Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: The Primary Results of a Randomised Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
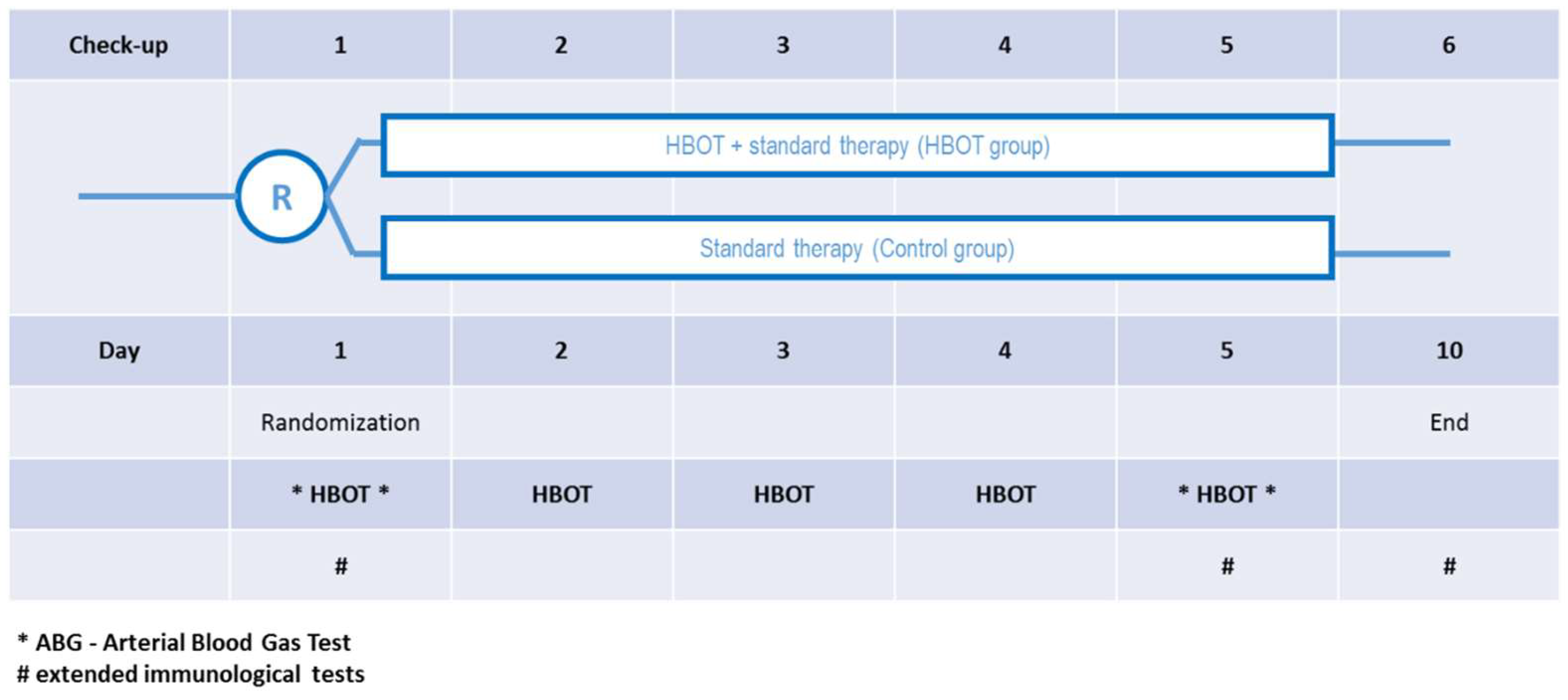
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Blood Serum Collection
2.3. Interleukin 6 Detection in the Serum
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining of Peripheral Blood Cells
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
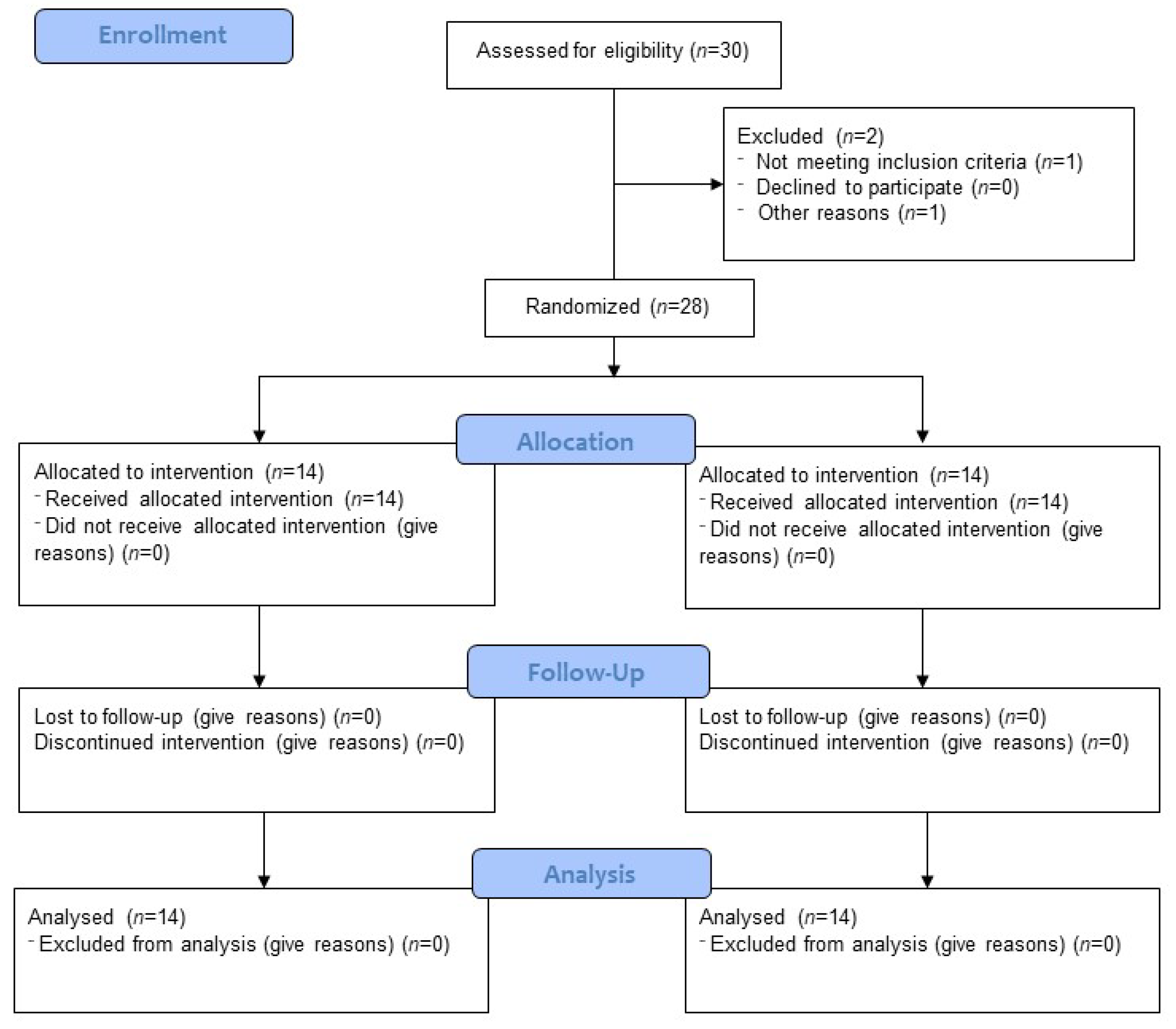
3.1. Participants
3.2. Blood Gas Test
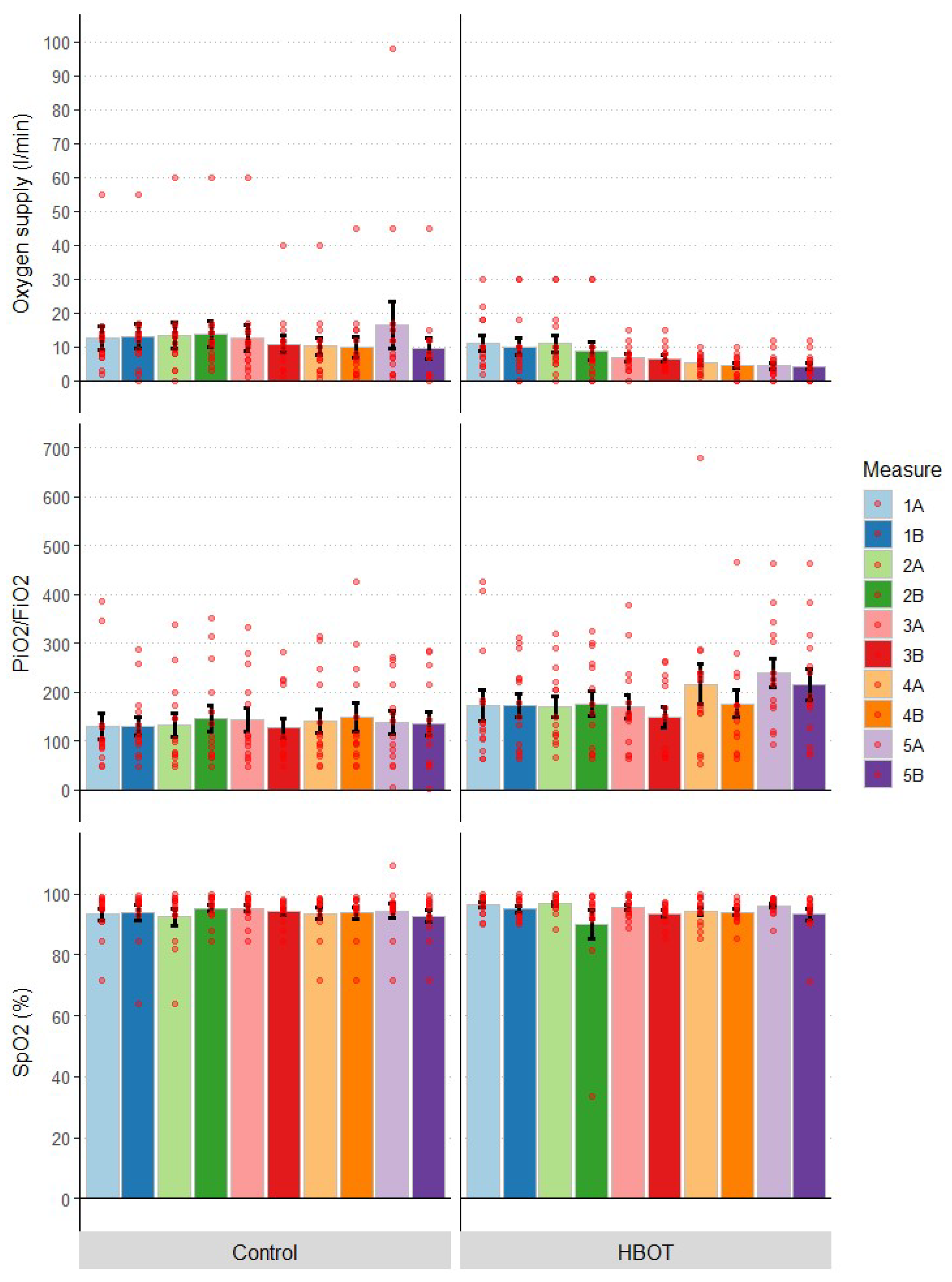
3.3. Oxygen Supply
3.4. Biochemistry
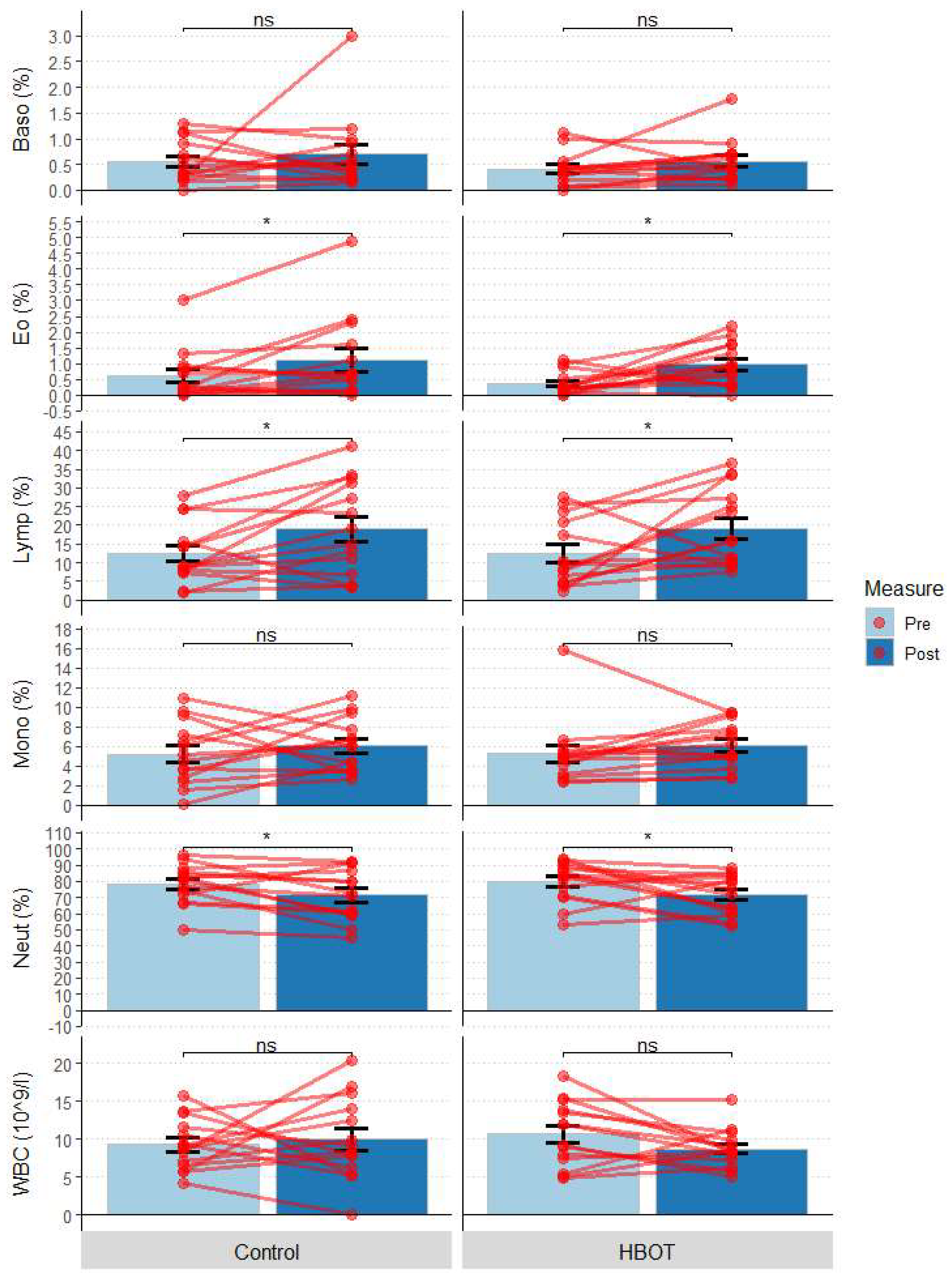
3.5. Complete Blood Count (CBC)
3.6. Immunology
3.6.1. T-Cell Subpopulations
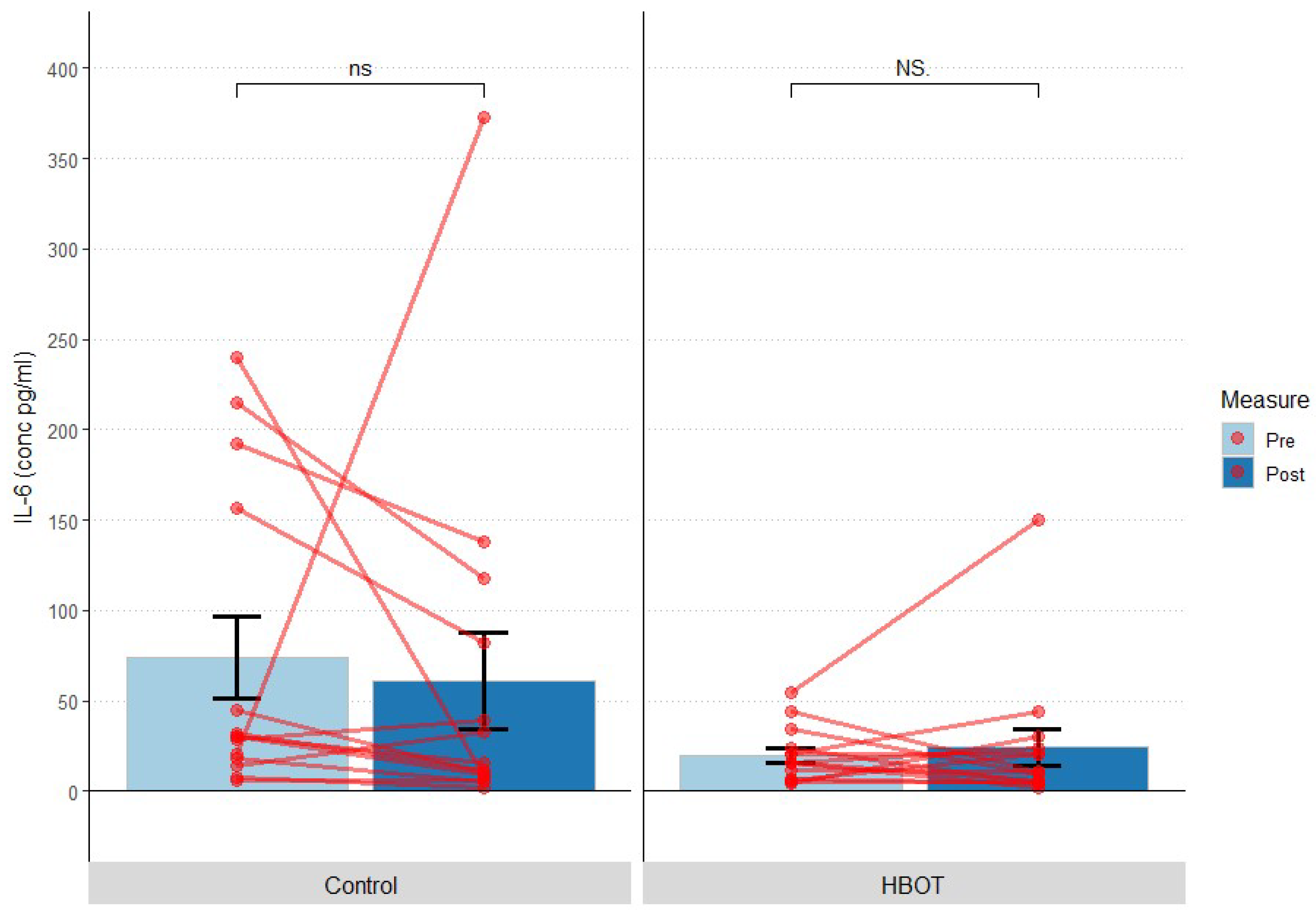
3.6.2. Interleukin 6
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanche, S.; Lin, Y.T.; Xu, C.; Romero-Severson, E.; Hengartner, N.; Ke, R. High Contagiousness and Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchette, L.; Sebastian, W.; Liu, T. A Comprehensive Review of COVID-19 Virology, Vaccines, Variants, and Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Sci. 2021, 41, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.; Sharma, K.; Silakari, O. The interplay between inflammatory pathways and COVID-19: A critical review on pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J.; Hlh Across Speciality Collaboration, U.K. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Jiang, T.; An, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; et al. Clinical and pathological investigation of patients with severe COVID-19. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e138070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nile, S.H.; Nile, A.; Qiu, J.; Li, L.; Jia, X.; Kai, G. COVID-19: Pathogenesis, cytokine storm and therapeutic potential of interferons. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Etayo, F.J.; Suarez-Fernandez, P.; Cabrera-Marante, O.; Arroyo, D.; Garcinuno, S.; Naranjo, L.; Pleguezuelo, D.E.; Allende, L.M.; Mancebo, E.; Lalueza, A.; et al. T-Helper Cell Subset Response Is a Determining Factor in COVID-19 Progression. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 624483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boechat, J.L.; Chora, I.; Morais, A.; Delgado, L. The immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 immunopathology—Current perspectives. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, P. The T cell immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habel, J.R.