Cardiorenal Syndrome: Challenges in Everyday Clinical Practice and Key Points towards a Better Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Current Definition and Classification of the Syndrome
1.2. Preventing CRS: Is It Possible to Identify the Patients at Risk?
1.3. New Insights into CRS Pathophysiology and the Emerging Role of Serum Chloride
1.4. Acute Tubular Injury vs. Permissive WRF: The Overestimated Role of Creatinine
1.5. Diagnosis of Acute CRS: The Need for a Panel of Multiple Biomarkers
1.5.1. Cardiac Biomarkers
1.5.2. Renal Biomarkers
1.5.3. Other Biomarkers
1.5.4. Novel Diagnostic Methods
1.6. Treatment and Management of CRS: Questions to Be Answered?
1.7. Cardiorenal Anemia Syndrome (CRAS): A New Area of Research and a Potent Therapeutic Target in CRS
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, T. A Clinical Lecture ON PAROXYSMAL DYSPNOEA IN CARDIORENAL PATIENTS: WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO “CARDIAC” AND “URAEMIC” ASTHMA: Delivered at University College Hospital, London, November 12th, 1913. BMJ 1913, 2, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Haapio, M.; House, A.A.; Anavekar, N.; Bellomo, R. Cardiorenal syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; McCullough, P.; Anker, S.D.; Anand, I.; Aspromonte, N.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Berl, T.; Bobek, I.; Cruz, D.N.; et al. Cardio-renal syndromes: Report from the consensus conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatamizadeh, P.; Fonarow, G.C.; Budoff, M.J.; Darabian, S.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Cardiorenal syndrome: Pathophysiology and potential targets for clinical management. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangaswami, J.; Mathew, R.O. Pathophysiological Mechanisms in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Müller, C.; Damman, K.; Murray, P.T.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C.; McCullough, P.A. Pathogenesis of cardiorenal syndrome type 1 in acute decompensated heart failure: Workgroup statements from the eleventh consensus conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 182, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uduman, J. Epidemiology of Cardiorenal Syndrome. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.P.; Carvalho, A.; Peres, L.A.B. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients from a single centre in Brazil: A retrospective cohort analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.; Nga, H.S.; Menezes, P.; Bridi, R.; Balbi, A.; Ponce, D. Acute kidney injury in septic patients admitted to emergency clinical room: Risk factors and outcome. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, M.R.; Komajda, M.; Murray-Thomas, T.; Underwood, J.; Ticho, B. Prevalence and impact of worsening renal function in patients hospitalized with decompensated heart failure: Results of the prospective outcomes study in heart failure (POSH). Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, D.E.; Butler, J.; Wang, Y.; Abraham, W.T.; O’Connor, C.M.; Gottlieb, S.S.; Loh, E.; Massie, B.M.; Rich, M.W.; Stevenson, L.W.; et al. Incidence, predictors at admission, and impact of worsening renal function among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Forman, D.E.; Abraham, W.T.; Gottlieb, S.S.; Loh, E.; Massie, B.M.; O’Connor, C.M.; Rich, M.W.; Stevenson, L.W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Relationship between heart failure treatment and development of worsening renal function among hospitalized patients. Am. Heart J. 2004, 147, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohria, A.; Hasselblad, V.; Stebbins, A.; Pauly, D.F.; Fonarow, G.C.; Shah, M.; Yancy, C.W.; Califf, R.M.; Stevenson, L.W.; Hill, J.A. Cardiorenal Interactions: Insights From the ESCAPE Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, M.E.; Astor, B.C.; Bash, L.D.; Matsushita, K.; Wang, Y.; Coresh, J. Albuminuria and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Independently Associate with Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blecker, S.; Matsushita, K.; Köttgen, A.; Loehr, L.R.; Bertoni, A.G.; Boulware, L.E.; Coresh, J. High-Normal Albuminuria and Risk of Heart Failure in the Community. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, J.R.