The Effect of Cadmium on Sleep Parameters Assessed in Polysomnographic Studies: A Case–Control Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Polysomnography
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination of Blood and Urine Cadmium Concentration
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Evidence for Role of Cadmium in OSA
4.2. The Influence of Cadmium on Sleep Bruxism (SB) Intensity
4.3. Evidence for the Role of Cadmium in Sleep Architecture Alterations
4.4. Study Strengths
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
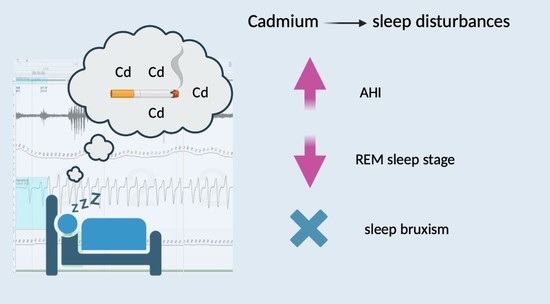
- Cadmium is an independent factor for increased AHI, similarly to age, gender and smoking status.
- Cadmium is not a risk factor for sleep bruxism.
- Cadmium favors sleep disturbances, including sleep fragmentation, and results in the limitation of the duration of the REM sleep stage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Cadmium. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp5.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Ishizaki, M.; Suwazono, Y.; Kido, T.; Nishijo, M.; Honda, R.; Kobayashi, E.; Nogawa, K.; Nakagawa, H. Estimation of Biological Half-Life of Urinary Cadmium in Inhabitants after Cessation of Environmental Cadmium Pollution Using a Mixed Linear Model. Food Addit. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, P.; Faroon, O.; Pappas, R.S. Cadmium and Cadmium/Zinc Ratios and Tobacco-Related Morbidities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2017, 14, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, H.S.; Kang, H.T. Cigarette Smoking in Men and Women and Electronic Cigarette Smoking in Men Are Associated with Higher Risk of Elevated Cadmium Level in the Blood. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Zhang, Q.C.; Yan, C.A.; Tang, G.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Ma, L.Q.; Gu, R.H.; Xiang, P. Heavy metal(loid)s in agriculture soils, rice, and wheat across China: Status assessment and spatiotemporal analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérida-ortega, Á.; López-carrillo, L.; Rangel-moreno, K.; Ramirez, N.; Rothenberg, S.J. Tobacco Smoke Exposure and Urinary Cadmium in Women from Northern Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Kumar, A.; Lal, A.; Pant, M. Cellular Mechanisms of Cadmium-Induced Toxicity: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2014, 24, 378–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, E.; Figueroa, S.; Oset-Gasque, M.J.; González, M.P. Apoptosis and Necrosis: Two Distinct Events Induced by Cadmium in Cortical Neurons in Culture. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Morucci, G.; Pacini, A. Cadmium-Induced Neurotoxicity: Still Much Ado. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wallin, M.; Barregard, L.; Sallsten, G.; Lundh, T.; Ohlsson, C.; Mellström, D.; Andersson, E.M. Smoking-Induced Risk of Osteoporosis Is Partly Mediated by Cadmium from Tobacco Smoke: The MrOS Sweden Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scinicariello, F.; Buser, M.C. Blood Cadmium and Depressive Symptoms in Young Adults (Aged 20–39 Years). Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buser, M.C.; Scinicariello, F. Cadmium, Lead, and Depressive Symptoms: Analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, e515–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Fagerberg, B.; Sallsten, G.; Borné, Y.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G.; Barregard, L.; Andersson, E.M. Smoking-Induced Risk of Future Cardiovascular Disease Is Partly Mediated by Cadmium in Tobacco: Malmö Diet and Cancer Cohort Study. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salcedo-Bellido, I.; Gómez-Peña, C.; Pérez-Carrascosa, F.M.; Vrhovnik, P.; Mustieles, V.; Echeverría, R.; Fiket, Ž.; Pérez-Díaz, C.; Barrios-Rodríguez, R.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.J.; et al. Adipose Tissue Cadmium Concentrations as a Potential Risk Factor for Insulin Resistance and Future Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in GraMo Adult Cohort. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijo, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Suwazono, Y.; Nogawa, K.; Kido, T. Causes of Death in Patients with Itai-Itai Disease Suffering from Severe Chronic Cadmium Poisoning: A Nested Case–Control Analysis of a Follow-up Study in Japan. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, P.; Arcella, D.; Heraud, F.; Cappé, S.; Fabiansson, S. Impact of Refining the Assessment of Dietary Exposure to Cadmium in the European Adult Population. Food Addit. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for Scoring Respiratory Events in Sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2012, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sateia, M.J. International Classification of Sleep Disorders-Third Edition. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeppler, M.; Brandt, K. Contributions to Automated Trace Analysis—Part V. Determination of Cadmium in Whole Blood and Urine by Electrothermal Atomic-Absorption Spectrophotometry. Fresenius’ Z. Anal. Chem. 2009, 300, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adatia, A.; Wahab, M.; Shahid, I.; Moinuddin, A.; Killian, K.J.; Satia, I. Effects of Cigarette Smoke Exposure on Pulmonary Physiology, Muscle Strength and Exercise Capacity in a Retrospective Cohort with 30,000 Subjects. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asker, S.; Asker, M.; Yeltekin, A.C.; Aslan, M.; Demir, H. Serum Levels of Trace Minerals and Heavy Metals in Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients: Correlates and Clinical Implications. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrù, G.; Storari, M.; Scano, A.; Piras, V.; Taibi, R.; Viscuso, D. Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction—An Overview of Predictive Laboratory Biomarkers. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6939–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataka, A.; Kotoulas, S.; Kalamaras, G.; Tzinas, A.; Grigoriou, I.; Kasnaki, N.; Argyropoulou, P. Does Smoking Affect OSA? What about Smoking Cessation? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.S.; McSharry, D.G.; Malhotra, A. Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Lancet 2014, 383, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frosztega, W.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Nowacki, D.; Michalek-Zrabkowska, M.; Poreba, R.; Wojakowska, A.; Kanclerska, J.; Mazur, G.; Martynowicz, H. Polysomnographic Assessment of Effects of Tobacco Smoking and Alcohol Consumption on Sleep Bruxism Intensity. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieckiewicz, M.; Bogunia-Kubik, K.; Mazur, G.; Danel, D.; Smardz, J.; Wojakowska, A.; Poreba, R.; Dratwa, M.; Chaszczewska-Markowska, M.; Winocur, E.; et al. Genetic Basis of Sleep Bruxism and Sleep Apnea—Response to a Medical Puzzle. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzel, T.; Hahad, O.; Kuntic, M.; Keaney, J.F.; Deanfield, J.E.; Daiber, A. Effects of Tobacco Cigarettes, e-Cigarettes, and Waterpipe Smoking on Endothelial Function and Clinical Outcomes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, K.; Narkiewicz, K.; Leontsinis, I.; Konstantinidis, D.; Mihas, C.; Andrikou, I.; Thomopoulos, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Tsioufis, K. Acute Effects of Electronic and Tobacco Cigarette Smoking on Sympathetic Nerve Activity and Blood Pressure in Humans. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; Bindu, B.; Singh, G.P.; Schaller, B. Sleep Disorders: Is the Trigemino-Cardiac Reflex a Missing Link? Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unno, K.; Yamoto, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Kataoka, A.; Ozaki, T.; Mochizuki, T.; Honda, K.; Miura, N.; Ikeda, M. Acute Enhancement of Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep in Rats after Drinking Water Contaminated with Cadmium Chloride. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.E.; Nasseth, D.; Hungerford, S. Augmented Depression and Reduced Excitability of the Central Nervous System (CNS) by Cadmium in the Rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1985, 22, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristakesian, E.A.; Vataev, S.I.; Golubev, N.S.; Oganesian, G.A.; Slepian, E.I. The Effect of Cadmium on the EEG and the Representation of Different Forms of Wakefulness and Rest in the Frog Rana Temporaria in Its Diurnal Cycle. Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol. 1991, 27, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vataev, S.I.; Mal’gina, N.A.; Oganesian, G.A. The Effect of Cadmium on the Structure of the Circadian Cycle of Waking-Sleep and on the EEG in Wistar Rats. Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol. 1994, 30, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aristakesian, E.A.; Kiiashchenko, L.I.; Oganesian, G.A. The Effect of Cadmium on the Wakefulness—Sleep Cycle in Rats in Early Postnatal Ontogeny. Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol. 1996, 32, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pacini, S.; Fiore, M.G.; Magherini, S.; Morucci, G.; Branca, J.J.V.; Gulisano, M.; Ruggiero, M. Could Cadmium Be Responsible for Some of the Neurological Signs and Symptoms of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 79, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, R.; Williams, S.; Adamantidis, A. REM Sleep and Memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 44, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesta, D.; Socci, V.; De Gennaro, L.; Ferrara, M. Sleep and Emotional Processing. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 40, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.J. Sleep Fragmentation and Arousals from Sleep-Time Scales, Associations, and Implications. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korostovtseva, L.; Bochkarev, M.; Sviryaev, Y. Sleep and Cardiovascular Risk. Sleep Med. Clin. 2021, 16, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smereczański, N.M.; Brzóska, M.M. Current Levels of Environmental Exposure to Cadmium in Industrialized Countries as a Risk Factor for Kidney Damage in the General Population: A Comprehensive Review of Available Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Becker, K.; Friedrich, C.; Helm, D.; Krause, C.; Seifert, B. The German Environmental Survey 1990/1992 (GerES II): Cadmium in Blood, Urine and Hair of Adults and Children. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2000, 10, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Parameter | Average | Median | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHI (n/h) | 24.22 ± 25.34 | 14.85 | 0.50 | 86.20 |
| ODI (n/h) | 23.45 ± 24.11 | 13.65 | 0.00 | 86.70 |
| Snore (% of TST) | 25.79 ± 22.29 | 26.75 | 0.00 | 75.40 |
| Average SpO2 (%) | 91.57 ± 4.50 | 92.55 | 74.60 | 95.80 |
| Minimal SpO2 (%) | 79.82 ± 10.46 | 83.00 | 51.00 | 93.00 |
| SpO2 duration <90% (%) | 16.01 ± 25.02 | 4.10 | 0.00 | 86.60 |
| SL (min) | 19.97 ± 15.79 | 13.65 | 1.00 | 64.60 |
| WASO (min) | 59.03 ± 44.11 | 44.50 | 7.50 | 186.10 |
| SE (%) | 82.80 ± 12.24 | 85.25 | 36.50 | 97.40 |
| N1 (% of TST) | 7.14 ± 7.74 | 3.40 | 0.30 | 32.70 |
| N2 (% of TST) | 52.03 ± 21.45 | 50.30 | 28.60 | 181.00 |
| N3 (% of TST) | 25.37 ± 20.55 | 23.00 | 6.40 | 146.50 |
| REM (% of TST) | 21.31 ± 6.53 | 21.70 | 0.00 | 34.40 |
| ArI (n/h) | 7.96 ± 13.57 | 3.75 | 0.10 | 88.30 |
| BEI (n/h) | 4.17 ± 3.29 | 3.30 | 0.00 | 13.60 |
| Phasic bruxism episode index (n/h) | 1.79 ± 2.18 | 1.40 | 0.00 | 10.70 |
| Tonic bruxism episode index (n/h) | 1.60 ± 1.39 | 1.10 | 0.00 | 5.50 |
| Mixed bruxism episode index (n/h) | 0.81 ± 0.80 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 3.40 |
| AI (n/h) | 11.96 ± 17.80 | 3.05 | 0.00 | 69.20 |
| OA (n/h) | 9.89 ± 15.60 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 62.40 |
| MA (n/h) | 0.88 ± 2.39 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 14.20 |
| CA (n/h) | 1.19 ± 2.77 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 16.80 |
| HI (n/h) | 12.26 ± 12.15 | 8.35 | 0.10 | 50.60 |
| Average pulse (bpm) | 62.47 ± 8.83 | 61.35 | 48.70 | 94.40 |
| Maximal pulse (bpm) | 94.95 ± 14.28 | 96.50 | 64.00 | 140.00 |
| Minimal pulse (bpm) | 46.29 ± 11.37 | 48.00 | 4.60 | 71.0 |
