Decreased Physical and Daily Living Activities in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease on Hemodialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
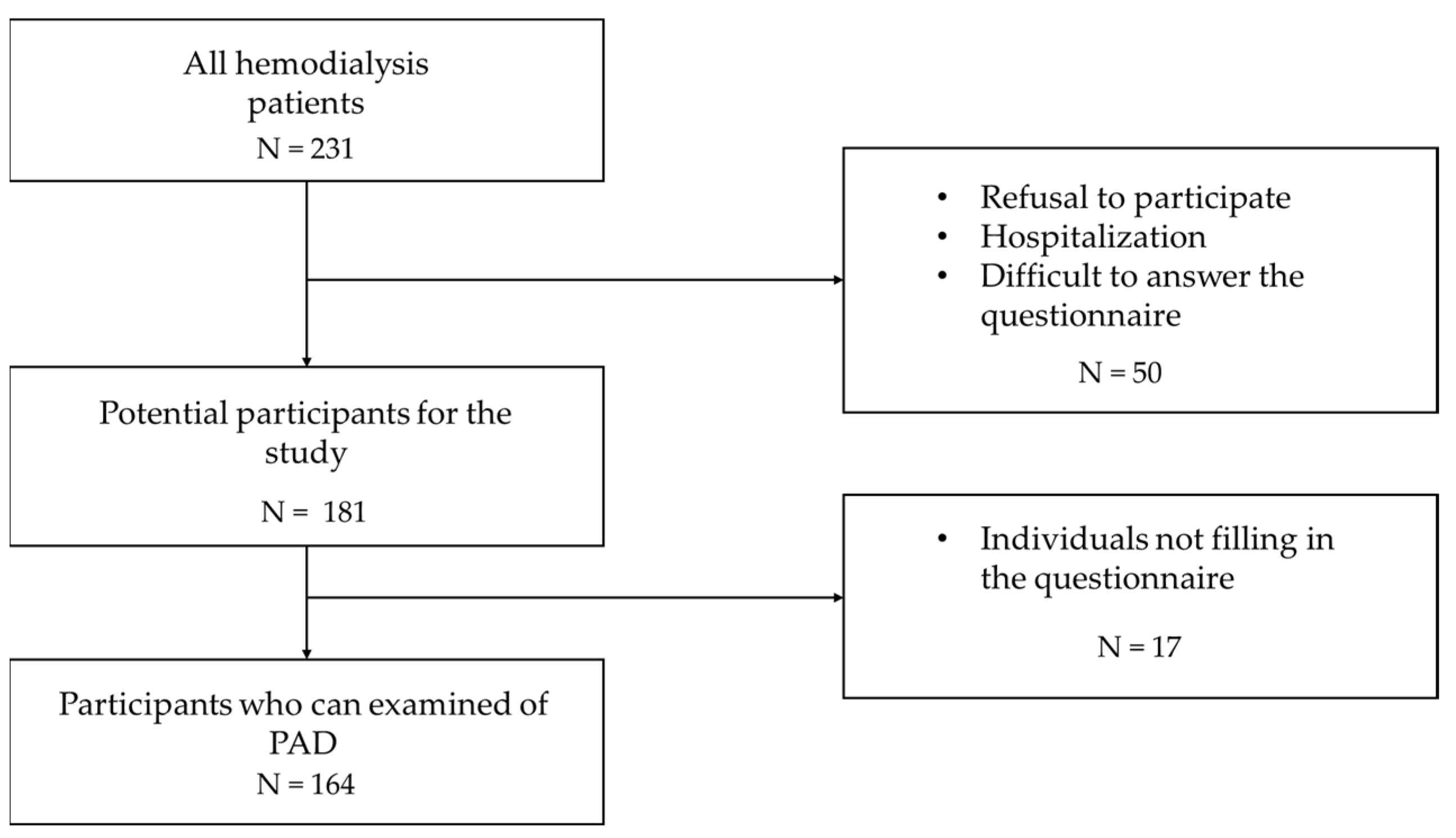
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Evaluation Measurements and Factors
2.2.1. ADL Difficulty
2.2.2. Life-Space Assessment
2.2.3. Kihon Checklist (KCL)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Data
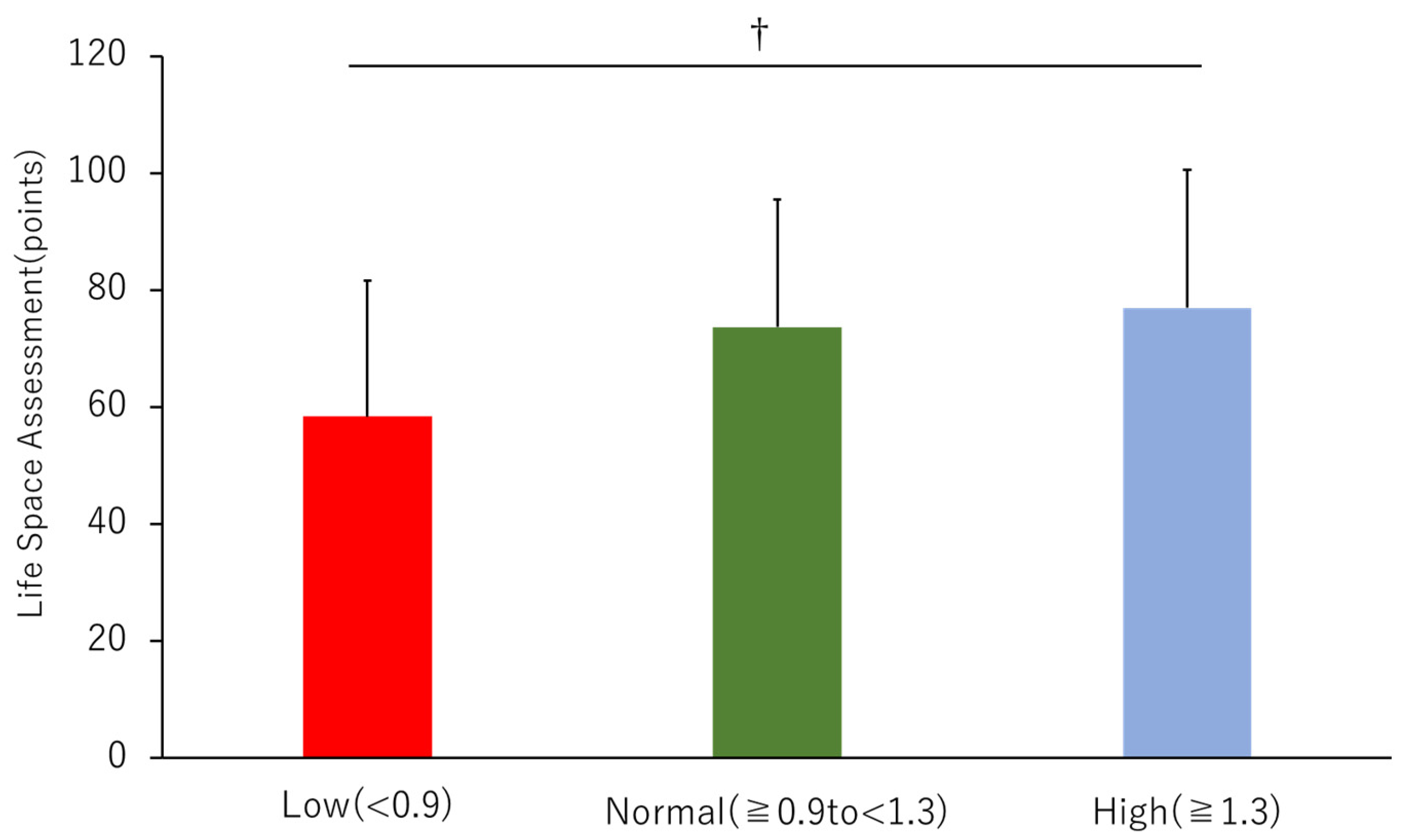
3.2. Life-Space Assessment (LSA)
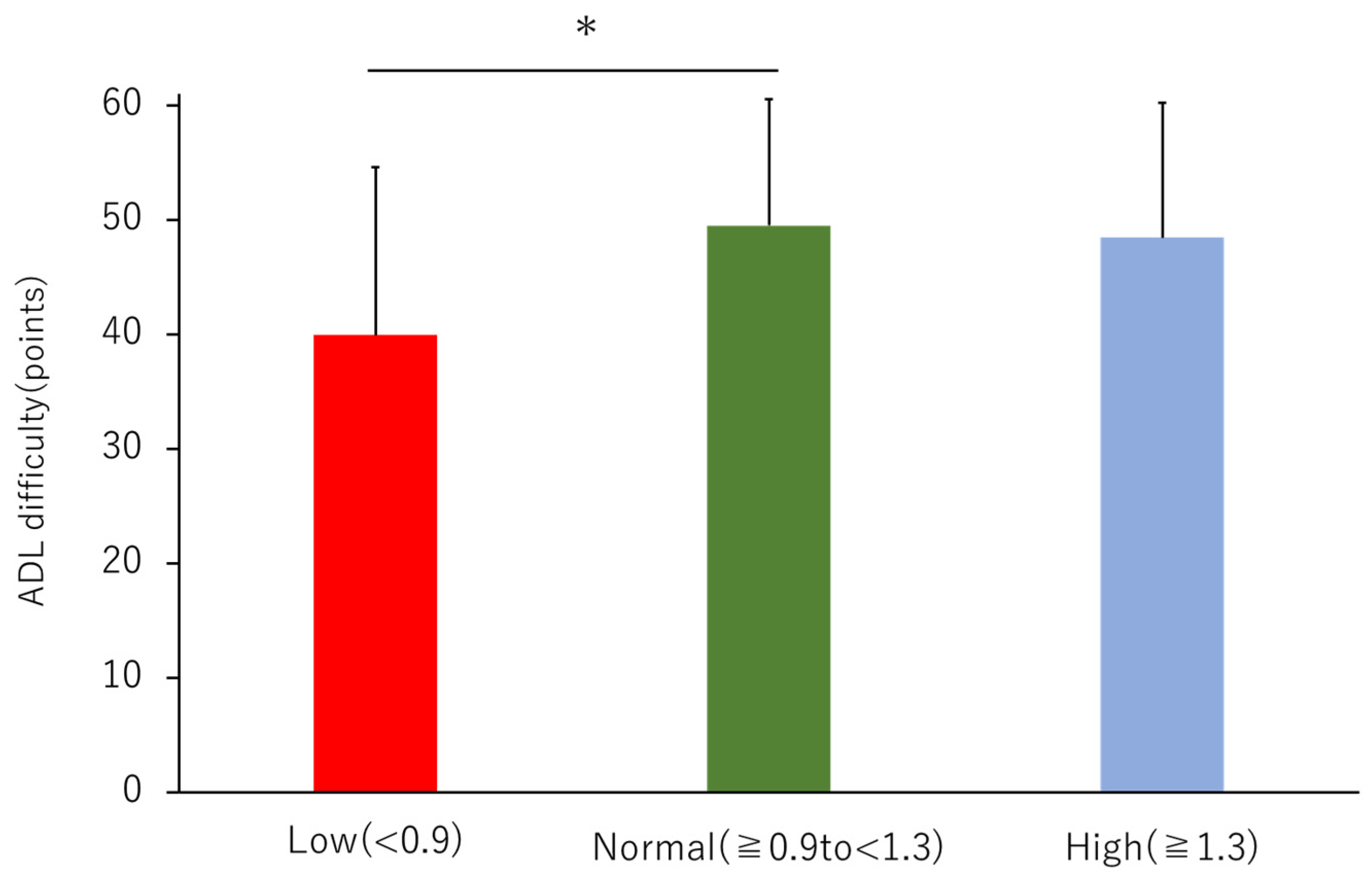
3.3. ADL Difficulty
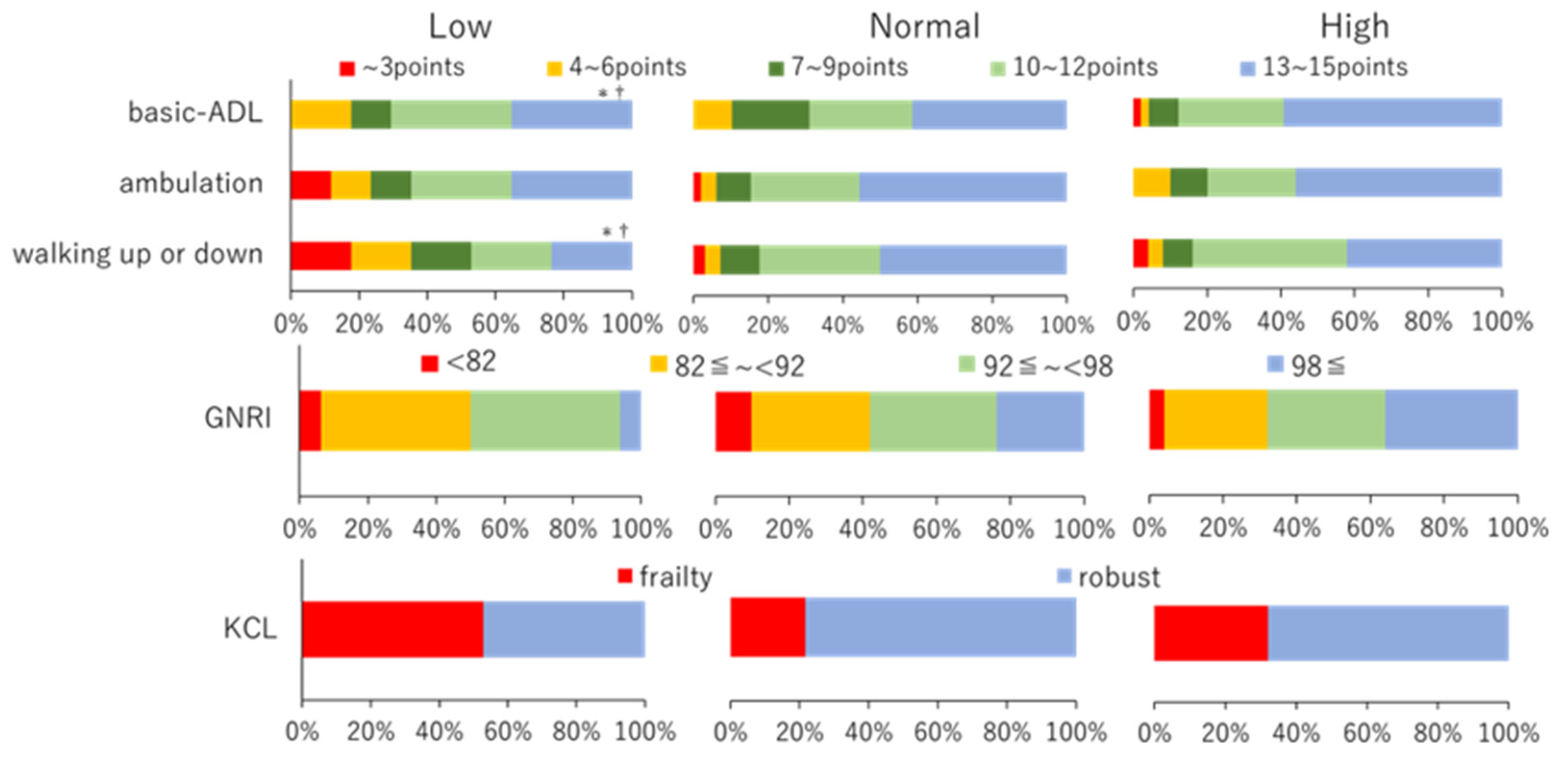
3.4. Nutritional Index
3.5. Frailty
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohtake, T.; Oka, M.; Ikee, R.; Mochida, Y.; Ishioka, K.; Moriya, H.; Hidaka, S.; Kobayashi, S. Impact of lower limbs’ arterial calcification on the prevalence and severity of PAD in patients on hemodialysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Oka, M.; Maesato, K.; Ikee, R.; Mano, T.; Moriya, H.; Ohtake, T.; Kobayashi, S. Peripheral arterial occlusive disease is more prevalent in patients with hemodialysis: Comparison with the findings of multidetector-row computed tomography. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Tsuchida, A.; Kawai, H.; Matsuo, H.; Wakamatsu, R.; Maezawa, A.; Yano, S.; Kawada, T.; Nojima, Y. Ankle-brachial blood pressure index predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morooka, H.; Tanaka, A.; Inaguma, D.; Maruyama, S. Peripheral artery disease at the time of dialysis initiation and mortality: A prospective observational multicenter study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e042315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Krolewski, A.S.; Rosner, B.; Arky, R.A.; Speizer, F.E.; Hennekens, C.H. A prospective study of maturity-onset diabetes mellitus and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in women. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991, 151, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberly, L.E.; Cohen, J.D.; Prineas, R.; Yang, L.; Intervention Trial Research group. Impact of incident diabetes and incident nonfatal cardiovascular disease on 18-year mortality: The multiple risk factor intervention trial experience. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauret, G.J.; Fokkenrood, H.J.; Bendermacher, B.L.; Scheltinga, M.R.; Teijink, J.A. Physical activity monitoring in patients with intermittent claudication. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2014, 47, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, R.; Roshanravan, B.; Shimoda, T.; Mamorita, N.; Yoneki, K.; Harada, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, A.; Takeuchi, Y.; Matsunaga, A. Physical activity dose for hemodialysis patients: Where to begin? Results from a prospective cohort study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M.; Ogawa, M.; Dos Santos, M.R.; Kondo, H.; Suga, K.; Itoh, H.; Tabata, Y. Effects of intradialytic resistance exercise on protein energy wasting, physical performance and physical activity in ambulatory patients on dialysis: A single-center preliminary study in a Japanese dialysis facility. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2016, 20, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kutsuna, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Harada, M.; Shimoda, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Isobe, Y.; Imamura, K.; Matsunaga, Y.; Matsuzawa, R.; et al. Perceived difficulty in activities of daily living and survival in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Uchida, H.A.; Kakio, Y.; Okuyama, Y.; Umebayashi, R.; Wada, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Rakugi, H.; et al. Peripheral artery disease is associated with frailty in chronic hemodialysis patients. Vascular 2018, 26, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelle, D.M.; Klaassen, G.; van Adrichem, E.; Bakker, S.J.; Corpeleijn, E.; Navis, G. Physical inactivity: A risk factor and target for intervention in renal care. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakousis, N.D.; Biliou, S.; Pyrgioti, E.E.; Georgakopoulos, P.N.; Liakopoulos, V.; Papanas, N. Frailty, sarcopenia and diabetic kidney disease: Where do we stand? Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinzato, T.; Nakai, S.; Fujita, Y.; Takai, I.; Morita, H.; Nakane, K.; Maeda, K. Determination of Kt/V and protein catabolic rate using pre- and postdialysis blood urea nitrogen concentrations. Nephron 1994, 67, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Uchida, H.A.; Kakio, Y.; Okuyama, Y.; Okuyama, M.; Umebayashi, R.; Wada, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Rakugi, H.; et al. The prevalence of frailty and its associated factors in Japanese hemodialysis patients. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kutsuna, T.; Yoneki, K.; Harada, M.; Shimoda, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Murayama, N.; Matsuzawa, R.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshida, A.; et al. Determinants of difficulty in activities of daily living in ambulatory patients undergoing hemodialysis. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2018, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.S.; Bodner, E.V.; Allman, R.M. Measuring life-space mobility in community-dwelling older adults. J. Am. Geriatr Soc. 2003, 51, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, C.; Sawyer Baker, P.; Roth, D.L.; Brown, C.J.; Brodner, E.V.; Allman, R.M. Assessing mobility in older adults: The UAB Study of Aging Life-Space Assessment. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 1008–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Satake, S. English translation of the Kihon Checklist. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2015, 15, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewo Sampaio, P.Y.; Sampaio, R.A.; Yamada, M.; Arai, H. Systematic review of the Kihon Checklist: Is it a reliable assessment of frailty? Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, S.; Senda, K.; Hong, Y.J.; Miura, H.; Endo, H.; Sakurai, T.; Kondo, I.; Toba, K. Validity of the Kihon Checklist for assessing frailty status. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Yabushita, N.; Kim, M.J.; Matsuo, T.; Seino, S.; Tanaka, K. Assessment of vulnerable older adults’ physical function according to the Japanese Long-Term Care Insurance (LTCI) system and Fried’s criteria for frailty syndrome. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 55, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowling, C.B.; Muntner, P.; Sawyer, P.; Sanders, P.W.; Kutner, N.; Kennedy, R.; Allman, R.M. Community mobility among older adults with reduced kidney function: A study of life-space. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, K.L.; Chertow, G.M.; Ng, A.V.; Mulligan, K.; Carey, S.; Schoenfeld, P.Y.; Kent-Braun, J.A. Physical activity levels in patients on hemodialysis and healthy sedentary controls. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 2564–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossola, M.; Di Stasio, E.; Antocicco, M.; Pepe, G.; Tazza, L.; Zuccalà, G.; Laudisio, A. Functional impairment is associated with an increased risk of mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, M.A.; Cucato, G.G.; Lanza, F.C.; Peixoto, R.A.O.; Zerati, A.E.; Puech-Leao, P.; Wolosker, N.; Ritti-Dias, R.M. Relationship between gait speed and physical function in patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease. Clinics 