Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of MRONJ in Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Microbiological Examination
2.3. Histological Examination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, F.; Matsumoto, Y. Basic and clinical associations between bone and cancer. Immunol. Med. 2020, 43, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroz-Munoz, M.; Izadmehr, S.; Arumugam, D.; Wong, B.; Kirschenbaum, A.; Levine, A.C. Mechanisms of Osteoblastic Bone Metastasis in Prostate Cancer: Role of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Cui, X.; Ma, H.; Tang, X. Comparison of denosumab and zoledronic acid for the treatment of solid tumors and multiple myeloma with bone metastasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Wen, X.; Li, H.; Li, W. Meta-analysis of clinical trials to assess denosumab over zoledronic acid in bone metastasis. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2021, 43, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldvaser, H.; Amir, E. Role of Bisphosphonates in Breast Cancer Therapy. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Zheng, M.; Mohanlal, R. Indirect Evaluation of Bone Saturation with Zoledronic Acid After Long-Term Dosing. Oncologist 2019, 24, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.I.; Chen, L.W.; Liu, W.C.; Lin, C.T.; Ho, Y.Y.; Tsai, W.H.; Yang, K.C. Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2021, 86 (Suppl. 1), S78–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Aghaloo, T.; Carlson, E.R.; Ward, B.B.; Kademani, D. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons’ Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws—2022 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 920–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avishai, G.; Muchnik, D.; Masri, D.; Zlotogorski-Hurvitz, A.; Chaushu, L. Minimizing MRONJ after Tooth Extraction in Cancer Patients Receiving Bone-Modifying Agents. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Kaneko, T.; Kamimoto, A.; Wada, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Furuchi, M.; Iinuma, T. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw after tooth extraction in patients receiving pharmaceutical treatment for osteoporosis: A retrospective cohort study. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutome, S.; Otsuru, M.; Hayashida, S.; Murata, M.; Yanamoto, S.; Sawada, S.; Kojima, Y.; Funahara, M.; Iwai, H.; Umeda, M.; et al. Relationship between tooth extraction and development of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: A growing epidemic. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advisory Task Force on Bisphosphonate-Related Ostenonecrosis of the Jaws, American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Fantasia, J.; Goodday, R.; Aghaloo, T.; Mehrotra, B.; O’Ryan, F.; American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2014 update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1938–1956, Erratum in J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 1440; Erratum in J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limones, A.; Sáez-Alcaide, L.M.; Díaz-Parreño, S.A.; Helm, A.; Bornstein, M.M.; Molinero-Mourelle, P. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) in cancer patients treated with denosumab vs. zoledronic acid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2020, 25, e326–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, V.; Campisi, G.; Bedogni, A. One changing and challenging scenario: The treatment of cancer patients with bone metastases by bisphosphonates and denosumab, the cost-benefit evaluation of different options, and the risk of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). Support Care Cancer 2022, 30, 7047–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Kuroshima, S.; Sawase, T. Clinical considerations for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A comprehensive literature review. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2021, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlRowis, R.; Aldawood, A.; AlOtaibi, M.; Alnasser, E.; AlSaif, I.; Aljaber, A.; Natto, Z. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ): A Review of Pathophysiology, Risk Factors, Preventive Measures and Treatment Strategies. Saudi Dent. J. 2022, 34, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarom, N.; Shapiro, C.L.; Peterson, D.E.; Van Poznak, C.H.; Bohlke, K.; Ruggiero, S.L.; Migliorati, C.A.; Khan, A.; Morrison, A.; Anderson, H.; et al. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: MASCC/ISOO/ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2270–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Min, B.J.; Kim, G.J.; Lim, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Ahn, K.M.; Kim, J.H. Identifying genetic variants underlying medication-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer and osteoporosis: A case control study. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Singh, S.; McDonough, C.W.; Lamba, J.K.; Hamadeh, I.; Holliday, L.S.; Wang, D.; Katz, J.; Lakatos, P.A.; Balla, B.; et al. Genome-wide Association Study Identified Chromosome 8 Locus Associated with Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucur, A.; Dinca, O.; Vladan, C. Ghidul de Practică în Medicina Dentară: Algoritmul Terapeutic la Pacienții Sub Terapie Antire-sorbtivă/Antiangiogenică. Available online: https://cmdr.ro/document/ghid-de-practica-algoritmul-terapeutic-la-pacientii-sub-terapie-antiresorbtiva_antiangiogenica/2019 (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Mauceri, R.; Coppini, M.; Attanasio, M.; Bedogni, A.; Bettini, G.; Fusco, V.; Giudice, A.; Graziani, F.; Marcianò, A.; Nisi, M.; et al. MRONJ in breast cancer patients under bone modifying agents for cancer treatment-induced bone loss (CTIBL): A multi-hospital-based case series. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.Y.; Kok, S.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Chiu, W.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Cheng, S.J.; Chang, H.H.; Lee, J.J. Prognosis of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in metastatic prostate cancer patients. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikesue, H.; Doi, K.; Morimoto, M.; Hirabatake, M.; Muroi, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Takenobu, T.; Hashida, T. Risk evaluation of denosumab and zoledronic acid for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients with bone metastases: A propensity score-matched analysis. Support Care Cancer 2022, 30, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikesue, H.; Mouri, M.; Tomita, H.; Hirabatake, M.; Ikemura, M.; Muroi, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Takenobu, T.; Tomii, K.; Kawakita, M.; et al. Associated characteristics and treatment outcomes of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients receiving denosumab or zoledronic acid for bone metastases. Support Care Cancer 2021, 29, 4763–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Du, S. Efficacy and Safety of Zoledronic Acid and Pamidronate Disodium in the Treatment of Malignant Skeletal Metastasis: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, S.; Vijayvargiya, M. Single Dose Therapy of Zoledronic Acid for the Treatment of Transient Osteoporosis of Hip. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 43, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Drug-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Jaws How to Diagnose, Prevent, and Treat It; Quintessence Publishing: Batavia, IL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mânea, H.C.; Urechescu, H.C.; Balica, N.C.; Pricop, M.O.; Baderca, F.; Poenaru, M.; Horhat, I.D.; Jifcu, E.M.; Cloşca, R.M.; Sarău, C.A. Bisphosphonates-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw—Epidemiological, clinical and histopathological aspects. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 825–831. [Google Scholar]
- Lazăr, A.C.; Socaciu, R.; Mureşan, O.; Păcurar, M. Retrospective study regarding the appearance of osteonecrosis related to bisphosphonate therapy. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Biguetti, C.C.; De Oliva, A.H.; Healy, K.; Mahmoud, R.H.; Custódio, I.D.C.; Constantino, D.H.; Ervolino, E.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Fakhouri, W.D.; Matsumoto, M.A. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws after tooth extraction in senescent female mice treated with zoledronic acid: Microtomographic, histological and immunohistochemical characterization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, O.; Surlin, V.; Munteanu, C.; Camen, A.; Petrescu, G.S.; Andrei, E.; Ciobanu, A. Incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw due to bisphosphonate treatment in the city of Craiova. Arch. Euromed. 