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Hayden, M.R. The Role of Overweight and Obesity in the Cardiorenal Syndrome. Cardiorenal Med. 2011, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzuoli, A.; Testani, J.M.; Ruocco, G.; Pellegrini, M.; Ronco, C.; Nuti, R. Different diuretic dose and response in acute decompensated heart failure: Clinical characteristics and prognostic significance. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 224, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, S.E.; Bradley, G.P. The effect of increased intra-abdominal pressure on renal function in man. J. Clin. Investig. 1947, 26, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalfino, L.; Tullo, L.; Donadio, I.; Malcangi, V.; Brienza, N. Intra-abdominal hypertensionand acute renal failurein critically ill patients. Intensiv. Care Med. 2008, 34, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; van Deursen, V.M.; Navis, G.; Voors, A.A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Increased Central Venous Pressure Is Associated With Impaired Renal Function and Mortality in a Broad Spectrum of Patients With Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winton, F.R. The influence of venous pressure on the isolated mammalian kidney. J. Physiol. 1931, 72, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Vikneswaran, G.; Rola, P.; Raju, S.; Bhat, R.S.; Jayakumar, A.; Alva, A. Combination of Inferior Vena Cava Diameter, Hepatic Venous Flow, and Portal Vein Pulsatility Index: Venous Excess Ultrasound Score (VEXUS Score) in Predicting Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Cardiorenal Syndrome: A Prospective Cohort Study. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaubien-Souligny, W.; Rola, P.; Haycock, K.; Bouchard, J.; Lamarche, Y.; Spiegel, R.; Denault, A.Y. Quantifying systemic congestion with Point-Of-Care ultrasound: Development of the venous excess ultrasound grading system. Ultrasound J. 2020, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaubien-Souligny, W.; Benkreira, A.; Robillard, P.; Bouabdallaoui, N.; Chassé, M.; Desjardins, G.; Lamarche, Y.; White, M.; Bouchard, J.; Denault, A. Alterations in Portal Vein Flow and Intrarenal Venous Flow Are Associated With Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, U.; Wettersten, N.; Garimella, P.S. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiology. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.R.; O’connor, C.M.; Sopko, G.; Hasselblad, V.; Califf, R.M.; Stevenson, L.W. Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness (ESCAPE): Design and rationale. Am. Heart J. 2001, 141, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvasmäki, T.; Haapio, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Sionis, A.; Silva-Cardoso, J.; Tolppanen, H.; Lindholm, M.G.; Pulkki, K.; Parissis, J.; Harjola, V.-P.; et al. Acute kidney injury in cardiogenic shock: Definitions, incidence, haemodynamic alterations, and mortality. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Strawn, W.B. Role of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Proinflammatory Mediators in Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison-Bernard, L.M. The renal renin-angiotensin system. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2009, 33, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Malvin, R.L. Stimulation of renal sodium reabsorption by angiotensin II. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1977, 232, F298–F306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, P.C.; Doran, A.C.; Onat, D.; Wong, K.Y.; Ahmad, M.; Sabbah, H.N.; Demmer, R.T. Venous Congestion, Endothelial and Neurohormonal Activation in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Cause or Effect? Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2015, 12, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Clementi, A.; de Cal, M.; Brocca, A.; Day, S.; Pastori, S.; Bolin, C.; Vescovo, G.; Ronco, C. Oxidative Stress: Dual Pathway Induction in Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1 Pathogenesis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 391790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilis, P.; Vordoni, A.