The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in Patients Who Have Undergone Abdominal Operation, in Terms of Bowel Function Post-Operatively: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reporting Guideline and Registration
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Primary and Secondary Outcome Measures
2.4. Search Methods
2.5. Study Selection
2.6. Data Extraction
2.7. Risk of Bias
2.8. Geometry of the Networks
2.9. Assessment of Transitivity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. Assessment of Inconsistency
2.12. Assessment of Small-Study Effects
3. Results
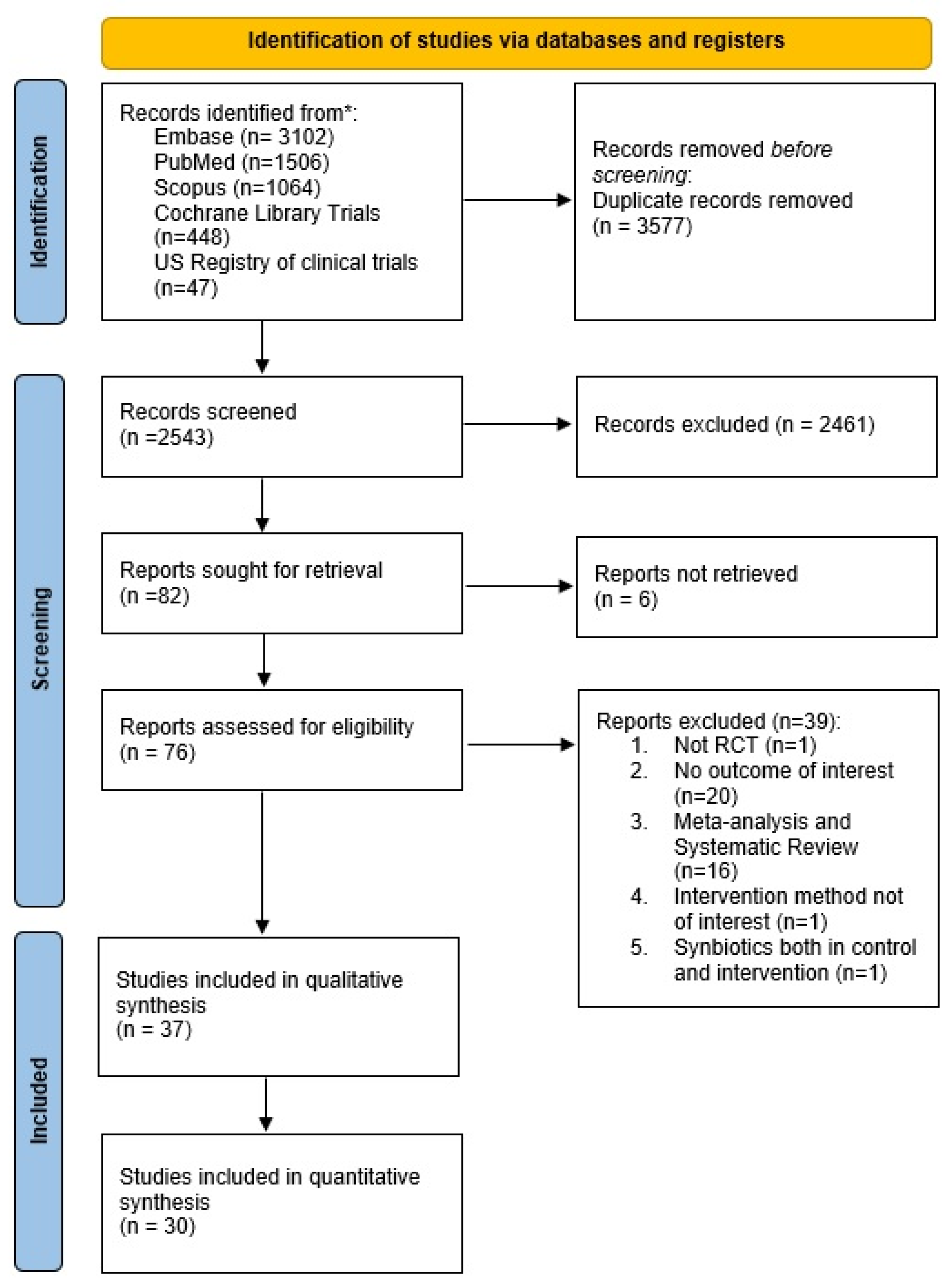
3.1. Search Results
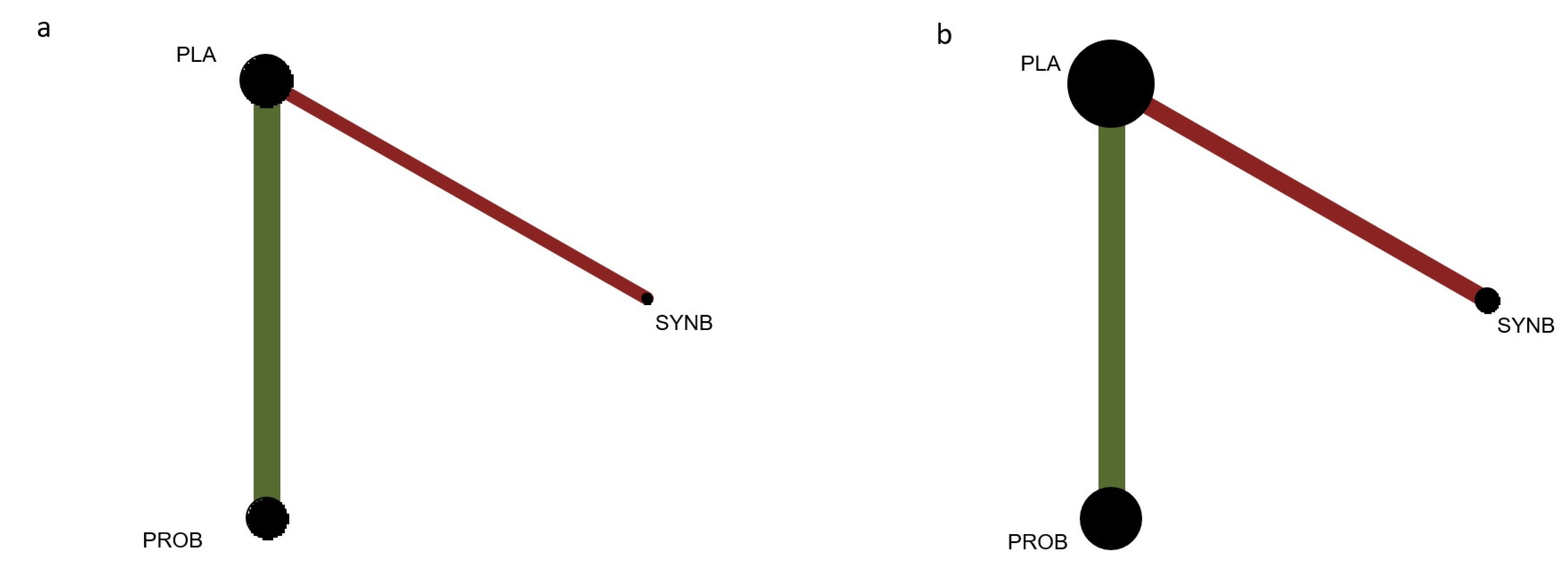
3.2. Geometry of the Networks
3.3. Risk of Bias
3.4. Assessment of Transitivity and Inconsistency
3.5. Primary Outcomes
3.6. Secondary Outcomes
3.7. Small-Study Effects
3.8. Quality of the Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arumugam, S.; Lau, C.S.M.; Chamberlain, R.S. Probiotics and Synbiotics Decrease Postoperative Sepsis in Elective Gastrointestinal Surgical Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 20, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzotta, E.; Villalobos-Hernandez, E.C.; Fiorda-Diaz, J.; Harzman, A.; Christofi, F.L. Postoperative Ileus and Postoperative Gastrointestinal Tract Dysfunction: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Novel Treatment Strategies Beyond Colorectal Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Protocols. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 583422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, S.M.; Moreira, J.P.; Mendes, L.C.; Amaral, T.M.; Andrade, A.R.; Santos, A.R.; Abelha, F.J. Evaluation of the Quality of Recovery and the Postoperative Health Status after Elective Surgery. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 68, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.; Kjellgren, K.; Unosson, M.; Årestedt, K. Postoperative Recovery and Its Association with Health-Related Quality of Life among Day Surgery Patients. BMC Nurs. 2012, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayes, N.; Seehofer, D.; Neuhaus, P. Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics in Surgery—Are They Only Trendy, Truly Effective or Even Dangerous? Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2009, 394, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate Use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoji, I.D.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Okpeku, M.; Adeleke, M.A. Multi-Strain Probiotics: Synergy among Isolates Enhances Biological Activities. Biology 2021, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajela, N.; Ramakrishna, B.S.; Nair, G.B.; Abraham, P.; Gopalan, S.; Ganguly, N.K. Gut Microbiome, Gut Function, and Probiotics: Implications for Health. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 34, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert Consensus Document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) Consensus Statement on the Definition and Scope of Prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and Prebiotics in Intestinal Health and Disease: From Biology to the Clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.C.; Hart, A.L.; Kamm, M.A.; Stagg, A.J.; Knight, S.C. