Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Difficult Issue of Subclinical GCA in Patients with Apparently Isolated PMR
3. Are There Clinical Predictive Factors of GCA in PMR Patients?
4. PMR and GCA Pathogenesis: Clues to Identified Specifics Disease Biomarkers
4.1. Elevation of Acute Phase Reactant
4.2. Vascular Remodelling Markers
5. The Role of Imaging in Identifying GCA
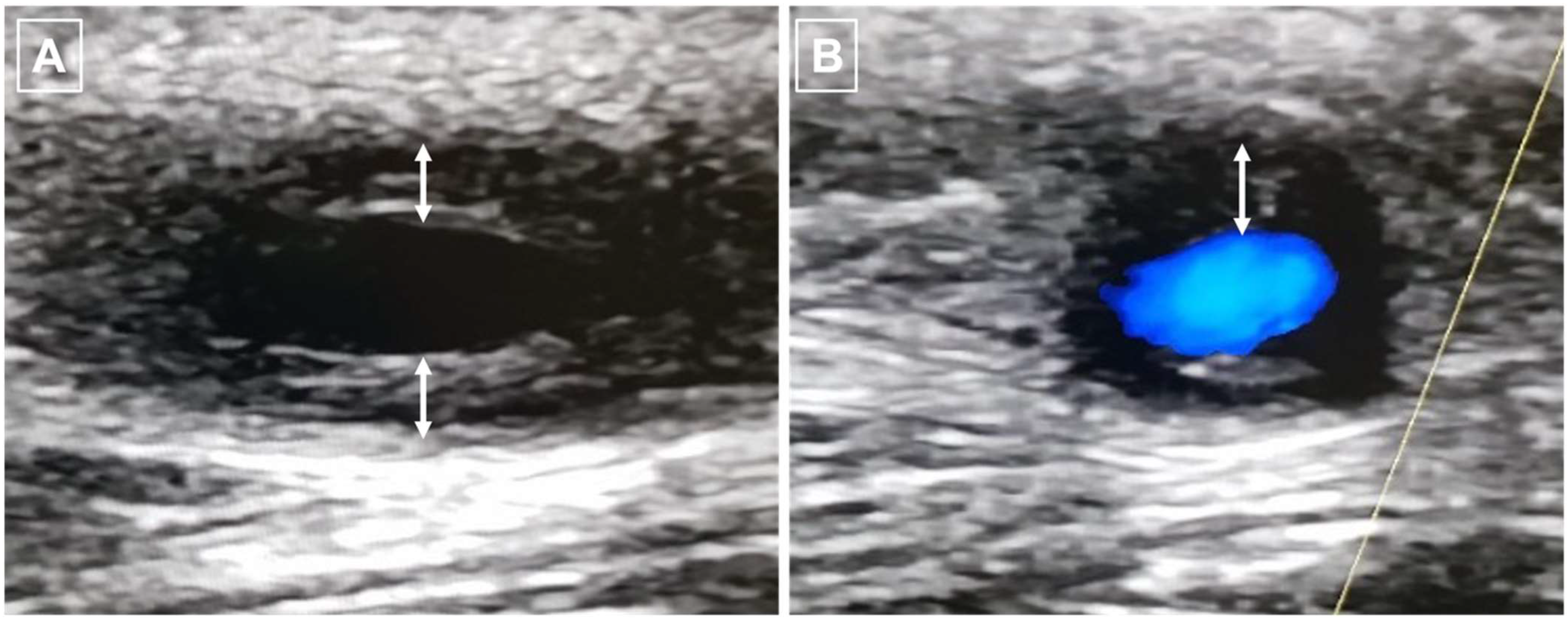
5.1. Ultrasound (US) Imaging
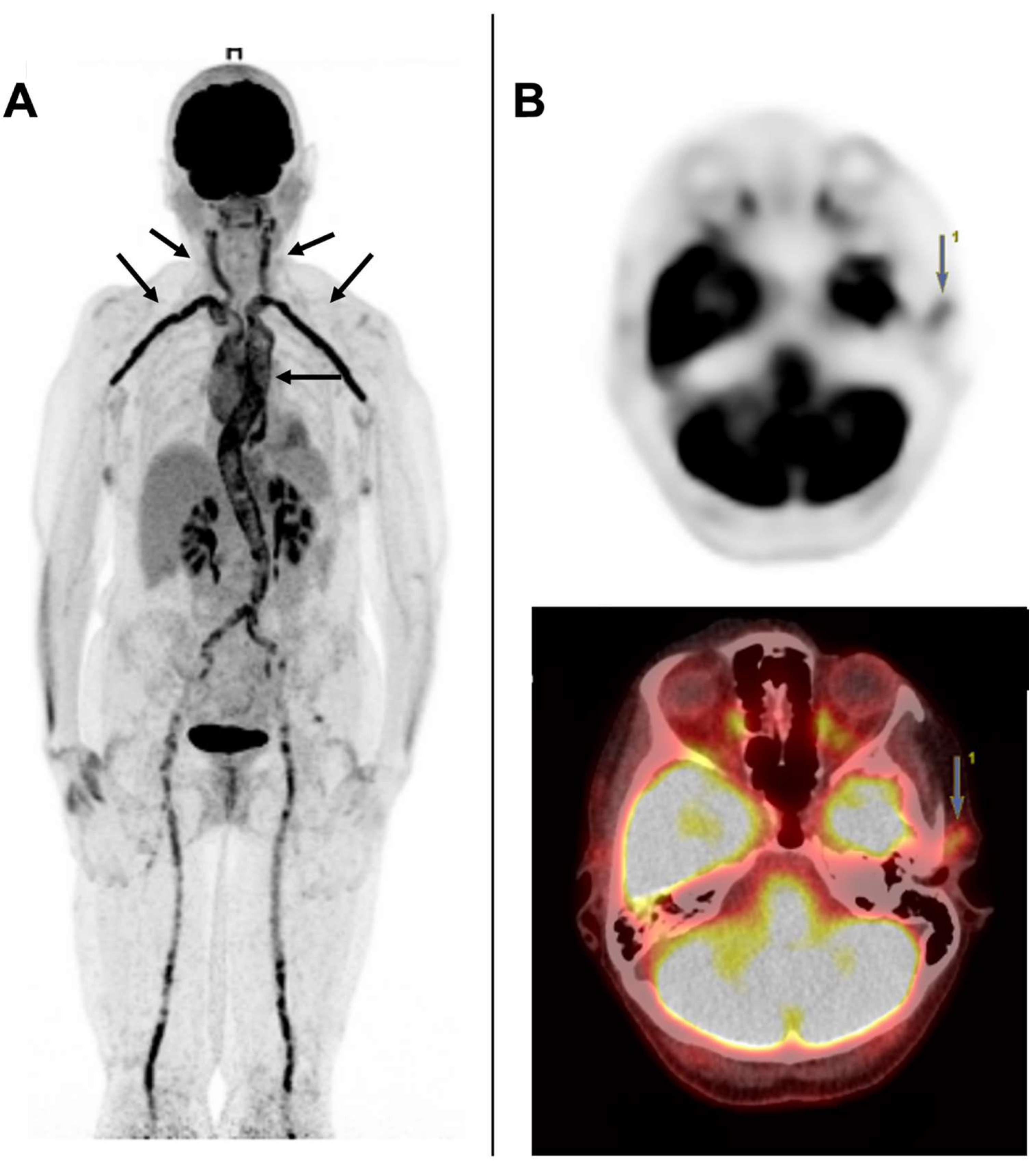
5.2. [18F] FDG-PET/CT
5.3. MRI and CTA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-Gay, M.A.; Matteson, E.L.; Castañeda, S. Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Lancet 2017, 390, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camellino, D.; Giusti, A.; Girasole, G.; Bianchi, G.; Dejaco, C. Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Drugs Aging 2019, 36, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttgereit, F.; Dejaco, C.; Matteson, E.L.; Dasgupta, B. Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2016, 315, 2442–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Ramiro, S.; Duftner, C.; Besson, F.L.; Bley, T.A.; Blockmans, D.; Brouwer, E.; Cimmino, M.A.; Clark, E.; Dasgupta, B.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Use of Imaging in Large Vessel Vasculitis in Clinical Practice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maz, M.; Chung, S.A.; Abril, A.; Langford, C.A.; Gorelik, M.; Guyatt, G.; Archer, A.M.; Conn, D.L.; Full, K.A.; Grayson, P.C.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmich, B.; Agueda, A.; Monti, S.; Buttgereit, F.; De Boysson, H.; Brouwer, E.; Cassie, R.; Cid, M.C.; Dasgupta, B.; Dejaco, C.; et al. 2018 Update of the EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Large Vessel Vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brack, A.; Martinez-Taboada, V.; Stanson, A.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Disease Pattern in Cranial and Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, D.; Karabayas, M.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Goel, R.; Goodyear, C.S.; Grayson, P.C.; McAdoo, S.P.; Mason, J.C.; Owen, C.; et al. Large-Vessel Vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2022, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Duftner, C.; Buttgereit, F.; Matteson, E.L.; Dasgupta, B. The Spectrum of Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Revisiting the Concept of the Disease. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, F.; Kermani, T.A.; Crowson, C.S.; Green, A.B.; Salvarani, C.; Matteson, E.L.; Warrington, K.J. Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis: A Cohort Study. Rheumatology 2014, 54, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koster, M.J.; Matteson, E.L.; Warrington, K.J. Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis: Diagnosis, Monitoring and Management. Rheumatology 2018, 57, ii32–ii42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kermani, T.A.; Warrington, K.; Crowson, C.S.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Hunder, G.G.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L. Large-Vessel Involvement in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study of the Incidence-Trends and Prognosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boysson, H.; Daumas, A.; Vautier, M.; Parienti, J.-J.; Liozon, E.; Lambert, M.; Samson, M.; Ebbo, M.; Dumont, A.; Sultan, A.; et al. Large-Vessel Involvement and Aortic Dilation in Giant-Cell Arteritis. A Multicenter Study of 549 Patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espitia, O.; Néel, A.; Leux, C.; Connault, J.; Espitia-Thibault, A.; Ponge, T.; Dupas, B.; Barrier, J.H.; Hamidou, M.A.; Agard, C. Giant Cell Arteritis with or without Aortitis at Diagnosis. A Retrospective Study of 22 Patients with Longterm Follow-up. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Rodriguez, T.R.V.; Lopez-Diaz, M.J.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Martin, J.; Llorca, J. Epidemiology of Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmig, A.K.; Gozzoli, D.; Werlen, L.; Ewald, H.; Aschwanden, M.; Blockmans, D.; Brouwer, E.; Buchanan, R.R.; Camellino, D.; Campochiaro, C.; et al. Subclinical Giant Cell Arteritis in New Onset Polymyalgia Rheumatica A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 55, 152017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Amor-Dorado, J.C.; Llorca, J. Giant Cell Arteritis without Clinically Evident Vascular Involvement in a Defined Population. Arthritis Care Res. 2004, 51, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.A.; Gromnica-Ihle, E. Incidence of Temporal Arteritis in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Prospective Study Using Colour Doppler Ultrasonography of the Temporal Arteries. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamrin, B.; Jonsson, N.; Landberg, T. Involvement of Large Vessels in Polymyalgia Arteritica. Lancet 1965, 285, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, B.; Malmvall, B.-E. The Epidemiology of Giant Cell Arteritis Including Temporal Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Incidences of Different Clinical Presentations and Eye Complications. Arthritis Rheum. 