Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine vs. Remifentanil for Postoperative Analgesia and Opioid-Related Side Effects after Gynecological Laparoscopy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design & Participants
2.2. Randomization and Blinding
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Outcome Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
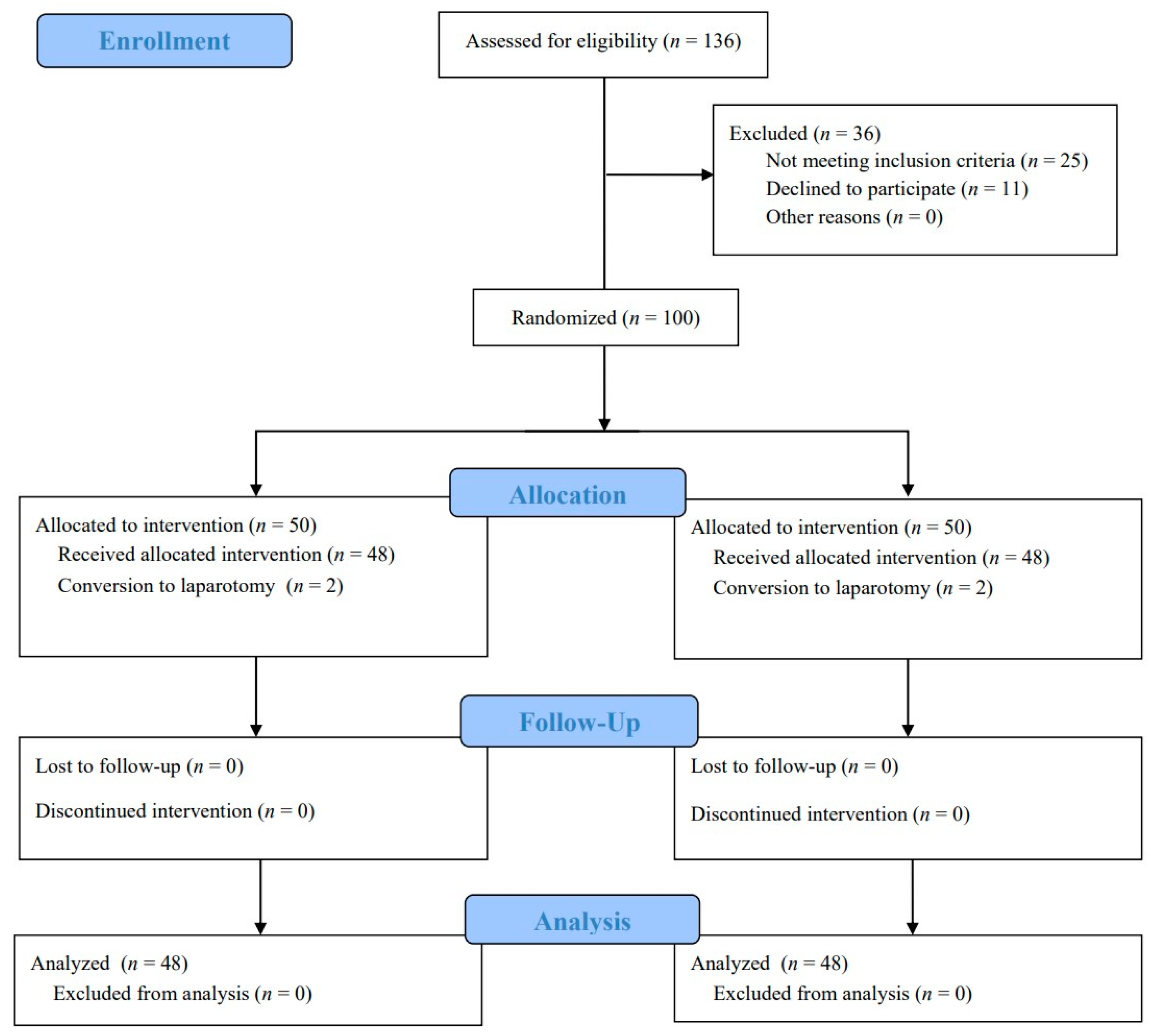
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Intraoperative Findings
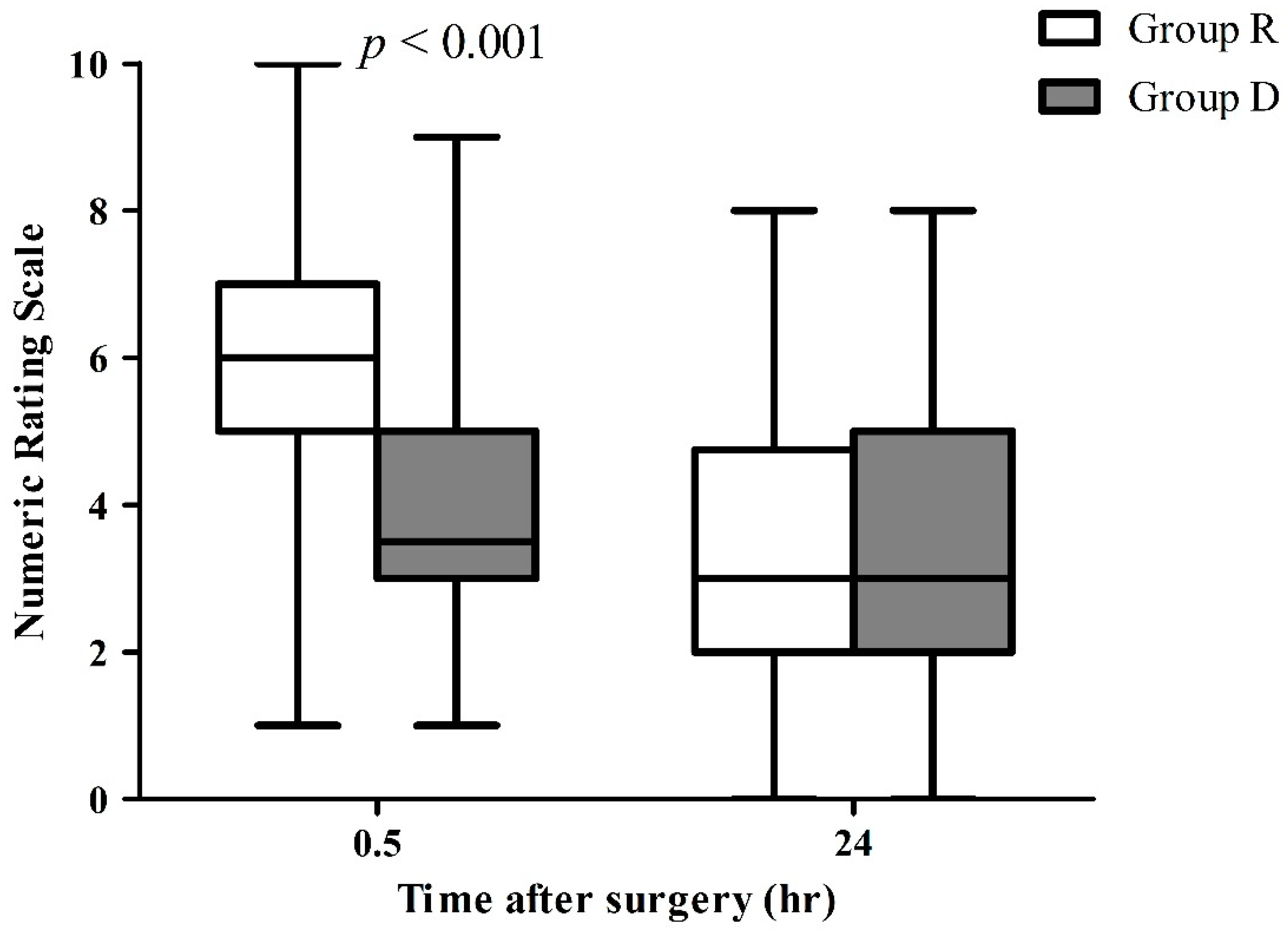
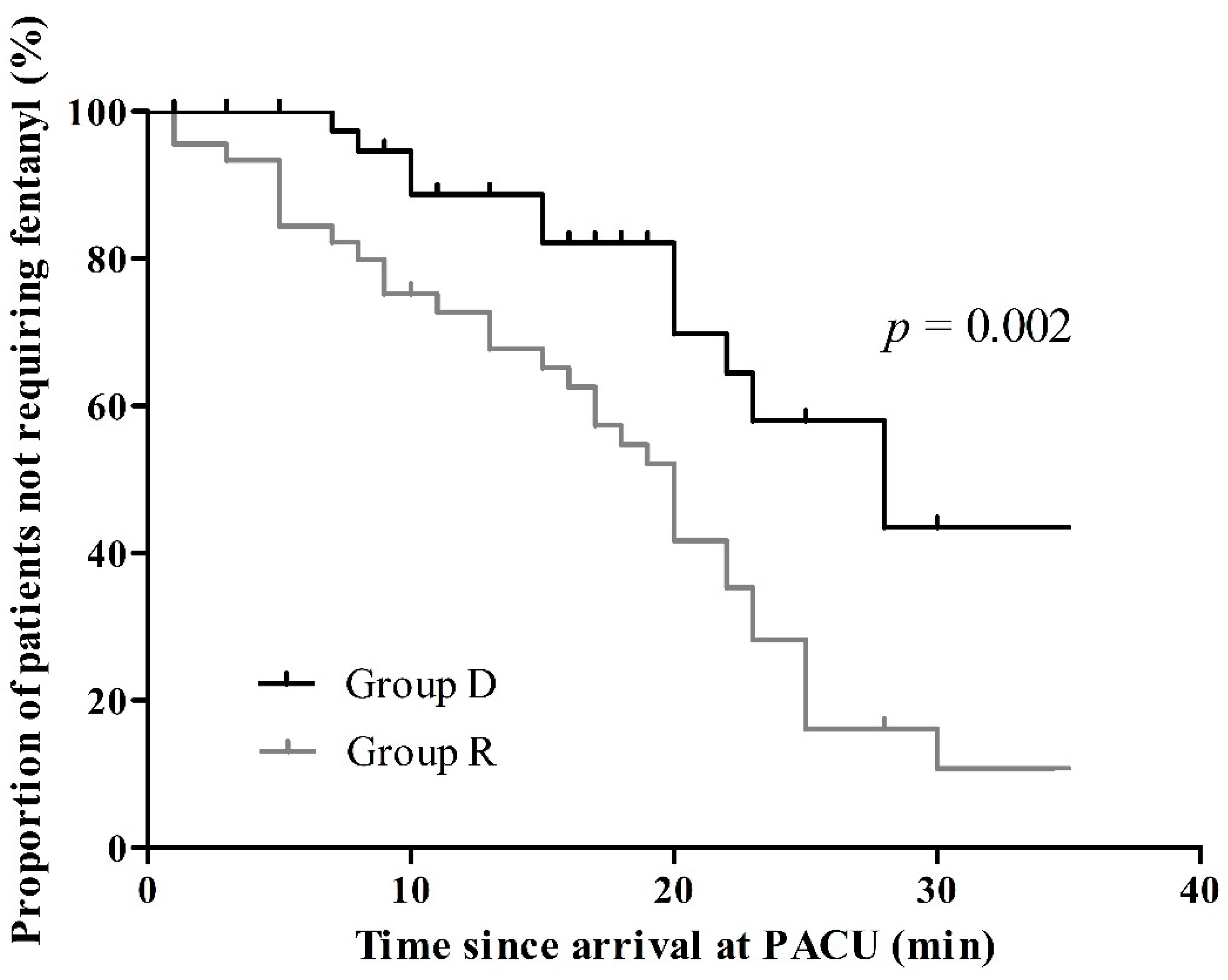
3.3. Postoperative Pain
3.4. Other Postoperative Findings
3.5. Ancillary Cytokine Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vinik, H.R.; Kissin, I. Rapid development of tolerance to analgesia during remifentanil infusion in humans. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 86, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, T.J.; Belani, K.G.; Bergese, S.; Chung, F.; Diemunsch, P.; Habib, A.S.; Jin, Z.; Kovac, A.L.; Meyer, T.A.; Urman, R.D.; et al. Fourth Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 411–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanthanna, H.; Ladha, K.S.; Kehlet, H.; Joshi, G.P. Perioperative Opioid Administration: A Critical Review of Opioid-free versus Opioid-sparing Approaches. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.-C.; Xia, M.-L.; Shu, S.-J.; Chen, F.; Jiang, L.-S. Attenuation of Remifentanil-Induced Hyperalgesia by Betulinic Acid Associates with Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Spinal Dorsal Horn. Pharmacology 2018, 102, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Xu, Z.-Z.; Wang, X.; Park, J.Y.; Zhuang, Z.-Y.; Tan, P.-H.; Gao, Y.-J.; Roy, K.; Corfas, G.; Lo, E.H.; et al. Distinct roles of matrix metalloproteases in the early- and late-phase development of neuropathic pain. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, W.C.; Wilson, C.L.; López-Boado, Y.S. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.-L.; He, S.-F.; Hu, X.-W.; Wong, G.T.C.; Zhang, Y. Dexmedetomidine Combined with General Anesthesia Provides Similar Intraoperative Stress Response Reduction When Compared with a Combined General and Epidural Anesthetic Technique. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhana, N.; Goa, K.L.; McClellan, K.J. Dexmedetomidine. Drugs 2000, 59, 263–268; Discussion 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvan, E.G.; Öç, B.; Uzun, Ş.; Karabulut, E.; Coşkun, F.; Aypar, Ü. Dexmedetomidine and postoperative shivering in patients undergoing elective abdominal hysterectomy. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 25, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xia, Z. Dexmedetomidine in perioperative acute pain management: A non-opioid adjuvant analgesic. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, K.-L.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.-L.; Yu, Y.-H. Prevention of Remifentanil Induced Postoperative Hyperalgesia by Dexmedetomidine via Regulating the Trafficking and Function of Spinal NMDA Receptors as well as PKC and CaMKII Level In Vivo and In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüfek, A.; Kaya, S.; Tokgöz, O.; Fırat, U.; Evliyaoğlu, O.; Çelik, F.; Karaman, H. The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on bupivacaine-induced sciatic nerve inflammation is mediated by mast cells. Clin. Investig. Med. 2013, 36, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonocito, C.; Noto, A.; Crimi, C.; Sanfilippo, F. Remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia: Current perspectives on mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Local Reg. Anesth. 2018, 11, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, M.S. Intraoperative Use of Remifentanil for TIVA: Postoperative Pain, Acute Tolerance, and Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015, 29 (Suppl. 1), S16–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grape, S.; Kirkham, K.R.; Frauenknecht, J.; Albrecht, E. Intra-operative analgesia with remifentanil vs. dexmedetomidine: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Anaesthesia 2019, 74, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerink, M.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Barends, C.R.M.; Absalom, A.R.; Colin, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloeil, H.; Garot, M.; Lebuffe, G.; Gerbaud, A.; Bila, J.; Cuvillon, P.; Dubout, E.; Oger, S.; Nadaud, J.; Becret, A.; et al. Balanced Opioid-free Anesthesia with Dexmedetomidine versus Balanced Anesthesia with