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. Oxidative Stress Management in Cardiorenal Diseases: Focus on Novel Antidiabetic Agents, Finerenone, and Melatonin. Life 2022, 12, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terami, N.; Ogawa, D.; Tachibana, H.; Hatanaka, T.; Wada, J.; Nakatsuka, A.; Eguchi, J.; Horiguchi, C.S.; Nishii, N.; Yamada, H.; et al. Long-Term Treatment with the Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, Dapagliflozin, Ameliorates Glucose Homeostasis and Diabetic Nephropathy in db/db Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Perco, P.; Mulder, S.; Leierer, J.; Hansen, M.K.; Heinzel, A.; Mayer, G. Canagliflozin reduces inflammation and fibrosis biomarkers: A potential mechanism of action for beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilis, P.; Sagris, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Siasos, G.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in rodents. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazory, M.R.C.A.; Costanzo, M.R. The dynamic relationship between serum chloride and cardiorenal syndrome. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berend, K.; van Hulsteijn, L.H.; Gans, R.O. Chloride: The queen of electrolytes? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanberg, J.S.; Rao, V.; ter Maaten, J.M.; Laur, O.; Brisco, M.A.; Wilson, F.P.; Grodin, J.L.; Assefa, M.; Broughton, J.S.; Planavsky, N.J.; et al. Hypochloremia and Diuretic Resistance in Heart Failure: Mechanistic Insights. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e003180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Maaten, J.M.; Damman, K.; Hanberg, J.S.; Givertz, M.M.; Metra, M.; O’connor, C.M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Ponikowski, P.; Cotter, G.; Davison, B.; et al. Hypochloremia, Diuretic Resistance, and Outcome in Patients With Acute Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e003109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotchen, T.A.; Luke, R.G.; Ott, C.E.; Galla, J.H.; Whitescarver, S. Effect of Chloride on Renin and Blood Pressure Responses to Sodium Chloride. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 98, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, C.S. Regulation of Renal Blood Flow by Plasma Chloride. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 71, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuthbert, J.J.; Pellicori, P.; Rigby, A.; Pan, D.; Kazmi, S.; Shah, P.; Clark, A.L. Low serum chloride in patients with chronic heart failure: Clinical associations and prognostic significance. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodin, J.L.; Simon, J.; Hachamovitch, R.; Wu, Y.; Jackson, G.; Halkar, M.; Starling, R.C.; Testani, J.M.; Tang, W.W. Prognostic Role of Serum Chloride Levels in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudim, M.; Loungani, R.; Doerfler, S.M.; Coles, A.; Greene, S.J.; Cooper, L.B.; Fiuzat, M.; O’Connor, C.M.; Rogers, J.G.; Mentz, R.J. Worsening renal function during decongestion among patients hospitalized for heart failure: Findings from the Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness (ESCAPE) trial. Am. Heart J. 2018, 204, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakabe, A.; Hata, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Okazaki, H.; Matsushita, M.; Shibata, Y.; Nishigoori, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Asai, K.; Shimizu, W. Worsening renal function definition is insufficient for evaluating acute renal failure in acute heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2018, 5, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisco, M.A.; Zile, M.R.; Hanberg, J.S.; Wilson, F.P.; Parikh, C.R.; Coca, S.G.; Tang, W.W.; Testani, J.M. Relevance of Changes in Serum Creatinine During a Heart Failure Trial of Decongestive Strategies: Insights From the DOSE Trial. J. Card. Fail. 2016, 22, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metra, M.; Cotter, G.; Senger, S.; Edwards, C.; Cleland, J.G.; Ponikowski, P.; Cursack, G.C.; Milo, O.; Teerlink, J.R.; Givertz, M.M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Creatinine Increases During an Acute Heart Failure Admission in Patients With and Without Residual Congestion: A Post Hoc Analysis of the PROTECT Data. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolfo, D.; Stenner, E.; Merlo, M.; Porto, A.; Moras, C.; Barbati, G.; Aleksova, A.; Buiatti, A.; Sinagra, G. Prognostic Impact of BNP Variations in Patients Admitted for Acute Decompensated Heart Failure with In-Hospital Worsening Renal Function. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Zeng, X.; Tang, X.; Ma, L.; Mai, H.; Gou, S.; Liu, F.; Fu, P. Improving the diagnostic accuracy of acute myocardial infarction with the use of high-sensitive cardiac troponin T in different chronic kidney disease stages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzuoli, A.; Gallotta, M.; Quatrini, I.; Nuti, R. Natriuretic peptides (BNP and NT-proBNP): Measurement and relevance in heart failure. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2010, 6, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Yi, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; Xiao, T.; Bai, Y.; Ye, P.; Luo, L. The ability of NT-proBNP to detect chronic heart failure and predict all-cause mortality is higher in elderly Chinese coronary artery disease patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosselmann, H.; Egstrup, M.; Rossing, K.; Gustafsson, I.; Gustafsson, F.; Tonder, N.; Kistorp, C.N.; Goetze, J.P.; Schou, M. Prognostic significance of cardiovascular biomarkers and renal dysfunction in outpatients with systolic heart failure: A long term follow-up study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 170, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasevska, I.; Enhörning, S.; Persson, M.; Nilsson, P.M.; Melander, O. Copeptin predicts coronary artery disease cardiovascular and total mortality. Heart 2016, 102, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klip, I.T.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Hillege, H.L.; Struck, J.; Squire, I.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Dickstein, K. Prognostic value of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in patients with heart failure after an acute myocardial infarction. Heart 2011, 97, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, M.S.N.; Sharma, U.; Pandey, V.; Kankare, S. Serum cystatin C as a marker of renal function in detection of early acute kidney injury. Indian J. Nephrol. 2013, 23, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorgyan, M.M.; Voronina, N.P.; Goncharova, N.V.; Kozaruk, T.V.; Russkikh, G.S.; Bogdanova, L.A.; Korolenko, T.A. Cystatin C as a Marker of Progressing Cardiovascular Events during Coronary Heart Disease. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 162, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, J.V.; Souza, F.L.; Salgado, B.J. How to understand the association between cystatin C levels and cardiovascular disease: Imbalance, counterbalance, or consequence? J. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.N.; de Cal, M.; Garzotto, F.; Perazella, M.A.; Lentini, P.; Corradi, V.; Piccinni, P.; Ronco, C. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early biomarker for acute kidney injury in an adult ICU population. Intensiv. Care Med. 2010, 36, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, A.S.; Wettersten, N.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Mueller, C.; Filippatos, G.; Nowak, R.; Hogan, C.; Kontos, M.C.; Cannon, C.M.; Müller, G.A.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Acute Kidney Injury During Acute Heart Failure Hospitalizations: The AKINESIS Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, L.G.; Chawla, L.S. Biomarkers in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Blood Purif. 2014, 37 (Suppl. S2), 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medić, B.; Rovčanin, B.; Jovanović, G.B.; Radojević-Škodrić, S.; Prostran, M. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Cardiovascular Diseases: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 854070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Nishikimi, T.; Kuwahara, K. Atrial and brain natriuretic peptides: Hormones secreted from the heart. Peptides 2019, 111, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, R.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Sandberg, S.M.; Heublein, D.M.; Scott, C.G.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Urinary C-Type Natriuretic Peptide: A new heart failure biomarker. JACC Heart Fail. 2013, 1, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, L.R.; Abbey-Hosch, S.; Dickey, D.M. Natriuretic Peptides, Their Receptors, and Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate-Dependent Signaling Functions. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Xu, Y.; Xia, X. Urinary C-type natriuretic peptide excretion: A promising biomarker to detect underlying renal injury and remodeling both acutely and chronically. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.-J.; Park, J.J.; Ali, T.; Lee, S. Artificial intelligence for the diagnosis of heart failure. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, J.; Sanford, D. Treatment of Cardiorenal Syndrome. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, G.S.; Loehrke, M.; Wilt, J.L. Acute cardiorenal syndrome: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2018, 85, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullens, W.; Dauw, J.; Martens, P.; Meekers, E.; Nijst, P.; Verbrugge, F.H.; Chenot, F.; Moubayed, S.; Dierckx, R.; Blouard, P.; et al. Acetazolamide in Decompensated Heart Failure with Volume Overload trial (ADVOR): Baseline characteristics. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.S.; Planavsky, N.; Hanberg, J.S.; Ahmad, T.; Brisco-Bacik, M.A.; Wilson, F.P.; Jacoby, D.; Chen, M.; Tang, W.W.; Cherney, D.Z.; et al. Compensatory Distal Reabsorption Drives Diuretic Resistance in Human Heart Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3414–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Kiang, A. Acute Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure: From Dogmas to Advances. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulenberger, C.E.; Jiang, A.; Devabhakthuni, S.; Ivaturi, V.; Liu, T.; Reed, B.N. Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Chlorothiazide versus Oral Metolazone in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure and Loop Diuretic Resistance. Pharmacotherapy 2016, 36, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbrugge, F.H.; Martens, P.; Ameloot, K.; Haemels, V.; Penders, J.; Dupont, M.; Tang, W.H.W.; Droogné, W.; Mullens, W. Spironolactone to increase natriuresis in congestive heart failure with cardiorenal syndrome. Acta Cardiol. 2019, 74, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Felker, G.M.; Givertz, M.M.; Kalogeropoulos, A.P.; Konstam, M.A.; Mann, D.L.; Margulies, K.B.; McNulty, S.E.; Mentz, R.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Spironolactone in Acute Heart Failure: The ATHENA-HF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco-Bacik, M.A.; ter Maaten, J.M.; Houser, S.R.; Vedage, N.A.; Rao, V.; Ahmad, T.; Wilson, F.P.; Testani, J.M. Outcomes Associated With a Strategy of Adjuvant Metolazone or High-Dose Loop Diuretics in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Propensity Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Laribi, S.; Teerlink, J.R.; Mebazaa, A. Agents with vasodilator properties in acute heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, C.; Starling, R.; Hernandez, A.; Armstrong, P.; Dickstein, K.; Hasselblad, V.; Heizer, G.; Komajda, M.; Massie, B.; McMurray, J.; et al. Effect of Nesiritide in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebazaa, A.; Nieminen, M.S.; Packer, M.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Kleber, F.X.; Pocock, S.J.; Thakkar, R.; Padley, R.J.; Põder, P.; Kivikko, M.; et al. Levosimendan vs Dobutamine for Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: The SURVIVE Randomized Trial. JAMA 2007, 297, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Colucci, W.; Fisher, L.; Massie, B.M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Young, J.; Padley, R.J.; Thakkar, R.; Delgado-Herrera, L.; Salon, J.; et al. Effect of Levosimendan on the Short-Term Clinical Course of Patients With Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2013, 1, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testani, J.M.; Kimmel, S.E.; Dries, D.L.; Coca, S.G. Prognostic Importance of Early Worsening Renal Function After Initiation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Therapy in Patients With Cardiac Dysfunction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, B.A.; Goldsmith, S.R.; Lee, K.L.; Redfield, M.M.; Felker, G.M.; O’connor, C.M.; Chen, H.H.; Rouleau, J.L.; Givertz, M.M.; Semigran, M.J.; et al. Cardiorenal Rescue Study in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Rationale and Design of CARRESS-HF, for the Heart Failure Clinical Research Network. J. Card. Fail. 2012, 18, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenzi, G.; Muratori, M.; Cosentino, E.R.; Rinaldi, E.R.; Donghi, V.; Milazzo, V.; Ferramosca, E.; Borghi, C.; Santoro, A.; Agostoni, P. Continuous Ultrafiltration for Congestive Heart Failure: The CUORE Trial. J. Card. Fail. 2014, 20, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umanath, K.; Emani, S. Getting to the Heart of the Matter: Review of Treatment of Cardiorenal Syndrome. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Muciño-Bermejo, M.-J.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Tonini, E.; Estremadoyro, C.; Samoni, S.; Sharma, A.; Galván, J.D.J.Z.; Crepaldi, C.; Brendolan, A.; et al. Peritoneal Dialysis in Patients with Refractory Congestive Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. Cardiorenal Med. 2015, 5, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hwiesh, A.K.; Abdul-Rahman, I.S.; Al-Audah, N.; Al-Hwiesh, A.; Al-Harbi, M.; Taha, A.; Al-Shahri, A.; Ghazal, S.; Amir, R.; Al-Audah, N.; et al. Tidal peritoneal dialysis versus ultrafiltration in type 1 cardiorenal syndrome: A prospective randomized study. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 42, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapiboon, W.; Kingjun, T.; Wongluechai, L.; Leawnoraset, W. Outcomes after Acute Peritoneal Dialysis for Critical Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1. Cardiorenal Med. 2021, 11, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysohoou, C.; Bougatsos, G.; Magkas, N.; Skoumas, J.; Kapota, A.; Kopelias, J.; Bliouras, N.; Tsioufis, K.; Petras, D.; Tousoulis, D. Peritoneal dialysis as a therapeutic solution in elderly patients with cardiorenal syndrome and heart failure: A case-series report. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2020, 61, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.T.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Dember, L.M.; Gallieni, M.; Harris, D.C.; Lok, C.E.; Mehrotra, R.; Stevens, P.E.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; Cheung, M.; et al. Dialysis initiation, modality choice, access, and prescription: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilis, P.; Sagris, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Siasos, G.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. Pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and heart failure outcomes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 188, 109927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilis, P.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. SGLT2 inhibitors and kidney diseases: A clinical perspective. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.; Kosiborod, M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Cherney, D.Z. Renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, J. Sodium–glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure: Potential Mechanisms of Action, Adverse Effects and Future Developments. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 14, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneto, H.; Obata, A.; Kimura, T.; Shimoda, M.; Okauchi, S.; Shimo, N.; Matsuoka, T.-A.; Kaku, K. Beneficial effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for preservation of pancreatic β -cell function and reduction of insulin resistance. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Baar, M.J.; van Ruiten, C.C.; Muskiet, M.H.; van Bloemendaal, L.; Ijzerman, R.G.; van Raalte, D.H. SGLT2 Inhibitors in Combination Therapy: From Mechanisms to Clinical Considerations in Type 2 Diabetes Management. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilis, P.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Katsimichas, T.; Oikonomou, E.; Siasos, G.; Aggeli, C.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The impact of SGLT2 inhibition on imaging markers of cardiac function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 180, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Choi, I.-J.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, P.-J.; Chang, K.; Baek, S.H.; Chung, W.S.; Seung, K.-B. Impact of Cardiorenal Anemia Syndrome on Short- and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized with Heart Failure. Cardiorenal Med. 2016, 6, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenveld, H.F.; Januzzi, J.L.; Damman, K.; van Wijngaarden, J.; Hillege, H.L.