Adult-Onset Neuroepidemiology in Finland: Lessons to Learn and Work to Do
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nuances of Rarity
3. High Risk and Even Higher Risk
4. Known Unknowns
5. Great Unknowns
6. Perspectives and Pitfalls
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavalli-Sforza, L.L.; Piazza, A. Human genomic diversity in Europe: A summary of recent research and prospects for the future. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 1993, 1, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, O.; Lu, T.T.; Nothnagel, M.; Junge, O.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Caliebe, A.; Balascakova, M.; Bertranpetit, J.; Bindoff, L.A.; Comas, D.; et al. Correlation between genetic and geographic structure in Europe. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norio, R. Finnish Disease Heritage I: Characteristics, causes, background. Hum. Genet. 2003, 112, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norio, R. Finnish Disease Heritage II: Population prehistory and genetic roots of Finns. Hum. Genet. 2003, 112, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Fu, Y.X. Exploring population size changes using SNP frequency spectra. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uusimaa, J.; Kettunen, J.; Varilo, T.; Järvelä, I.; Kallijärvi, J.; Kääriäinen, H.; Laine, M.; Lapatto, R.; Myllynen, P.; Niinikoski, H.; et al. The Finnish genetic heritage in 2022—From diagnosis to translational research. Dis. Model. Mech. 2022, 15, dmm049490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmela, E.; Lappalainen, T.; Fransson, I.; Andersen, P.M.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Fiebig, A.; Sistonen, P.; Savontaus, M.-L.; Schreiber, S.; Kere, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms uncovers population structure in Northern Europe. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM); University of Helsinki and the National Institute for Health and Welfare. Population Genetics of Finns. Available online: https://www.helsinki.fi/en/hilife-helsinki-institute-life-science/units/fimm/research-fimm/human-genomics-health-and-disease/population-genetics-finns (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Kerminen, S.; Havulinna, A.S.; Hellenthal, G.; Martin, A.R.; Sarin, A.-P.; Perola, M.; Palotie, A.; Salomaa, V.; Daly, M.J.; Ripatti, S.; et al. Fine-Scale Genetic Structure in Finland. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lappalainen, T.; Laitinen, V.; Salmela, E.; Andersen, P.; Huoponen, K.; Savontaus, M.L.; Lahermo, P. Migration waves to the Baltic Sea region. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2008, 72, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palo, J.U.; Ulmanen, I.; Lukka, M.; Ellonen, P.; Sajantila, A. Genetic markers and population history: Finland revisited. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerminen, S.; Cerioli, N.; Pacauskas, D.; Havulinna, A.S.; Perola, M.; Jousilahti, P.; Salomaa, V.; Daly, M.J.; Vyas, R.; Ripatti, S.; et al. Changes in the fine-scale genetic structure of Finland through the 20th century. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vähämurto, L.; Pahkala, K.; Magnussen, C.G.; Mikkilä, V.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Kähönen, M.; Laitinen, T.; Taittonen, L.; Tossavainen, P.; Lehtimäki, T.; et al. East-west differences migration in Finland: Association with cardiometabolic risk markers, I.M.T. The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Scand. J. Public. Health 2016, 44, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousilahti, P.; Laatikainen, T.; Salomaa, V.; Pietilä, A.; Vartiainen, E.; Puska, P. 40-Year CHD Mortality Trends and the Role of Risk Factors in Mortality Decline: The North Karelia Project Experience. Glob. Heart 2016, 11, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manderbacka, K.; Lindell, E.; Suomela, T.; Lumme, S.; Koskinen, S.; Parikka, S. Toteutuuko Alueellinen Tasa-Arvo Menetetyissä Elinvuosissa? Is There Regional Equality in Potential Life-Years Lost? Tutkimuksesta Tiiviisti 35/2022. Terveyden ja Hyvinvoinnin Laitos, Helsinki. Available online: https://urn.fi/URN:ISBN:978-952-343-910-8 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Hyppönen, J.; Kytö, V.; Kälviäinen, R. Unverricht-Lundborg disease (EPM1) in Finland: A nationwide population-based study. Neurology 2020, 95, e3117–e3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.; Hietala, M.; Siitonen, A.; Päivärinta, M.; Majamaa, K. Epidemiology of Huntington’s disease in Finland. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Majamaa, K. Stable low prevalence of Huntington’s disease in Finland. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 8, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, M.D.; Wexler, N.S.; Wexler, A.R.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Douglas, I.; Evans, S.J.; Smeeth, L. The Prevalence of Huntington’s Disease. Neuroepidemiology 2016, 46, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvonen, V.; Hietala, M.; Kairisto, V.; Savontaus, M.L. The occurrence of dominant spinocerebellar ataxias among 251 Finnish ataxia patients and the role of predisposing large normal alleles in a genetically isolated population. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2005, 111, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvonen, V.; Kulmala, S.M.; Ignatius, J.; Penttinen, M.; Savontaus, M.L. Dissecting the epidemiology of a trinucleotide repeat disease—Example of FRDA in Finland. Hum. Genet. 2002, 110, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasson, J.; Juvonen, V.; Sistonen, P.; Ignatius, J.; Johansson, D.; Björck, E.J.; Wahlström, J.; Melberg, A.; Holmgren, G.; Forsgren, L.; et al. Evidence for a common Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) founder mutation in Scandinavia. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 8, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipponen, J.; Helisalmi, S.; Raivo, J.; Siitonen, A.; Doi, H.; Rusanen, H.; Lehtilahti, M.; Ryytty, M.; Laakso, M.; Tanaka, F.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of hereditary ataxia in Finland. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakonen, A.H.; Heiskanen, S.; Juvonen, V.; Lappalainen, I.; Luoma, P.T.; Rantamäki, M.; Van Goethem, G.; Löfgren, A.; Hackman, P.; Paetau, A.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA polymerase W748S mutation: A common cause of autosomal recessive ataxia with ancient European origin. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hakonen, A.H.; Davidzon, G.; Salemi, R.; Bindoff, L.; Van Goethem, G.; DiMauro, S.; Thorburn, D.; Suomalainen, A. Abundance of the POLG disease mutations in Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and the United States explained by single ancient European founders. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 15, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jokela, M.; Hietala, M.; Karhu, J.; Martikainen, M.H.; Kaasinen, V. Särö-X-esimutaatio-oireyhtymä (FXTAS)—Magneettikuvauksesta apua diagnosointiin. Duodecim 2019, 135, 683–686. [Google Scholar]