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics: Recent Advances. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.H.; Adiamah, A.; Kushairi, A.; Varadhan, K.K.; Krznaric, Z.; Kulkarni, A.D.; Neal, K.R.; Lobo, D.N. Perioperative Probiotics or Synbiotics in Adults Undergoing Elective Abdominal Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Huang, W.; Tao, J.; Wei, Z. Prophylactic Effects of Probiotics or Synbiotics on Postoperative Ileus after Gastrointestinal Cancer Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-Analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers RG, S.J. Chapter 8: Assessing Risk of Bias in a Randomized Trial. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3; Cochrane: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzer, G.; Carpenter, J.R.; Rücker, G. Meta-Analysis with R (Use R!); Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-21415-3. [Google Scholar]
- Salanti, G. Indirect and Mixed-Treatment Comparison, Network, or Multiple-Treatments Meta-Analysis: Many Names, Many Benefits, Many Concerns for the next Generation Evidence Synthesis Tool. Res. Synth. Methods 2012, 3, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, D.M.; Ades, A.E.; Higgins, J.P.T. Simultaneous Comparison of Multiple Treatments: Combining Direct and Indirect Evidence. BMJ 2005, 331, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.M.; Davey, J.; Clarke, M.J.; Thompson, S.G.; Higgins, J.P. Predicting the Extent of Heterogeneity in Meta-Analysis, Using Empirical Data from the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Spiegelhalter, D.J. A Re-Evaluation of Random-Effects Meta-Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2009, 172, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayes, N.; Hansen, S.; Seehofer, D.; Muller, A.R.; Serke, S.; Bengmark, S.; Neuhaus, P. Early Enteral Supply of Fiber and Lactobacilli versus Conventional Nutrition: A Controlled Trial in Patients with Major Abdominal Surgery. Nutrition 2002, 18, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayes, N.; Seehofer, D.; Hansen, S.; Boucsein, K.; Muller, A.R.; Serke, S.; Bengmark, S.; Neuhaus, P. Early Enteral Supply of Lactobacillus and Fiber versus Selective Bowel Decontamination: A Controlled Trial in Liver Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2002, 74, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, H.; Nagino, M.; Kamiya, S.; Komatsu, S.; Mayumi, T.; Takagi, K.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Tanaka, R.; Nimura, Y. Synbiotics Reduce Postoperative Infectious Complications: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Biliary Cancer Patients Undergoing Hepatectomy. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2005, 390, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayes, N.; Seehofer, D.; Theruvath, T.; Schiller, R.A.; Langrehr, J.M.; Jonas, S.; Bengmark, S.; Neuhaus, P. Supply of Pre- and Probiotics Reduces Bacterial Infection Rates after Liver Transplantation--a Randomized, Double-Blind Trial. Am. J. Transpl. 2005, 5, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayes, N.; Seehofer, D.; Theruvath, T.; Mogl, M.; Langrehr, J.M.; Nussler, N.C.; Bengmark, S.; Neuhaus, P. Effect of Enteral Nutrition and Synbiotics on Bacterial Infection Rates after Pylorus-Preserving Pancreatoduodenectomy: A Randomized, Double-Blind Trial. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvat, M.; Krebs, B.; Potrc, S.; Ivanecz, A.; Kompan, L. Preoperative Synbiotic Bowel Conditioning for Elective Colorectal Surgery. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2010, 122 (Suppl. 2), 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepenhorst, G.M.; van Ruler, O.; Besselink, M.G.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Wijnandts, P.R.; Renooij, W.; Gouma, D.J.; Gooszen, H.G.; Boermeester, M.A. Influence of Prophylactic Probiotics and Selective Decontamination on Bacterial Translocation in Patients Undergoing Pancreatic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Shock 2011, 35, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qin, H.; Yang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Randomised Clinical Trial: The Effects of Perioperative Probiotic Treatment on Barrier Function and Post-Operative Infectious Complications in Colorectal Cancer Surgery—A Double-Blind Study. Aliment. Pharm. 2011, 33, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, M.; Miyoshi, M.; Kanbara, Y.; Aoyama, M.; Sakaki, H.; Shuno, K.; Hirata, K.; Takahashi, M.; Ueno, K.; Tabata, S.; et al. Effects of Perioperative Synbiotic Treatment on Infectious Complications, Intestinal Integrity, and Fecal Flora and Organic Acids in Hepatic Surgery With or Without Cirrhosis. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2011, 35, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangell, P.; Thorlacius, H.; Syk, I.; Ahrne, S.; Molin, G.; Olsson, C.; Jeppsson, B. Lactobacillus Plantarum 299v Does Not Reduce Enteric Bacteria or Bacterial Translocation in Patients Undergoing Colon Resection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Yano, M.; Motoori, M.; Kishi, K.; Miyashiro, I.; Ohue, M.; Ohigashi, H.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Ishikawa, O. Impact of Perioperative Administration of Synbiotics in Patients with Esophageal Cancer Undergoing Esophagectomy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Surgery 2012, 152, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Du, P.; Gao, J.; Yang, B.R.; Fang, W.J.; Ying, C.M. Preoperative Probiotics Decrease Postoperative Infectious Complications of Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 343, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russolillo, N.; Ferrero, A.; Vigano, L.; Langella, S.; Briozzo, A.; Ferlini, M.; Migliardi, M.; Capussotti, L. Impact of Perioperative Symbiotic Therapy on Infectious Morbidity after Hpb Surgery in Jaundiced Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Updat. Surg. 2014, 66, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Nishigaki, E.; Abe, T.; Fukaya, M.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Nagino, M. Randomized Clinical Trial of the Effect of Perioperative Synbiotics versus No Synbiotics on Bacterial Translocation after Oesophagectomy. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzampassi, K.; Stavrou, G.; Damoraki, G.; Georgitsi, M.; Basdanis, G.; Tsaousi, G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. A Four-Probiotics Regimen Reduces Postoperative Complications After Colorectal Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 2776–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, M.; Tong, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Peng, H.; Lan, P.; Zhang, P.; Huang, N.; et al. Positive Regulatory Effects of Perioperative Probiotic Treatment on Postoperative Liver Complications after Colorectal Liver Metastases Surgery: A Double-Center and Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammohan, A.; Sathyanesan, J.; Rajendran, K.; Pitchaimuthu, A.; Perumal, S.K.; Balaraman, K.; Ramasamy, R.; Palaniappan, R.; Govindan, M. Synbiotics in Surgery for Chronic Pancreatitis: Are They Truly Effective? A Single-Blind Prospective Randomized Control Trial. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommacal, H.M.; Bersch, V.P.; Vitola, S.P.; Osvaldt, A.B. Perioperative Synbiotics Decrease Postoperative Complications in Periampullary Neoplasms: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, M.L.; da Silva, R.S.; Nicoli, J.R.; Bruna-Romero, O.; da Silva, R.G.; de Vasconcelos Generoso, S.; Correia, M.I. Randomized Clinical Trial: Impact of Oral Administration of Saccharomyces Boulardii on Gene Expression of Intestinal Cytokines in Patients Undergoing Colon Resection. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Sakamoto, E.; Norimizu, S.; Shingu, Y.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Nagino, M. Efficacy of Perioperative Synbiotics Treatment for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection after Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Surg. Today 2016, 46, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, M.; Endo, I.; Yamamoto, S.; Inokawa, H.; Kubo, M.; Udaka, T.; Sogabe, O.; Maeda, H.; Shirakawa, K.; Okazaki, E.; et al. Perioperative Supplementation with Bifidobacteria Improves Postoperative Nutritional Recovery, Inflammatory Response, and Fecal Microbiota in Patients Undergoing Colorectal Surgery: A Prospective, Randomized Clinical Trial. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2016, 35, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.K.; Said, S.; Rajandram, R.; Wang, Z.; Roslani, A.C.; Chin, K.F. Pre-Surgical Administration of Microbial Cell Preparation in Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chen, H.; Hong, L.; Feng, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Shi, C.; Wu, W.; Gao, R.; et al. The Effect of Perioperative Probiotics Treatment for Colorectal Cancer: Short-Term Outcomes of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8432–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Miyake, T.; Kokuryo, T.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Nagino, M. Effect of Perioperative Synbiotic Treatment on Bacterial Translocation and Postoperative Infectious Complications after Pancreatoduodenectomy. Dig. Surg. 2016, 33, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flesch, A.T.; Tonial, S.T.; Contu, P.C.; Damin, D.C. Perioperative Synbiotics Administration Decreases Postoperative Infections in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2017, 44, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Xia, L.; Rao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X. Effects of Fiber and Probiotics on Diarrhea Associated with Enteral Nutrition in Gastric Cancer Patients: A Prospective Randomized and Controlled Trial. Medicine 2017, 96, e8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Guan, Z. Effects of Probiotics Combined