Hematological Ratios Are Associated with Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Patients That Present with Suspected Infection at the Emergency Department
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
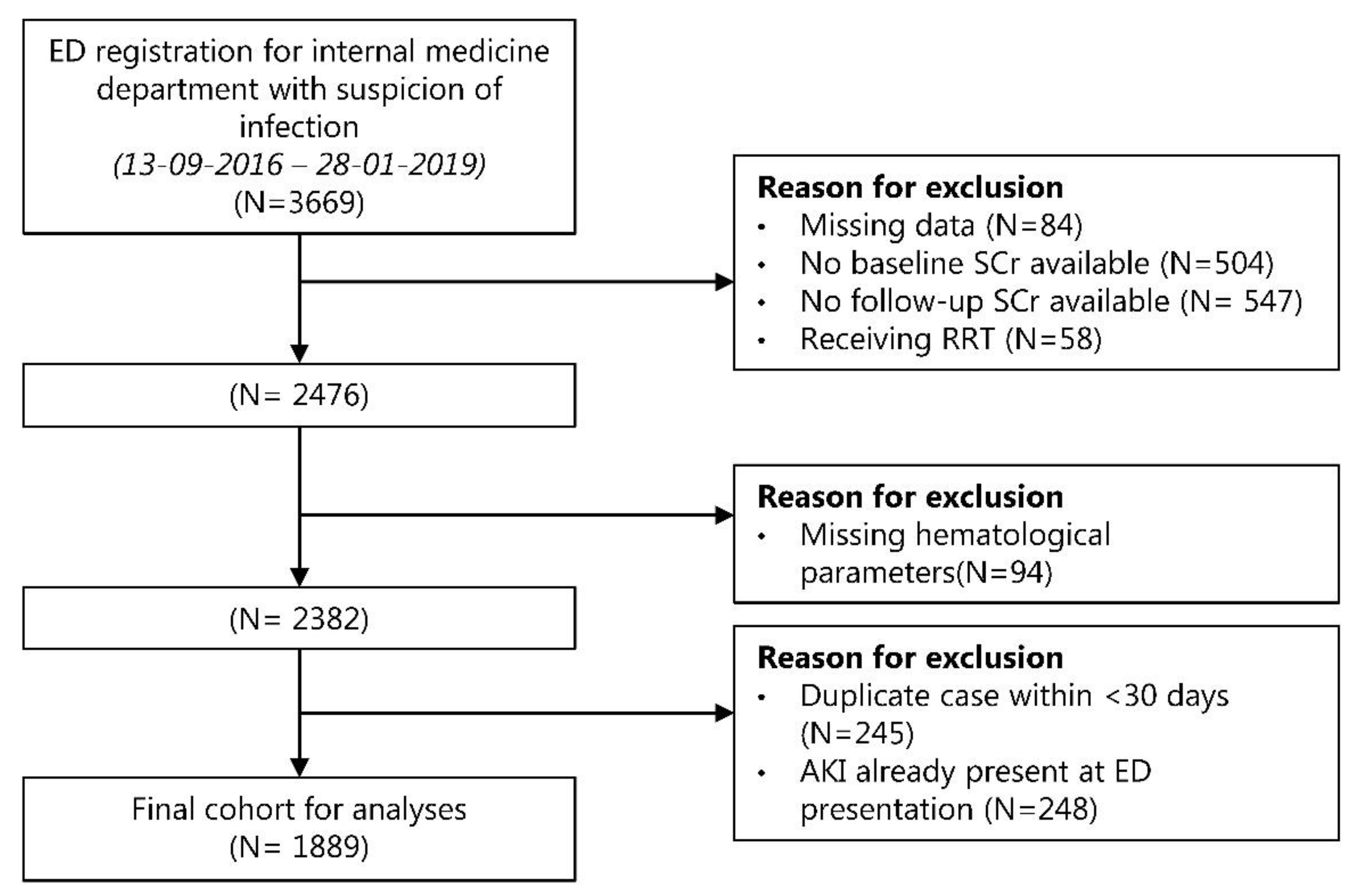
2.2. Study Population and Data Collection
2.3. Hematological Ratios
2.4. Outcomes and Definitions
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Incidence of AKI
3.3. Hematological Ratios in AKI and Non-AKI Patients
3.4. Associations between Hematological Ratios and AKI
3.5. Association between Hematological Ratios and Mortality
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, M.E.; Blaine, C.; Dawnay, A.; Devonald, M.A.J.; Ftouh, S.; Laing, C.; Latchem, S.; Lewington, A.; Milford, D.V.; Ostermann, M. The definition of acute kidney injury and its use in practice. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2012, 380, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameire, N.H.; Bagga, A.; Cruz, D.; De Maeseneer, J.; Endre, Z.; Kellum, J.A.; Liu, K.D.; Mehta, R.L.; Pannu, N.; Van Biesen, W.; et al. Acute kidney injury: An increasing global concern. Lancet 2013, 382, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challiner, R.; Ritchie, J.P.; Fullwood, C.; Loughnan, P.; Hutchison, A.J. Incidence and consequence of acute kidney injury in unselected emergency admissions to a large acute UK hospital trust. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chertow, G.M.; Burdick, E.; Honour, M.; Bonventre, J.V.; Bates, D.W. Acute Kidney Injury, Mortality, Length of Stay, and Costs in Hospitalized Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3365–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Leonard, A.C.; Harrison, K.; Meganathan, K.; Christianson, A.L.; Thakar, C.V. Mortality and Recovery Associated with Kidney Failure due to Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, W.L.S.; Khan, S.S.; Ebben, J.P.; Pereira, B.J.G.; Collins, A.J. Chronic kidney disease: The distribution of health care dollars. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarjou, A.; Agarwal, A. Sepsis and Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugan, R.; Karajala-Subramanyam, V.; Lee, M.; Yende, S.; Kong, L.; Carter, M.; Angus, D.C.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury in non-severe pneumonia is associated with an increased immune response and lower survival. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarbock, A.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury revisited: Pathophysiology, prevention and future therapies. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waikar, S.S.; Betensky, R.A.; Emerson, S.C.; Bonventre, J. V Imperfect gold standards for kidney injury biomarker evaluation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gameiro, J.; Lopes, J.A. Complete blood count in acute kidney injury prediction: A narrative review. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts-rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manda, G.; Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Radulescu, A.; Codreanu, C. Patterns of peripheral cellular immune disorders in severe rheumatoid arthritis. Roum. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 13, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.A.; Bosonnet, L.; Raraty, M.; Sutton, R.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Campbell, F.; Ghaneh, P. Preoperative platelet-lymphocyte ratio is an independent significant prognostic marker in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Surg. 2009, 197, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uffen, J.W.; Oomen, P.; de Regt, M.; Oosterheert, J.J.; Kaasjager, K. The prognostic value of red blood cell distribution width in patients with suspected infection in the emergency department. BMC Emerg. Med. 2019, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Berg, M.J.; Huisman, A.; van den Bemt, P.M.L.A.; Schobben, A.F.A.M.; Egberts, A.C.G.; van Solinge, W.W. Linking laboratory and medication data: New opportunities for pharmacoepidemiological research. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, C.-H.; Eun Jung, D.; Park, Y.S.; Bae, J.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, W.H.; Bahk, J.-H. Neutrophil, Lymphocyte, and Platelet Counts and Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiovascular Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2018, 32, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, W.-F.; Douglas, I.S.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Kao, H.-C.; Fang, Y.-T.; Huang, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-T.; Huang, K.-T.; Wang, Y.-H.; et al. Development and validation of immune dysfunction score to predict 28-day mortality of sepsis patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.N.; Jong, W.C.; Lee, J. Delta neutrophil index in automated immature granulocyte counts for assessing disease severity of patients with sepsis. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2008, 38, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Alfeilat, M.; Slotki, I.; Shavit, L. Single emergency room measurement of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio for early detection of acute kidney injury (AKI). Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, P.; Wu, X. Relation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio to acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis and septic shock: A retrospective study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 70, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, H.; Cakmak, M.; Inan, O.; Darcin, T.; Akcay, A. Can neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio be independent risk factor for predicting acute kidney injury in patients with severe sepsis? Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlar, H.; Şaşkın, H. Are Pre and Postoperative Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Associated with Early Postoperative AKI Following CABG? Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 33, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Park, J.Y.; Ok, S.-H.; Shin, I.-W.; Sohn, J.-T. Association Between the Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio and Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiovascular Surgery: A Retrospective Observational Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kong, Y.-G.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.-K. Acute kidney injury after burn surgery: Preoperative neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio as a predictive factor. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2019, 63, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, Y.S.; Yoon, C.-Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.W.; Kong, T.; You, J.S.; Park, J.W.; Chung, S.P. Delta Neutrophil Index for the Prediction of the Development of Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in the Emergency Department. Shock 2019, 52, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Zou, G.; He, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, L.; Lu, Z. Development and External Validation a Novel Inflammation-Based Score for Acute Kidney Injury and Prognosis in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, F.; Li, M.; Yuan, J.-J.; Chang, X.-N.; Wei, B.-H.; Du, H.; Dong, C.-M. Relationship between platelet/lymphocyte ratio and prognosis of patients with septic acute kidney injury: A pilot study. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.-F.; Liu, W.-Y.; Zeng, F.-F.; Zheng, M.-H.; Shi, H.