2019, 74, e1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Heimburger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Kaysen, G.A.; Bergstrom, J. Are there two types of malnutrition in chronic renal failure? Evidence for relationships between malnutrition, inflammation and atherosclerosis (MIA syndrome). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, J. Intradialytic exercise in hemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.P.; Nakamura, Y.M.P.; Murakami, T.P.; Tsukahara, H.P.; Watanabe, Y.O.; Matsuoka, Y.M.; Ohsawa, I.M.P.; Gotoh, H.M.P.; Inagaki, T.G.S.; Oguchi, E.P.P. Rehabilitation improves prognosis and activities of daily living in hemodialysis patients with low activities of daily living. Phys. Ther. Res. 2017, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | All (n = 164) | Low (n = 17) | Normal (n = 97) | High (n = 50) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 62.7 ± 11.2 | 67.9 ± 12.0 | 61.8 ± 11.7 | 62.6 ± 9.5 | 0.113 |
| Male, n (%) | 118 (72.0%) | 9 (52.9%) † | 66 (68.0%) | 43 (86.0%) | 0.013 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.5 ± 4.3 | 21.1 ± 3.3 † | 22.3 ± 4.5 † | 22.5 ± 4 | 0.090 |
| Smoking history, n (%) | 30 (18.2%) | 4 (23.5%) | 15 (15.5%) | 11 (22.0%) | 0.526 |
| Number of oral medicines | 8.1 ± 2.9 | 9.6 ± 3.8 | 7.8 ± 2.7 | 8.1 ± 2.8 | 0.067 |
| Dialysis sessions/week | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0 | 0.288 |
| Dialysis duration (month) | 157.3 ± 120.7 | 171.7 ± 134.8 | 150.9 ± 107.7 | 164.8 ± 139.9 | 0.703 |
| Dialysis time (hour) | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 0.645 |
| Kt/V sp | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 0.092 |
| Dry weight | 61.6 ± 15.4 | 55.2 ± 11.6 † | 59.9 ± 15.3† | 67.1 ± 15.4 | 0.005 |