| Paramerer | Average ≥ Me | Average < Me | p | Average ≥ Q1 | Average < Q1 | p | Average <Q3 | Average ≥Q3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cadmium blood concentration (µg/L) | 0.57 ± 0.46 | 0.14 ± 0.07 | 0.000 | 0.46 ± 0.42 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.006 | 0.20 ± 0.10 | 0.85 ± 0.54 | 0.000 |
| AHI (n/h) | 30.49 ± 26.72 | 17.35 ± 22.38 | 0.086 | 27.92 ± 26.70 | 13.14 ± 17.35 | 0.094 | 20.13 ± 21.99 | 36.50 ± 31.52 | 0.063 |
| ODI (n/h) | 29.34 ± 25.69 | 17.00 ± 20.97 | 0.090 | 27.24 ± 25.59 | 12.09 ± 14.63 | 0.071 | 19.74 ± 20.49 | 34.59 ± 31.19 | 0.076 |
| Snore (%) | 27.00 ± 24.58 | 24.46 ± 20.01 | 0.710 | 27.48 ± 22.89 | 20.73 ± 20.56 | 0.391 | 22.15 ± 19.04 | 36.72 ± 28.31 | 0.060 |
| Average SpO2 (%) | 90.29 ± 5.58 | 92.97 ± 2.33 | 0.048 | 90.88 ± 4.94 | 93.62 ± 1.72 | 0.081 | 92.58 ± 2.81 | 88.52 ± 6.94 | 0.008 |
| Minimal SpO2 (%) | 76.04 ± 12.13 | 83.95 ± 6.24 | 0.010 | 77.76 ± 11.03 | 86.00 ± 4.96 | 0.022 | 82.94 ± 6.62 | 70.45 ± 14.19 | 0.000 |
| SpO2 duration <90% (min) | 20.03 ± 29.24 | 11.60 ± 19.15 | 0.270 | 19.30 ± 27.48 | 6.12 ± 11.47 | 0.132 | 10.22 ± 16.15 | 33.38 ± 37.61 | 0.006 |
| SL (min) | 21.76 ± 18.74 | 18.01 ± 11.91 | 0.438 | 20.34 ± 16.84 | 18.85 ± 12.74 | 0.789 | 19.18 ± 13.12 | 22.33 ± 22.64 | 0.573 |
| WASO (min) | 64.73 ± 41.07 | 52.79 ± 47.42 | 0.376 | 67.04 ± 46.18 | 35.01 ± 26.38 | 0.035 | 56.71 ± 43.45 | 65.99 ± 47.47 | 0.552 |
| SE (%) | 82.17 ± 9.90 | 83.49 ± 14.61 | 0.726 | 82.29 ± 10.57 | 84.32 ± 16.84 | 0.640 | 83.21 ± 12.77 | 81.55 ± 10.96 | 0.702 |
| N1 (% of TST) | 6.77 ± 6.79 | 7.55 ± 8.82 | 0.743 | 7.06 ± 7.83 | 7.38 ± 7.82 | 0.907 | 7.45 ± 8.45 | 6.20 ± 5.29 | 0.647 |
| N2 (% of TST) | 49.49 ± 9.09 | 54.80 ± 29.72 | 0.419 | 48.07 ± 8.84 | 63.88 ± 39.02 | 0.033 | 51.91 ± 24.38 | 52.37 ± 8.75 | 0.951 |
| N3 (% of TST) | 23.30 ± 10.39 | 27.62 ± 27.91 | 0.493 | 23.30 ± 9.30 | 31.55 ± 38.51 | 0.253 | 25.97 ± 23.10 | 23.55 ± 10.16 | 0.740 |
| REM (% of TST) | 20.41 ± 7.16 | 22.29 ± 5.77 | 0.348 | 21.54 ± 7.04 | 20.61 ± 4.87 | 0.687 | 22.46 ± 5.25 | 17.85 ± 8.79 | 0.041 |
| Bruxism episodes index (n/h) | 4.20 ± 3.25 | 4.14 ± 3.41 | 0.955 | 4.64 ± 3.23 | 2.80 ± 3.20 | 0.111 | 3.60 ± 2.93 | 6.03 ± 3.87 | 0.039 |
| Phasic bruxism | 2.06 ± 2.38 | 1.50 ± 1.96 | 0.407 | 2.02 ± 2.23 | 1.14 ± 1.96 | 0.253 | 1.34 ± 1.65 | 3.27 ± 3.05 | 0.012 |
| Tonic bruxism | 1.48 ± 1.04 | 1.73 ± 1.69 | 0.559 | 1.74 ± 1.28 | 1.19 ± 1.66 | 0.261 | 1.55 ± 1.47 | 1.75 ± 1.13 | 0.701 |
| Mixed bruxism | 0.70 ± 0.63 | 0.94 ± 0.94 | 0.323 | 0.93 ± 0.84 | 0.49 ± 0.56 | 0.119 | 0.74 ± 0.83 | 1.05 ± 0.65 | 0.289 |
| ArI (n/h) | 9.53 ± 18.08 | 6.23 ± 5.53 | 0.427 | 8.30 ± 15.43 | 6.93 ± 5.32 | 0.775 | 6.38 ± 5.83 | 12.70 ± 25.50 | 0.184 |
| AI (n/h) | 14.81 ± 19.43 | 8.84 ± 15.70 | 0.272 | 13.77 ± 19.13 | 6.55 ± 12.19 | 0.249 | 9.85 ± 15.61 | 18.30 ± 22.91 | 0.176 |
| OA (n/h) | 11.72 ± 16.39 | 7.89 ± 14.82 | 0.422 | 11.26 ± 16.57 | 5.78 ± 11.97 | 0.319 | 7.62 ± 12.78 | 16.71 ± 21.34 | 0.094 |
| MA (n/h) | 1.22 ± 3.14 | 0.50 ± 1.09 | 0.330 | 1.02 ± 2.68 | 0.46 ± 1.22 | 0.515 | 0.84 ± 2.56 | 0.99 ± 1.92 | 0.858 |
| CA (n/h) | 1.88 ± 3.71 | 0.43 ± 0.51 | 0.083 | 1.49 ± 3.15 | 0.28 ± 0.24 | 0.216 | 1.38 ± 3.16 | 0.62 ± 0.78 | 0.439 |