- Haataja, R.; Väisänen, M.L.; Li, M.; Ryynänen, M.; Leisti, J. The fragile X syndrome in Finland: Demonstration of a founder effect by analysis of microsatellite haplotypes. Hum. Genet. 1994, 94, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, N.; Kajanoja, E.; Smits, B.; Pietrofesa, J.; Curley, D.; Wang, D.; Ju, W.; Nolin, S.; Dobkin, C.; Ryynänen, M.; et al. Fragile X founder effects and new mutations in Finland. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996, 64, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpioja, A.; Krüger, J.; Hurme-Niiranen, A.; Solje, E.; Katisko, K.; Lipponen, J.; Lehtilahti, M.; Remes, A.M.; Majamaa, K.; Kytövuori, L. Cognitive impairment is not uncommon in patients with biallelic RFC1 AAGGG repeat expansion, but the expansion is rare in patients with cognitive disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2022, 103, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainio, M.T.; Aaltio, J.; Hyttinen, V.; Kortelainen, M.; Ojanen, S.; Paetau, A.; Tienari, P.; Ylikallio, E.; Auranen, M.; Tyynismaa, H. Effectiveness of clinical exome sequencing in adult patients with difficult-to-diagnose neurological disorders. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 145, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Ansakorpi, H.; Grönroos, M.; Martikainen, M.H.; Majamaa, K. The development of a national registry for rare neurological disorders in finland—Piloting efforts with huntington’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, A63–A64. [Google Scholar]
- Ruano, L.; Melo, C.; Silva, M.C.; Coutinho, P. The global epidemiology of hereditary ataxia and spastic paraplegia: A systematic review of prevalence studies. Neuroepidemiology 2014, 42, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Hietala, M.; Kytö, V.; Kaasinen, V. Wilson’s Disease in Finland: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 2323–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Kytövuori, L.; Kaasinen, V. Clinical spectrum and genotype-phenotype associations in Finnish patients with Wilson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 448, 120620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingwell, E.; Marriott, J.J.; Jetté, N.; Pringsheim, T.; Makhani, N.; A Morrow, S.; Fisk, J.D.; Evans, C.; Béland, S.G.; Kulaga, S.; et al. Incidence and prevalence of multiple sclerosis in Europe: A systematic review. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walton, C.; King, R.; Rechtman, L.; Kaye, W.; Leray, E.; Marrie, R.A.; Robertson, N.; La Rocca, N.; Uitdehaag, B.; Van Der Mei, I.; et al. Rising prevalence of multiple sclerosis worldwide: Insights from the Atlas of MS, third edition. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirttisalo, A.L.; Soilu-Hänninen, M.; Sumelahti, M.L.; Krökki, O.; Murtonen, A.; Hänninen, K.; Sipilä, J.O.T. Changes in multiple sclerosis epidemiology in Finland over five decades. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 142, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, B.J. Spatial analysis of global prevalence of multiple sclerosis suggests need for an updated prevalence scale. Mult. Scler. Int. 2014, 2014, 124578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fältmarsch, R. Biochemistry in Acid Sulphate Soil Landscapes and Small Urban Centres in Western Finland. Ph.D. Dissertation, Åbo Akademi University, Turku, Finland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Häsänen, E.; Kinnunen, E.; Alhonen, P. Relationships between the prevalence of multiple sclerosis and some physical and chemical properties of soil. Sci. Total Environ. 1986, 58, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T. A letter to the editor concerning “Geochemistry of multiple sclerosis in Finland”. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirttisalo, A.L.; Soilu-Hänninen, M.; Sipilä, J.O.T. Multiple sclerosis epidemiology in Finland: Regional differences and high incidence. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2019, 139, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T. Nordic clues for uncovering the aetiology of Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 50, 102804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.; Ng, H.S.; Poyser, C.; Lucas, R.M.; Tremlett, H. Multiple sclerosis incidence: A systematic review of change over time by geographical region. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 63, 103932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grytten, N.; Aarseth, J.H.; Lunde, H.M.; Myhr, K.M. A 60-year follow-up of the incidence and prevalence of multiple sclerosis in Hordaland County, Western Norway. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Pirttisalo, A.L.; Sumelahti, M.L.; Soilu-Hänninen, M. Miksi MS-tauti yleistyy? Duodecim 2022, 138, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Soilu-Hänninen, M.; Ruuskanen, J.O.; Rautava, P.; Kytö, V. Epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome in Finland 2004-2014. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2017, 22, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siuko, M.; Valori, M.; Kivelä, T.; Setälä, K.; Morin, A.; Kwan, T.; Pastinen, T.; Tienari, P. Exome and regulatory element sequencing of neuromyelitis optica patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 289, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.; Jaakonmäki, N.; Nylund, M.; Kupila, L.; Matilainen, M.; Airas, L. Frequency and etiology of acute transverse myelitis in Southern Finland. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 46, 102562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherieh, S.; Afshari-Safavi, A.; Vaheb, S.; Kiani, M.; Ghaffary, E.M.; Barzegar, M.; Shaygannejad, V.; Zabeti, A.; Mirmosayyeb, O. Worldwide prevalence of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) and neuromyelitis optica (NMO): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjutsalo, V.; Sjöberg, L.; Tuomilehto, J. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: A cohort study. Lancet 2008, 371, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parviainen, A.; But, A.; Siljander, H.; Knip, M. Decreased Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes in Young Finnish Children. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silman, A.J.; Pearson, J.E. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, S265–S272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinne, U.K.; Panelius, M.; Kivalo, E.; Hokkanen, E.; Meurman, T. Multiple sclerosis in Finland. Further studies on its distribution and prevalence. Acta Neurol. Scandinav. 1968, 44, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, R. Adult Dystonia in Finland: The Prevalence, Comorbidities, Retirement and DBS in Dystonia in the Years 2007–2016. Dissertation, Helsinki University, Helsinki, Finland, 2020. Page 66. Available online: https://helda.helsinki.fi/handle/10138/318912 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Xu, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Fan, D.; Zhan, S.; Wang, S. Global variation in prevalence and incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majounie, E.; E Renton, A.; Mok, K.; Dopper, E.G.; Waite, A.; Rollinson, S.; Chiò, A.; Restagno, G.; Nicolaou, N.; Simon-Sanchez, J.; et al. Frequency of the C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanhisuanto, M.; Solje, E.; Jokela, M.; Sipilä, J.O.T. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in southwestern and eastern Finland. Neuroepidemiology, 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Sabel, C.E.; Boyle, P.J.; Löytönen, M.; Gatrell, A.C.; Jokelainen, M.; Flowerdew, R.; Maasilta, P. Spatial clustering of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Finland at place of birth and place of death. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 157, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laaksovirta, H.; Launes, J.; Jansson, L.; Traynor, B.J.; Kaivola, K.; Tienari, P.J. ALS in Finland: Major Genetic Variants and Clinical Characteristics of Patients With and Without the C9orf72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion. Neurol. Genet. 2022, 8, e665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostalski, H.; Korhonen, V.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Solje, E.; Krüger, J.; Gen, F.; Kaivola, K.; Eide, P.K.; Lambert, J.-C.; Julkunen, V.; et al. A Novel Genetic Marker for the C9orf72 Repeat Expansion in the Finnish Population. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 83, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logroscino, G.; Piccininni, M.; Graff, C.; Hardiman, O.; Ludolph, A.C.; Moreno, F.; Otto, M.; Remes, A.M.; Rowe, J.B.; Seelaar, H.; et al. Incidence of Syndromes Associated With Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration in 9 European Countries. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penttilä, S.; Jokela, M.; Bouquin, H.; Saukkonen, A.M.; Toivanen, J.; Udd, B. Late onset spinal motor neuronopathy is caused by mutation in CHCHD10. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penttilä, S.; Jokela, M.; Saukkonen, A.M.; Toivanen, J.; Palmio, J.; Lähdesmäki, J.; Sandell, S.; Shcherbii, M.; Auranen, M.; Ylikallio, E.; et al. CHCHD10 mutations and motor neuron disease: The distribution in Finnish patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jokela, M.E.; Jääskeläinen, S.K.; Sandell, S.; Palmio, J.; Penttilä, S.; Saukkonen, A.; Soikkeli, R.; Udd, B. Spontaneous activity in electromyography may differentiate certain benign lower motor neuron disease forms from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 355, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, M. Late-Onset Spinal Motor Neuronopathy—A New Neuromuscular Disease. Dissertation, University of Turku, Turku, Finland, 2015. Available online: https://www.utupub.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/117735/AnnalesD1211Jokela.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Ortiz, R.; Scheperjans, F.; Mertsalmi, T.; Pekkonen, E. The prevalence of adult-onset isolated dystonia in Finland 2007–2016. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børhaug, E.; Vedeler, C.A. Neurosarcoidosis—A patient series. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforen. 2021, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Wermuth, L.; Bech, S.; Petersen, M.S.; Joensen, P.; Weihe, P.; Grandjean, P. Prevalence and incidence of Parkinson’s disease in The Faroe Islands. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2008, 118, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokkanen, E. Epidemiology of myasthenia gravis in Finland. J. Neurol. Sci. 1969, 9, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirskanen, R. Genetic aspects in myasthenia gravis. A family study of 264 Finnish patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1977, 56, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Soilu-Hänninen, M.; Rautava, P.; Kytö, V. Hospital admission and prevalence trends of adult myasthenia gravis in Finland in 2004–2014: A retrospective national registry study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 407, 116520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabre, L.; Westerberg, E.; Liik, M.; Punga, A.R. Diversity in mental fatigue and social profile of patients with myasthenia gravis in two different Northern European countries. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerberg, E.; Punga, A.R. Epidemiology of Myasthenia Gravis in Sweden 2006–2016. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldingh, M.I.; Maniaol, A.H.; Brunborg, C.; Dekker, L.; Heldal, A.T.; Lipka, A.; Popperud, T.H.; Niks, E.H.; Verschuuren, J.; Tallaksen, C.M. Geographical Distribution of Myasthenia Gravis in Northern Europe—Results from a Population-Based Study from Two Countries. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 44, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Honkasalo, M.L.; Kaprio, J.; Heikkilä, K.; Sillanpää, M.; Koskenvuo, M. A population-based survey of headache and migraine in 22,809 adults. Headache 1993, 33, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforow, R. Headache in a random sample of 200 persons: A clinical study of a population in northern Finland. Cephalalgia 1981, 1, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Ruuskanen, J.O.; Rautava, P.; Kytö, V. Adult Migraine Hospital Admission Trends in Finland: A Nationwide Registry Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crespi, J.; Gulati, S.; Salvesen, Ø.; Bratbak, D.F.; Dodick, D.W.; Matharu, M.S.; Tronvik, E. Epidemiology of diagnosed cluster headache in Norway. Cephalalgia Rep. 2022, 5, 25158163221075569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlöf, C.; Linde, M. One-year prevalence of migraine in Sweden: A population-based study in adults. Cephalalgia 2001, 21, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayzenberg, I.; Katsarava, Z.; Sborowski, A.; Chernysh, M.; Osipova, V.; Tabeeva, G.; Yakhno, N.; Steiner, T.; Burden, O.B.O.L.T. The prevalence of primary headache disorders in Russia: A countrywide survey. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toom, K.; Raidvee, A.; Allas, K.-H.; Floria, E.; Juhkami, K.; Klimušev, G.; Leping, M.; Liidemann, M.; Milovidov, A.; Liivak, K.; et al. The prevalence of primary headache disorders in the adult population of Estonia. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, S.; Paljärvi, L.; Vapalahti, M. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in patients investigated for presumed normal pressure hydrocephalus: A clinical and neuropathological study. Acta Neurochir. 1999, 141, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovinen, J.; Kastinen, S.; Komulainen, S.; Oinas, M.; Avellan, C.; Frantzen, J.; Rinne, J.; Ronkainen, A.; Kauppinen, M.; Lönnrot, K.; et al. Familial idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 368, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korhonen, V.E.; Remes, A.M.; Helisalmi, S.; Rauramaa, T.; Sutela, A.; Vanninen, R.; Suhonen, N.-M.; Haapasalo, A.; Hiltunen, M.; Jääskeläinen, J.E.; et al. Prevalence of C9ORF72 Expansion in a Large Series of Patients with Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2019, 47, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisell, M.; Höglund, M.; Wikkelsø, C. National and regional incidence of surgery for adult hydrocephalus in Sweden. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2005, 112, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udd, B.; Juvonen, V.; Hakamies, L.; Nieminen, A.; Wallgren-Pettersson, C.; Cederquist, K.; Savontaus, M.L. High prevalence of Kennedy’s disease in Western Finland—Is the syndrome underdiagnosed? Acta Neurol. Scand. 1998, 98, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silander, K.; Meretoja, P.; Juvonen, V.; Ignatius, J.; Pihko, H.; Saarinen, A.; Wallden, T.; Herrgård, E.; Aula, P.; Savontaus, M.L. Spectrum of mutations in Finnish patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related neuropathies. Hum. Mutat. 1998, 12, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttila, M.; Kytövuori, L.; Helisalmi, S.; Kallio, M.; Laitinen, M.; Hiltunen, M.; Kärppä, M.; Majamaa, K. Molecular Epidemiology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease in Northern Ostrobothnia, Finland: A Population-Based Study. Neuroepidemiology 2017, 49, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.I.; Ghelue, M.V.; Lund, I.; Jonsrud, C.; Arntzen, K.A. The prevalence of hereditary neuromuscular disorders in Northern Norway. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e01948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braathen, G.J.; Sand, J.C.; Lobato, A.; Høyer, H.; Russell, M.B. Genetic epidemiology of Charcot–Marie–Tooth in the general population. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanen, J. Clinical characteristics of familial and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Finland. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1993, 87, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isotalo, J.; Gardberg, M.; Verkkoniemi-Ahola, A.; Paetau, A.; Martikainen, M.H.; Korpela, J.; Rummukainen, J.; Jääskeläinen, S.K.; Parkkola, R.; Kaasinen, V. Phenotype and incidence of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Finland in 1997–2013. Duodecim 2015, 131, 465–474. [Google Scholar]
- Rantalaiho, T.; Färkkilä, M.; Vaheri, A.; Koskiniemi, M. Acute encephalitis from 1967 to 1991. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 184, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, P.O. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Sweden. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 65, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Kälviäinen, R. Adult onset epilepsy incidence in Finland over 34 years: A nationwide registry study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keränen, T.; Riekkinen, P.J.; Sillanpää, M. Incidence and prevalence of epilepsy in adults in eastern Finland. Epilepsia 1989, 30, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantanen, A.M.; Sairanen, J.; Kälviäinen, R. Incidence of the different stages of status epilepticus in Eastern Finland: A population-based study. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 101, 106413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posti, J.P.; Sankinen, M.; Sipilä, J.O.T.; Ruuskanen, J.O.; Rinne, J.; Rautava, P.; Kytö, V. Fatal traumatic brain injuries during 13 years of successive alcohol tax increases in Finland—A nationwide population-based registry study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posti, J.P.; Cajanus, K.; Tornio, A.; Ruuskanen, J.O.; Luoto, T.M.; Rautava, P.; Kytö, V. Causes of Fatal Traumatic Brain Injury in Finland. J. Neurosurg. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posti, J.P.; Sipilä, J.O.T.; Luoto, T.M.; Rautava, P.; Kytö, V. A decade of geriatric traumatic brain injuries in Finland: Population-based trends. Age Ageing 2020, 49, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posti, J.P.; Luoto, T.M.; Sipilä, J.O.T.; Rautava, P.; Kytö, V. Changing epidemiology of traumatic brain injury among the working-aged in Finland: Admissions and neurosurgical operations. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 146, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazinova, A.; Rehorcikova, V.; Taylor, M.S.; Buckova, V.; Majdan, M.; Psota, M.; Peeters, W.; Feigin, V.; Theadom, A.; Holkovic, L.; et al. Epidemiology of Traumatic Brain Injury in Europe: A Living Systematic Review. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 1411–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huttunen, J.; Kurki, M.I.; Fraunberg, M.V.U.Z.; Koivisto, T.; Ronkainen, A.; Rinne, J.; Jääskeläinen, J.E.; Kälviäinen, R.; Immonen, A. Epilepsy after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A population-based, long-term follow-up study. Neurology 2015, 84, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, A.-M.; Saloheimo, P.; Huhtakangas, J.; Salminen, H.; Juvela, S.; Bode, M.K.; Hillbom, M.; Tetri, S. Poststroke epilepsy in long-term survivors of primary intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2017, 88, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natukka, T.; Raitanen, J.; Haapasalo, H.; Auvinen, A. Incidence trends of adult malignant brain tumors in Finland, 1990–2016. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korja, M.; Raj, R.; Seppä, K.; Luostarinen, T.; Malila, N.; Seppälä, M.; Mäenpää, H.; Pitkäniemi, J. Glioblastoma survival is improving despite increasing incidence rates: A nationwide study between 2000 and 2013 in Finland. Neurol. Oncol. 2019, 21, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruun, E.; Virta, L.J.; Kälviäinen, R.; Keränen, T. Co-morbidity and clinically significant interactions between antiepileptic drugs and other drugs in elderly patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 73, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, E.; Kälviäinen, R.; Keränen, T. Outcome of initial antiepileptic drug treatment in elderly patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 127, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, E.; Virta, L.J.; Kälviäinen, R.; Keränen, T. Choice of the first anti-epileptic drug in elderly patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy: A Finnish retrospective study. Seizure 2015, 31, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watkins, L.; O’Dwyer, M.; Shankar, R. New anti-seizure medication for elderly epileptic patients. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2019, 20, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantanen, A.M.; Reinikainen, M.; Parviainen, I.; Kälviäinen, R. Long-term outcome of refractory status epilepticus in adults: A retrospective population-based study. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 133, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Vestergaard, M.; Pedersen, M.G.; Pedersen, C.B.; Olsen, J.; Sidenius, P. Incidence and prevalence of epilepsy in Denmark. Epilepsy Res. 2007, 76, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Linehan, C.; Tomson, T.; Marson, T.; Dreier, J.W.; Collaborators, E.S.B.A.C.E. Incidence of epilepsy in Denmark 1977–2016. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, s103–s522. [Google Scholar]
- Näyhä, S. Geographic variations in cardiovascular mortality in Finland 1961–1985. Scand. J. Soc. Med. Suppl. 1989, 40, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nuotio, J.; Laitinen, T.T.; Juonala, M. Mistä ero sepelvaltimotaudissa idän ja lännen välillä johtuu? Duodecim 2020, 136, 2583–2589. [Google Scholar]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Sarti, C.; Narva, E.V.; Salmi, K.; Sivenius, J.; Kaarsalo, E.; Salomaa, V.; Torppa, J. The Finmonica Stroke Register: Community-based Stroke Registration and Analysis of Stroke Incidence in Finland, 1983–1985. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1992, 135, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivenius, J.; Tuomilehto, J.; Immonen-Räihä, P.; Kaarisalo, M.; Sarti, C.; Torppa, J.; Kuulasmaa, K.; Mähönen, M.; Lehtonen, A.; Salomaa, V. Continuous 15-year decrease in incidence and mortality of stroke in Finland: The Finstroke study. Stroke 2004, 35, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fogelholm, R.; Murros, K.; Rissanen, A.; Ilmavirta, M. Decreasing incidence of stroke in central Finland, 1985–1993. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1997, 95, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havulinna, A.S.; Pääkkönen, R.; Karvonen, M.; Salomaa, V. Geographic patterns of incidence of ischemic stroke and acute myocardial infarction in Finland during 1991–2003. Ann. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komulainen, T.; Koivisto, A.; Jäkälä, P. Incidence of first-ever transient ischemic attack in Eastern Finland. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 146, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammintausta, A.; Lehtonen, A.; Immonen-Raiha, P.; Kaarisalo, M.; Torppa, J.; Airaksinen, K.E.; Salomaa, V. Stroke morbidity in Swedish- and Finnish-speaking populations of Turku, Finland. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2009, 43, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyyppä, M.T.; Mäki, J. Why do Swedish-speaking Finns have longer active life? An area for social capital research. Health Promot. Int. 2001, 16, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volanen, S.M.; Suominen, S.; Lahelma, E.; Koskenvuo, M.; Silventoinen, K. Sense of coherence and its determinants: A comparative study of the Finnish-speaking majority and the Swedish-speaking minority in Finland. Scand. J. Public. Health 2006, 34, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korja, M.; Kaprio, J. Controversies in epidemiology of intracranial aneurysms and SAH. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korja, M.; Lehto, H.; Juvela, S.; Kaprio, J. Incidence of subarachnoid hemorrhage is decreasing together with decreasing smoking rates. Neurology 2016, 84, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindbohm, J.V.; Kaprio, J.; Jousilahti, P.; Salomaa, V.; Korja, M. Sex, Smoking, and Risk for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke 2016, 47, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korja, M.; Silventoinen, K.; McCarron, P.; Zdravkovic, S.; Skytthe, A.; Haapanen, A.; de Faire, U.; Pedersen, N.L.; Christensen, K.; Koskenvuo, M.; et al. Genetic epidemiology of spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage: Nordic Twin Study. Stroke 2010, 41, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindbohm, J.V.; Rautalin, I.; Jousilahti, P.; Salomaa, V.; Kaprio, J.; Korja, M. Physical activity associates with subarachnoid hemorrhage risk—A population-based long-term cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rautalin, I.; Lindbohm, J.V.; Kaprio, J.; Korja, M. Substantial Within-Country Variation in the Incidence of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Nationwide Finnish Study. Neurology 2021, 97, e52–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivipelto, M.; Helkala, E.-L.; Soininen, H.; Laakso, M.P.; Hänninen, T.; Hallikainen, M.; Alhainen, K.; Iivonen, S.; Mannermaa, A.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele, elevated midlife total cholesterol level, and high midlife systolic blood pressure are independent risk factors for late-life Alzheimer disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 137, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathobiology of Alzheimer’s disease. In Proceedings of the Fifth Paulo Foundation International Symposium, Hanasaari, Espoo, Finland, 17–19 June 1988; Volume 21, pp. 67–136.