| Water removal | 2.8 ± 1.1 | 2.1 ± 0.6 *,† | 2.8 ± 1.1 | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 0.022 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 11.0 ± 1.1 | 10.7 ± 0.9 | 11.1 ± 1.2 | 11.2 ± 1.1 | 0.277 |
| Alb (g/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 0.132 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 65.3 ± 14.1 | 58.5 ± 16.0 | 66.3 ± 14.0 | 65.5 ± 13.3 | 0.105 |
| Cre (mg/dL) | 11.7 ± 2.9 | 9.8 ± 1.9 *† | 11.9 ± 3.1 | 12.1 ± 2.6 | 0.013 |
| HDL-c | 44.3 ± 14.4 | 40.9 ± 11.7 | 45.2 ± 15.2 | 44.0 ± 14.0 | 0.512 |
| LDL-c | 85.8 ± 28.5 | 75.4 ± 25.4 | 89.1 ± 31.0 | 82.8 ± 23.4 | 0.128 |
| DM, n (%) | 68 (41.4%) | 12 (70.6%) * | 36 (37.1%) | 20 (40.0%) | 0.035 |
| HTN, n (%) | 97 (59.1%) | 8 (47.1%) | 60 (61.9%) | 29 (58.0%) | 0.511 |
| DLP, n (%) | 13 (7.9%) | 2 (11.8%) | 5 (5.2%) | 6 (12.0%) | 0.289 |
| MI, n (%) | 19 (11.6%) | 3 (17.6%) | 10 (10.3%) | 6 (12.0%) | 0.681 |
| stroke, n (%) | 28 (17.1%) | 2 (11.8%) | 19 (19.6%) | 7 (14.0%) | 0.577 |
| ABI right | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| ABI left | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| ba PWV right (cm/s) | 1761 ± 467.5 | 1978.1 ± 679.6 | 1731.7 ± 434.5 | 1755.8 ± 447.2 | 0.164 |
| ba PWV left (cm/s) | 1790.6 ± 543.7 | 2017.4 ± 755.2 | 1756.3 ± 532.3 | 1784.8 ± 477.9 | 0.205 |
| LSA | ADL Difficulty | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Standard Coefficient β | Standard Error | p | Factor | Standard Coefficient β | Standard Error | p |
| Dialysis duration | −0.216 | 0.013 | 0.001 | Age | −0.213 | 0.059 | <0.001 |
| GNRI | 0.156 | 0.171 | 0.024 | KCL total | −0.669 | 0.139 | <0.001 |
| KCL total | −0.452 | 0.332 | <0.001 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.360 | Adjusted R2 | 0.590 | ||||
| Characteristics | All (n = 164) | Low (n = 17) | Normal (n = 97) | High (n = 50) | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNRI | 92 ± 9.2 | 89.4 ± 6.7 | 91.2 ± 10.5 | 94.5 ± 6.4 | 2.914 | 0.057 |