| HI (n/h) | 15.68 ± 14.26 | 8.51 ± 8.09 | 0.049 | 14.15 ± 12.97 | 6.58 ± 7.01 | 0.073 | 10.28 ± 10.32 | 18.21 ± 15.56 | 0.060 |
| Parameter | Average < Me | Average ≥ Me | p | Average < Q1 | Average ≥ Q1 | p | Average < Q3 | Average ≥ Q3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cadmium urine concentration (µg/g of creatinine) | 0.34 ± 0.11 | 1.22 ± 0.62 | 0.000 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 0.94 ± 0.63 | 0.001 | 0.47 ± 0.23 | 1.70 ± 0.54 | 0.000 |
| AHI (n/h) | 16.85 ± 20.31 | 31.59 ± 28.09 | 0.053 | 13.94 ± 18.00 | 27.24 ± 26.59 | 0.147 | 20.02 ± 21.25 | 36.81 ± 32.92 | 0.056 |
| ODI (n/h) | 15.76 ± 18.82 | 31.14 ± 26.68 | 0.033 | 13.13 ± 15.00 | 26.49 ± 25.57 | 0.125 | 19.49 ± 19.77 | 35.34 ± 32.26 | 0.058 |
| Snore (%) | 25.50 ± 21.83 | 26.08 ± 23.25 | 0.933 | 16.74 ± 22.37 | 28.45 ± 21.89 | 0.146 | 26.30 ± 21.26 | 24.25 ± 26.20 | 0.794 |
| Average SpO2 (%) | 93.13 ± 2.20 | 90.00 ± 5.61 | 0.019 | 93.57 ± 1.88 | 90.98 ± 4.88 | 0.110 | 92.58 ± 2.75 | 88.53 ± 7.02 | 0.008 |
| Minimal SpO2 (%) | 83.64 ± 7.13 | 76.00 ± 11.94 | 0.014 | 84.80 ± 5.35 | 78.35 ± 11.18 | 0.087 | 82.42 ± 7.15 | 72.00 ± 14.72 | 0.003 |
| SpO2 duration <90% (% of TST) | 9.09 ± 17.30 | 22.93 ± 29.70 | 0.066 | 9.26 ± 11.33 | 17.99 ± 27.62 | 0.338 | 9.70 ± 15.55 | 34.94 ± 37.32 | 0.003 |
| SL (min) | 18.64 ± 14.18 | 21.30 ± 17.48 | 0.582 | 26.03 ± 16.90 | 18.19 ± 15.24 | 0.170 | 19.42 ± 14.16 | 21.62 ± 20.63 | 0.694 |
| WASO (min) | 51.02 ± 41.30 | 67.05 ± 46.30 | 0.232 | 52.01 ± 41.65 | 61.10 ± 45.20 | 0.573 | 54.00 ± 42.31 | 74.14 ± 48.00 | 0.193 |
| SE (%) | 84.00 ± 14.26 | 81.59 ± 10.01 | 0.519 | 79.21 ± 18.12 | 83.85 ± 10.03 | 0.297 | 83.76 ± 12.99 | 79.91 ± 9.58 | 0.372 |
| N1 (% of TST) | 8.13 ± 9.03 | 6.15 ± 6.25 | 0.402 | 7.73 ± 7.61 | 6.97 ± 7.88 | 0.788 | 7.10 ± 8.06 | 7.27 ± 7.04 | 0.949 |
| N2 (% of TST) | 54.99 ± 28.66 | 49.06 ± 10.12 | 0.366 | 62.24 ± 42.09 | 49.02 ± 8.69 | 0.087 | 52.56 ± 23.83 | 50.42 ± 12.58 | 0.778 |
| N3 (% of TST) | 26.85 ± 27.73 | 23.88 ± 9.54 | 0.637 | 33.69 ± 40.26 | 22.92 ± 9.00 | 0.147 | 26.11 ± 22.80 | 23.15 ± 12.06 | 0.684 |
| REM (% of TST) | 21.74 ± 5.09 | 20.87 ± 7.80 | 0.664 | 22.09 ± 6.54 | 21.08 ± 6.60 | 0.671 | 22.03 ± 4.80 | 19.15 ± 10.10 | 0.208 |
| Bruxism episode index (n/h) | 4.11 ± 3.92 | 4.22 ± 2.56 | 0.914 | 3.65 ± 3.41 | 4.32 ± 3.29 | 0.576 | 3.98 ± 3.41 | 4.79 ± 2.92 | 0.501 |
| Phasic bruxism episode index (n/h) | 1.81 ± 2.74 | 1.77 ± 1.43 | 0.945 | 1.44 ± 1.99 | 1.90 ± 22.25 | 0.567 | 1.62 ± 2.32 | 2.35 ± 1.61 | 0.360 |
| Tonic bruxism episode index (n/h) | 1.55 ± 1.62 | 1.65 ± 1.12 | 0.812 | 1.55 ± 1.87 | 1.62 ± 1.24 | 0.898 | 1.61 ± 1.47 | 1.58 ± 1.12 | 0.959 |
| Mixed bruxism episode index (n/h) | 0.77 ± 0.83 | 0.86 ± 0.77 | 0.704 | 0.68 ± 0.66 | 0.85 ± 0.84 | 0.549 | 0.78 ± 0.84 | 0.94 ± 0.66 | 0.573 |
| ArI (n/h) | 6.99 ± 5.50 | 8.93 ± 18.57 | 0.640 | 6.51 ± 5.68 | 8.39 ± 15.18 | 0.706 | 6.29 ± 5.01 | 12.97 ± 25.98 | 0.160 |
| AI(n/h) | 8.26 ± 14.03 | 15.66 ± 20.58 | 0.171 | 7.09 ± 12.71 | 13.39 ± 18.97 | 0.331 | 9.95 ± 15.73 | 17.99 ± 22.75 | 0.198 |