with Enteral Nutrition on Immune Function and Inflammatory Response in Postoperative Patients with Gastric Cancer. J. BUON 2018, 23, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajramagic, S.; Hodzic, E.; Mulabdic, A.; Holjan, S.; Smajlovic, S.V.; Rovcanin, A. Usage of Probiotics and Its Clinical Significance at Surgically Treated Patients Sufferig from Colorectal Carcinoma. Med. Arch. 2019, 73, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polakowski, C.B.; Kato, M.; Preti, V.B.; Schieferdecker, M.E.M.; Ligocki Campos, A.C. Impact of the Preoperative Use of Synbiotics in Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrition 2019, 58, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xu, P.; Cen, Y.; Li, W. Effects of Preoperative Oral Administration of Glucose Solution Combined with Postoperative Probiotics on Inflammation and Intestinal Barrier Function in Patients after Colorectal Cancer Surgery. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kye, B.H.; Oh, H.K.; Cho, Y.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, J.Y.; Sung, N.Y.; Kang, S.B.; Seo, J.M.; et al. Effects of PrObiotics on the Symptoms and Surgical OuTComes after Anterior REsection of Colon Cancer (POSTCARE): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folwarski, M.; Dobosz, M.; Malgorzewicz, S.; Skonieczna-Zydecka, K.; Kazmierczak-Siedlecka, K. Effects of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG on Early Postoperative Outcome after Pylorus-Preserving Pancreatoduodenectomy: A Randomized Trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 25, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yin, X.; Chen, G.; Li, L.; Le, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ouyang, W.; Tong, J. Perioperative Probiotic Treatment Decreased the Incidence of Postoperative Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients Following Non-Cardiac Surgery: A Randomised Double-Blind and Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.J.; Oh, H.K.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.R.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, S.B. Effects of Probiotics on Bowel Function Restoration Following Ileostomy Closure in Rectal Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Color. Dis. 2021, 23, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yang, S.-W.; Yang, H.-Q.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.-J. Effect of Bifid Triple Viable Combined with Enteral Nutrition Support on Gastrointestinal Function and Nutritional Indexes in Patients with Gastric Cancer after Operation. World Chin. J. Dig. 2020, 28, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, B. Prebiotic and Synbiotic Treatment before Colorectal Surgery--Randomised Double Blind Trial. Coll. Antropol. 2016, 40, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xia, Y.; Shi, C.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qin, H. Effects of Perioperative Probiotics Administration on Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Chin. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 22, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Probiotics Regulate Gut Microbiota: An Effective Method to Improve Immunity. Molecules 2021, 26, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, K.L.