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, J.-Y. Prognostic value of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, Q. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts postoperative acute kidney injury in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after hepatectomy. Medicine 2021, 100, e25335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, L.; Martín, M.M.; Ortiz-López, R.; Alvarez-Castillo, A.; Ruiz, C.; Uribe, L.; González-Rivero, A.F.; Pérez-Cejas, A.; Jiménez, A. Association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the first seven days of sepsis and mortality. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2020, in press, corrected proof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Lupoi, D.M.; Valeriani, E.; Fogolari, M.; Locorriere, L.; Beretta Anguissola, G.; Battifoglia, G.; Caputo, D.; Coppola, A.; Costantino, S.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios in septic patients outside the intensive care unit. Medicina 2021, 57, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Nan, C.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Su, H.X. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is associated with all-cause mortality among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2019, 490, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo-Téllez, S.A.; Méndez-García, L.A.; Flores-Rebollo, C.; Alba-Flores, F.; Alcántara-Suárez, R.; Manjarrez-Reyna, A.N.; Baltazar-López, N.; Hernández-Guzmán, V.A.; León-Pedroza, J.I.; Zapata-Arenas, R.; et al. The neutrophil-to-monocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-neutrophil ratio at admission predict in-hospital mortality in mexican patients with severe sars-cov-2 infection (Covid-19). Microorganisms 2020, 81, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, J.; Fonseca, J.A.; Dias, J.M.; Milho, J.; Rosa, R.; Jorge, S.; Lopes, J.A. Neutrophil, lymphocyte and platelet ratio as a predictor of postoperative acute kidney injury in major abdominal surgery. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Ning, Y.; Shen, B.; Wang, C.; Luo, Z.; Xu, J.; Ding, X. Dynamics in perioperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte*platelet ratio as a predictor of early acute kidney injury following cardiovascular surgery. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Value of neutrophil to lymphocytes and platelets ratio for predicting 28-day mortality in sepsis patients. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2021, 33, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor of mortality for sepsis: Interaction effect with disease severity—A retrospective study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, H.Z.; Kahraman, S.; Arslan, C.; Yildirim, C.; Erturk, M.; Kalkan, A.K.; Yildiz, M. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts mortality in infective endocarditis. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2020, 32, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenberg, C.; Wan, L.; Egi, M.; May, C.N.; Bellomo, R. Renal blood flow in experimental septic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsey, G.R.; Li, L.; Okusa, M.D. Inflammation in acute kidney injury. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 2008, 109, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Dorze, M.; Legrand, M.; Payen, D.; Ince, C. The role of the microcirculation in acute kidney injury. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2009, 15, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.R.; Rabb, H. The innate immune response in ischemic acute kidney injury. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabb, H.; O’Meara, Y.M.; Maderna, P.; Coleman, P.; Brady, H.R. Leukocytes, cell adhesion molecules and ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.