| OAI (n/h) | 7.19 ± 13.21 | 12.60 ± 17.57 | 0.255 | 6.07 ± 12.59 | 11.01 ± 16.38 | 0.385 | 7.94 ± 12.91 | 15.75 ± 21.52 | 0.153 |
| MAI (n/h) | 0.52 ± 1.08 | 1.23 ± 3.21 | 0.332 | 0.53 ± 1.26 | 0.98 ± 2.64 | 0.608 | 0.89 ± 2.58 | 0.85 ± 1.82 | 0.960 |
| CAI (n/h) | 0.55 ± 0.60 | 1.83 ± 3.81 | 0.127 | 0.50 ± 0.47 | 1.39 ± 3.13 | 0.380 | 1.12 ± 2.94 | 1.39 ± 2.31 | 0.781 |
| HI (n/h) | 8.60 ± 7.95 | 15.91 ± 14.53 | 0.045 | 6.86 ± 7.28 | 13.85 ± 12.90 | 0.111 | 10.08 ± 8.40 | 18.81 ± 18.60 | 0.037 |
| Average pulse (bpm) | 59.56 ± 9.30 | 65.37 ± 7.45 | 0.027 | 59.58 ± 13.22 | 63.31 ± 7.12 | 0.244 | 61.00 ± 9.15 | 66.86 ± 6.28 | 0.055 |
| Maximal pulse (bpm) | 94.64 ± 11.09 | 47.95 ± 11.64 | 0.085 | 91.70 ± 20.09 | 95.91 ± 12.30 | 0.419 | 94.88 ± 15.51 | 45.36 ± 12.06 | 0.952 |
| Minimal pulse (bpm) | 44.62 ± 11.09 | 47.95 ± 11.64 | 0.336 | 41.16 ± 13.23 | 47.79 ± 10.50 | 0.105 | 46.59 ± 11.30 | 45.36 ± 12.06 | 0.760 |
| Variable | Cadmium Blood Concentration (µg/L) | p | Cadmium Urine Concentration [µg/g of Creatinine] | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHI (n/h) | 0.44 | <0.05 | 0.36 | <0.05 |
| ODI (n/h) | 0.44 | <0.05 | 0.38 | <0.05 |
| Snore (%) | 0.33 | <0.05 | −0.02 | >0.05 |
| Average SpO2 (%) | −0.57 | <0.05 | −0.56 | <0.05 |
| SpO2 duration <90% (% of TST) | 0.47 | <0.05 | 0.50 | <0.05 |
| Average desaturation | 0.45 | <0.05 | 0.52 | <0.05 |
| Minimal SpO2 (%) | −0.54 | <0.05 | −0.53 | <0.05 |
| Minimal pulse | −0.46 | <0.05 | 0.07 | >0.05 |
| REM (% of TST) | −0.44 | <0.05 | −0.08 | >0.05 |
| ArI (n/h) | 0.60 | <0.05 | 0.42 | <0.05 |
| AI (n/h) | 0.29 | >0.05 | 0.32 | <0.05 |
| OAI (n/h) | 0.33 | <0.05 | 0.35 | <0.05 |
| HI (n/h) | 0.48 | <0.05 | 0.29 | >0.05 |
| Parameter | RC | SEM of RC | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −37.024 | 15.156 | 0.0193 |
| Age | 0.480 | 0.234 | 0.0438 |
| Cadmium urine concentration (µg/g of creatinine) | 15.795 | 5.921 | 0. 0111 |
| Male | 22.955 | 7.106 | 0.0025 |
| Smoking | 11.765 | 3.226 | 0.0257 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frosztega, W.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Gac, P.; Lachowicz, G.; Poreba, R.; Mazur, G.; Martynowicz, H. The Effect of Cadmium on Sleep Parameters Assessed in Polysomnographic Studies: A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123899
Frosztega W, Wieckiewicz M, Gac P, Lachowicz G, Poreba R, Mazur G, Martynowicz H. The Effect of Cadmium on Sleep Parameters Assessed in Polysomnographic Studies: A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123899
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrosztega, Weronika, Mieszko Wieckiewicz, Pawel Gac, Gabriella Lachowicz, Rafal Poreba, Grzegorz Mazur, and Helena Martynowicz. 2023. "The Effect of Cadmium on Sleep Parameters Assessed in Polysomnographic Studies: A Case–Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123899
APA StyleFrosztega, W., Wieckiewicz, M., Gac, P., Lachowicz, G., Poreba, R., Mazur, G., & Martynowicz, H. (2023). The Effect of Cadmium on Sleep Parameters Assessed in Polysomnographic Studies: A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123899