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Tacey, M.A. Nausea, Vomiting and Return of Bowel Function after Colorectal Surgery. ANZ J. Surg. 2015, 85, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; O’Grady, G.; Milne, T.; Jaung, R.; Vather, R.; Bissett, I.P. Prospective Comparison of Return of Bowel Function after Left versus Right Colectomy. ANZ J. Surg. 2018, 88, E242–E247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Gadir, A.A.; Dhir, R. Probiotics: Reiterating What They Are and What They Are Not. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics Mechanism of Action on Immune Cells and Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Cells 2023, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, H.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Ren, L.-F.; Li, Z.-J.; Zhang, L. How Do Intestinal Probiotics Restore the Intestinal Barrier? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, X.; Liu, W. Current Status of Probiotics as Supplements in the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 789063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, P.O.; Bindels, L.B.; Saulnier, D.M.; Reid, G.; Nova, E.; Holmgren, K.; O’Toole, P.W.; Bunn, J.; Delzenne, N.; Scott, K.P. Can Prebiotics and Probiotics Improve Therapeutic Outcomes for Undernourished Individuals? Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, D.; Nigam, P.S. The Gut Microbiota Influenced by the Intake of Probiotics and Functional Foods with Prebiotics Can Sustain Wellness and Alleviate Certain Ailments like Gut-Inflammation and Colon-Cancer. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Quintero, D.F.; Kok, C.R.; Hutkins, R. The Future of Synbiotics: Rational Formulation and Design. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 919725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.J.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. Mechanisms of Postoperative Ileus. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2004, 16, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, W.; Hernández, A.V.; Garcia-Sabrido, J.L. Is Gum Chewing Useful for Ileus After Elective Colorectal Surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2009, 13, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Lara, L.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Misera, A.; Maciejewska, D.; Marlicz, W. A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression Evaluating the Efficacy and Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics and Synbiotics in the Prevention of Surgical Site Infections and Surgery-Related Complications. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Śliżewska, K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids by Human Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary Fiber and Prebiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelton, R. Postbiotic Metabolites: How Probiotics Regulate Health. Integr. Med. 2020, 19, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, N.; Dangi, P.; Chaudhary, V.; Sablania, V.; Dewan, A.; Joshi, S.; Siddqui, S.; Yadav, A.N. Probiotics and Bioactive Metabolite Production. In Probiotics for Human Nutrition in Health and Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 171–198. [Google Scholar]
| Time to first flatus | |||
| Probiotics | −0.47 [−0.78 to −0.17] | ||