2020, 10, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ciobanu, G.A.; Camen, A.; Ionescu, M.; Vlad, D.; Mercuț, V.; Staicu, I.E.; Petrescu, G.S.; Asan, A.A.; Popescu, S.M. Biphosphonates related osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients—Epidemiological study. Rom. J. Oral Rehabil. 2022, 14, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo-Zamora, G.; Martínez, Y.; Moreno, J.A.; Ortiz-Ruíz, A.J. Treatment of Stage 2 Medication-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Case Series. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chęciński, M.; Wróbel, K.; Sikora, M. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Mandible Treated with Marginal Resection: A Case Report. Surgeries 2022, 3, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, G.; Mauceri, R.; Bertoldo, F.; Bettini, G.; Biasotto, M.; Colella, G.; Consolo, U.; Di Fede, O.; Favia, G.; Fusco, V.; et al. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of Jaws (MRONJ) Prevention and Diagnosis: Italian Consensus Update 2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwech, N.; Nilsson, J.; Gabre, P. Incidence and risk factors for medication-related osteonecrosis after tooth extraction in cancer patients-A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2023, 9, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello-Suanzes, J.; Rollon-Ugalde, V.; Castaño-Seiquer, A.; Lledo-Villar, E.; Herce-Lopez, J.; Infante-Cossio, P.; Rollon-Mayordomo, A. Preventive dental management of osteonecrosis of the jaws related to zoledronic acid treatment. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutome, S.; Hayashida, S.; Funahara, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Yanamoto, S.; Umeda, M. Factors affecting development of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients receiving high-dose bisphosphonate or denosumab therapy: Is tooth extraction a risk factor? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasilakis, A.D.; Pepe, J.; Napoli, N.; Palermo, A.; Magopoulos, C.; Khan, A.A.; Zillikens, M.C.; Body, J.J. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw and Antiresorptive Agents in Benign and Malignant Diseases: A Critical Review Organized by the ECTS. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1441–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlDhalaan, N.A.; BaQais, A.; Al-Omar, A. Medication-related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Aljohani, S.; Fliefel, R.; Ecke, S.; Ristow, O.; Burian, E.; Troeltzsch, M.; Pautke, C.; Ehrenfeld, M. Infection as an Important Factor in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ). Medicina 2021, 57, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y. Review and Update of the Risk Factors and Prevention of Antiresorptive-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, A.; Goto, T.K.; Ojiri, H.; Takagiwa, M.; Hiraga, C.; Okamura, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Okuyama, Y.; Ogino, N.; Yamauchi, H.; et al. CT imaging features of antiresorptive agent-related osteonecrosis of the jaw/medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2018, 47, 20170323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Brown, J.E.; Van Poznak, C.; Ibrahim, T.; Stemmer, S.M.; Stopeck, A.T.; Diel, I.J.; Takahashi, S.; Shore, N.; Henry, D.H.; et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of osteonecrosis of the jaw: Integrated analysis from three blinded active-controlled phase III trials in cancer patients with bone metastases. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.J. Pharmacoepidemiology and clinical characteristics of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 41, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.G.; Hwang, J.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Na, J.Y.; Han, S.S. Risk factors of osteonecrosis of the jaw after tooth extraction in osteoporotic patients on oral bisphosphonates. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2017, 47, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcianò, A.; Rubino, E.; Peditto, M.; Mauceri, R.; Oteri, G. Oral Surgical Management of Bone and Soft Tissues in MRONJ Treatment: A Decisional Tree. Life 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. A decade of bisphosphonate bone complications: What it has taught us about bone physiology. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, e247-58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verborgt, O.; Gibson, G.J.; Schaffler, M.B. Loss of osteocyte integrity in association with microdamage and bone remodeling after fatigue in vivo. J. Bone Min. Res. 2000, 15, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verborgt, O.; Tatton, N.A.; Majeska, R.J.; Schaffler, M.B. Spatial distribution of Bax and Bcl-2 in osteocytes after bone fatigue: Complementary roles in bone remodeling regulation? J. Bone Min. Res. 2002, 17, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, J.I.; Plotkin, L.I.; Stewart, S.A.; Weinstein, R.S.; Parfitt, A.M.; Manolagas, S.C.; Bellido, T. Osteocyte apoptosis is induced by weightlessness in mice and precedes osteoclast recruitment and bone loss. J. Bone Min. Res. 2006, 21, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonewald, L.F. The amazing osteocyte. J. Bone Min. Res. 2022, 26, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ashrafi, S.H.; Schraufnagel, D.E. The canalicular structure of compact bone in the rat at different ages. Microsc. Microanal. 