Remifentanil for Major or Intermediate Noncardiac Surgery: The Postoperative and Opioid-free Anesthesia (POFA) Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Kim, B.I.; Byun, S.H.; Kim, E.; Sung, S.Y.; Jung, J.Y. Cardiac arrest in a patient with anterior fascicular block after administration of dexmedetomidine with spinal anesthesia: A case report. Medicine 2016, 95, e5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, A.; Blais, D.M.; Jones, G.M.; Burcham, P.; Stawicki, S.P.; Cook, C.H.; Murphy, C. Predictors of dexmedetomidine-associated hypotension in critically ill patients. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2016, 6, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Ren, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. The Opioid-Sparing Effect of Perioperative Dexmedetomidine Plus Sufentanil Infusion during Neurosurgery: A Retrospective Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.-L.; Chi, P. The Opioid-Sparing Effect of Perioperative Dexmedetomidine Combined with Oxycodone Infusion during Open Hepatectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, E.; Catak, T.; Basar, H.; Cebeci, Z.; Coskun, I.; Saltali, A.; Altinbas, A. Prevalence study for postoperative nausea vomiting: A training hospital example. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 24, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.-G.; Ge, X.-Y.; Zhu, H.; Liang, X.; Gong, H.-X.; Zhong, M.; Xiao, X. Dexmedetomidine for antiemesis in gynecologic surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14566–14576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhou, M.; Feng, J.-J.; Wu, L.; Fang, S.-P.; Ge, X.-Y.; Sun, H.-J.; Ren, P.-C.; Lv, X. Efficacy of dexmedetomidine on postoperative nausea and vomiting: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8450–8471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Bao, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Comparison of dexmedetomidine and fentanyl as local anesthetic adjuvants in spinal anesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 3413–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Dexmedetomidine alleviates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Li, L.; Lu, S.; Li, K.; Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, G. The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 94, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Hu, X.; Sha, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H. Dexmedetomidine Ameliorates Acute Stress-Induced Kidney Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis through Inhibition of the ROS/JNK Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4035310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Shen, W.; Song, P.; Song, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Meng, Z.; Liu, J. Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury in rats by inhibiting caveolin-1 downstream signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20204279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Shen, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhang, K.; Guo, M.; Wang, F.; Qin, K. Dexmedetomidine Ameliorates Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Aged Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group R | Group D | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 48) | (n = 48) | ||
| Age | 43.9 ± 10.7 | 41.7 ± 9.5 | 0.28 |
| Height (cm) | 159.0 ± 5.7 | 160.5 ± 4.9 | 0.16 |
| Weight (kg) | 58.5 ± 10.1 | 58.3 ± 7.2 | 0.90 |
| ASA classification (I/II) | 34/14 | 39/9 | 0.23 |
| Type of surgery | 0.15 | ||
| Hysterectomy a | 29 (60.5%) | 25 (52.1%) | |
| Myomectomy b | 4 (8.3%) | 6 (12.5%) | |
| Cystectomy/Cyst enucleation only | 10 (20.8%) | 15 (31.2%) | |
| Adnexectomy only | 5 (10.4%) | 2 (4.2%) |
| Group R (n = 48) | Group D (n = 48) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anesthetic duration (min) | 148.0 ± 51.2 | 141.4 ± 5.4 | 0.47 |
| Time to eye opening (min) | 5.1 ± 1.7 | 5.1 ± 1.8 | 0.93 |
| Time to extubation (min) | 5.7 ± 1.8 | 5.7 ± 2.0 | 0.95 |
| Intraoperative hypotension | 22 (45.8%) | 11 (22.9%) | 0.018 |
| Intraoperative bradycardia | 7 (14.6%) | 3 (6.3%) | 0.18 |
| Remifentanil dose (μg/kg/min) | 0.1 ± 0.04 | ||
| Dexmedetomidine dose (μg/kg/h) | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| Group R (n = 48) | Group D (n = 48) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 h after surgery | |||
| Rescue analgesic use | 32 (66.7%) | 12 (25%) | <0.001 |
| PONV | 9 (18.8%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.008 |