- Haapasalo, A.; Hiltunen, M. A report from the 8th Kuopio Alzheimer Symposium. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2018, 8, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngandu, T.; Lehtisalo, J.; Solomon, A.; Levälahti, E.; Ahtiluoto, S.; Antikainen, R.; Bäckman, L.; Hänninen, T.; Jula, A.; Laatikainen, T.; et al. A 2 year multidomain intervention of diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring versus control to prevent cognitive decline in at-risk elderly people (FINGER): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiltunen, M.; Mannermaa, A.; Thompson, D.; Easton, D.; Pirskanen, M.; Helisalmi, S.; Koivisto, A.M.; Lehtovirta, M.; Ryynanen, M.; Soininen, H. Genome-wide linkage disequilibrium mapping of late-onset alzheimer’s disease in Finland. Neurology 2001, 57, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolppanen, A.M.; Lavikainen, P.; Solomon, A.; Kivipelto, M.; Soininen, H.; Hartikainen, S. Incidence of stroke in people with Alzheimer disease: A national register-based approach. Neurology 2013, 80, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetsonen, V.; Kuvaja-Köllner, V.; Välimäki, T.; Selander, T.; Martikainen, J.; Koivisto, A.M. Total cost of care increases significantly from early to mild Alzheimer’s disease: 5-year ALSOVA follow-up. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memory disorders. In Current Care Guidelines; The Finnish Medical Society Duodecim: Helsinki, Finland, 2021; Available online: http://Kaypahoito.fi (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Tolppanen, A.M.; Taipale, H.; Koponen, M.; Lavikainen, P.; Tanskanen, A.; Tiihonen, J.; Hartikainen, S. Cohort profile: The Finnish Medication and Alzheimer’s disease (MEDALZ) study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Statistics Finland’s Free-of-Charge Statistical Databases. Population According to Age (1-Year) and Sex by Area, 1972–2022. Available online: https://statfin.stat.fi/PxWeb/pxweb/en/StatFin/StatFin__vaerak/statfin_vaerak_pxt_11re.px/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Solomon, A.; Ngandu, T.; Soininen, H.; Hallikainen, M.M.; Kivipelto, M.; Laatikainen, T. Validity of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease diagnoses in Finnish national registers. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamaki, B.; Hartikainen, S.; Tolppanen, A.M. The effect of comorbidities on survival in persons with Alzheimer’s disease: A matched cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivunen, K.; Sillanpää, E.; Munukka, M.; Portegijs, E.; Rantanen, T. Cohort Differences in Maximal Physical Performance: A Comparison of 75- and 80-Year-Old Men and Women Born 28 Years Apart. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munukka, M.; Koivunen, K.; von Bonsdorff, M.; Sipilä, S.; Portegijs, E.; Ruoppila, I.; Rantanen, T. Birth cohort differences in cognitive performance in 75- and 80-year-olds: A comparison of two cohorts over 28 years. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Social Insurance Institution of Finland (KELA). Existing, New and Withdrawn Entitlements to Reimbursement of Drug Expenses. Available online: https://raportit.kela.fi/ibi_apps/WFServlet?IBIF_ex=NIT084AL&YKIELI=S (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Blom, E.S.; Viswanathan, J.; Kilander, L.; Helisalmi, S.; Soininen, H.; Lannfelt, L.; Ingelsson, M.; Glaser, A.; Hiltunen, M. Low prevalence of APP duplications in Swedish and Finnish patients with early-onset alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovelet-Lecrux, A.; Frebourg, T.; Tuominen, H.; Majamaa, K.; Campion, D.; Remes, A.M. APP locus duplication in a Finnish family with dementia and intracerebral haemorrhage. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1158–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marttila, R.J.; Rinne, U.K. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease in Finland. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1976, 53, 81–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kuopio, A.M.; Marttila, R.J.; Helenius, H.; Rinne, U.K. Changing epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease in southwestern Finland. Neurology 1999, 52, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isotalo, J.; Vahlberg, T.; Kaasinen, V. Unchanged long-term rural-to-urban incidence ratio of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knekt, P.; Kilkkinen, A.; Rissanen, H.; Marniemi, J.; Sääksjärvi, K.; Heliövaara, M. Serum vitamin D and the risk of Parkinson disease. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havulinna, A.S.; Tienari, P.J.; Marttila, R.J.; Martikainen, K.K.; Eriksson, J.G.; Taskinen, O.; Moltchanova, E.; Karvonen, M. Geographical variation of medicated parkinsonism in Finland during 1995 to 2000. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Kaasinen, V. No Change in the Age-Adjusted Incidence of Parkinson’s Disease in Finland for More Than 25 Years. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 2116–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadastik-Eerme, L.; Taba, N.; Asser, T.; Taba, P. Incidence and Mortality of Parkinson’s Disease in Estonia. Neuroepidemiology 2019, 53, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kytövuori, L.; Sipilä, J.; Doi, H.; Hurme-Niiranen, A.; Siitonen, A.; Koshimizu, E.; Miyatake, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Tanaka, F.; Majamaa, K. Biallelic expansion in RFC1 as a rare cause of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylikotila, P.; Sipilä, J.; Alapirtti, T.; Ahmasalo, R.; Koshimizu, E.; Miyatake, S.; Hurme-Niiranen, A.; Siitonen, A.; Doi, H.; Tanaka, F.; et al. Association of biallelic RFC1 expansion with early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martikainen, M.H.; Päivärinta, M.; Hietala, M.; Kaasinen, V. Clinical and imaging findings in Parkinson disease associated with the A53E SNCA mutation. Neurol. Genet. 2015, 1, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanen, P.; Palin, E.; Pohjolan-Pirhonen, R.; Pöyhönen, M.; Rinne, J.O.; Päivärinta, M.; Martikainen, M.H.; Kaasinen, V.; Hietala, M.; Gardberg, M.; et al. SNCA mutation p.Ala53Glu is derived from a common founder in the Finnish population. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 50, 168.e5–168.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaasinen, V.; Hietala, M.; Kuoppamäki, M. PARK2-geenin mutaatioon liittyvä Parkinsonin tauti. Duodecim 2015, 131, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Sipilä, J.O.T.; Kytövuori, L.; Rauramaa, T.; Rauhamaa, H.; Kaasinen, V.; Majamaa, K. A severe neurodegenerative disease with Lewy bodies and a mutation in the glucocerebrosidase gene. NPJ Park. Dis. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paisán-Ruíz, C.; Evans, E.W.; Jain, S.; Xiromerisiou, G.; Gibbs, J.R.; Eerola, J.; Gourbali, V.; Hellström, O.; Duckworth, J.; Papadimitriou, A.; et al. Testing association between LRRK2 and Parkinson’s disease and investigating linkage disequilibrium. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Silva, R.; Greenfield, J.; Cook, A.; Bonney, H.; Vallortigara, J.; Hunt, B.; Giunti, P. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of the progressive ataxias. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 56–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walsh, S.; Merrick, R.; Brayne, C. Tackling the burden of stroke with primordial prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1061. [Google Scholar]
