Aortopathies: From Etiology to the Role of Arterial Stiffness
Abstract
:1. Aorta: Embryogenesis and Anatomy
1.1. Structure of the Aortic Wall
1.2. Embryological, Structural, and Mechanical Heterogeneity
1.3. Biochemical and Molecular Regulatory Systems
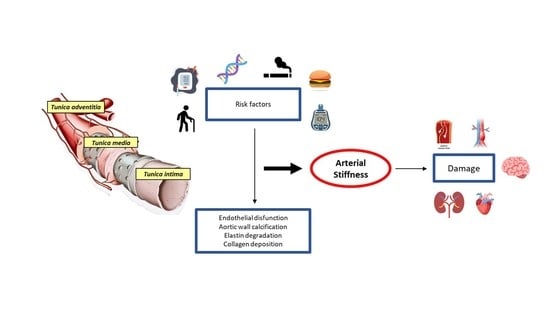
2. Causes of Aortic Disease
3. Aortopathies and Genetics
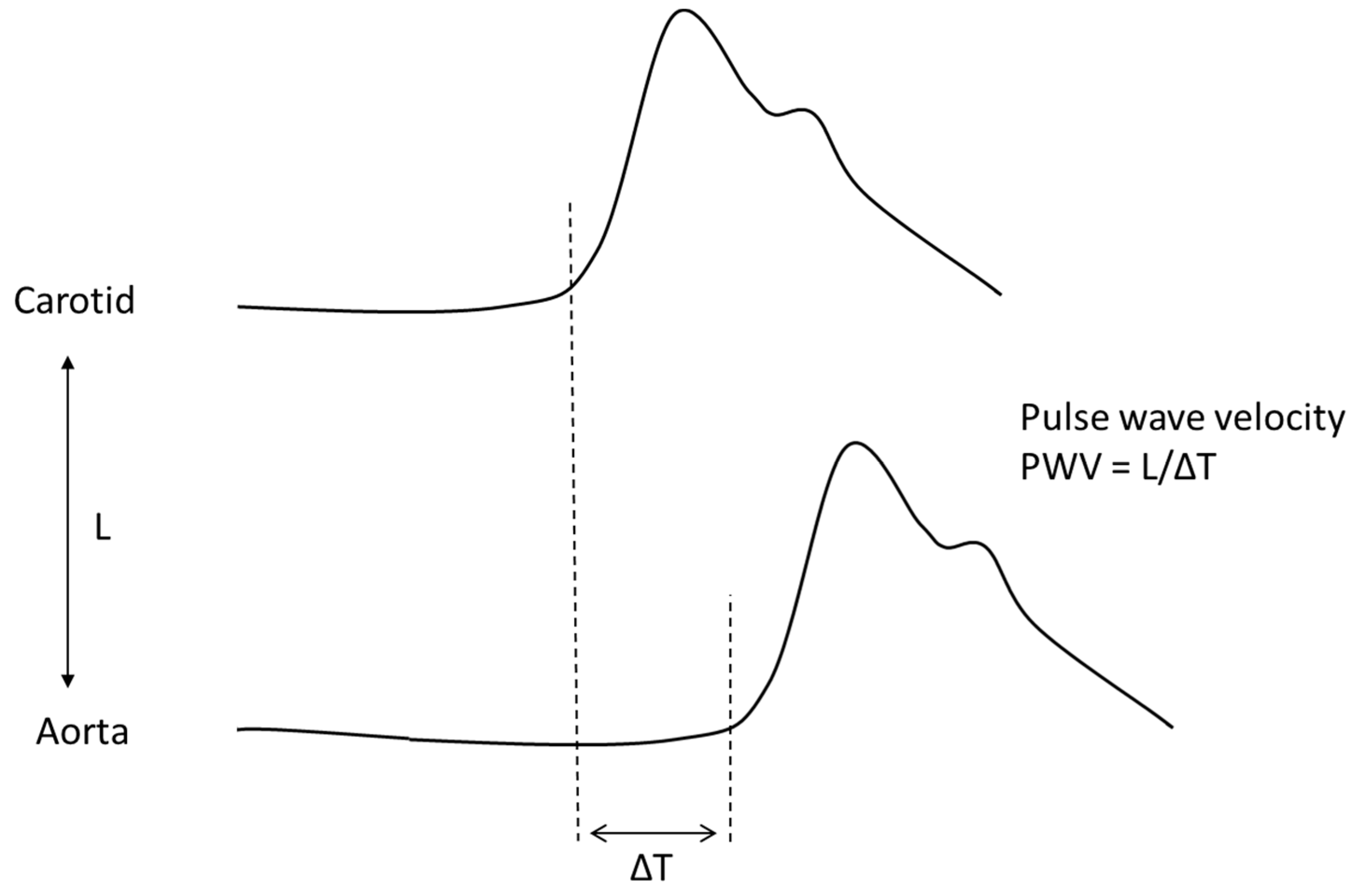
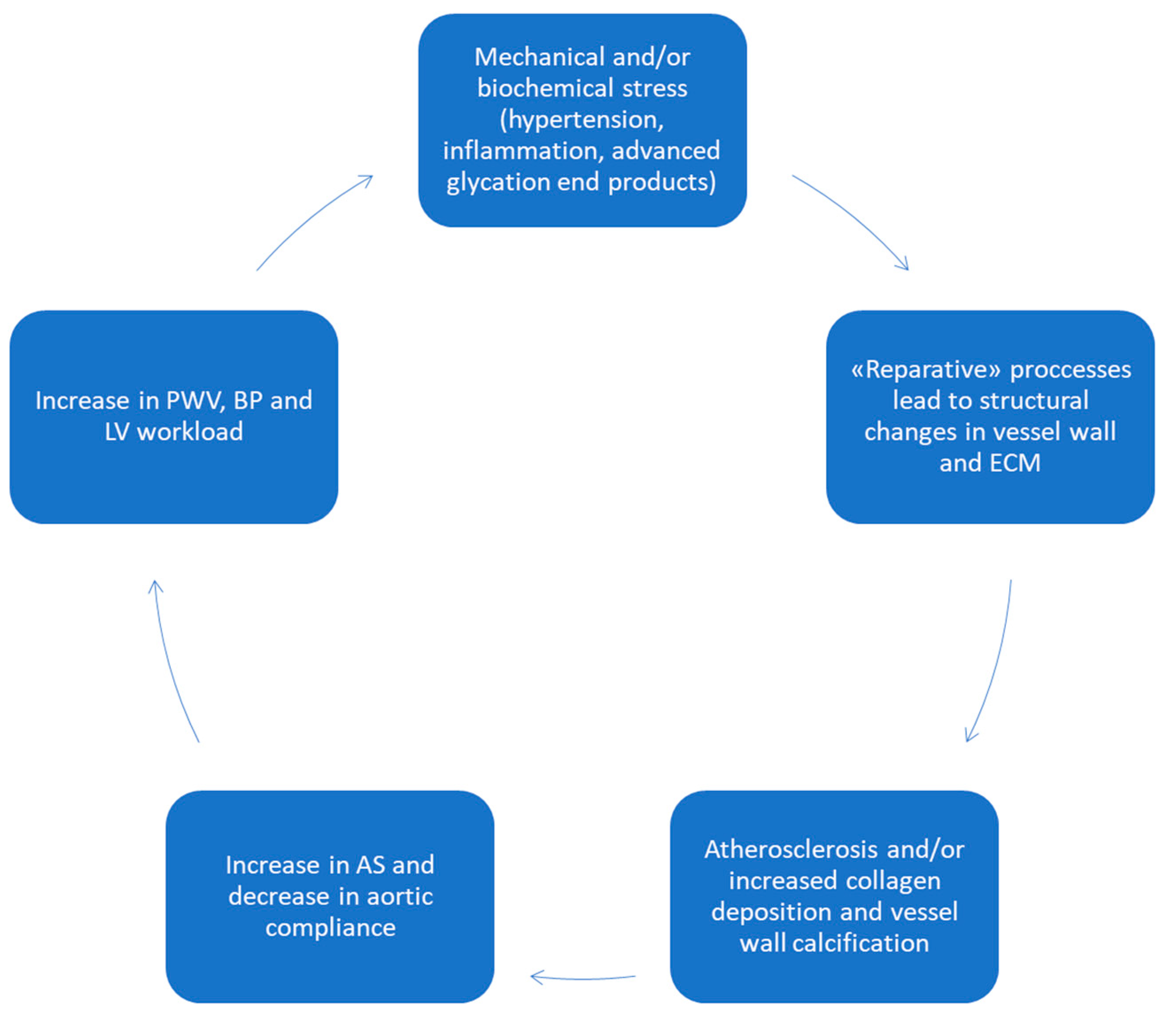
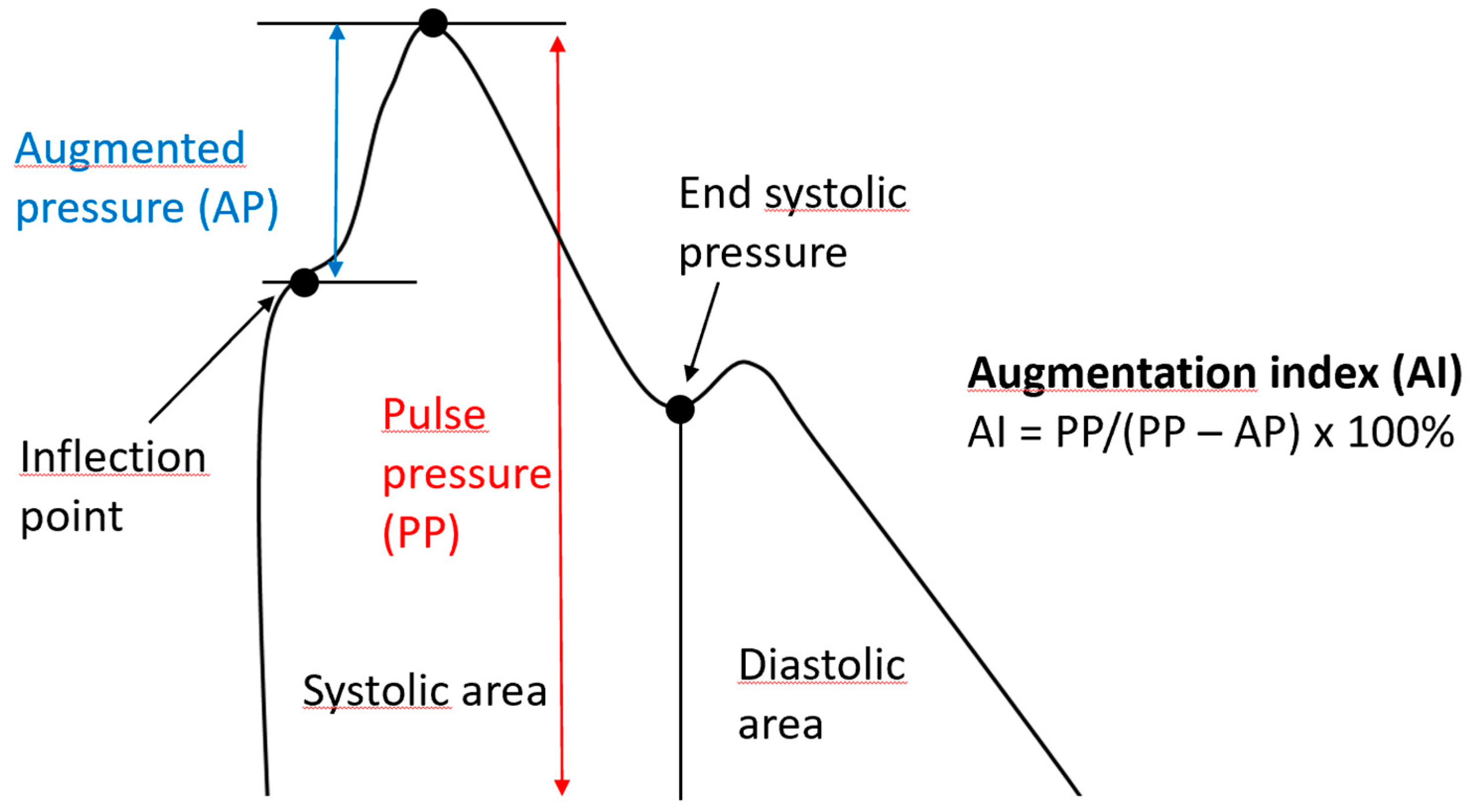
4. Aortic Wall Physiopathology and Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’amati, G.; Leone, O.; Nistri, S.; Roghi, A.; Angelini, A.; Basso, C.; Biagini, E.; Colombo, E.; Mele, D.; Pepe, G.; et al. Cambi di paradigma in tema di aorta: Implicazioni cliniche e terapeutiche La biopatologia dell’aorta. G. Ital. Cardiol. 2013, 14, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamamsy, I.; Yacoub, M.H. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of thoracic aortic aneurysms. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2009, 6, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolinsky, H.; Glagov, S. A Lamellar Unit of Aortic Medial Structure and Function in Mammals. Circ. Res. 1967, 20, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carman, C.V.; Springer, T.A. Structural Basis of Integrin Regulation and Signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 619–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Candales, A.; Holmes, D.R.; Liao, S.; Scott, M.J.; Wickline, S.A.; Thompson, R.W. Decreased vascular smooth muscle cell density in medial degeneration of human abdominal aortic aneurysms. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rowe, V.L.; Stevens, S.L.; Reddick, T.T.; Freeman, M.B.; Donnell, R.; Carroll, R.C.; Goldman, M.H. Vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in aneurysmal, occlusive, and normal human aortas. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, S.K.; Brooke, B.S.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Sorensen, L.; Wythe, J.D.; Schwartz, R.S.; Keating, M.T.; Li, D.Y. A critical role for elastin signaling in vascular morphogenesis and disease. Development 2003, 130, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamagishi, H. Cardiac Neural Crest. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2020, 13, a036715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddy, J.M.; Jones, J.A.; Spinale, F.G.; Ikonomidis, J.S. Regional heterogeneity within the aorta: Relevance to aneurysm disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 136, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolinsky, H. Comparison of Medial Growth of Human Thoracic and Abdominal Aortas. Circ. Res. 1970, 27, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goumans, M.-J.; Liu, Z.; Dijke, P.T. TGF-β signaling in vascular biology and dysfunction. Cell Res. 2008, 19, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keser, G. Inflammation-Induced Thrombosis: Mechanisms, Disease Associations and Management. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1478–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, D.; Dietz, H.C.; Oswald, G.L.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Halushka, M.K. Causes and histopathology of ascending aortic disease in children and young adults. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2011, 20, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allaire, E.; Schneider, F.; Saucy, F.; Dai, J.; Cochennec, F.; Michineau, S.; Zidi, M.; Becquemin, J.