-X.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Min, W.-P.; Sun, H.; Liu, W.; Garcia, B.; Jevnikar, A.M. NK Cells Induce Apoptosis in Tubular Epithelial Cells and Contribute to Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7489–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, H.R.; Rabb, H. Immune cells in experimental acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.A.; Noel, S.; Sadasivam, M.; Hamad, A.R.A.; Rabb, H. Role of Immune Cells in Acute Kidney Injury and Repair. Nephron 2017, 137, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, K.; Yuen, P.S.T.; Eisner, C.; Hu, X.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Schnermann, J.; Star, R.A. Reduced production of creatinine limits its use as marker of kidney injury in sepsis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Aspelin, P.; Barsoum, R.S.; Burdmann, E.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Herzog, C.A.; Joannidis, M.; Kribben, A.; Levey, A.S.; et al. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Waikar, S.S.; Bonventre, J. V Creatinine kinetics and the definition of acute kidney injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Total (N = 1889) | No AKI (N = 1729) | AKI (N = 160) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 62 (50–70) | 62 (49–70) | 64 (54–72) |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 1029 (54.5) | 938 (54.3) | 91 (56.9) |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Charlson Comorbidity Index, median (IQR) | 5.0 (3.0–7.0) | 5.0 (3.0–7.0) | 5.0 (4.0–7.8) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 618 (32.7) | 551 (31.9) | 67 (41.9) |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n (%) | 367 (19.4) | 324 (18.7) | 43 (26.9) |
| Sever liver disease, n (%) | 20 (1.1) | 18 (1.0) | 2 (1.3) |
| Congestive heart failure, n (%) | 105 (5.1) | 88 (5.6) | 17 (10.6) |
| Myocardial infarction, n (%) | 174 (9.2) | 159 (9.2) | 15 (9.4) |
| Peripheral vascular disease, n (%) | 144 (7.6) | 125 (7.2) | 19 (11.9) |
| Cerebrovascular disease, n (%) | 203 (10.7) | 178 (10.3) | 25 (15.6) |
| Kidney Transplant, n (%) | 254 (13.9) | 226 (13.1) | 28 (17.5) |
| Immunocompromised, n (%) | 821 (43.5) | 748 (43.3) | 73 (45.6) |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | |||
| Stage 1 | 6 (0.3) | 4 (0.2) | 2 (1.3) |
| Stage 2 | 81 (4.3) | 78 (4.5) | 3 (1.9) |
| Stage 3 | 270 (14.3) | 240 (13.9) | 30 (18.8) |
| Stage 4 | 115 (6.1) | 97 (5.6) | 18 (11.3) |
| Stage 5 | 39 (2.1) | 28 (1.6) | 11 (6.9) |
| Medication | |||
| ACE inhibitor or angiotensin-receptor blockers, n (%) | 501 (26.5) | 448 (25.9) | 53 (33.1) |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 389 (20.6) | 345 (20.0) | 44 (27.5) |
| PPI, n (%) | 1,003 (53.1) | 913 (52.8) | 90 (56.3) |
| NSAID, n (%) | 76 (4.0) | 72 (4.2) | 4 (2.5) |
| Disease severity in ED | |||
| qSOFA-score ≥2, n (%) | 98 (5.2) | 86 (5.0) | 12 (7.5) |
| Provisional diagnosis in the ED | |||
| Lower-respiratory-tract infection, n (%) | 415 (22.0) | 374 (21.6) | 41 (25.6) |
| Viral respiratory-tract infection, n (%) | 293 (15.5) | 281 (16.3) | 12 (7.5) |
| Urinary-tract infection, n (%) | 334 (17.7) | 299 (17.3) | 35 (21.9) |
| Gastro-intestinal infection, n (%) | 262 (13.9) | 247 (14.3) | 15 (9.4) |
| Skin infection, n (%) | 131 (6.9) | 122 (7.1) | 9 (5.6) |
| Other (infectious) diagnosis, n (%) | 454 (24.0) | 406 (23.5) | 48 (30.0) |
| Laboratory | |||
| Baseline serum creatinine (umol/L) | 79 (63.0–116.0) | 78.0 (63.0–113.0) | 99.0 (63.3–161.5) |
| Baseline eGFR CKD-EPI (ml/min) | 80.6 (52.3–98.9) | 81.4 (53.9–99.1) | 61.9 (33.7–97.0) |
| Total (N = 1889) | No AKI (N = 1729) | AKI (N = 160) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified delta-neutrophil index (IQR) | 1.17 (0.41–4.73) | 1.18 (0.41–4.47) | 1.15 (0.38–7.89) | 0.64 |
| Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (IQR) | 6.92 (3.27–13.04) | 6.80 (3.17–12.73) | 8.52 (4.38–17.92) | <0.001 |
| Monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (IQR) | 0.70 (0.40–1.19) | 0.70 (0.40–1.19) | 0.70 (0.43–1.31) | 0.43 |
| Segmented-neutrophil-monocyte ratio (IQR) | 8.99 (5.73–14.11) | 8.83 (5.62–13.88) | 10.97 (7.03–17.10) | <0.001 |
| Platelet-lymphocyte ratio (IQR) | 225.36 (137.40–387.90) | 225.06 (136.91–382.96) | 243.85 (139.47–439.62) | 0.50 |
| Neutrophil-lymphocyte-and-platelets ratio (IQR) | 3.15 (1.51–6.82) | 3.03 (1.45–6.55) | 4.84 (2.01–10.24) | <0.001 |
| Systemic immune-inflammation index (IQR) | 1469.48 (609.94–3226.94) | 1463.68 (586.76–3177.88) | 1612.76 (792.82–3858.33) | 0.08 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratios | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 1 a (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 2 b (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 3 c (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 4 d (95% CI) |
| Modified DNI | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤0.5931 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 0.5931–2.7088 | 0.7 (0.5–1.0) | 0.7 (0.5–1.0) | 0.7 (0.5–1.0) | 0.7 (0.5–1.0) | 0.7 (0.5–1.1) |
| Tertile 3, >2.7088 | 1.0 (0.7–1.4) | 1.0 (0.7–1.4) | 1.0 (0.7–1.4) | 1.0 (0.7–1.4) | 1.0 (0.7–1.4) |
| NLR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤4.2805 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 4.2805–10.2276 | 1.4 (1.0–2.2) | 1.4 (1.0–2.1) | 1.4 (1.0–2.1) | 1.3 (0.9–2.1) | 1.3 (0.9–2.0) |
| Tertile 3, >10.2276 | 2.1 (1.4–3.1) | 2.0 (1.4–3.0) | 2.0 (1.3–2.9) | 1.9 (1.3–2.9) | 1.8 (1.2–2.8) |
| MLR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤0.5057 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 0.5057–0.9830 | 1.1 (0.8–1.7) | 1.1 (0.7–1.6) | 1.1 (0.7–1.6) | 1.0 (0.7–1.6) | 1.0 (0.7–1.5) |
| Tertile 3, >0.9830 | 1.2 (0.9–1.8) | 1.2 (0.8–1.7) | 1.2 (0.8–1.7) | 1.2 (0.8–1.7) | 1.1 (0.8–1.7) |
| SMR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤6.7500 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 6.7500–11.9633 | 1.8 (1.2–2.8) | 1.8 (1.2–2.7) | 1.8 (1.2–2.7) | 1.7 (1.1–2.7) | 1.7 (1.1–2.6) |
| Tertile 3, >11.9633 | 2.2 (1.4–3.3) | 2.2 (1.4–3.3) | 2.1 (1.4–3.2) | 2.0 (1.3–3.1) | 2.0 (1.3–3.0) |
| PLR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤161.6468 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 161.6468–314.6356 | 0.9 (0.6–1.3) | 0.9 (0.6–1.3) | 0.8 (0.6–1.3) | 0.8 (0.6–1.2) | 0.8 (0.6–1.3) |
| Tertile 3, 314.6356 | 1.1 (0.8–1.6) | 1.1 (0.7–1.6) | 1.1 (0.7–1.5) | 1.1 (0.7–1.5) | 1.0 (0.7–1.5) |
| NLPR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤1.9151 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 1.9151–5.0605 | 1.4 (1.0–2.2) | 1.4 (0.9–2.2) | 1.4 (0.9–2.2) | 1.4 (0.9–2.1) | 1.3 (0.9–2.0) |
| Tertile 3, >5.0605 | 2.4 (1.6–3.5) | 2.3 (1.5–3.4) | 2.2 (1.5–3.2) | 2.2 (1.4–3.3) | 2.1 (1.4–3.2) |
| SII index | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤869.43 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 869.43–2414.46 | 1.4 (1.0–2.0) | 1.3 (0.9–2.0) | 1.3 (0.9–2.0) | 1.3 (0.9–1.9) | 1.3 (0.8–1.9) |
| Tertile 3, >2414.46 | 1.6 (1.1–2.4) | 1.5 (1.0–2.3) | 1.5 (1.0–2.3) | 1.5 (1.0–2.2) | 1.4 (0.9–2.1) |
| Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratios | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 1 a (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 2 b (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 3 c (95% CI) | Adjusted HR: Model 4 d (95% CI) |
| Modified DNI | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤0.5931 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 0.5931–2.7088 | 0.8 (0.5–1.1) | 0.9 (0.5–1.4) | 0.8 (0.5–1.4) | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) | 0.8 (0.5–1.4) |
