Plasma-Derived Hemopexin as a Candidate Therapeutic Agent for Acute Vaso-Occlusion in Sickle Cell Disease: Preclinical Evidence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plasma-Derived Hemopexin
2.2. Preparation of Heme-Albumin
2.3. Preparation of Hemoglobin
2.4. HUVEC Cell Culture Experiments
2.5. HUVEC Stimulation and Flow Cytometry
2.6. In Vitro Stimulation
2.7. HO-1 Western Blot
2.8. Multiplex Cytokine Assays
2.9. Animal Experiments
2.10. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
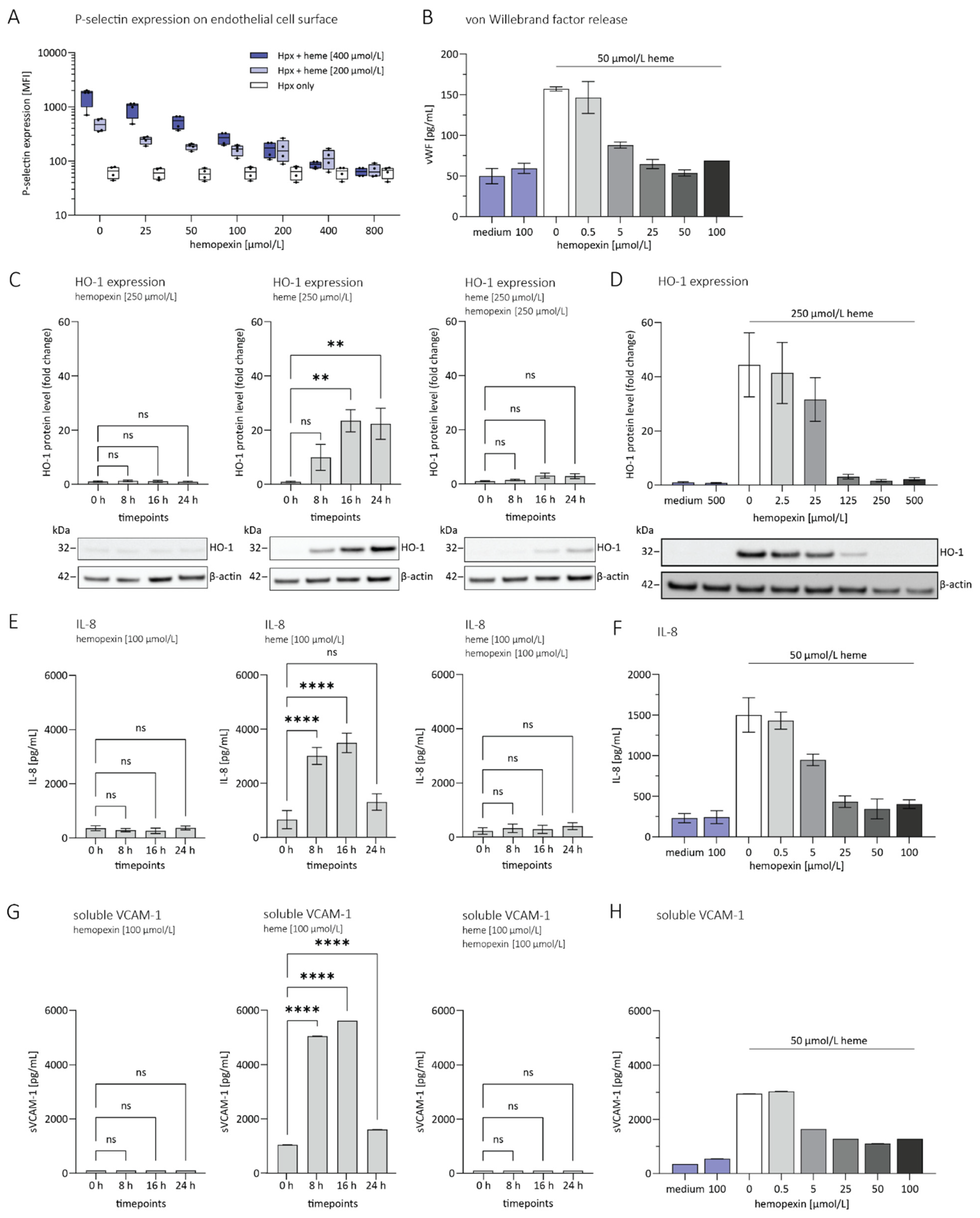
3.1. Hemopexin Protects against Endothelial Activation and Inflammation
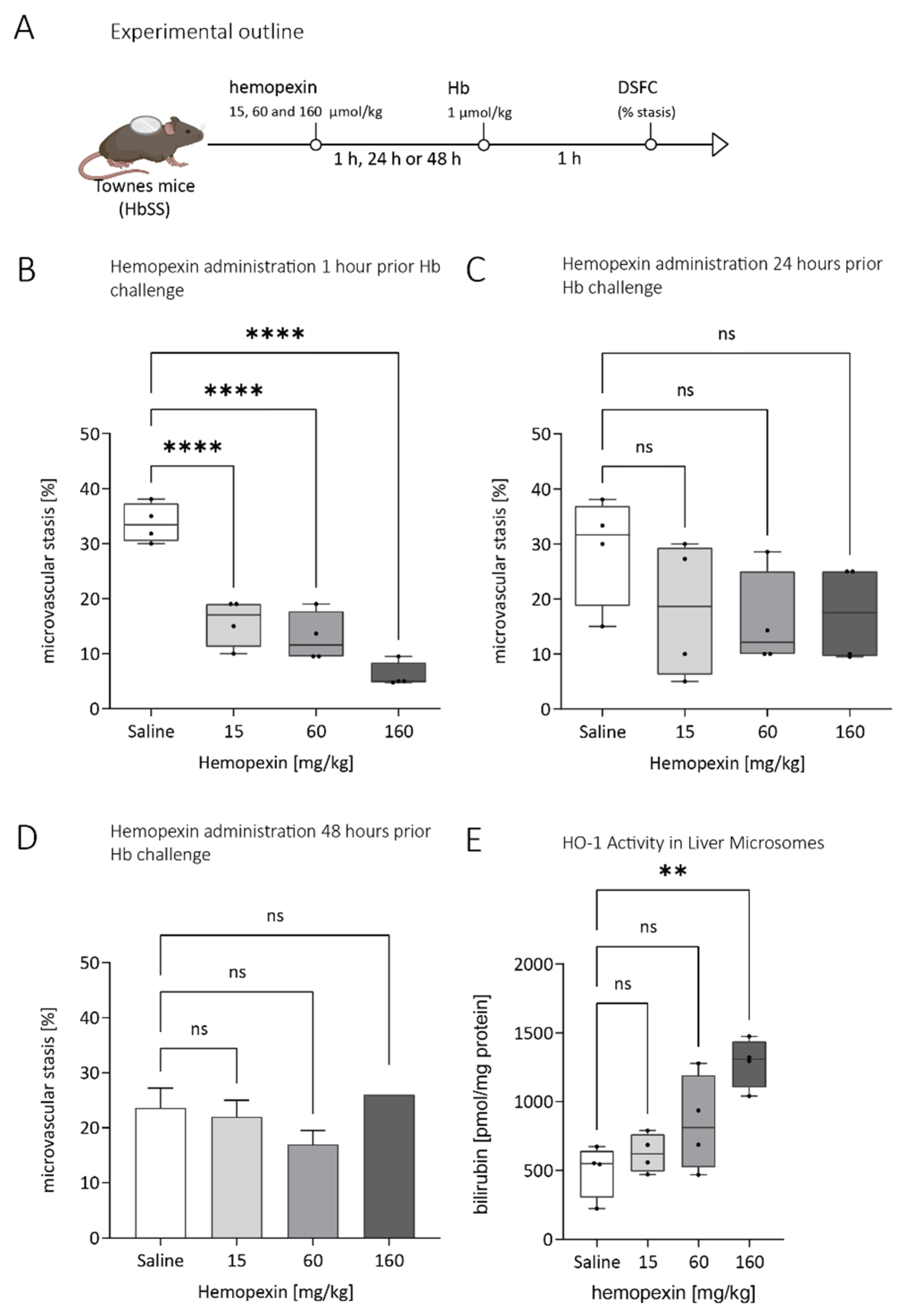
3.2. Duration of Protective Effect of Hemopexin Administered to Townes SS Mice at Different Doses and Different Times before VOC Challenge with Hemoglobin
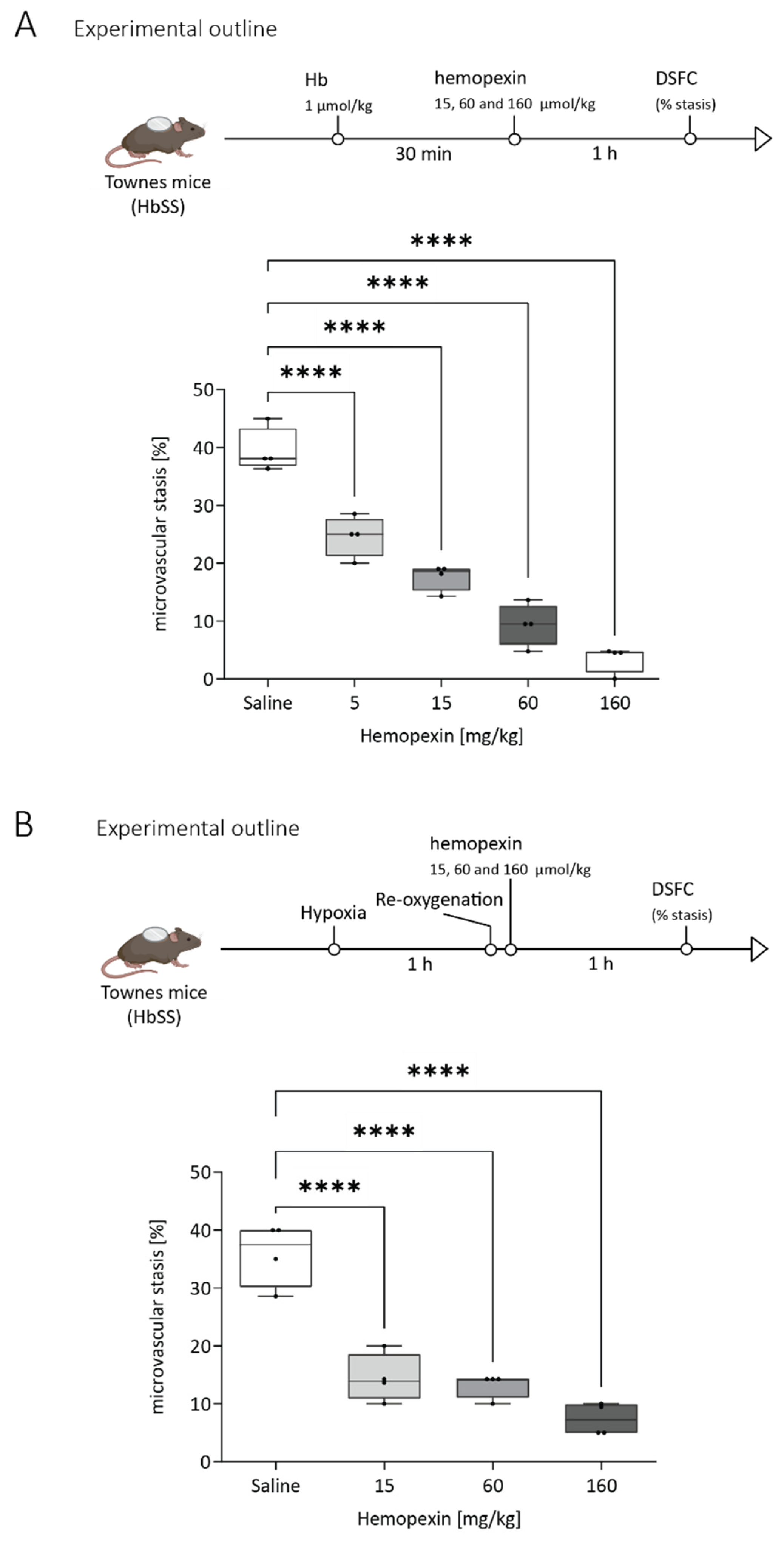
3.3. Protective Effect of Hemopexin Administration at Different Doses after VOC Challenge with Hemoglobin or Hypoxia
3.4. Pre-Complexed Hemopexin with Heme Does Resolve Hemoglobin Induced Stasis in a Dose-Dependent Manner
3.5. Hemopexin Pharmacokinetics in Animal Models
3.6. Hemopexin Is Well-Tolerated in Animal Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ware, R.E.; de Montalembert, M.; Tshilolo, L.; Abboud, M.R. Sickle Cell Disease. Lancet 2017, 390, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, G.J.; Piel, F.B.; Reid, C.D.; Gaston, M.H.; Ohene-Frempong, K.; Krishnamurti, L.; Smith, W.R.; Panepinto, J.A.; Weatherall, D.J.; Costa, F.F.; et al. Sickle Cell Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zennadi, R.; Chien, A.; Xu, K.; Batchvarova, M.; Telen, M.J. Sickle Red Cells Induce Adhesion of Lymphocytes and Monocytes to Endothelium. Blood 2008, 112, 3474–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundd, P.; Gladwin, M.T.; Novelli, E.M. Pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2019, 