-P.; Kirsch, M.; Gervais, M. New Insight in Aetiopathogenesis of Aortic Diseases. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2009, 37, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, J.R.; Bruneval, P.; Angelini, A.; Bartoloni, G.; Basso, C.; Batoroeva, L.; Buja, L.M.; Butany, J.; D’Amati, G.; Fallon, J.T.; et al. Consensus statement on surgical pathology of the aorta from the Society for Cardiovascular Pathology and the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology: I. Inflammatory diseases. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2015, 24, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halushka, M.K.; Angelini, A.; Bartoloni, G.; Basso, C.; Batoroeva, L.; Bruneval, P.; Buja, L.M.; Butany, J.; D’Amati, G.; Fallon, J.T.; et al. Consensus statement on surgical pathology of the aorta from the Society for Cardiovascular Pathology and the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology: II. Noninflammatory degenerative diseases—Nomenclature and diagnostic criteria. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2016, 25, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, M.E.; Dietz, H.C. Lessons on the pathogenesis of aneurysm from heritable conditions. Nature 2011, 473, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyal, A.; Keramati, A.R.; Czarny, M.J.; Resar, J.R.; Mani, A. The Genetics of Aortopathies in Clinical Cardiology. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2017, 11, 1179546817709787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, H.C.; Cutting, C.R.; Pyeritz, R.E.; Maslen, C.L.; Sakai, L.Y.; Corson, G.M.; Puffenberger, E.G.; Hamosh, A.; Nanthakumar, E.J.; Curristin, S.M.; et al. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation. Nature 1991, 352, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.C.S. Marfan syndrome: Clinical diagnosis and management. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 15, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, N.C.; Tran, J.R.; Bektas, A. Marfan’s syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 1978–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isekame, Y.; Gati, S.; Aragon-Martin, J.A.; Bastiaenen, R.; Seshasai, S.R.K.; Child, A. Cardiovascular Management of Adults with Marfan Syndrome. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2016, 11, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milewicz, D.M.; Dietz, H.C.; Miller, D.C. Treatment of Aortic Disease in Patients with Marfan Syndrome. Circulation 2005, 111, e150–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detaint, D.; Michelena, H.I.; Nkomo, V.T.; Vahanian, A.; Jondeau, G.; Sarano, M.E. Aortic dilatation patterns and rates in adults with bicuspid aortic valves: A comparative study with Marfan syndrome and degenerative aortopathy. Heart 2013, 100, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loeys, B.L.; Dietz, H.C.; Braverman, A.C.; Callewaert, B.L.; De Backer, J.; Devereux, R.B.; Hilhorst-Hofstee, Y.; Jondeau, G.; Faivre, L.; Milewicz, D.M.; et al. The revised Ghent nosology for the Marfan syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verstraeten, A.; Alaerts, M.; Van Laer, L.; Loeys, B. Marfan Syndrome and Related Disorders: 25 Years of Gene Discovery. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Alom, S.; BinSaeid, J.; Harky, A. Loeys–Dietz syndrome pathology and aspects of cardiovascular management: A systematic review. Vascular 2020, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCarrick, G.; Black, J.H.; Bowdin, S.; El-Hamamsy, I.; Frischmeyer-Guerrerio, P.A.; Guerrerio, A.L.; Sponseller, P.D.; Loeys, B.; Dietz, H.C. Loeys–Dietz syndrome: A primer for diagnosis and management. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Yagi, H.; Hara, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Fujita, D.; Nawata, K.; Inuzuka, R.; Taniguchi, Y.; Harada, M.; Toko, H.; et al. Pathophysiology and Management of Cardiovascular Manifestations in Marfan and Loeys–Dietz Syndromes. Int. Heart J. 2016, 57, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loeys, B.L.; Schwarze, U.; Holm, T.; Callewaert, B.L.; Thomas, G.H.; Pannu, H.; De Backer, J.F.; Oswald, G.L.; Symoens, S.; Manouvrier, S.; et al. Aneurysm Syndromes Caused by Mutations in the TGF-β Receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfait, F.; Francomano, C.; Byers, P.; Belmont, J.; Berglund, B.; Black, J.; Bloom, L.; Bowen, J.M.; Brady, A.F.; Burrows, N.P.; et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byers, P.H.; Belmont, J.; Black, J.; De Backer, J.; Frank, M.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Johnson, D.; Pepin, M.; Robert, L.; Sanders, L.; et al. Diagnosis, natural history, and management in vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marom, R.; Rabenhorst, B.M.; Morello, R. Management of Endocrine Disease: Osteogenesis imperfecta: An update on clinical features and therapies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, R95–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J.C.; Forlino, A.; Bächinger, H.P.; Bishop, N.J.; Byers, P.H.; De Paepe, A.; Fassier, F.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Kozloff, K.M.; Krakow, D.; et al. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Niemelä, K.; Kuusinen, P.; Tarkka, M. Coronary artery dissection, combined aortic valve replacement and coronary bypass grafting in osteogenesis imperfecta. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 1, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyens, A.; Albuisson, J.; Boel, A.; Al-Essa, M.; Al-Manea, W.; Bonnet, D.; Bostan, O.; Boute, O.; Busa, T.; Canham, N.; et al. Arterial tortuosity syndrome: 40 new families and literature review. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhandari, R.; Aatre, R.D.; Kanthi, Y. Diagnostic approach and management of genetic aortopathies. Vasc. Med. 2020, 25, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-C.; Papke, C.L.; Tran-Fadulu, V.; Regalado, E.S.; Avidan, N.; Johnson, R.J.; Kim, D.H.; Pannu, H.; Willing, M.C.; Sparks, E.; et al. Mutations in Smooth Muscle Alpha-Actin (ACTA2) Cause Coronary Artery Disease, Stroke, and Moyamoya Disease, Along with Thoracic Aortic Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siu, S.C.; Silversides, C.K. Bicuspid Aortic Valve Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2789–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bossone, E.; Eagle, K.A. Epidemiology and management of aortic disease: Aortic aneurysms and acute aortic syndromes. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 18, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, N.; Smelt, J.; Jahangiri, M. Bicuspid aortic valve aortopathy: Genetics, pathophysiology and medical therapy. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 17, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepe, G.; Giusti, B.; Attanasio, M.; Comeglio, P.; Porciani, M.C.; Giurlani, L.; Montesi, G.F.; Calamai, G.C.; Vaccari, M.; Favilli, S.; et al. A Major Involvement of the Cardiovascular System in Patients Affected by Marfan Syndrome: Novel Mutations in Fibrillin 1 Gene. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1997, 29, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini-Canterin, F.; Carerj, S.; Di Bello, V.; Di Salvo, G.; La Carrubba, S.; Vriz, O.; Pavan, D.; Balbarini, A.; Nicolosi, G.L.; On behalf of the Research Group of the Italian Society of Cardiovascular Echography (SIEC). Arterial stiffness and ventricular stiffness: A couple of diseases or a coupling disease? A review from the cardiologist’s point of view. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2009, 10, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanoli, L.; Lentini, P.; Briet, M.; Castellino, P.; House, A.A.; London, G.M.; Malatino, L.; McCullough, P.A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Boutouyrie, P. Arterial Stiffness in the Heart Disease of CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcante, J.; Lima, J.A.; Redheuil, A.; Al-Mallah, M. Aortic Stiffness: Current understanding and future directions. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Bortel, L.M.; Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Chowienczyk, P.; Cruickshank, J.; De Backer, T.; Filipovsky, J.; Huybrechts, S.; Mattace-Raso, F.U.; Protogerou, A.; et al. Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najjar, S.S.; Scuteri, A.; Shetty, V.; Wright, J.G.; Muller, D.C.; Fleg, J.L.; Spurgeon, H.P.; Ferrucci, L.; Lakatta, E.G. Pulse Wave Velocity Is an Independent Predictor of the Longitudinal Increase in Systolic Blood Pressure and of Incident Hypertension in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stacey, R.B.; Bertoni, A.G.; Eng, J.; Bluemke, D.A.; Hundley, W.G.; Herrington, D. Modification of the Effect of Glycemic Status on Aortic Distensibility by Age in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Hypertension 2010, 55, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancia, G.; De Backer, G.; Dominiczak, A.; Cífková, R.; Fagard, R.; Germano, G.; Grassi, G.; Heagerty, A.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Laurent, S.; et al. 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos, J.A.; Segers, P.; Hughes, T.; Townsend, R. Large-Artery Stiffness in Health and Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1237–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutouyrie, P.; Chowienczyk, P.; Humphrey, J.D.; Mitchell, G.F. Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 864–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, R.; Gidaro, A.; Casu, G.; Merella, P.; Profili, N.I.; Donadoni, M.; Maioli, M.; Delitala, A.P. Aging of the Arterial System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tougaard, N.H.; Theilade, S.; Winther, S.A.; Tofte, N.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Hansen, T.W.; Rossing, P.; Frimodt-Møller, M. Carotid-Femoral Pulse Wave Velocity as a Risk Marker for Development of Complications in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Clemente, J.