| 0.05 [−0.48 to 0.59] | Synbiotics | −0.53 [−0.96 to −0.09] | |
| −0.47 [−0.78 to −0.17] | −0.53 [−0.96 to −0.09] | Placebo | |
| Time to first defecation | |||
| Probiotics | −0.70 [−1.23 to −0.18] | ||
| −0.55 [−1.69 to 0.60] | Synbiotics | −0.15 [−1.17 to 0.87] | |
| −0.70 [−1.23 to −0.18] | −0.15 [−1.17 to 0.87] | Placebo | |
| Post-operative hospitalization days | |||
| Probiotics | −0.76 [−2.57 to 1.04] | ||
| 2.31 [−0.19 to 4.80] | Synbiotics | −3.07 [−4.80 to −1.34] | |
| −0.84 [−5.27 to 3.59] | 1.47 [−2.20 to 5.13] | Prebiotics | −1.60 [−5.66 to 2.45] |
| −0.76 [−2.57 to 1.04] | −3.07 [−4.80 to −1.34] | −1.60 [−5.66 to 2.45] | Placebo |
| Post-operative ileus | |||
| Probiotics | 0.38 [0.14–0.98] | ||
| 0.47 [0.12–1.79] | Synbiotics | 0.81 [0.31–2.08] | |
| 0.38 [0.14–0.98] | 0.81 [0.31–2.08] | Placebo | |
| Post-operative abdominal distension | |||
| Probiotics | 0.63 [0.48–0.82] | ||
| 1.88 [0.39–8.98] | Synbiotics | 1.55 [0.26–8.50] | 0.33 [0.07–1.55] |
| 0.80 [0.08–8.22] | 1.55 [0.26–8.50] | Prebiotics | 0.50 [0.05–5.08] |
| 0.63 [0.48–0.82] | 0.33 [0.07–1.55] | 0.50 [0.05–5.08] | Placebo |
| Rank | SUCRA Time to First Flatus | SUCRA Time to First Defecation | SUCRA Post-Operative Hospitalization Days | SUCRA Post-Operative Ileus | SUCRA Post-Operative Abdominal Distension |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Synbiotics (78.3) | Probiotics (91.1) | Synbiotics (91.6) | Probiotics (92.1) | Synbiotics (79.4) |
| 2 | Probiotics (71.2) | Synbiotics (39.5) | Prebiotics (54.7) | Synbiotics (40.2) | Probiotics (54.6) |
| 3 | Placebo (0.5) | Placebo (19.4) | Probiotics (39.6) | Ins (17.6) | Prebiotics (54.0) |
| 4 | Placebo (14.0) | Placebo (12.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioannidis, O.; Chatzakis, C.; Tirta, M.; Anestiadou, E.; Zapsalis, K.; Symeonidis, S.; Bitsianis, S.; Kotidis, E.; Pramateftakis, M.G.; Mantzoros, I.; et al. The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in Patients Who Have Undergone Abdominal Operation, in Terms of Bowel Function Post-Operatively: A Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124150
Ioannidis O, Chatzakis C, Tirta M, Anestiadou E, Zapsalis K, Symeonidis S, Bitsianis S, Kotidis E, Pramateftakis MG, Mantzoros I, et al. The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in Patients Who Have Undergone Abdominal Operation, in Terms of Bowel Function Post-Operatively: A Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124150
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoannidis, Orestis, Christos Chatzakis, Maria Tirta, Elissavet Anestiadou, Konstantinos Zapsalis, Savvas Symeonidis, Stefanos Bitsianis, Efstathios Kotidis, Manousos George Pramateftakis, Ioannis Mantzoros, and et al. 2023. "The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in Patients Who Have Undergone Abdominal Operation, in Terms of Bowel Function Post-Operatively: A Network Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124150
APA StyleIoannidis, O., Chatzakis, C., Tirta, M., Anestiadou, E., Zapsalis, K., Symeonidis, S., Bitsianis, S., Kotidis, E., Pramateftakis, M. G., Mantzoros, I., & Angelopoulos, S. (2023). The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in Patients Who Have Undergone Abdominal Operation, in Terms of Bowel Function Post-Operatively: A Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124150