- James, L.M.; Georgopoulos, A.P. High Correlations among Worldwide Prevalences of Dementias, Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, and Motor Neuron Diseases Indicate Common Causative Factors. Neurosci. Insights 2022, 17, 26331055221117598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, J.O.T. Regarding: High Correlations among Worldwide Prevalences of Dementias, Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis and Motor Neuron Diseases Indicate Common Causative Factors. Neurosci. Insights 2022, 17, 26331055221129634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipilä, J.O.T. Should we rethink neurodegeneration? Explor. Neurosci. 2022, 1, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrogan, A.; Madle, G.C.; Seaman, H.E.; de Vries, C.S. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome worldwide. A systematic literature review. Neuroepidemiology 2009, 32, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; Mahjoub, Y.; Shaver, L.; Pringsheim, T. Prevalence and Incidence of Huntington’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, L.; Tikkanen, M.; Rantanen, K.; Aarnio, K.; Korhonen, A.; Saaros, A.; Laivuori, H.; Gissler, M.; Ijäs, P. Stroke in Pregnancy and Puerperium: Validated Incidence Trends With Risk Factor Analysis in Finland 1987–2016. Neurology 2021, 96, e2564–e2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joutsa, J.; Gardberg, M.; Röyttä, M.; Kaasinen, V. Diagnostic accuracy of parkinsonism syndromes by general neurologists. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipilä, J.O.T. Treatment Courses of Patients Newly Diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis in 2012–2018. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Moock, S.; Feng, Y.S.; Maeurer, M.; Dippel, F.W.; Kohlmann, T. Systematic literature review and validity evaluation of the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) and the Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite (MSFC) in patients with multiple sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reito, A.; Sanmark, E.; Tuovinen, T.; Seppälä, T.T.; Kuitunen, I.; Ponkilainen, V.; Ekman, E.; Kauppila, J.H. Enabler or suppressor?—Survey on the effects of the Act on the Secondary Use of Health and Social Data on medical research. Suom. Lääkäril 2022, 78, e30589. [Google Scholar]
- Sipilä, J.O.T. Rekisteritutkijan karu todellisuus. Suom. Lääkäril 2023, 79, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Laakso, S.M.; Viitala, M.; Kuusisto, H.; Sarasoja, T.; Hartikainen, P.; Atula, S.; Tienari, P.J.; Soilu-Hänninen, M. Multiple sclerosis in Finland 2018-Data from the national register. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2019, 140, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
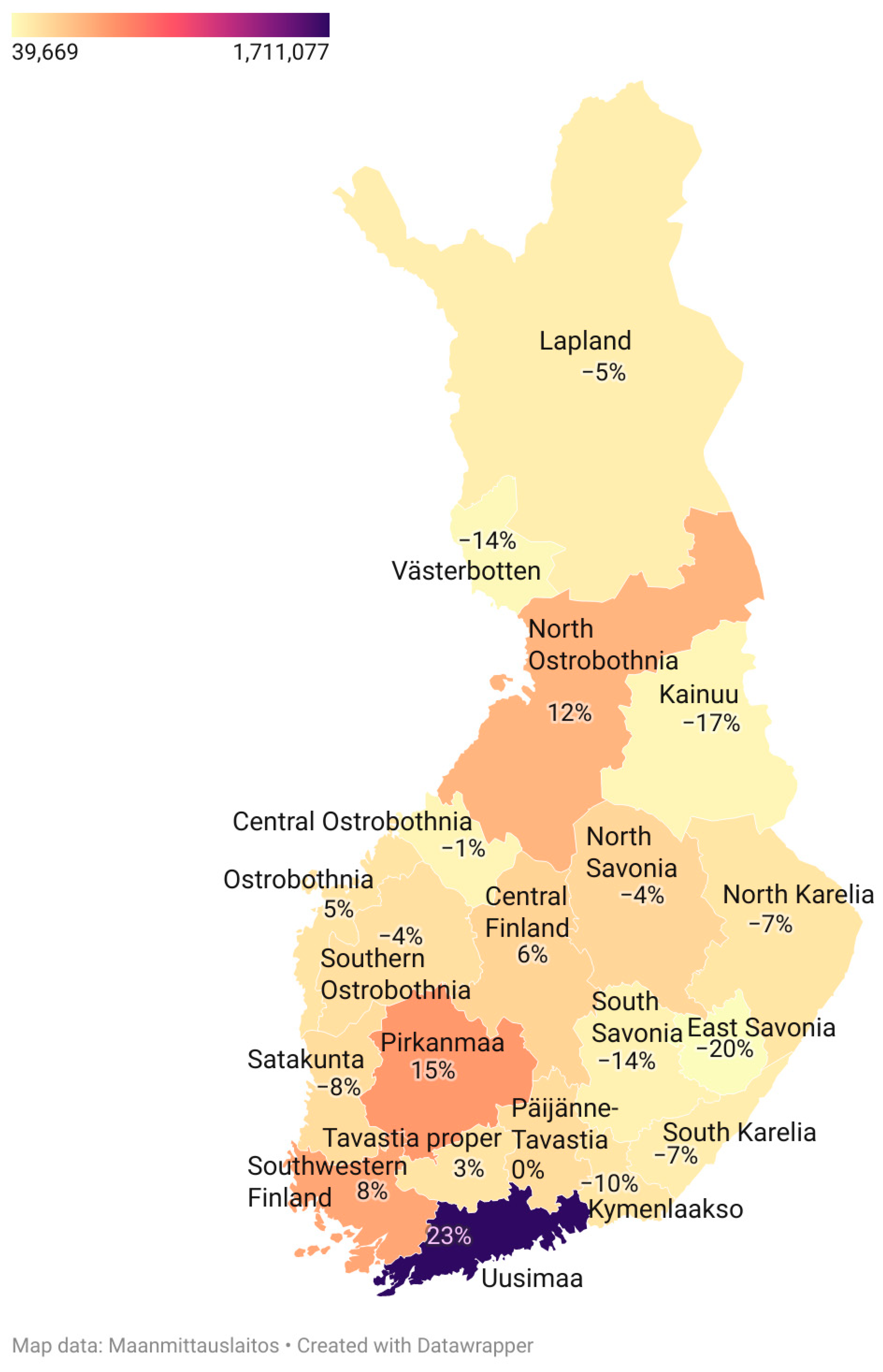


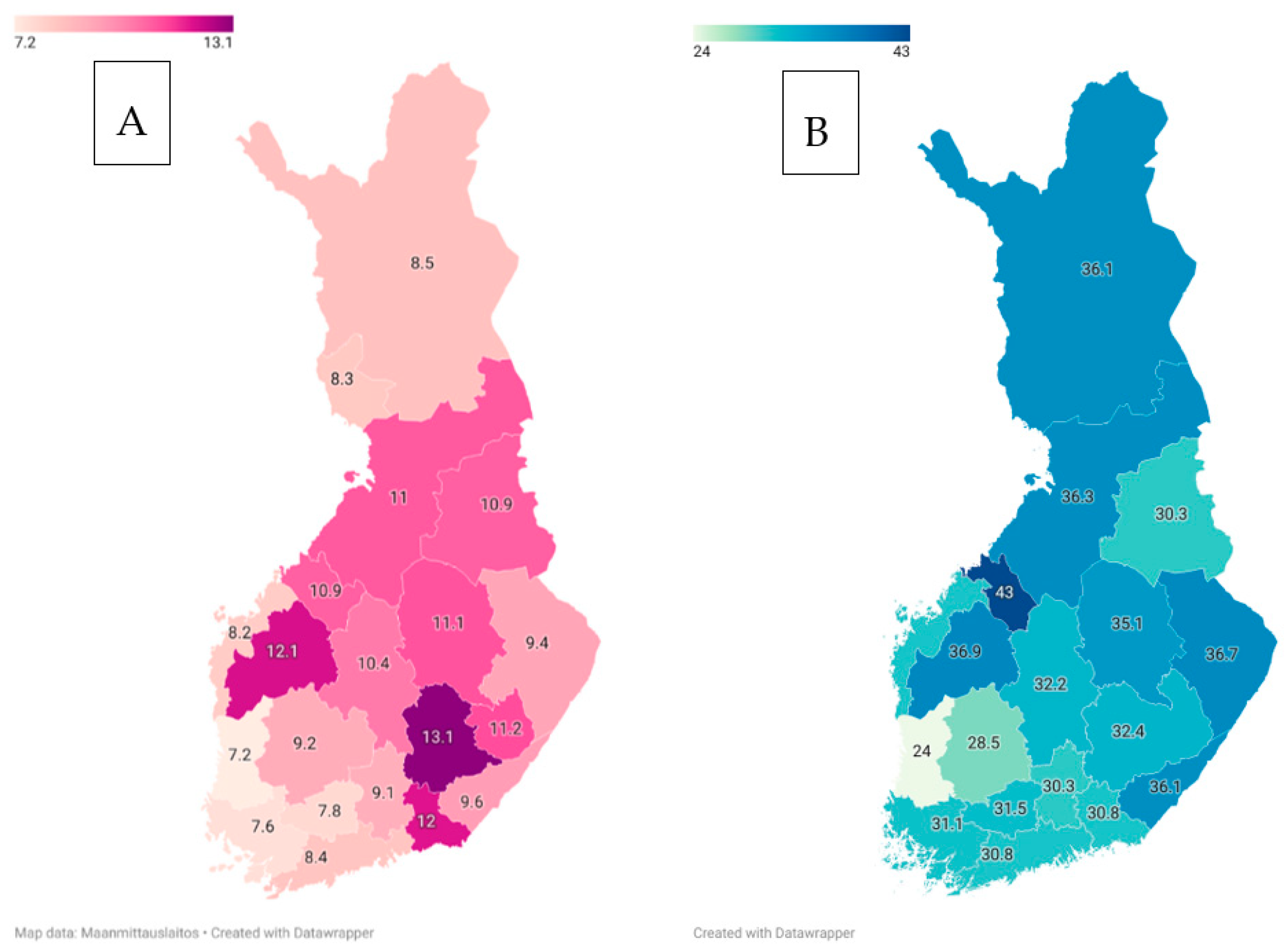
| Disorder | Approximate Incidence | Approximate Prevalence | Substantial within-Country Variation | Compared to Western European Populations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 8–12 | 150–300 | Yes | ↑ |
| GBS | 1 | ? | ? | ↔ |
| ALS | 5 | 11 | Yes | ↑ |
| AD | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| PD | 45 | 300? | Yes | ↔ |
| IS | ? | ? | Yes | ↑ |
| SAH | 9 | ? | Yes | ↑ |
| TBI | 350 | 610 | ? | ↔ |
| HD | 0.2 | 1.5–2.5 | No | ↓ |
| WD | 0.02 | 0.5 | No | ↓ |
| EPM1 | 0.02 | 1.5 | No | ↑ |
| FRDA | 0 | 0 | n.a. | ↓ |
| SCA3 | 0 | 0 | n.a. | ↓ |
| Disorder | N |
|---|---|
| Parkinson’s disease and comparable movement disorders | 16,400 |
| Epilepsy | 60,650 |
| Alzheimer’s disease | 61,165 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sipilä, J.O.T. Adult-Onset Neuroepidemiology in Finland: Lessons to Learn and Work to Do. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123972
Sipilä JOT. Adult-Onset Neuroepidemiology in Finland: Lessons to Learn and Work to Do. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123972
Chicago/Turabian StyleSipilä, Jussi O. T. 2023. "Adult-Onset Neuroepidemiology in Finland: Lessons to Learn and Work to Do" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123972
APA StyleSipilä, J. O. T. (2023). Adult-Onset Neuroepidemiology in Finland: Lessons to Learn and Work to Do. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123972