-M.; Cano, A.; Albert, L.; Giménez-Palop, O.; Romero, A.; Berlanga, E.; Vendrell, J.; Llauradó, G. Arterial Stiffness in Type 1 Diabetes: The Case for the Arterial Wall Itself as a Target Organ. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson, S.S.; Butlin, M.; Graves, M.; Taviani, V.; Avolio, A.P.; McEniery, C.M.; Wilkinson, I.B. The Relationship of Age with Regional Aortic Stiffness and Diameter. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Aznaouridis, K.; Stefanadis, C. Prediction of Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality With Arterial Stiffness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armentano, R.L.; Barra, J.G.; Levenson, J.; Simon, A.; Pichel, R.H. Arterial Wall Mechanics in Conscious Dogs. Circ. Res. 1995, 76, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, L.; Blaise, S.; Romier, B.; Laffargue, M.; Gayral, S.; El Btaouri, H.; Kawecki, C.; Guillot, A.; Martiny, L.; Debelle, L.; et al. Matrix ageing and vascular impacts: Focus on elastin fragmentation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, T. Atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. Hypertens. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, I.B.; MacCallum, H.; Flint, L. The influence of heart rate on augmentation index and central arterial pressure in hu-mans. J. Physiol. 2000, 525 Pt 1, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Shao, L.; Zhu, M. Central Aortic Systolic Blood Pressure Exhibits Advantages Over Brachial Blood Pressure Measurements in Chronic Kidney Disease Risk Prediction in Women. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.R.; Stepanek, J.; Cevette, M.; Covalciuc, M.; Hurst, R.T.; Tajik, A.J. Noninvasive Measurement of Central Vascular Pressures with Arterial Tonometry: Clinical Revival of the Pulse Pressure Waveform? Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roman, M.J.; Devereux, R.B.; Kizer, J.R.; Lee, E.T.; Galloway, J.M.; Ali, T.; Umans, J.G.; Howard, B.V. Central Pressure More Strongly Relates to Vascular Disease and Outcome Than Does Brachial Pressure: The Strong Heart Study. Hypertension 2007, 50, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nistri, S.; Grande-Allen, J.; Noale, M.; Basso, C.; Siviero, P.; Maggi, S.; Crepaldi, G.; Thiene, G. Aortic elasticity and size in bicuspid aortic valve syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safar, M.E.; London, G.M.; Plante, G.E. Arterial Stiffness and Kidney Function. Hypertension 2004, 43, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyasirinant, T.; Rajiah, P.; Setser, R.M.; Lieber, M.L.; Lever, H.M.; Desai, M.Y.; Flamm, S.D. Aortic Stiffness Is Increased in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Myocardial Fibrosis: Novel Insights in Vascular Function from Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Muñoz, A.; Guala, A.; Dux-Santoy, L.; Teixidó-Turà, G.; Servato, M.L.; Valente, F.; Garrido-Oliver, J.; Galian-Gay, L.; Gutiérrez, L.; Fernandez-Galera, R.; et al. False lumen rotational flow and aortic stiffness are associated with aortic growth rate in patients with chronic aortic dissection of the descending aorta: A 4D flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2022, 24, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, I.; Kazaz, Z.; Altun, G.; Cansu, A. Augmentation index and aortic pulse wave velocity in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.X.; Luo, J.; Balaram, S.K.