Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure
Abstract
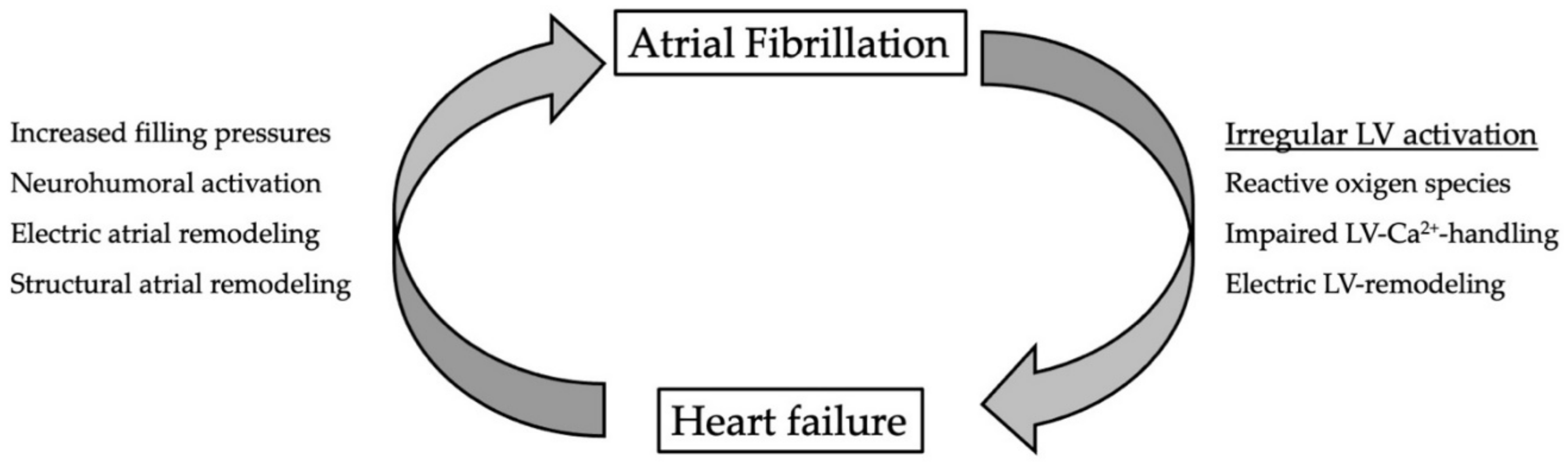
:1. Introduction
1.1. Impact of AF on Atrial Function
1.2. Impact of AF on Left-Ventricular Function
1.3. Keep the Rhythm or Slow the Rate? AF Management in Patients with Heart Failure
2. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyse, D.G.; Waldo, A.L.; DiMarco, J.P.; Domanski, M.J.; Rosenberg, Y.; Schron, E.B.; Kellen, J.C.; Greene, H.L.; Mickel, M.C.; Dalquist, J.E.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management I. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.; Talajic, M.; Nattel, S.; Wyse, D.G.; Dorian, P.; Lee, K.L.; Bourassa, M.G.; Arnold, J.M.; Buxton, A.E.; Camm, A.J.; et al. Congestive Heart Failure I. Rhythm control versus rate control for atrial fibrillation and heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2667–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujovic, N.; Dobrev, D.; Marinkovic, M.; Russo, V.; Potpara, T.S. The role of amiodarone in contemporary management of complex cardiac arrhythmias. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.C.; Tiwari, N.; Di Biase, L. Amiodarone is associated with increased short-term mortality in elderly atrial fibrillation patients with preserved ejection fraction. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 63, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Purerfellner, H.; Meyer, C.; Acou, W.J.; Schratter, A.; Ling, Z.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y.; Martinek, M.; Kiuchi, M.G.; et al. Rhythm control for patients with atrial fibrillation complicated with heart failure in the contemporary era of catheter ablation: A stratified pooled analysis of randomized data. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2863–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalife, J.; Kaur, K. Atrial remodeling, fibrosis, and atrial fibrillation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 25, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- Sohns, C.; Marrouche, N.F. Atrial fibrillation and cardiac fibrosis. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisbal, F.; Baranchuk, A.; Braunwald, E.; Bayés de Luna, A.; Bayés-Genís, A. Atrial Failure as a Clinical Entity. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Wilber, D.; Hindricks, G.; Jais, P.; Akoum, N.; Marchlinski, F.; Kholmovski, E.; Burgon, N.; Hu, N.; Mont, L.; et al. Association of atrial tissue fibrosis identified by delayed enhancement MRI and atrial fibrillation catheter ablation: The DECAAF study. JAMA 2014, 311, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Greene, T.; Dean, J.M.; Kholmovski, E.G.; Boer, L.M.; Mansour, M.; Calkins, H.; Marchlinski, F.; Wilber, D.; Hindricks, G.; et al. Efficacy of LGE-MRI-guided fibrosis ablation versus conventional catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: The DECAAF II trial: Study design. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowallick, J.T.; Staab, W.; Schuster, A.; Backhaus, S.J.; Weber-Kruger, M.; Bauer, L.; Sohns, C.; Lotz, J.; Hasenfuss, G.; Luthje, L.; et al. Reverse left ventricular structural remodeling after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with preserved left ventricular function: Insights from cardiovascular magnetic resonance native T1 mapping. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.; Costello, B.T.; Taylor, A.J.; Gutman, S.J.; Voskoboinik, A.; McLellan, A.J.A.; Peck, K.Y.; Sugumar, H.; Iles, L.; Pathik, B.; et al. Regression of Diffuse Ventricular Fibrosis Following Restoration of Sinus Rhythm with Catheter Ablation in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Systolic Dysfunction: A Substudy of the CAMERA MRI Trial. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soulat-Dufour, L.; Lang, S.; Addetia, K.; Ederhy, S.; Adavane-Scheuble, S.; Chauvet-Droit, M.; Jean, M.L.; Nhan, P.; Ben Said, R.; Kamami, I.; et al. Restoring Sinus Rhythm Reverses Cardiac Remodeling and Reduces Valvular Regurgitation in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotecha, D.; Flather, M.D.; Altman, D.G.; Holmes, J.; Rosano, G.; Wikstrand, J.; Packer, M.; Coats, A.J.S.; Manzano, L.; Bohm, M.; et al. Heart Rate and Rhythm and the Benefit of Beta-Blockers in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2885–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabel, S.; Knierim, M.; Stehle, T.; Alebrand, F.; Paulus, M.; Sieme, M.; Herwig, M.; Barsch, F.; Kortl, T.; Poppl, A.; et al. Effects of Atrial Fibrillation on the Human Ventricle. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 994–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Brachmann, J.; Andresen, D.; Siebels, J.; Boersma, L.; Jordaens, L.; Merkely, B.; Pokushalov, E.; Sanders, P.; Proff, J.; et al. Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation with Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohns, C.; Marrouche, N.F.; Costard-Jackle, A.; Sossalla, S.; Bergau, L.; Schramm, R.; Fuchs, U.; Omran, H.; Rubarth, K.; Dumitrescu, D.; et al. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with end-stage heart failure and eligibility for heart transplantation. ESC Heart Fail 2021, 8, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Taylor, A.J.; Costello, B.T.; Kaye, D.M.; McLellan, A.J.A.; Voskoboinik, A.; Sugumar, H.; Lockwood, S.M.; Stokes, M.B.; Pathik, B.; et al. Catheter Ablation Versus Medical Rate Control in Atrial Fibrillation and Systolic Dysfunction: The CAMERA-MRI Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugumar, H.; Prabhu, S.; Voskoboinik, A.; Young, S.; Gutman, S.J.; Wong, G.R.; Parameswaran, R.; Nalliah, C.J.; Lee, G.; McLellan, A.J. Atrial remodeling following catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation-mediated cardiomyopathy: Long-term follow-up of CAMERA-MRI study. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, D.L.; Piccini, J.P.; Monahan, K.H.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Silverstein, A.P.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Poole, J.E.; Bahnson, T.D.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B.; et al. Ablation Versus Drug Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure: Results from the CABANA Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 1377–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Camm, A.J.; Goette, A.; Brandes, A.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; Fetsch, T.; van Gelder, I.C.; Haase, D.; Haegeli, L.M.; et al. Early Rhythm-Control Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, A.; Magnussen, C.; Ozga, A.K.; Suling, A.; Brandes, A.; Breithardt, G.; Camm, A.J.; Crijns, H.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; et al. Early Rhythm Control Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Circulation 2021, 144, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkash, R.; Wells, G.A.; Rouleau, J.; Talajic, M.; Essebag, V.; Skanes, A.; Wilton, S.B.; Verma, A.; Healey, J.S.; Sterns, L.; et al. Randomized Ablation-Based Rhythm-Control Versus Rate-Control Trial in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: Results from the RAFT-AF trial. Circulation 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignole, M.; Pentimalli, F.; Palmisano, P.; Landolina, M.; Quartieri, F.; Occhetta, E.; Calo, L.; Mascia, G.; Mont, L.; Vernooy, K.; et al. AV junction ablation and cardiac resynchronization for patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and narrow QRS: The APAF-CRT mortality trial. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trial | Inclusion Criteria | Intervention | Rhythm Control Strategy | Primary Endpoint | Follow-Up | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFFIRM Wyse et al. | Not HF dependent, 26% with impaired LV function | Anti-arrhythmic drugs vs rate control | Amiodarone, Disopyramide, Flecainide, Moricizine, Procainamide, Propafenone, Quinidine, Sotalol, electrical cardioversion if necessary | All cause mortality | 60 month | Neutral |
| Roy et al. | LV-EF ≤ 35% | Anti-arrhythmic drugs vs. rate control | Amiodaron, Sotalol, Dofetilide & electrical cardioversion if necessary | Cardiovascular death | 60 month | Neutral |
| CASTLE-AF Marrouche et al. | LV-EF ≤ 35% | Catheter ablation vs. Medical therapy (rate or rhythm control) | Catheter ablation (PVI) | Death from any cause or hospitalization for worsening heart failure | 60 month | Favors catheter ablation |
| CAMERA-MRI Prabhu et al. | Idiopathic Cardiomyopathy, LV-EF ≤ 45% | Catheter Ablation vs. Medical Rate Control | Catheter ablation (PVI) | Change in LV-EF | 6 month | Favors catheter ablation |
| CABANA-substudy Packer et al. | Clinically stable heart failure | Catheter ablation vs. Medical therapy (rate or rhythm control) | Catheter ablation (PVI) | Death, Disabling stroke, Serious bleeding, or Cardiac arrest | 60 month | Catheter ablation produced clinically important improvements in survival, freedom from AF recurrence, and quality of life relative to drug therapy. |
| EAST-AFNET 4- substudy Rillig et al. | Heart failure (independent of LV-EF) | Rhythm vs. Rate control | Catheter ablation (PVI), antiarrhythmic drugs, electrical cardioversion if necessary | Cardiovascular death, stroke, or hospitalization for worsening of heart failure or for acute coronary syndrome | 72 month | Favors rhythm control |
| RAFT-Parkash et al. | NYHA II-III, elevated NT-pro-BNP | Catheter Ablation vs. Medical Rate Control | Catheter ablation (PVI) | All cause mortality and all HF events | 60 month | Non-significant trend for improved outcomes with ablation-based rhythm control over rate-control |
| APAF-CRT Brignole et al. | HF-hospitalization in previous year (independent of LV-EF) | Pace and ablate strategy vs. Medical Rate Control | AV-node ablation + CRT-implantation | All cause mortality | 48 month | Favors “Pace and ablate” |
| Chen et al. (Meta-Analysis) | “Heart Failure” not specified | Anti-arrhythmic drugs vs. rate control, Catheter ablation vs rate control, Pooled Analysis | Every Intervention allowed | All-cause mortality, Re-hospitalization, Stroke, and Thromboembolic events | Varying | Favors catheter ablation for rhythm control |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergau, L.; Bengel, P.; Sciacca, V.; Fink, T.; Sohns, C.; Sommer, P. Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092510
Bergau L, Bengel P, Sciacca V, Fink T, Sohns C, Sommer P. Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(9):2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092510
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergau, Leonard, Philipp Bengel, Vanessa Sciacca, Thomas Fink, Christian Sohns, and Philipp Sommer. 2022. "Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 9: 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092510
APA StyleBergau, L., Bengel, P., Sciacca, V., Fink, T., Sohns, C., & Sommer, P. (2022). Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(9), 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092510