2002, 8, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, G.A.; Gheorghiţă, M.I.; Petrescu, O.M.; Popescu, S.M.; Staicu, I.E. Mandibulectomy Reconstruction with Pectoralis Major Island Flap Associated with Primary Reconstruction Plate for Mandibular Medication-Related Osteonecrosis. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2021, 47, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campisi, G.; Bedogni, A.; Fusco, V. Raccomandazioni Clinico-Terapeutiche Sull’Osteonecrosi delle Ossa Mascellari (ONJ) Farmaco-Relata e Sua Prevenzione; Srl, N.D.F., Ed.; Palermo University Press: Palermo, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- McGowan, K.; McGowan, T.; Ivanovski, S. Risk factors for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: A systematic review. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincă, O.; Zurac, S.; Stăniceanu, F.; Bucur, M.B.; Bodnar, D.C.; Vlădan, C.; Bucur, A. Clinical and histopathological studies using fibrin-rich plasma in the treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wróbel, K.; Sikora, M.; Chęciński, M.; Jas, M.; Chlubek, D. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—A Continuing Issue. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, A.; Blandamura, S.V.; Lokmic, Z.; Palumbo, V.; Ragazzo, M.; Ferrari, F.; Tregnaghi, A.; Pietrogrande, F.; Procopio, O.; Saia, G.; et al. Bisphosphonate-associated jawbone osteonecrosis: A correlation between imaging techniques and histopathology. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2008, 105, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.Y.; Ma, M.C.; Wang, M.C.; Hsue, S.S. The status of jaw lesions and medication-related osteonecrosis of jaw in patients with multiple myeloma. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 2021, 120, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petia, F.; Elena, G.; Nikolai, V.; Bakardjiev, A.G. Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws—Diagnosis and Management. In A Textbook of Advanced Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Paparella, M.; Brandizzi, D.; Santini-Araujo, E.; Cabrini, R. Histopathological features of osteonecrosis of the jaw associated with bisphosphonates. Histopathology 2011, 60, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favia, G.; Pilolli, G.P.; Maiorano, E. Histologic and histomorphometric features of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: An analysis of 31 cases with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Bone 2009, 45, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, R.; Antonelli, A.; Battistelli, S.; Schwendener, R.; Magnani, M.; Rossi, L. Macrophage depletion by free bisphosphonates and zoledronate-loaded red blood cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimachi, K.; Kajiya, H.; Nakayama, S.; Ikebe, T.; Okabe, K. Zoledronic acid inhibits RANK expression and migration of osteoclast precursors during osteoclastogenesis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2011, 383, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almăşan, H.A.; Băciuţ, M.; Rotaru, H.; Bran, S.; Almăşan, O.C.; Băciuţ, G. Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of bisphosphonates. Discussion over 52 cases. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2011, 52, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

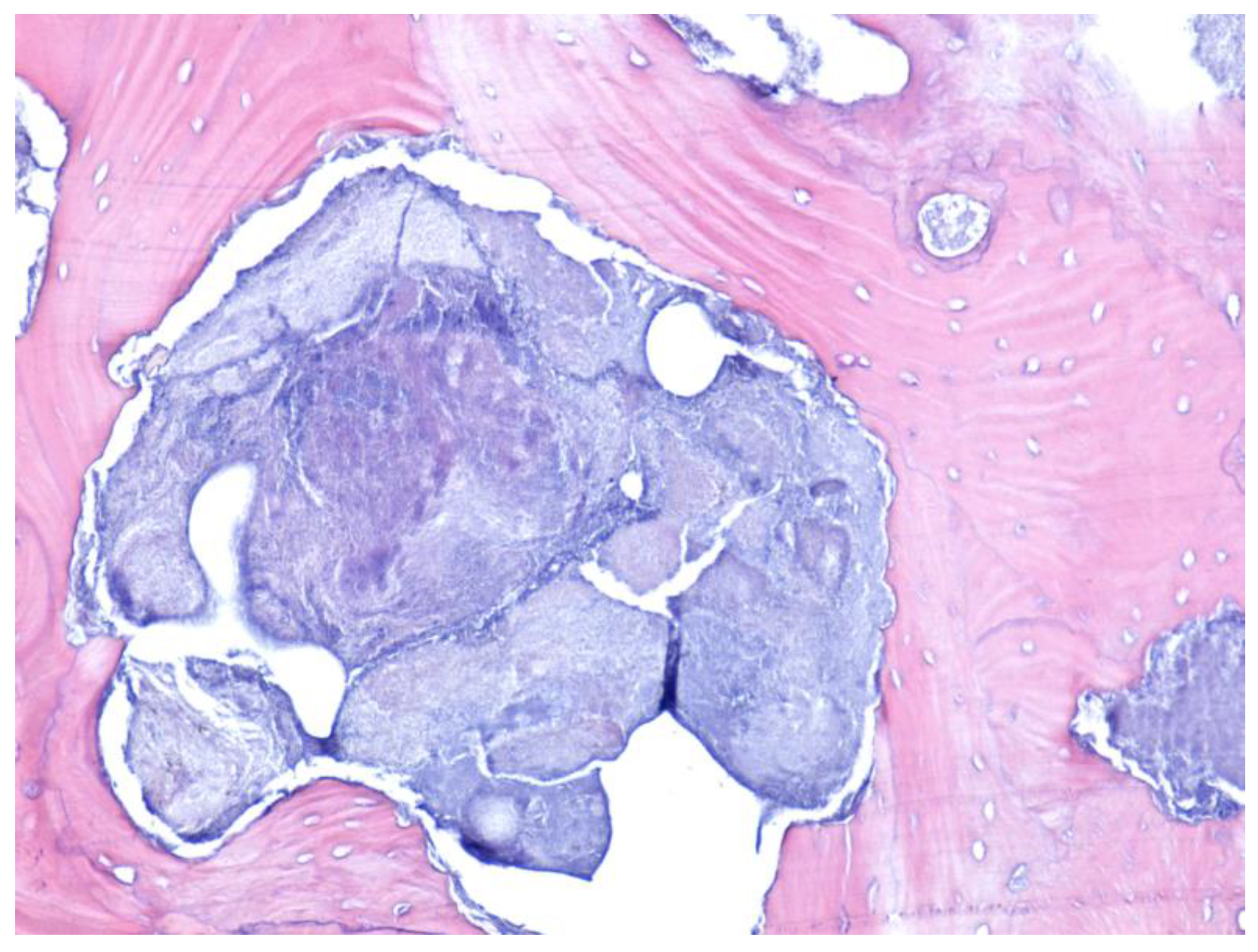
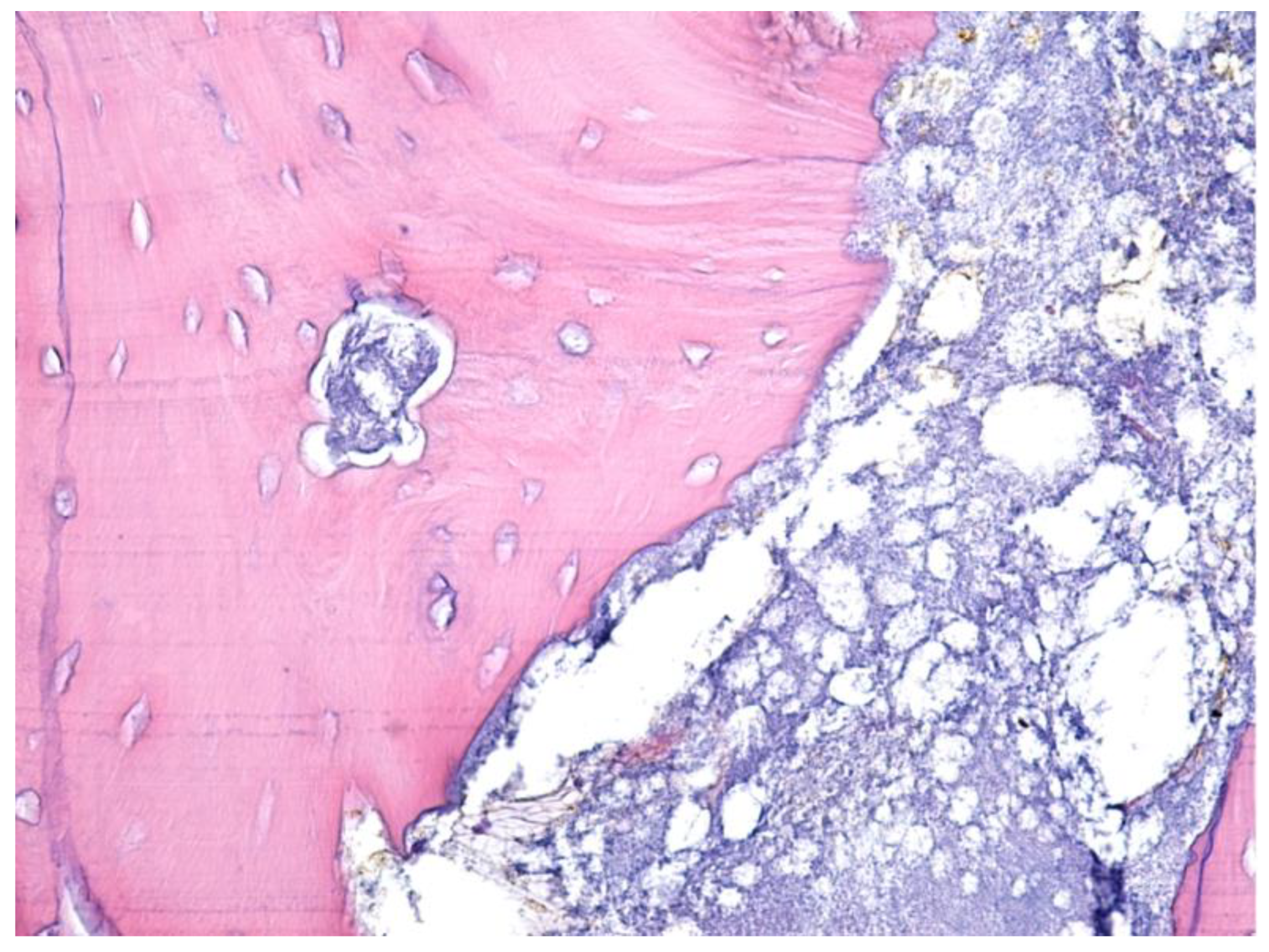
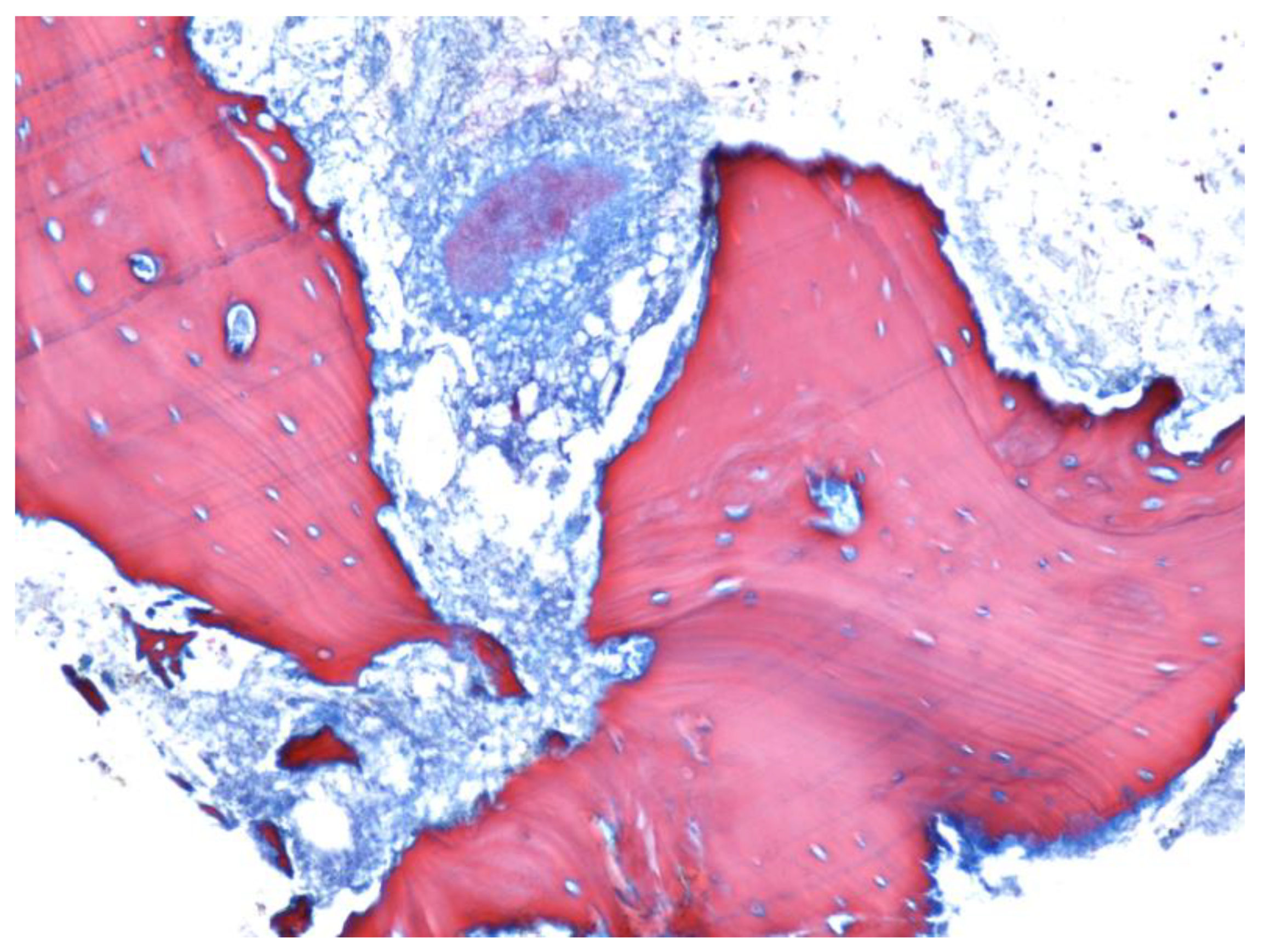
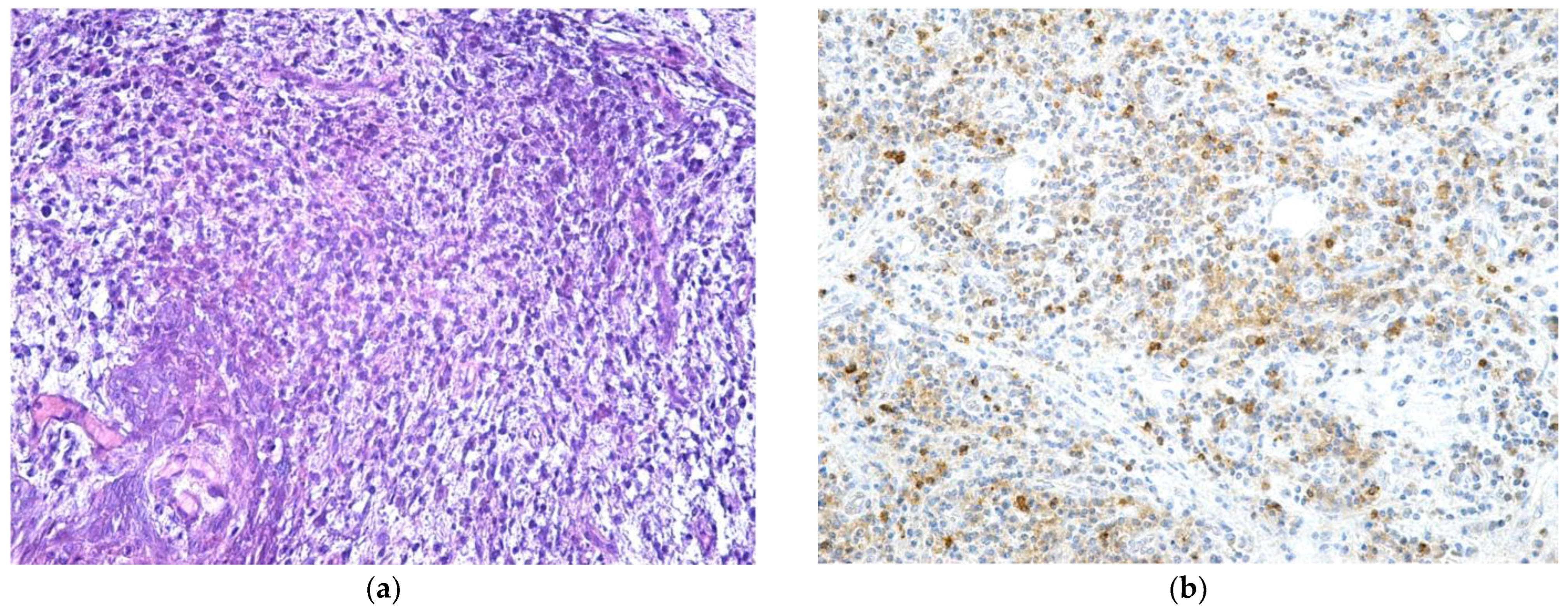
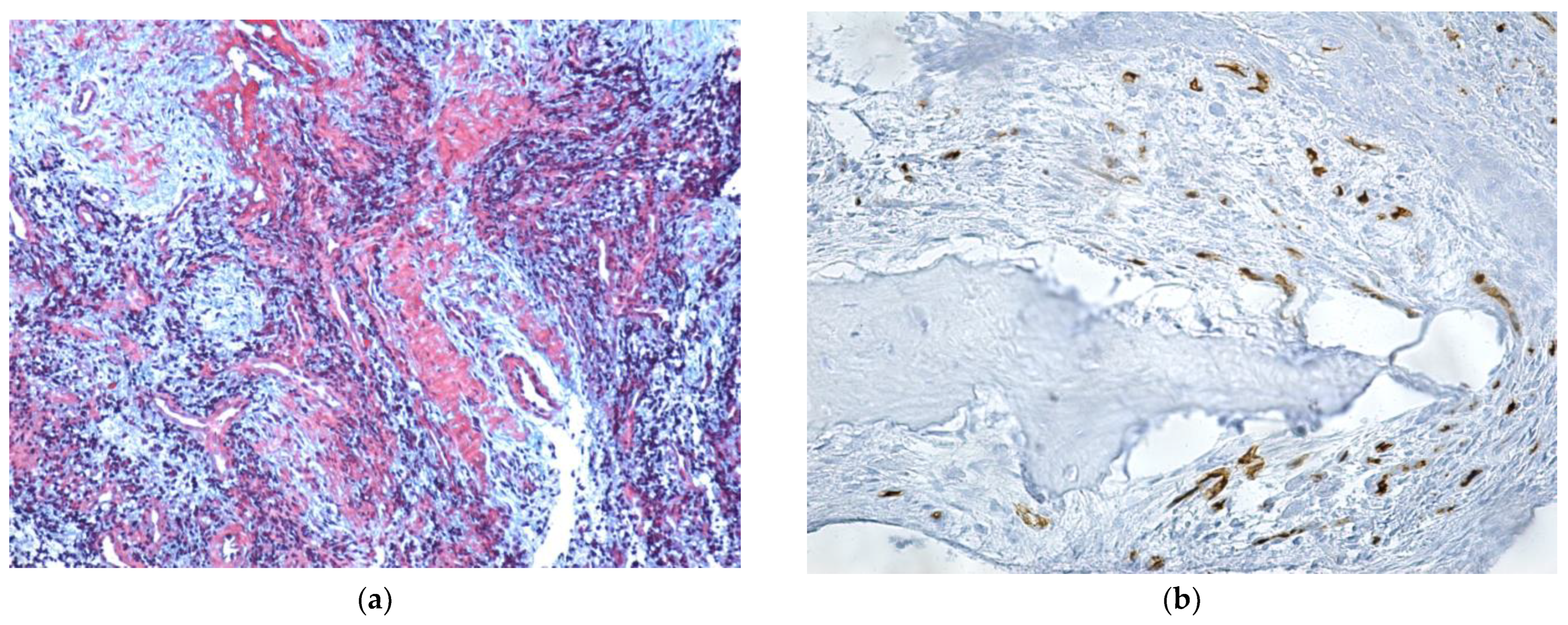
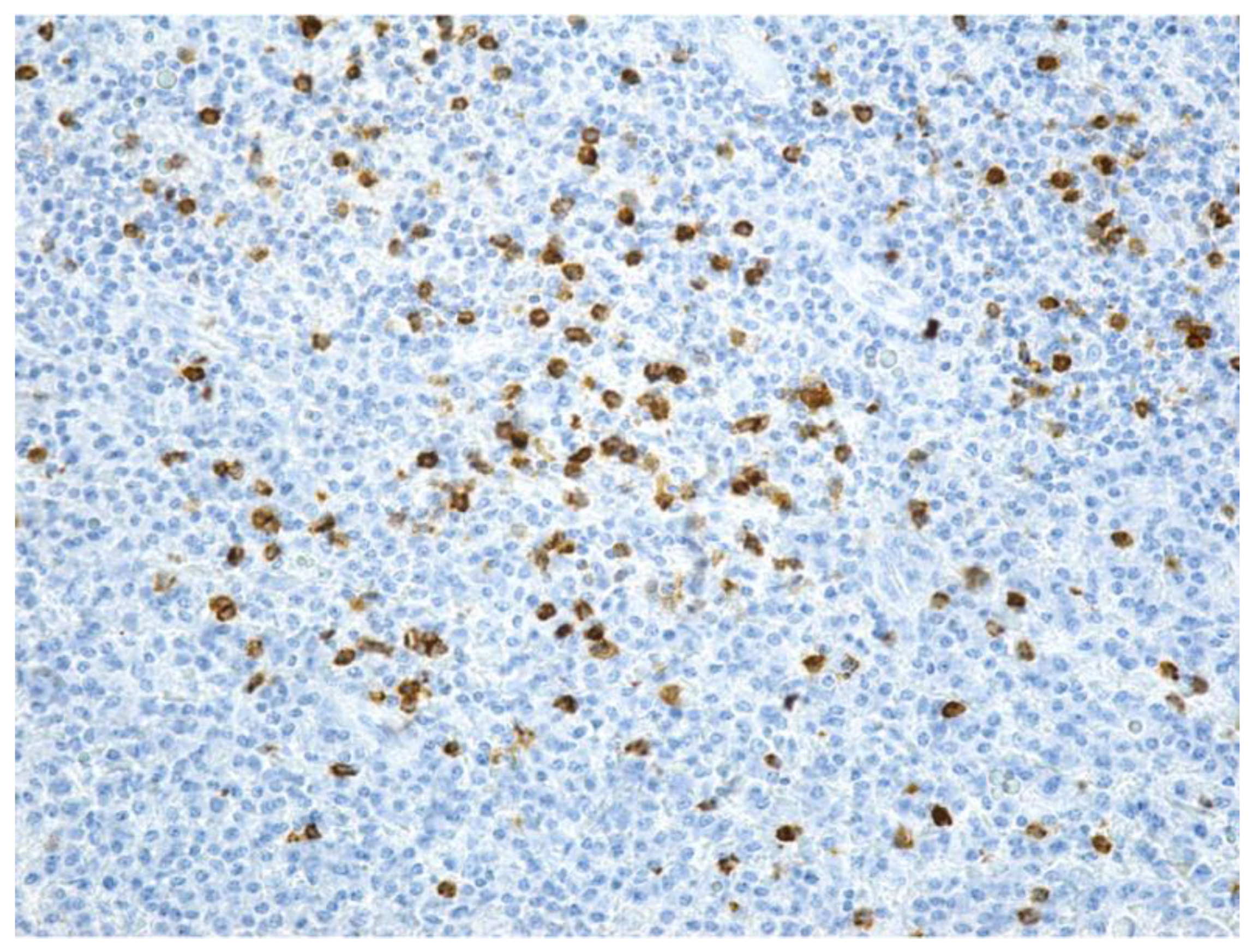
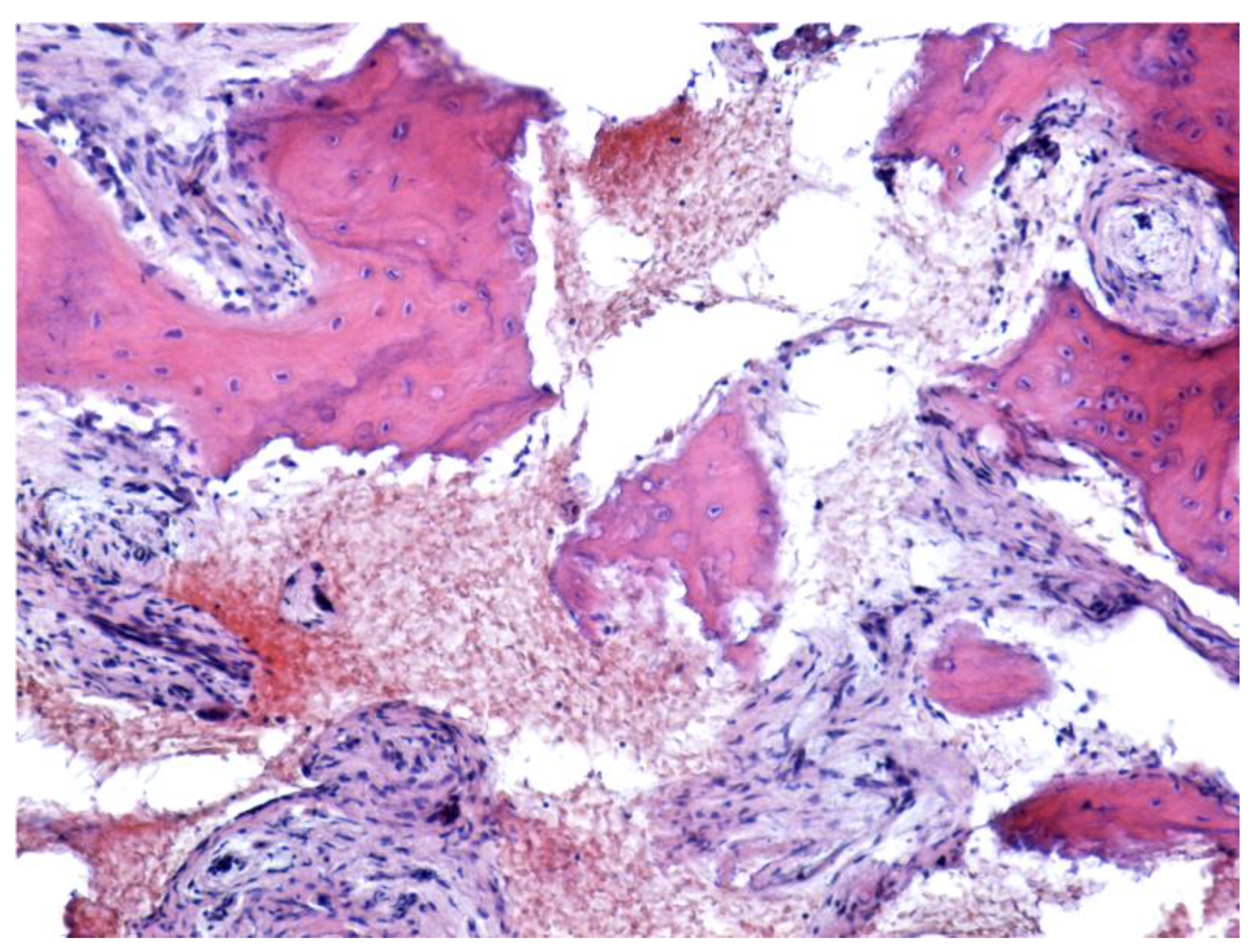
| Parameter | Values | Craiova (no/%) | Constanța (no/%) | Total | p ** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (100%) | Females | Males | Total (100%) | Females | Males | ||||
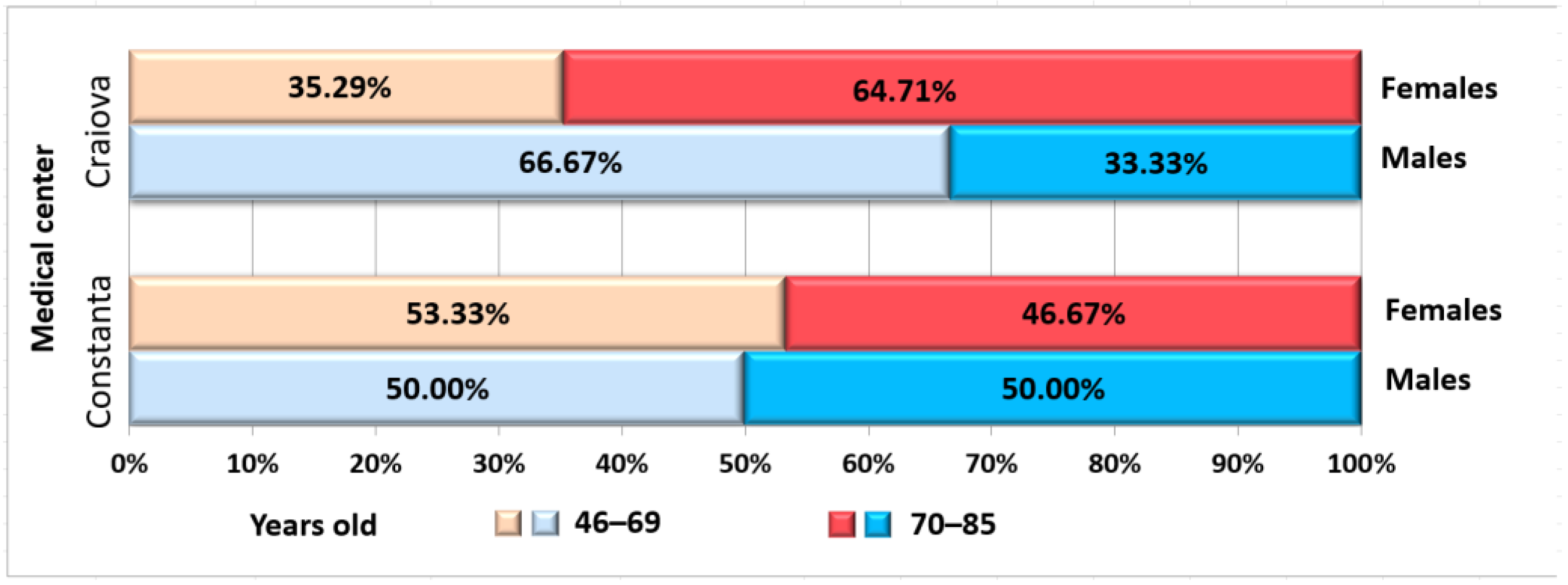
| Number (%) | - | 26 | 17 (65.38%) | 9 (34.62%) | 25 (100%) | 15 (60%) | 10 (40%) | 51 | - |
| Age | <70 * | 12 | 6 (50%) | 6 (50%) | 13 | 8 (61.54%) | 5 (38.46%) | 25 | 0.676 |
| ≥70 * | 14 | 11 (78.57%) | 3 (21.43%) | 12 | 7 (58.33%) | 5 (41.67%) | 26 | ||
| Age (mean ± SD) | <70 * | 61.50 ± 5.80 | 62.66 ± 3.72 | 60.33 ± 7.55 | 64.49 ± 4.19 | 63 ± 4.56 | 67.4 ± 1.14 | - | - |
| ≥70 * | 76.35 ± 4.21 | 75.81 ± 4.33 | 78.33 ± 3.78 | 78.66 ± 4.73 | 79.4 ± 4.31 | 77.6 ± 5.59 | - | ||
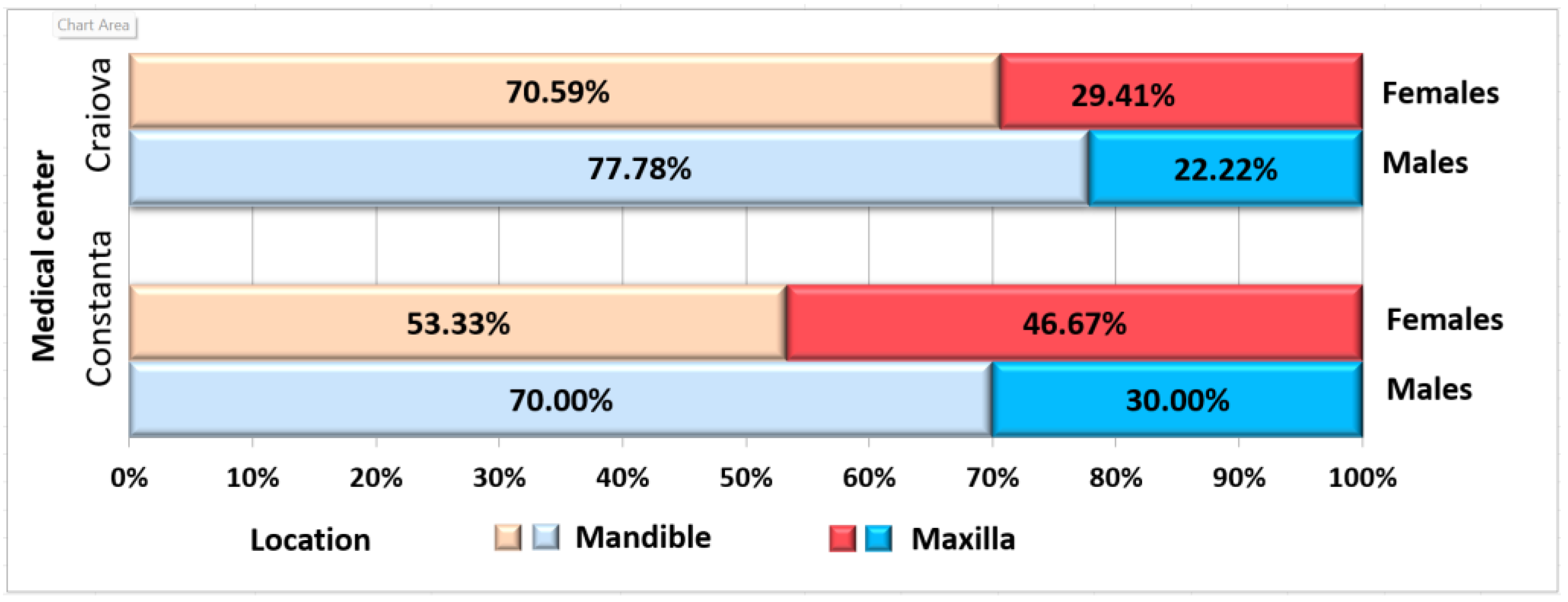
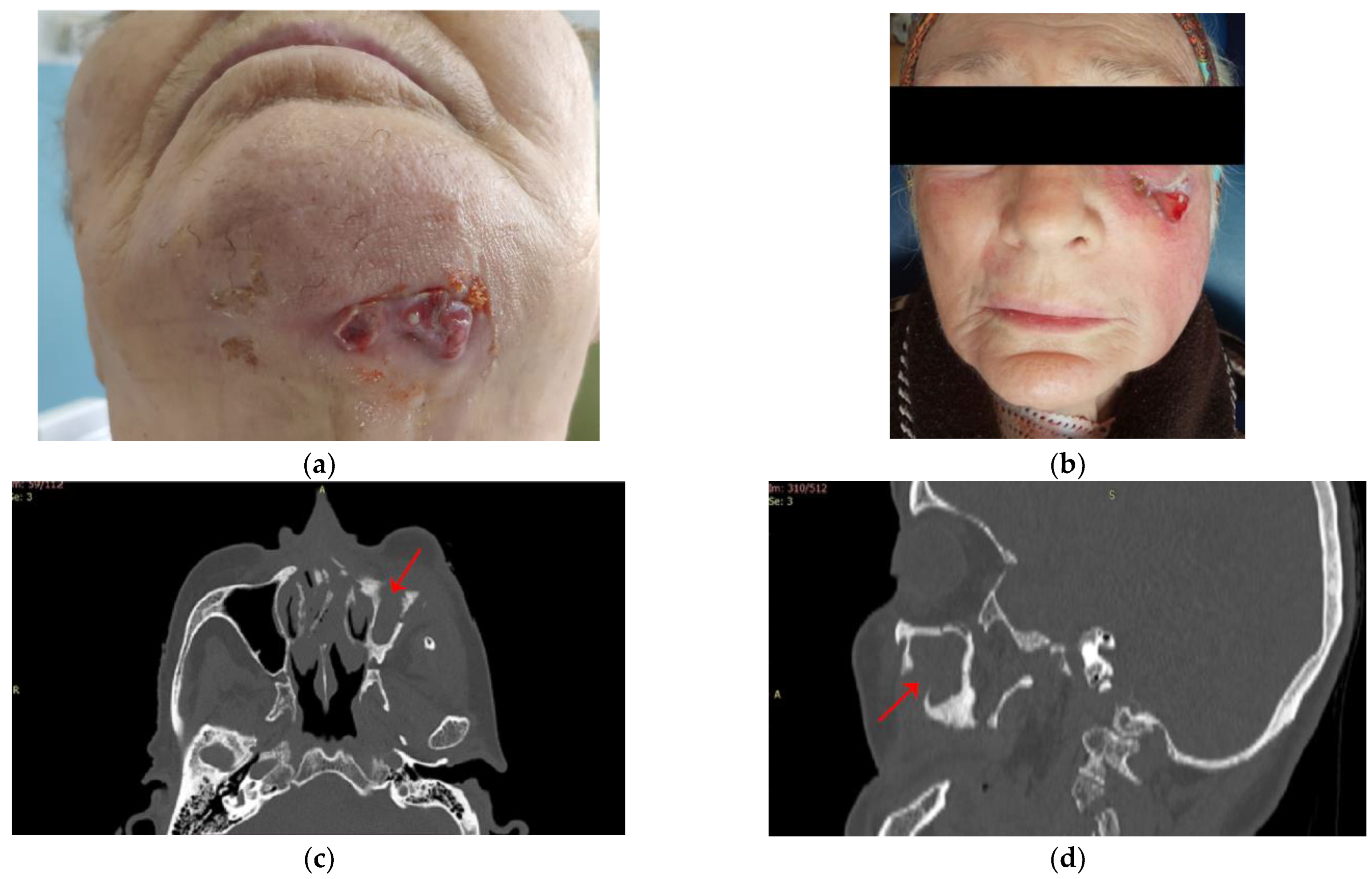
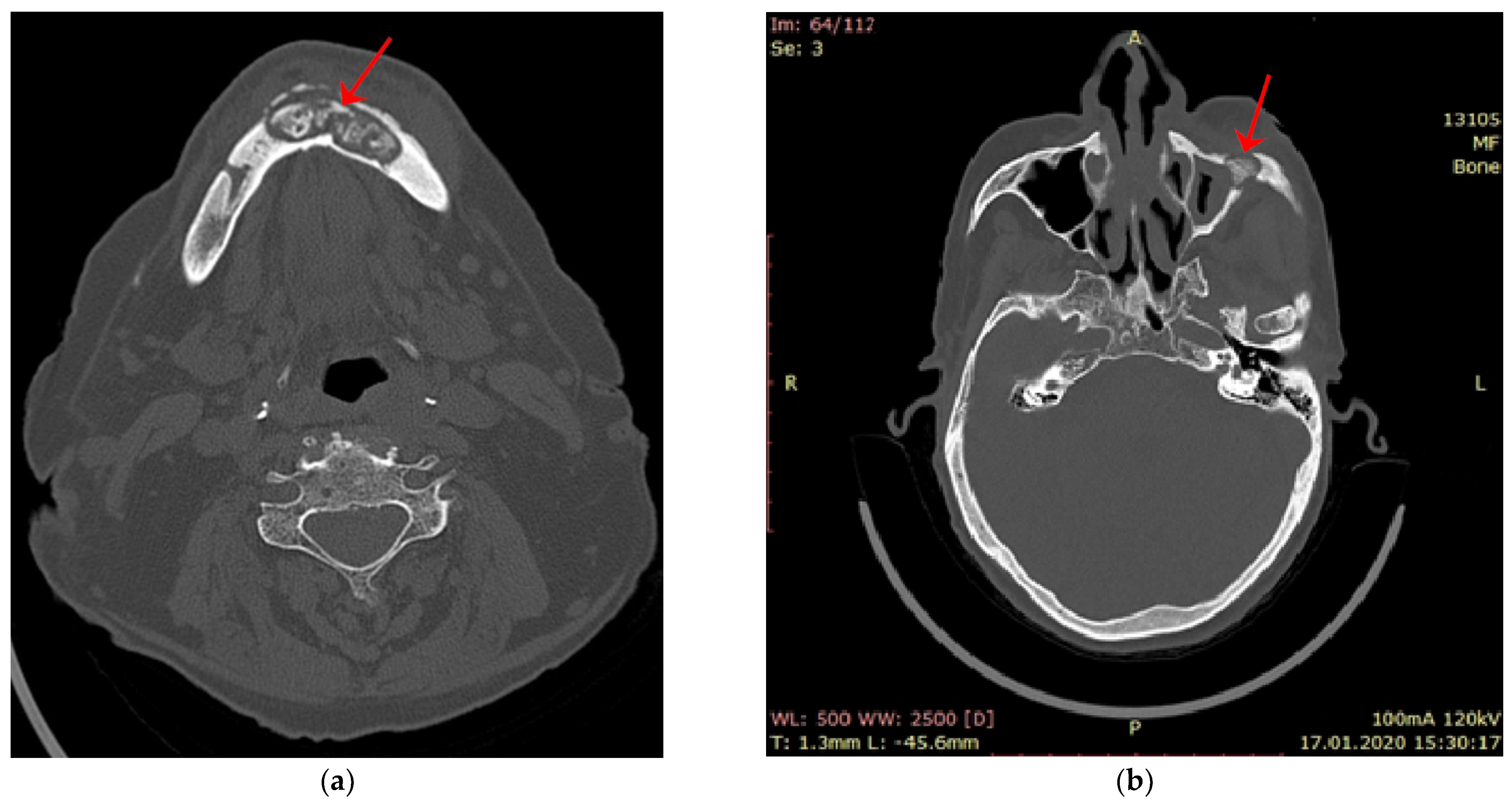
| Localization | Mandible | 19 | 12 (63.16%) | 7 (36.84%) | 15 | 8 (53.33%) | 7 (46.67%) | 34 | 0.322 |
| Maxilla | 7 | 5 (71.43%) | 2 (28.57%) | 10 | 7 (70%) | 3 (30%) | 17 | ||
| Position in dental arch | Posterior | 24 | 16 (66.67%) | 8 (33.33%) | 24 | 14 (58.33%) | 10 (41.67%) | 48 | 1.00 *** |
| Anterior | 2 | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | 1 | 1 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 3 | ||
| Stage | 2 | 21 | 13 (65%) | 7 (35%) | 16 | 13 (65%) | 7 (35%) | 37 | 0.180 |
| 3 | 5 | 4 (66.67%) | 2 (33.33%) | 9 | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | 14 | ||
| Intervention | Sequestrectomy | 22 | 13 (86.67%) | 2 (13.33%) | 24 | 15 (65.22%) | 8 (34.78%) | 46 | 0.350 *** |
| Resection | 4 | 4 (36.36%) | 7 (63.64%) | 1 | 0 (0%) | 2 (100%) | 5 | ||
| No | 15 | 9 (60%) | 6 (40%) | 20 | 10 (50%) | 10 (50%) | 35 | ||
| Parameter | Values | Craiova (no/%) | Constanța (no/%) | Total | p * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (100%) | Females | Males | Total (100%) | Females | Males | ||||
| Bacterial colonies | Yes | 20 | 14 (70%) | 6 (30%) | 7 | 5 (71.43%) | 2 (28.57%) | 27 | <0.0005 |
| No | 6 | 3 (50%) | 3 (50%) | 18 | 10 (55.56%) | 8 (44.44%) | 24 | ||
| Epithelium | Yes | 7 | 6 (85.71%) | 1 (14.29%) | 16 | 9 (56.25%) | 7 (43.75%) | 23 | 0.008 |