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; van de Sandt, C.E.; Juno, J.A.; Chaurasia, P.; Wragg, K.; Koutsakos, M.; Hensen, L.; Jia, X.; Chua, B.; et al. Suboptimal SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8(+) T cell response associated with the prominent HLA-A*02:01 phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24384–24391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riou, C.; du Bruyn, E.; Stek, C.; Daroowala, R.; Goliath, R.T.; Abrahams, F.; Said-Hartley, Q.; Allwood, B.W.; Hsiao, N.Y.; Wilkinson, K.A.; et al. Relationship of SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4 response to COVID-19 severity and impact of HIV-1 and tuberculosis coinfection. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e149125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Z.; et al. The role of interleukin-6 in monitoring severe case of coronavirus disease 2019. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratton, C.W.; Tang, Y.W.; Lu, H. Pathogenesis-directed therapy of 2019 novel coronavirus disease. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1320–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allado, E.; Poussel, M.; Valentin, S.; Kimmoun, A.; Levy, B.; Nguyen, D.T.; Rumeau, C.; Chenuel, B. The Fundamentals of Respiratory Physiology to Manage the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 615690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFee, R.B. COVID-19: Therapeutics and interventions currently under consideration. Dis. Mon. 2020, 66, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, C.; Kot, J. Oxygen: A Stimulus, Not “Only” a Drug. Medicina 2021, 57, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wolde, S.D.; Hulskes, R.H.; Weenink, R.P.; Hollmann, M.W.; Van Hulst, R.A. The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygenation on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporesi, E.M.; Bosco, G. Mechanisms of action of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2014, 41, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, B.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Donniacuo, M.; Capuano, A.; Di Palma, D.; Imperatore, F.; Mazzon, E.; Di Paola, R.; Sodano, L.; Rossi, F. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces the toll-like receptor signaling pathway in multiple organ failures. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, A.C.; Whatmore, J.L.; Harries, L.W.; Winyard, P.G.; Eggleton, P.; Smerdon, G.R. Different oxygen treatment pressures alter inflammatory gene expression in human endothelial cells. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2013, 40, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thom, S.R.; Bhopale, V.M.; Velazquez, O.C.; Goldstein, L.J.; Thom, L.H.; Buerk, D.G. Stem cell mobilization by hyperbaric oxygen. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H1378–H1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestra, C.; Arya, A.K.; Leveque, C.; Virgili, F.; Germonpre, P.; Lambrechts, K.; Lafere, P.; Thom, S.R. Varying Oxygen Partial Pressure Elicits Blood-Borne Microparticles Expressing Different Cell-Specific Proteins-Toward a Targeted Use of Oxygen? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmeier, J.J.; Kirby, J.P.; Buckey, J.C.; Denham, D.W.; Evangelista, J.S.; Gelly, H.B.; Harlan, N.P.; Mirza, Z.K.; Ray, K.L.; Robins, M.; et al. Physiologic and biochemical rationale for treating COVID-19 patients with hyperbaric oxygen. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2021, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; Garcia-Montero, C.; Callejon-Pelaez, E.; Saez, M.A.; Alvarez-Mon, M.A.; Garcia-Honduvilla, N.; Monserrat, J.; Alvarez-Mon, M.; Bujan, J.; et al. A General Overview on the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Applications, Mechanisms and Translational Opportunities. Medicina 2021, 57, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganini, M.; Bosco, G.; Perozzo, F.A.G.; Kohlscheen, E.; Sonda, R.; Bassetto, F.; Garetto, G.; Camporesi, E.M.; Thom, S.R. The Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment for COVID-19: A Review. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1289, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, A.; Hightower, L.E. COVID-19, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT): What is the link? Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 25, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hawa, A.A.A.; Charipova, K.; Bekeny, J.C.; Johnson-Arbor, K.K. The evolving use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Wound Care 2021, 30, S8–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, M.R.; Geier, D.A. Respiratory conditions in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Important considerations regarding novel treatment strategies to reduce mortality. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harch, P.G.; Paul, G.; Harch, M.D. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Coronavirus Application. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2020, 26, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harch, P.G. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) respiratory failure. Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellberg, A.; De Maio, A.; Lindholm, P. Can hyperbaric oxygen safely serve as an anti-inflammatory treatment for COVID-19? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, R.E.; Weaver, L.K. Hyperbaric oxygen as a treatment for COVID-19 infection? Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2020, 47, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senniappan, K.; Jeyabalan, S.; Rangappa, P.; Kanchi, M. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Can it be a novel supportive therapy in COVID-19? Indian J. Anaesth. 2020, 64, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, P.R.; Miot, H.A.; Pincelli, T.P.H.; Fabro, A.T. From dermatological conditions to COVID-19: Reasoning for anticoagulation, suppression of inflammation, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Derm. Ther. 2021, 34, e14565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylikoski, J.; Markkanen, M. COVID-19 deaths can be reduced—Simply and safely! Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-Y.; Tang, Y.-C.; Zhong, X.-L.; Liang, Y.; Li, B.-J.; Tao, X.-L.; Liao, C.-B. Efficacy analysis of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients. Acad. J. Second Mil. Med. Univ. 2020, 6, 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, D.; Marroni, A.; Kot, J. Tenth European Consensus Conference on Hyperbaric Medicine: Recommendations for accepted and non-accepted clinical indications and practice of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2017, 47, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.T.Y.; Chen, R. Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on HBOT in Patients with Severe New Coronavirus Pneumonia: First Report Chinese. Chin. J. Naut. Med. Hyperb. Med. 2020, 27, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.B. Intermittent high dosage oxygen treats COVID-19 infection: The Chinese studies. Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, M.; Yamashita, M. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment attenuates cytokine induction after massive hemorrhage. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 278, E811–E816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Pan, S.; Wang, M.; Guo, Y. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be effective to improve hypoxemia in patients with severe COVID-2019 pneumonia: Two case reports. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2020, 47, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibodeaux, K.; Speyrer, M.; Raza, A.; Yaakov, R.; Serena, T.E. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in preventing mechanical ventilation in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective case series. J. Wound Care 2020, 29, S4–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boet, S.; Etherington, C.; Djaiani, G.; Tricco, A.C.; Sikora, L.; Katznelson, R. Efficacy and safety of hyperbaric oxygen treatment in SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) pneumonia: A systematic review. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2021, 51, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliaei, S.; SeyedAlinaghi, S.; Mehrtak, M.; Karimi, A.; Noori, T.; Mirzapour, P.; Shojaei, A.; MohsseniPour, M.; Mirghaderi, S.P.; Alilou, S.; et al. The effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) on coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2021, 26, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, T.; Shaikh, A.; Kirthika, N. Effective Outcome of HBOT as an Adjuvant Therapy in Patients Diagnosed with COVID-19 in a Tertiary Care Hospital—A Preliminary Study. J. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 8, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannellotto, M.; Duarte, M.; Keller, G.; Larrea, R.; Cunto, E.; Chediack, V.; Mansur, M.; Brito, D.M.; Garcia, E.; Di Salvo, H.E.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen as an adjuvant treatment for patients with COVID-19 severe hypoxaemia: A randomised controlled trial. Emerg. Med. J. 2022, 39, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for patients with COVID-19. Emerg. Med. J. 2022, 39, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellberg, A.; Douglas, J.; Pawlik, M.T.; Kraus, M.; Oscarsson, N.; Zheng, X.; Bergman, P.; Franberg, O.; Kowalski, J.H.; Nyren, S.P.; et al. Randomised, controlled, open label, multicentre clinical trial to explore safety and efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen for preventing ICU admission, morbidity and mortality in adult patients with COVID-19. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e046738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenstein, S.A.; Castellano, M.L.; Slone, E.S.; Gillette, B.; Liu, H.; Alsamarraie, C.; Jacobson, A.M.; Wall, S.P.; Adhikari, S.; Swartz, J.L.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for COVID-19 patients with respiratory distress: Treated cases versus propensity-matched controls. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2020, 47, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, S.I.T.; Gomez, M.D.C.R.; Ramirez Nava, J.C.; Ayala, V.R.; Sommer, B.; Solis Chagoyan, H.; Calixto, E.; Montaño-Ramirez, L.M.; Romero Martinez, B.S.; Flores Soto, E. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Efficacy as an Adjuvant for the Systemic Inflammation Reduction in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Respir. Open Access 2022, 4, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Balushi, A.; AlShekaili, J.; Al Kindi, M.; Ansari, Z.; Al-Khabori, M.; Khamis, F.; Ambusaidi, Z.; Al Balushi, A.; Al Huraizi, A.; Al Sulaimi, S.; et al. Immunological predictors of disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 110, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.; Schulte, S.; Wildner, N.H.; Wittner, M.; Brehm, T.T.; Ramharter, M.; Woost, R.; Lohse, A.W.; Jacobs, T.