| Tertile 3, >2.7088 | 1.2 (0.8–1.9) | 1.3 (0.8–2.0) | 1.3 (0.8–2.1) | 1.3 (0.8–2.1) | 1.3 (0.8–2.0) |
| NLR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤4.2805 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 4.2805–10.2276 | 1.3 (0.7–2.1) | 1.1 (0.6–1.9) | 1.2 (0.7–2.0) | 1.2 (0.7–2.1) | 1.2 (0.7–2.1) |
| Tertile 3, >10.2276 | 1.9 (1.2–3.1) | 1.6 (1.0–2.6) | 1.7 (1.0–2.8) | 1.8 (1.1–23.0) | 1.7 (1.0–2.9) |
| MLR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤0.5057 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 0.5057–0.9830 | 0.9 (0.5–1.5) | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) | 0.8 (0.5–1.4) | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) |
| Tertile 3, >0.9830 | 1.5 (0.9–2.2) | 1.2 (0.7–1.9) | 1.2 (0.7–1.9) | 1.2 (0.8–2.0) | 1.2 (0.7–1.9) |
| SMR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤6.7500 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 6.7500–11.9633 | 1.6 (1.0–2.7) | 1.5 (0.9–2.5) | 1.5 (0.9–2.5) | 1.5 (0.9–2.5) | 1.5 (0.9–2.5) |
| Tertile 3, >11.9633 | 1.9 (1.1–3.1) | 1.8 (1.1–2.9) | 1.9 (1.1–3.2) | 2.0(1.1–3.3) | 1.8 (1.1–3.1) |
| PLR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤161.6468 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 161.6468–314.6356 | 1.1 (0.7–1.9) | 1.1 (0.6–1.8) | 1.1 (0.6–1.8) | 1.1 (0.6–1.9) | 1.2 (0.7–2.1) |
| Tertile 3, 314.6356 | 2.0 (1.2–3.2) | 1.8 (1.1–2.9) | 1.7 (1.0–2.8) | 1.8 (1.1–2.9) | 1.7 (1.1–2.8) |
| NLPR | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤1.9151 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 1.9151–5.0605 | 2.6 (1.5–4.4) | 2.3 (1.3–3.9) | 2.4 (1.4–4.2) | 2.6 (1.5–4.5) | 2.5 (1.4–4.4) |
| Tertile 3, >5.0605 | 2.2 (1.3–3.9) | 1.8 (1.0–3.2) | 2.0 (1.2–3.6) | 2.2 (1.3–4.0) | 2.1 (1.2–3.7) |
| SII index | |||||
| Tertile 1, ≤869.43 | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) |
| Tertile 2, 869.43–2414.46 | 0.6 (0.3–1.0) | 0.5 (0.3–0.9) | 0.5 (0.3–1.0) | 0.6 (0.3–1.0) | 0.6 (0.3–1.1) |
| Tertile 3, >2414.46 | 1.9 (1.2–2.9) | 1.7 (1.1–2.6) | 1.7 (1.1–2.7) | 1.8 (1.2–2.9) | 1.8 (1.1–2.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Hond, T.A.P.; Ocak, G.; Groeneweg, L.; Oosterheert, J.J.; Haitjema, S.; Khairoun, M.; Kaasjager, K.A.H. Hematological Ratios Are Associated with Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Patients That Present with Suspected Infection at the Emergency Department. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041017
de Hond TAP, Ocak G, Groeneweg L, Oosterheert JJ, Haitjema S, Khairoun M, Kaasjager KAH. Hematological Ratios Are Associated with Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Patients That Present with Suspected Infection at the Emergency Department. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(4):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041017
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Hond, Titus A. P., Gurbey Ocak, Leonie Groeneweg, Jan Jelrik Oosterheert, Saskia Haitjema, Meriem Khairoun, and Karin A. H. Kaasjager. 2022. "Hematological Ratios Are Associated with Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Patients That Present with Suspected Infection at the Emergency Department" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 4: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041017
APA Stylede Hond, T. A. P., Ocak, G., Groeneweg, L., Oosterheert, J. J., Haitjema, S., Khairoun, M., & Kaasjager, K. A. H. (2022). Hematological Ratios Are Associated with Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Patients That Present with Suspected Infection at the Emergency Department. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(4), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041017