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Shahmirzadi, D.; Konofagou, E.E. Pulse wave imaging in normal, hypertensive and aneurysmal human aortas in vivo: A feasibility study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 4549–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, M.A.; Davies, J.M.; Griffin, K.J.; Bridge, K.I.; Johnson, A.B.; Sohrabi, S.; Baxter, P.D.; Scott, D.J.A. Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity is negatively correlated with aortic diameter. Hypertens. Res. 2014, 37, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The CAFE Investigators; Williams, B.; Lacy, P.; Thom, S.M.; Cruickshank, K.; Stanton, A.; Collier, D.; Hughes, A.; Thurston, H.; O’rourke, M.; et al. Differential Impact of Blood Pressure–Lowering Drugs on Central Aortic Pressure and Clinical Outcomes: Principal results of the Conduit Artery Function Evaluation (CAFE) study. Circulation 2006, 113, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetos, A.; Vasmant, D.; Thièry, P.; Safar, M. Effects of Ramipril on Arterial Hemodynamics. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1991, 18, S153–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesen, W.F.; Beltman, F.W.; Smit, A.J.; May, J.F.; De Graeff, P.A.; Muntinga, J.H.J.; Havinga, T.K.; Schuurman, F.H.; Van Der Veur, E.; Jong, B.M.-D.; et al. Reversal of Pathophysiologic Changes with Long-Term Lisinopril Treatment in Isolated Systolic Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2001, 37, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.F.; Dunlap, M.E.; Warnica, W.; Ducharme, A.; Arnold, J.M.O.; Tardif, J.-C.; Solomon, S.D.; Domanski, M.J.; Jablonski, K.A.; Rice, M.M.; et al. Long-Term Trandolapril Treatment Is Associated with Reduced Aortic Stiffness: The prevention of events with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition hemodynamic substudy. Hypertension 2007, 49, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schierling, W.; Matzner, J.; Apfelbeck, H.; Grothues, D.; Oberhoffer-Fritz, R.; Pfister, K. Pulse Wave Velocity for Risk Stratification of Patients with Aortic Aneurysm. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, G.M.; Asmar, R.G.; O’Rourke, M.F.; Safar, M.E. Mechanism(s) of selective systolic blood pressure reduction after a low-dose combination of perindopril/Indapamide in hypertensive subjects: Comparison with atenolol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Porteri, E.; Rizzoni, D. Arterial stiffness, hypertension, and rational use of nebivolol. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, B.; Lacy, P.S. Impact of Heart Rate on Central Aortic Pressures and Hemodynamics. Analysis From the CAFE (Conduit Artery Function Evaluation) Study: CAFE-Heart Rate. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirro, M.; Schillaci, G.; Mannarino, M.R.; Savarese, G.; Vaudo, G.; Siepi, D.; Paltriccia, R.; Mannarino, E. Effects of rosuvastatin on 3-nitrotyrosine and aortic stiffness in hypercholesterolemia. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 17, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, M.; Mahmud, A.; Feely, J. Advanced Glycation End-Products and Arterial Stiffness in Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldin, A.; Beckman, J.A.; Schmidt, A.M.; Creager, M.A. Advanced Glycation End Products: Sparking the Development of Diabetic Vascular Injury. Circulation 2006, 114, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batzias, K.