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J. Analysis of Co-inhibitory Receptor Expression in COVID-19 Infection Compared to Acute Plasmodium falciparum Malaria: LAG-3 and TIM-3 Correlate With T Cell Activation and Course of Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, H.C.; Huang, S.H.; Hung, C.H.; Tsai, S.M.; Kuo, H.R.; Huang, Y.R.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, S.C.; Kuo, C.H.; Wu, D.C.; et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Alleviates the Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis via the Reduction of IL-17a and GM-Csf Production of Autoreactive T Cells as Well as Boosting the Immunosuppressive IL-10 in the Central Nervous System Tissue Lesions. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Long, J.; Shao, D.C.; Song, H. Hyperbaric oxygen inhibits production of CD3+ T cells in the thymus and facilitates malignant glioma cell growth. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2780–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buras, J.A.; Holt, D.; Orlow, D.; Belikoff, B.; Pavlides, S.; Reenstra, W.R. Hyperbaric oxygen protects from sepsis mortality via an interleukin-10-dependent mechanism. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 2624–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, R.M.; Minter, L.M.; Osborne, B.A.; Granowitz, E.V. Hyperbaric oxygen inhibits stimulus-induced proinflammatory cytokine synthesis by human blood-derived monocyte-macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 134, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECHM. European Committee for Hyperbaric Medicine (ECHM) Position on Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) in Multiplace Chambers During Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbreak. Available online: http://www.echm.org/documents/ECHM%20position%20on%20HBOT%20and%20COVID-19%20(16th%20March%202020).pdf (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- UHMS Position Statement: Hyperbaric Oxygen (HBO2) for COVID-19 Patients. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2020, 47, 297–298. [CrossRef]
- Zant, A.E.; Figueroa, X.A.; Paulson, C.P.; Wright, J.K. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat lingering COVID-19 symptoms. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2022, 49, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellberg, A.; Abdel-Halim, L.; Hassler, A.; El Gharbi, S.; Al-Ezerjawi, S.; Bostrom, E.; Sundberg, C.J.; Pernow, J.; Medson, K.; Kowalski, J.H.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen for treatment of long COVID-19 syndrome (HOT-LoCO): Protocol for a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase II clinical trial. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e061870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.Y.; An, S.; Sohn, Y.; Cho, Y.; Hyun, J.H.; Baek, Y.J.; Kim, M.H.; Jeong, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ku, N.S.; et al. Environmental contamination in the isolation rooms of COVID-19 patients with severe pneumonia requiring mechanical ventilation or high-flow oxygen therapy. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferioli, M.; Cisternino, C.; Leo, V.; Pisani, L.; Palange, P.; Nava, S. Protecting healthcare workers from SARS-CoV-2 infection: Practical indications. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2020, 29, 200068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunny, C.L.A. Performing hyperbaric oxygen therapy for central retinal artery occlusion under COVID-19: From myringotomy to rapid viral test. Health Policy Technol. 2021, 10, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgok-Kangal, K.; Zaman, T.; Koc, B. The outcomes of COVID-19 measures in a hyperbaric oxygen therapy centre during the pandemic. Int. Marit. Health 2021, 72, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.J.; Wang, S.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, H.C.; Hung, C.T.; Huang, S.H. Proactive COVID-19 Infection Prevention Measures in a Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Center. Medicina 2020, 56, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.L.; Kim, S.J.; Tan, M.K.; Lim, K.H.; See, H.G. Provision of emergency hyperbaric oxygen treatment for a patient during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2021, 51, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Pre | Post | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SE | IQR | M | SE | IQR | ||
| Oxygen supply (L/min) | HBOT | 11.07 | 2.15 | 10.50 | 4.79 | 0.84 | 3.75 |
| Control | 12.50 | 3.44 | 5.75 | 9.62 | 2.99 | 10.00 | |
| PiO2/FiO2 | HBOT | 171.52 | 31.60 | 76.96 | 214.88 | 31.27 | 143.78 |
| Control | 129.34 | 27.68 | 36.55 | 134.91 | 24.21 | 132.35 | |
| SpO2 (%) | HBOT | 96.26 | 0.88 | 5.05 | 93.19 | 1.84 | 5.15 |
| Control | 93.30 | 1.96 | 5.55 | 92.68 | 1.94 | 5.60 | |
| Group | Pre | Post | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SE | IQR | M | SE | IQR | ||
| CRP (mg/dL) | HBOT | 3.83 | 1.16 | 3.65 | 1.54 | 0.77 | 0.75 |
| Control | 4.46 | 0.93 | 4.55 | 4.54 | 1.76 | 5.50 | |
| D-Dimer (mg/mL) | HBOT | 1.29 | 0.29 | 0.60 | 1.37 | 0.32 | 0.51 |
| Control | 4.92 | 2.86 | 1.13 | 5.46 | 2.90 | 2.34 | |
| Ferritin (mg/mL) | HBOT | 1186.36 | 355.55 | 749.25 | 741.63 | 126.43 | 695.00 |
| Control | 745.31 | 198.81 | 1034.00 | 580.68 | 154.46 | 736.70 | |
| LDH (µ/L) | HBOT | 304.53 | 40.39 | 147.75 | 258.93 | 39.55 | 130.25 |
| Control | 267.12 | 62.63 | 328.29 | 246.40 | 64.01 | 324.30 | |
| PCT (mg/mL) | HBOT | 0.086 | 0.018 | 0.055 | 0.071 | 0.014 | 0.025 |
| Control | 0.174 | 0.056 | 0.092 | 0.154 | 0.056 | 0.062 | |