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; van der Meer, P. Anemia and Mortality in Heart Failure Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, D.S.; Wexler, D.; Blum, M.; Keren, G.; Sheps, D.; Leibovitch, E.; Brosh, D.; Laniado, S.; Schwartz, D.; Yachnin, T.; et al. The use of subcutaneous erythropoietin and intravenous iron for the treatment of the anemia of severe, resistant congestive heart failure improves cardiac and renal function and functional cardiac class, and markedly reduces hospitalizations. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.B.; Abraham, W.T.; Albert, N.M.; Stough, W.G.; Gheorghiade, M.; Greenberg, B.H.; O’connor, C.M.; She, L.; Sun, J.L.; Yancy, C.W.; et al. Relation of Low Hemoglobin and Anemia to Morbidity and Mortality in Patients Hospitalized With Heart Failure (Insight from the OPTIMIZE-HF Registry). Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Yang, J.; Ackerson, L.M.; Lepper, K.; Robbins, S.; Massie, B.M.; Shlipak, M.G. Hemoglobin Level, Chronic Kidney Disease, and the Risks of Death and Hospitalization in Adults With Chronic Heart Failure: The Anemia in Chronic Heart Failure: Outcomes and Resource Utilization (ANCHOR) Study. Circulation 2006, 113, 2713–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzuoli, A.; Antonelli, G.; Nuti, R. Anemia in Cardio-Renal Syndrome: Clinical impact and pathophysiologic mechanisms. Heart Fail. Rev. 2011, 16, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrutinio, D.; Passantino, A.; Santoro, D.; Catanzaro, R. The cardiorenal anaemia syndrome in systolic heart failure: Prevalence, clinical correlates, and long-term survival. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2011, 13, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Putten, K.; Braam, B.; Jie, K.E.; Gaillard, C.A. Mechanisms of Disease: Erythropoietin resistance in patients with both heart and kidney failure. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2008, 4, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opasich, C.; Cazzola, M.; Scelsi, L.; De Feo, S.; Bosimini, E.; Lagioia, R.; Febo, O.; Ferrari, R.; Fucili, A.; Moratti, R.; et al. Blunted erythropoietin production and defective iron supply for erythropoiesis as major causes of anaemia in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 2232–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belonje, A.M.; Voors, A.A.; van der Meer, P.; van Gilst, W.H.; Jaarsma, T.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Endogenous Erythropoietin and Outcome in Heart Failure. Circulation 2010, 121, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelman, G.J.; Levin, N.W. Iron and anemia in human biology: A review of mechanisms. Heart Fail. Rev. 2008, 13, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A. Anemia of cardiorenal syndrome. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2021, 11, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, A.A.; Wanner, C.; Sarnak, M.J.; Piña, I.L.; McIntyre, C.W.; Komenda, P.; Kasiske, B.L.; Deswal, A.; Defilippi, C.R.; Cleland, J.G.F.; et al. Heart failure in chronic kidney disease: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Comin-Colet, J.; Ertl, G.; Komajda, M.; Mareev, V.; McDonagh, T.; Parkhomenko, A.; Tavazzi, L.; Levesque, V.; et al. Beneficial effects of long-term intravenous iron therapy with ferric carboxymaltose in patients with symptomatic heart failure and iron deficiency. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Filippatos, G.; Colet, J.C.; Willenheimer, R.; Dickstein, K.; Lüscher, T.; Gaudesius, G.; von Eisenhart Rothe, B.; Mori, C.; Greenlaw, N.; et al. The impact of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose on renal function: An analysis of the FAIR-HF study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, E.; Del Vecchio, L.