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Siasos, G.; Bletsa, E.; Stampouloglou, P.K.; Mistakidi, C.-V.; Noutsou, M.; Katsiki, N.; Karopoulos, P.; et al. Effects of Newer Antidiabetic Drugs on Endothelial Function and Arterial Stiffness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1232583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Pavlidis, G.; Thymis, J.; Birba, D.; Kalogeris, A.; Kousathana, F.; Kountouri, A.; Balampanis, K.; Parissis, J.; Andreadou, I.; et al. Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors, and Their Combination on Endothelial Glycocalyx, Arterial Function, and Myocardial Work Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus After 12-Month Treatment. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chilton, R.; Tikkanen, I.; Cannon, C.P.; Crowe, S.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Johansen, O.E. Effects of empagliflozin on blood pressure and markers of arterial stiffness and vascular resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 1180–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.-Y.; Park, K.-Y.; Kim, J.-D.; Hwang, W.-M.; Lim, D.-M. Effects of 6 Months of Dapagliflozin Treatment on Metabolic Profile and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction for Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients without Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 29, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugajin, A.; Iwakoshi, S.; Ichihashi, S.; Inoue, T.; Nakai, T.; Kishida, H.; Chanoki, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Mori, H.; Kichikawa, K. Prediction of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth After Endovascular Aortic Repair by Measuring Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 81, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishibe, T.; Kano, M.; Maekawa, K.; Akiyama, S.; Nukaga, S.; Koizumi, J.; Dardik, A.; Ogino, H. Association of preoperative pulse wave velocity to aneurysm sac shrinkage after endovascular aneurysm repair. Int. Angiol. 2021, 40, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaccio, C.; Nappi, F.; Al-Attar, N.; Sutherland, F.W.; Acar, C.; Nenna, A.; Trombetta, M.; Chello, M.; Rainer, A. Old Myths, New Concerns: The Long-Term Effects of Ascending Aorta Replacement with Dacron Grafts. Not All That Glitters Is Gold. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2016, 9, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hori, D.; Kusadokoro, S.; Mieno, M.N.; Fujimori, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kimura, N.; Yamaguchi, A. The effect of aortic arch replacement on pulse wave velocity after surgery. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 34, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pathology | Transmission | Mutated Gene; Protein and Its Function | Cardiovascular Clinical Features | Other Clinical Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marfan Syndrome type 1 | AD | FBN-1; fibrillin-1, structural component of microfibrils of ECM | Aortic root and ascending aorta dilatation, aneurysm, and dissection. Other features can include mitral valve prolapse or mitral valve calcification | Ectopia lentis, skin and skeletal manifestation, pneumothorax |
| Marfan Syndrome type 2 | AD | FBN-1; fibrillin-1. TGFBR 1 and 2; receptors in the TGF-β pathway that have a crucial role in ECM production and differentiation | Aortic root and ascending aorta dilatation, aneurysm, and dissection | Skeletal manifestation, but no ectopia lentis |