14, 263–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; Steinberg, M.H.; Gladwin, M.T. Intravascular Hemolysis and the Pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuel, J.W.; Vallelian, F.; Schaer, C.A.; Puglia, M.; Buehler, P.W.; Schaer, D.J. Different Target Specificities of Haptoglobin and Hemopexin Define a Sequential Protection System against Vascular Hemoglobin Toxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reiter, C.D.; Wang, X.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Hogg, N.; Cannon, R.O.; Schechter, A.N.; Gladwin, M.T. Cell-Free Hemoglobin Limits Nitric Oxide Bioavailability in Sickle-Cell Disease. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintagari, N.R.; Jana, S.; Alayash, A.I. Oxidized Ferric and Ferryl Forms of Hemoglobin Trigger Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Injury in Alveolar Type I Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendonça, R.; Silveira, A.A.A.; Conran, N. Red Cell DAMPs and Inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 65, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozza, M.T.; Jeney, V. Pro-Inflammatory Actions of Heme and Other Hemoglobin-Derived DAMPs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belcher, J.D.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, J.; Milbauer, L.; Abdulla, F.; Alayash, A.I.; Smith, A.; Nath, K.A.; Hebbel, R.P.; Vercellotti, G.M. Heme Triggers TLR4 Signaling Leading to Endothelial Cell Activation and Vaso-Occlusion in Murine Sickle Cell Disease. Blood 2014, 123, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaer, D.J.; Buehler, P.W.; Alayash, A.I.; Belcher, J.D.; Vercellotti, G.M. Hemolysis and Free Hemoglobin Revisited: Exploring Hemoglobin and Hemin Scavengers as a Novel Class of Therapeutic Proteins. Blood 2013, 121, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santiago, R.P.; Guarda, C.C.; Figueiredo, C.V.B.; Fiuza, L.M.; Aleluia, M.M.; Adanho, C.S.A.; Carvalho, M.O.S.; Pitanga, T.N.; Zanette, D.L.; Lyra, I.M.; et al. Serum Haptoglobin and Hemopexin Levels Are Depleted in Pediatric Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2018, 72, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Eberhard, U.; Javid, J.; Liem, H.H.; Hanstein, A.; Hanna, M. Plasma Concentrations of Hemopexin, Haptoglobin and Heme in Patients with Various Hemolytic Diseases. Blood 1968, 32, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belcher, J.D.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, J.; Abdulla, F.; Zhang, P.; Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, P.; Killeen, T.; Miescher, S.M.; Brinkman, N.; et al. Haptoglobin and Hemopexin Inhibit Vaso-Occlusion and Inflammation in Murine Sickle Cell Disease: Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yale, S.H.; Nagib, N.; Guthrie, T. Approach to the Vaso-Occlusive Crisis in Adults with Sickle Cell Disease. Am. Fam. Physician 2000, 61, 1349–1356, 1363–1364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Bhor, M.; Xie, L.; Paulose, J.; Yuce, H. Medical Resource Use and Costs of Treating Sickle Cell-Related Vaso-Occlusive Crisis Episodes: A Retrospective Claims Study. J. Health Econ. Outcomes Res 2020, 7, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizio, A.A.; Bhor, M.; Lin, X.; McCausland, K.L.; White, M.K.; Paulose, J.; Nandal, S.; Halloway, R.I.; Bronté-Hall, L. The Relationship between Frequency and Severity of Vaso-Occlusive Crises and Health-Related Quality of Life and Work Productivity in Adults with Sickle Cell Disease. Qual. Life Res. 2020, 29, 1533–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ataga, K.I.; Kutlar, A.; Kanter, J.; Liles, D.; Cancado, R.; Friedrisch, J.; Guthrie, T.H.; Knight-Madden, J.; Alvarez, O.A.; Gordeuk, V.R.; et