| Superior Rectus Muscle | r | - | −0.05 | 0.05 | −0.20 | 0.28 | −0.30 | |||
| p | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.30 | |||||
| Inferior Rectus Muscle | r | - | 0.16 | −0.04 | −0.09 | −0.67 | ||||
| p | 0.46 | 0.86 | 0.76 | 0.01 * | ||||||
| Temporalis Muscle | r | - | 0.46 | 0.10 | 0.18 | |||||
| p | 0.02 * | 0.71 | 0.54 | |||||||
| Masseter Muscle | r | - | −0.26 | 0.49 | ||||||
| p | 0.34 | 0.07 | ||||||||
| Refractive Error | r | - | 0.26 | |||||||
| p | 0.40 | |||||||||
| Visual Acuity | r | - | ||||||||
| p | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zieliński, G.; Matysik-Woźniak, A.; Pankowska, A.; Pietura, R.; Rejdak, R.; Jonak, K. High Myopia and Thickness of Extraocular and Masticatory Muscles—7T MRI, Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124166
Zieliński G, Matysik-Woźniak A, Pankowska A, Pietura R, Rejdak R, Jonak K. High Myopia and Thickness of Extraocular and Masticatory Muscles—7T MRI, Preliminary Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124166
Chicago/Turabian StyleZieliński, Grzegorz, Anna Matysik-Woźniak, Anna Pankowska, Radosław Pietura, Robert Rejdak, and Kamil Jonak. 2023. "High Myopia and Thickness of Extraocular and Masticatory Muscles—7T MRI, Preliminary Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124166
APA StyleZieliński, G., Matysik-Woźniak, A., Pankowska, A., Pietura, R., Rejdak, R., & Jonak, K. (2023). High Myopia and Thickness of Extraocular and Masticatory Muscles—7T MRI, Preliminary Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124166