| MASS | AD | FBN-1; fibrillin-1 | Mitral valve prolapse, aortic dilation without aneurysm formation | Nonspecific skin and skeletal marfanoid features, but no ectopia lentis |
| Loeys–Dietz Syndrome | AD | TGFBR 1 and 2 | Arterial tortuosity with rapidly progressive aortic aneurysms | Hypertelorism, bifid/broad uvula, or cleft palate |
| Vascular Ehlers–Danlos syndromes | AD | COL3A1 (more frequent); type III collagen COL1A1; type I collagen | Arterial fragility with aneurysm development, dissection, and rupture. Possible cardiac valve involvement | Skin and skeletal features, organ fragility, extensive bruising, and pneumothorax |
| Osteogenesis imperfecta | AD | COL1A1 and 2; type I collagen | Aortic dilatation and dissection, cardiac valve regurgitation | Scarce skeletal development is associated with bone fragility and smaller stature, blue sclerae, and hyperextensible ligaments |
| Arterial tortuosity syndrome (ATS) | AR | SLC2A10; GLUT10, that is linked with the TGF-β pathway | Tortuosity of the aorta and mid-sized arteries, as well as focal stenosis of segments of the pulmonary arteries and/or aorta | Atypical skin and skeletal features |
| Non syndromic aneurysm/dissection | / | NOTCH1; Nocht1, is important in cardiovascular embryogenesis. ACTA2; actin, a cytoskeletal protein MYH11; myosin, a cytoskeletal protein FBN-1; fibrillin TGFBR 1 and 2 | Aortic dilatation and/or aneurysm, bicuspid aortic valve | No systemic manifestation |
| Index | Definition | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Volume compliance | Change in arterial volume relative to the change in arterial pressure (influenced by wall stiffness, arterial size, and wall thickness) | ΔV/ΔP (mL/mmHg) |
| Arterial compliance | Area change for a given pressure step at fixed vessel length, estimation of compliance based on cross-sectional (rather than volume) measurements. | ΔD/ΔP (cm/mmHg) or (cm2/mmHg) |
| Arterial distensibility | Fractional change in cross-sectional area relative to the change in arterial pressure | (ΔD/ΔP × D) (mmHg−1) |
| Pulse wave velocity | Speed at which the arterial pulse propagates in the arteries (usually carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity) | PWV = √1/pDC (m/s) |
| Augmentation Index | The difference between the second and first systolic peaks as a percentage of pulse pressure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonfioli, G.B.; Rodella, L.; Rosati, R.; Carrozza, A.; Metra, M.; Vizzardi, E. Aortopathies: From Etiology to the Role of Arterial Stiffness. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123949
Bonfioli GB, Rodella L, Rosati R, Carrozza A, Metra M, Vizzardi E. Aortopathies: From Etiology to the Role of Arterial Stiffness. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123949
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonfioli, Giovanni Battista, Luca Rodella, Roberta Rosati, Alberto Carrozza, Marco Metra, and Enrico Vizzardi. 2023. "Aortopathies: From Etiology to the Role of Arterial Stiffness" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123949
APA StyleBonfioli, G. B., Rodella, L., Rosati, R., Carrozza, A., Metra, M., & Vizzardi, E. (2023). Aortopathies: From Etiology to the Role of Arterial Stiffness. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123949