| Group | Pre | Post | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SE | IQR | M | SE | IQR | ||
| WBC (109/L) | HBOT | 10.65 | 1.14 | 6.13 | 9.59 | 0.85 | 3.54 |
| Control | 9.28 | 0.90 | 4.62 | 8.05 | 0.97 | 3.64 | |
| Lymp (%) | HBOT | 12.41 | 2.36 | 14.77 | 19.69 | 3.05 | 17.55 |
| Control | 12.45 | 2.17 | 7.56 | 19.40 | 3.26 | 21.40 | |
| Neut (%) | HBOT | 79.94 | 3.34 | 16.68 | 71.41 | 3.72 | 22.85 |
| Control | 78.44 | 3.23 | 12.27 | 70.76 | 4.14 | 24.93 | |
| Mono (%) | HBOT | 5.27 | 0.88 | 2.12 | 5.64 | 0.61 | 2.93 |
| Control | 5.22 | 0.86 | 4.12 | 6.28 | 0.78 | 4.46 | |
| Baso (%) | HBOT | 0.41 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 0.43 |
| Control | 0.56 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.09 | 0.44 | |
| Eo (%) | HBOT | 0.37 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.90 | 0.18 | 0.93 |
| Control | 0.62 | 0.21 | 0.73 | 1.14 | 0.36 | 1.32 | |
| Group | Pre | Post | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SE | IQR | M | SE | IQR | ||
| CD3 (% CD45+) | HBOT | 5.97 | 0.95 | 4.05 | 13.76 | 2.29 | 11.03 |
| Control | 5.96 | 1.73 | 5.18 | 9.58 | 2.23 | 11.65 | |
| CD4 (% CD3+) | HBOT | 56.41 | 3.98 | 17.45 | 62.80 | 3.15 | 14.80 |
| Control | 46.58 | 5.05 | 24.00 | 52.19 | 5.42 | 23.18 | |
| CD8 (% CD3+) | HBOT | 29.38 | 3.11 | 19.33 | 28.78 | 3.08 | 11.63 |
| Control | 33.10 | 4.62 | 16.23 | 32.86 | 3.87 | 14.05 | |
| Group | Pre | Post | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SE | IQR | M | SE | IQR | ||
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | HBOT | 14.80 | 19.91 | 4.02 | 17.35 | 24.47 | 10.18 |
| Control | 110.15 | 74.10 | 22.89 | 62.76 | 60.79 | 26.77 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siewiera, J.; Brodaczewska, K.; Jermakow, N.; Lubas, A.; Kłos, K.; Majewska, A.; Kot, J. Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: The Primary Results of a Randomised Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010008
Siewiera J, Brodaczewska K, Jermakow N, Lubas A, Kłos K, Majewska A, Kot J. Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: The Primary Results of a Randomised Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiewiera, Jacek, Klaudia Brodaczewska, Natalia Jermakow, Arkadiusz Lubas, Krzysztof Kłos, Aleksandra Majewska, and Jacek Kot. 2023. "Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: The Primary Results of a Randomised Clinical Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010008
APA StyleSiewiera, J., Brodaczewska, K., Jermakow, N., Lubas, A., Kłos, K., Majewska, A., & Kot, J. (2023). Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: The Primary Results of a Randomised Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010008