| No | 19 | 11 (57.89%) | 8 (42.11%) | 9 | 5 (55.56%) | 4 (44.44%) | 28 | ||
| Fibrous tissue | Yes | 7 | 8 (80%) | 2 (20%) | 19 | 13 (72.22%) | 5 (27.78%) | 26 | <0.0005 |
| No | 19 | 9 (56.25%) | 7 (43.75%) | 6 | 2 (28.57%) | 5 (71.43%) | 25 | ||
| Granulation tissue | Yes | 12 | 10 (76.92%) | 3 (23.08%) | 18 | 11 (61.11%) | 7 (38.89%) | 30 | 0.061 |
| No | 14 | 7 (53.85%) | 6 (46.15%) | 7 | 4 (57.14%) | 3 (42.86%) | 21 | 0.061 | |
| Inflammatory infiltrate | Yes | 25 | 16 (64%) | 9 (36%) | 22 | 14 (63.64%) | 8 (36.36%) | 47 | 0.350 ** |
| No | 1 | 1 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 3 | 1 (33.33%) | 2 (66.67%) | 4 | ||
| Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate | Yes | 19 | 13 (68.42%) | 6 (31.58%) | 20 | 14 (70%) | 6 (30%) | 39 | 0.560 |
| No | 7 | 4 (57.14%) | 3 (42.86%) | 5 | 1 (20%) | 4 (80%) | 12 | ||
| Macrophages | Yes | 2 | 2 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 1 | 0 (0%) | 1 (100%) | 3 | 1.00 |
| No | 24 | 15 (62.50%) | 9 (37.50%) | 24 | 15 (62.50%) | 9 (37.50%) | 48 | ||
| Hemorrhagic infiltration | Yes | 11 | 9 (64.29%) | 5 (35.71%) | 12 | 8 (72.73%) | 3 (27.27%) | 23 | 0.683 |
| No | 15 | 8 (66.67%) | 4 (33.33%) | 13 | 7 (50%) | 7 (50%) | 28 | ||
| Viable bone | Yes | 11 | 8 (72.73%) | 3 (27.27%) | 5 | 5 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 16 | 0.086 |
| No | 15 | 9 (60%) | 6 (40%) | 20 | 10 (50%) | 10 (50%) | 35 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciobanu, G.A.; Mogoantă, L.; Camen, A.; Ionescu, M.; Vlad, D.; Staicu, I.E.; Munteanu, C.M.; Gheorghiță, M.I.; Mercuț, R.; Sin, E.C.; et al. Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of MRONJ in Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103383
Ciobanu GA, Mogoantă L, Camen A, Ionescu M, Vlad D, Staicu IE, Munteanu CM, Gheorghiță MI, Mercuț R, Sin EC, et al. Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of MRONJ in Cancer Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(10):3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103383
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiobanu, George Adrian, Laurențiu Mogoantă, Adrian Camen, Mihaela Ionescu, Daniel Vlad, Ionela Elisabeta Staicu, Cristina Maria Munteanu, Mircea Ionuț Gheorghiță, Răzvan Mercuț, Elena Claudia Sin, and et al. 2023. "Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of MRONJ in Cancer Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 10: 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103383
APA StyleCiobanu, G. A., Mogoantă, L., Camen, A., Ionescu, M., Vlad, D., Staicu, I. E., Munteanu, C. M., Gheorghiță, M. I., Mercuț, R., Sin, E. C., & Popescu, S. M. (2023). Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of MRONJ in Cancer Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(10), 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103383