al. Crizanlizumab for the Prevention of Pain Crises in Sickle Cell Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandegriff, K.D.; Malavalli, A.; Wooldridge, J.; Lohman, J.; Winslow, R.M. MP4, a New Nonvasoactive PEG-Hb Conjugate. Transfusion 2003, 43, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbotosho, O.T.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Kato, G.J. The Worst Things in Life Are Free: The Role of Free Heme in Sickle Cell Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 561917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, N.S.; Grunenwald, A.; Rajaratnam, H.; Gnemmi, V.; Frimat, M.; Figueres, M.-L.; Knockaert, S.; Bouzekri, S.; Charue, D.; Noe, R.; et al. Intravascular Hemolysis Activates Complement via Cell-Free Heme and Heme-Loaded Microvesicles. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinchi, F.; da Silva, M.C.; Ingoglia, G.; Petrillo, S.; Brinkman, N.; Zuercher, A.; Cerwenka, A.; Tolosano, E.; Muckenthaler, M.U. Hemopexin Therapy Reverts Heme-Induced Proinflammatory Phenotypic Switching of Macrophages in a Mouse Model of Sickle Cell Disease. Blood 2016, 127, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, E.H.; Suzuki, T.; Funayama, R.; Nagashima, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sekine, H.; Tanaka, N.; Moriguchi, T.; Motohashi, H.; Nakayama, K.; et al. Nrf2 Suppresses Macrophage Inflammatory Response by Blocking Proinflammatory Cytokine Transcription. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.; Hunt, R.C. Hemopexin Joins Transferrin as Representative Members of a Distinct Class of Receptor-Mediated Endocytic Transport Systems. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 53, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darbari, D.S.; Sheehan, V.A.; Ballas, S.K. The Vaso-Occlusive Pain Crisis in Sickle Cell Disease: Definition, Pathophysiology, and Management. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 105, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, T.; Poplawska, M.; Cimpeanu, E.; Mo, G.; Dutta, D.; Lim, S.H. Vaso-Occlusive Crisis in Sickle Cell Disease: A Vicious Cycle of Secondary Events. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gentinetta, T.; Belcher, J.D.; Brügger-Verdon, V.; Adam, J.; Ruthsatz, T.; Bain, J.; Schu, D.; Ventrici, L.; Edler, M.; Lioe, H.; et al. Plasma-Derived Hemopexin as a Candidate Therapeutic Agent for Acute Vaso-Occlusion in Sickle Cell Disease: Preclinical Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030630
Gentinetta T, Belcher JD, Brügger-Verdon V, Adam J, Ruthsatz T, Bain J, Schu D, Ventrici L, Edler M, Lioe H, et al. Plasma-Derived Hemopexin as a Candidate Therapeutic Agent for Acute Vaso-Occlusion in Sickle Cell Disease: Preclinical Evidence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(3):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030630
Chicago/Turabian StyleGentinetta, Thomas, John D. Belcher, Valérie Brügger-Verdon, Jacqueline Adam, Tanja Ruthsatz, Joseph Bain, Daniel Schu, Lisa Ventrici, Monika Edler, Hadi Lioe, and et al. 2022. "Plasma-Derived Hemopexin as a Candidate Therapeutic Agent for Acute Vaso-Occlusion in Sickle Cell Disease: Preclinical Evidence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 3: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030630
APA StyleGentinetta, T., Belcher, J. D., Brügger-Verdon, V., Adam, J., Ruthsatz, T., Bain, J., Schu, D., Ventrici, L., Edler, M., Lioe, H., Patel, K., Chen, C., Nguyen, J., Abdulla, F., Zhang, P., Wassmer, A., Jain, M., Mischnik, M., Pelzing, M., ... Höbarth, G. (2022). Plasma-Derived Hemopexin as a Candidate Therapeutic Agent for Acute Vaso-Occlusion in Sickle Cell Disease: Preclinical Evidence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030630