| ADL difficulty-basic ADL (points) | 12.8 ± 2.9 | 11.1 ± 3.5 * | 13.1 ± 2.8 | 12.7 ± 2.8 | 3.659 | 0.028 |
| ADL difficulty-ambulation (points) | 19.9 ± 5.5 | 16.9 ± 6.8 | 20.4 ± 5.1 | 20.0 ± 5.6 | 2.954 | 0.055 |
| ADL difficulty-walking up or down (points) | 15.5 ± 4.4 | 12.0 ± 5.7 *,† | 16.1 ± 3.9 | 15.7 ± 4.2 | 6.747 | 0.002 |
| KCL total (points) | 6.4 ± 4.7 | 8.6 ± 6.0 | 5.9 ± 4.5 | 6.6 ± 4.4 | 2.953 | 0.090 |
| KCL physical (points) | 4.9 ± 3.6 | 6.8 ± 4.3 * | 4.5 ± 3.5 | 5.0 ± 3.4 | 3.823 | 0.048 |
| KCL depression (points) | 1.5 ± 1.6 | 1.8 ± 2.0 | 1.4 ± 1.5 | 1.6 ± 1.8 | 0.518 | 0.596 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamura, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Sakai, D.; Tsurumi, T.; Tamiya, H.; Ueno, A.; Kawamoto, S.; Shimoyama, M.; Yasu, T. Decreased Physical and Daily Living Activities in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease on Hemodialysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010135
Tamura Y, Takahashi H, Sakai D, Tsurumi T, Tamiya H, Ueno A, Kawamoto S, Shimoyama M, Yasu T. Decreased Physical and Daily Living Activities in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease on Hemodialysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamura, Yuma, Harunori Takahashi, Daiki Sakai, Tomoki Tsurumi, Hajime Tamiya, Asuka Ueno, Shinya Kawamoto, Masahiro Shimoyama, and Takanori Yasu. 2023. "Decreased Physical and Daily Living Activities in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease on Hemodialysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010135
APA StyleTamura, Y., Takahashi, H., Sakai, D., Tsurumi, T., Tamiya, H., Ueno, A., Kawamoto, S., Shimoyama, M., & Yasu, T. (2023). Decreased Physical and Daily Living Activities in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease on Hemodialysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010135