| Rescue antiemetic use | 32 (66.7%) | 12 (25%) | <0.001 |
| Sedation level (level 1/2/3) | 44/3/1 | 39/9/0 | 0.1 |
| Shivering | 6 (12.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.01 |
| Time of PACU stay (min) | 39.2 ± 5.5 | 33.8 ± 5.0 | <0.001 |
| 24 h after surgery | |||
| PCA use (ml) | 17.7 ± 14.1 | 17.2 ± 11.1 | 0.9 |
| Rescue analgesic use | 15 (31.3%) | 13 (27.1%) | 0.8 |
| PONV | 13 (27.1%) | 17 (36.4%) | 0.5 |
| Rescue antiemetic use | 3 (6.3%) | 2 (4.2%) | >0.999 |
| Shivering | 7 (14.6%) | 6 (12.5%) | >0.999 |
| Pruritus | 1 (2.1%) | 1 (2.1%) | >0.999 |
| Time to first flatus (h) | 20.1 ± 6.2 | 22.5 ± 5.8 | 0.06 |
| Group R | Group D | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 20) | (n = 20) | ||
| MnSOD (ng/mL) | 0.5 | ||
| T0 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | |
| T1 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | |
| T2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | |
| MMP-9 (pg/mL) | 0.6 | ||
| T0 | 187.3 ± 85.7 | 191.5 ± 100.9 | |
| T1 | 385.1 ± 211.3 | 352.4 ± 230.2 | |
| T2 | 331.9 ± 139.6 | 351.6 ± 209.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koo, J.M.; Chung, Y.-J.; Lee, M.; Moon, Y.E. Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine vs. Remifentanil for Postoperative Analgesia and Opioid-Related Side Effects after Gynecological Laparoscopy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010350
Koo JM, Chung Y-J, Lee M, Moon YE. Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine vs. Remifentanil for Postoperative Analgesia and Opioid-Related Side Effects after Gynecological Laparoscopy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010350
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoo, Jung Min, Youn-Jee Chung, Mihyeon Lee, and Young Eun Moon. 2023. "Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine vs. Remifentanil for Postoperative Analgesia and Opioid-Related Side Effects after Gynecological Laparoscopy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010350
APA StyleKoo, J. M., Chung, Y.-J., Lee, M., & Moon, Y. E. (2023). Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine vs. Remifentanil for Postoperative Analgesia and Opioid-Related Side Effects after Gynecological Laparoscopy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010350