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Haase, V.H.; Johansen, K.L.; Nangaku, M.; Tangri, N.; Waikar, S.S.; Więcek, A.; Cheung, M.; et al. Novel Anemia Therapies in Chronic Kidney Disease: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2023, 188, 109927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Comin Colet, J.; Filippatos, G.; Willenheimer, R.; Dickstein, K.; Drexler, H.; Lüscher, T.F.; Bart, B.; Banasiak, W.; Niegowska, J.; et al. Ferric Carboxymaltose in Patients with Heart Failure and Iron Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2436–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Assa, E.; Shacham, Y.; Shashar, M.; Leshem-Rubinow, E.; Gal-Oz, A.; Schwartz, I.F.; Schwartz, D.; Silverberg, D.S.; Chernin, G. Target Hemoglobin May Be Achieved with Intravenous Iron Alone in Anemic Patients with Cardiorenal Syndrome: An Observational Study. Cardiorenal Med. 2015, 5, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonko, D.O.; Grzeslo, A.; Witkowski, T.; Mandal, A.K.J.; Slater, R.M.; Roughton, M.; Foldes, G.; Thum, T.; Majda, J.; Banasiak, W.; et al. Effect of Intravenous Iron Sucrose on Exercise Tolerance in Anemic and Nonanemic Patients With Symptomatic Chronic Heart Failure and Iron Deficiency: FERRIC-HF: A Randomized, Controlled, Observer-Blinded Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedberg, K.; Young, J.B.; Anand, I.S.; Cheng, S.; Desai, A.S.; Diaz, R.; Maggioni, A.P.; McMurray, J.J.; O’Connor, C.; Pfeffer, M.A.; et al. Treatment of Anemia with Darbepoetin Alfa in Systolic Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.-P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Barany, P.; Covic, A.; De Francisco, A.; Del Vecchio, L.; Goldsmith, D.; Hörl, W.; London, G.; Vanholder, R.; Van Biesen, W.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines on anaemia management in chronic kidney disease: A European Renal Best Practice position statement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Szczech, L.; Tang, K.L.; Barnhart, H.; Sapp, S.; Wolfson, M.; Reddan, D. Correction of Anemia with Epoetin Alfa in Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Burdmann, E.A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Feyzi, J.M.; Ivanovich, P.; Kewalramani, R.; Levey, A.S.; et al. A Trial of Darbepoetin Alfa in Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Jackevicius, C.; Co, M.J.; Warner, A.L. Predictors of erythropoietin use in patients with cardiorenal anaemia syndrome. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2015, 23, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.M.; Sharma, N.; Dikdan, S. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor and Its Role in the Management of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denko, N.C. Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
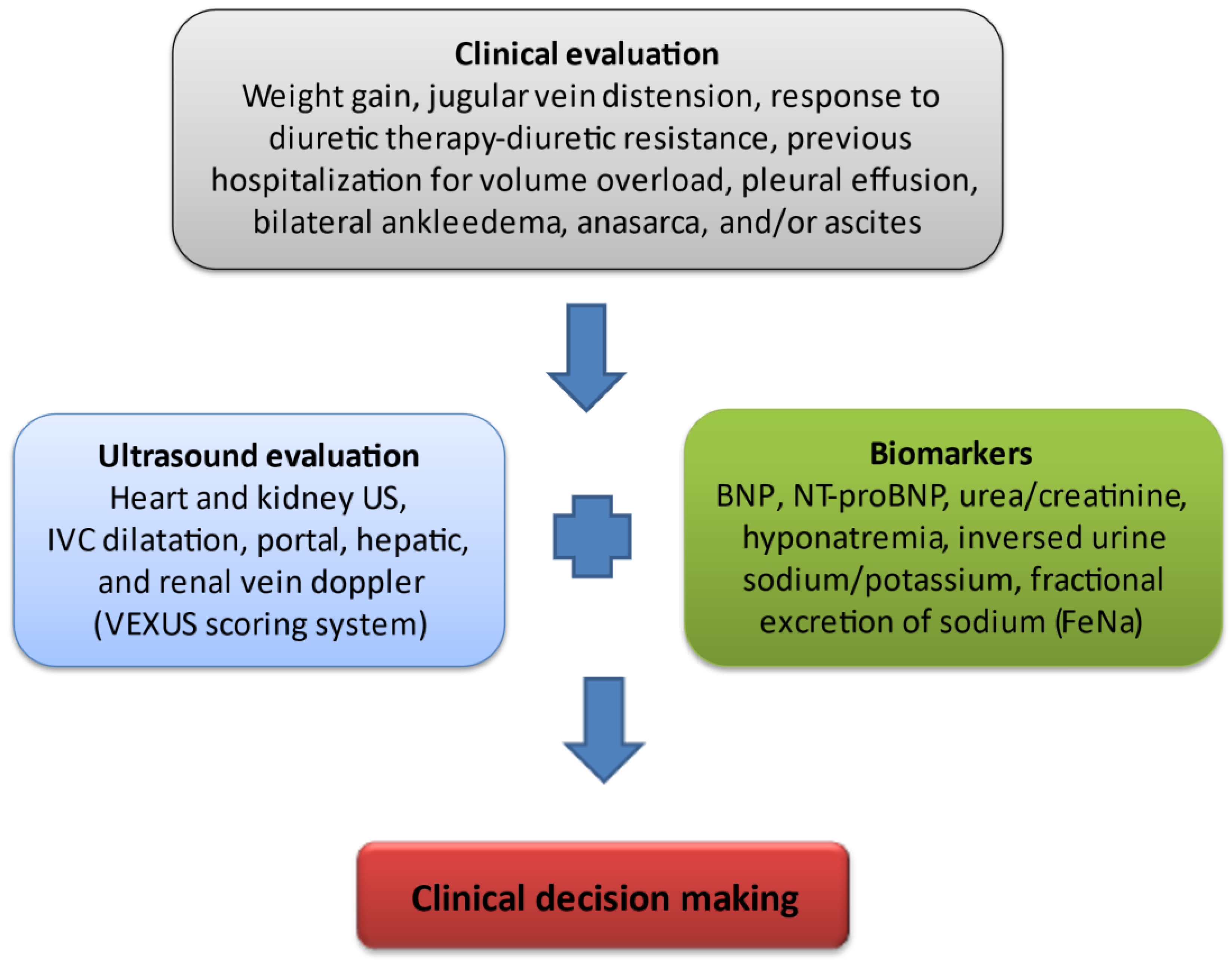
| Novel methods and biomarkers are required for accurate clinical classification of CRS. |
| Artificial intelligence support systems and clinical algorithms may be used to identify patients with CRS who are at risk of adverse outcomes. |
| Panel of novel plasma and urine biomarkers for risk stratification and for the distinction of WRF from true AKI. |
| Incorporation of improved methods of assessing venous congestion (VExUS) into routine clinical practice |
| Volume and Neurohormonal Control, SGLT2i, Inotropic support, Ultrafiltration, Iron repletion, Finerenone |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgopoulou, T.; Petrakis, I.; Dermitzaki, K.; Pleros, C.; Drosataki, E.; Aletras, G.; Foukarakis, E.; Lioudaki, E.; Androulakis, E.; Stylianou, K. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Challenges in Everyday Clinical Practice and Key Points towards a Better Management. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124121
Georgopoulou T, Petrakis I, Dermitzaki K, Pleros C, Drosataki E, Aletras G, Foukarakis E, Lioudaki E, Androulakis E, Stylianou K. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Challenges in Everyday Clinical Practice and Key Points towards a Better Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124121
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgopoulou, Theodora, Ioannis Petrakis, Kleio Dermitzaki, Christos Pleros, Eleni Drosataki, Georgios Aletras, Emmanouil Foukarakis, Eirini Lioudaki, Emmanuel Androulakis, and Kostas Stylianou. 2023. "Cardiorenal Syndrome: Challenges in Everyday Clinical Practice and Key Points towards a Better Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124121
APA StyleGeorgopoulou, T., Petrakis, I., Dermitzaki, K., Pleros, C., Drosataki, E., Aletras, G., Foukarakis, E., Lioudaki, E., Androulakis, E., & Stylianou, K. (2023). Cardiorenal Syndrome: Challenges in Everyday Clinical Practice and Key Points towards a Better Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124121