1981, 24, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myklebust, G.; Gran, J.T. A Prospective Study of 287 Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Temporal Arteritis: Clinical and Laboratory Manifestations at Onset of Disease and at the Time of Diagnosis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fauchald, P.; Rygvold, O.; Øystese, B. Temporal Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Clinical and Biopsy Findings. Ann. Intern. Med. 1972, 77, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzén, P.; Sutinen, S.; Von Knorring, J. Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica in a Region of Finland: An Epidemiologic, Clinical and Pathologic Study, 1984–1988. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Peña, D.; Martínez-Rodríguez, I.; Loricera, J.; Banzo, I.; Calderón-Goercke, M.; Calvo-Río, V.; González-Vela, C.; Corrales, A.; Castañeda, S.; Blanco, R.; et al. Predictors of Positive 18F-FDG PET/CT-Scan for Large Vessel Vasculitis in Patients with Persistent Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 48, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moosig, F.; Czech, N.; Mehl, C.; Henze, E.; Zeuner, R.A.; Kneba, M.; Schröder, J.O. Correlation between 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Accumulation in Large Vessels and Serological Markers of Inflammation in Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Quantitative PET Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamifar, A.; Ellingsen, T.; Hess, S.; Gerke, O.; Larsen, R.H.; Farahani, Z.A.; Hansen, P.S.; Hansen, I.M.J.; Petersen, H.; Marcussen, N.; et al. The Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients With Clinical Suspicion of Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteri-tis: A Prospective, Observational, and Cross-Sectional Study. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Kubota, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Minaminoto, R.; Morooka, M.; Ito, K.; Kano, T.; Kaneko, H.; Takashima, H.; Mimoiri, A. Whole-Body Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Patients with Active Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Evidence for Distinctive Bursitis and Large-Vessel Vasculitis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 22, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blockmans, D.; De Ceuninck, L.; Vanderschueren, S.; Knockaert, D.; Mortelmans, L.; Bobbaers, H. Repetitive 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Prospective Study in 35 Patients. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Font, C.; García-Martínez, A.; Espígol-Frigolé, G.; Sanmartí, R.; Cañete, J.D.; Grau, J.M.; Cid, M.C. Development of Ischemic Complications in Patients With Giant Cell Arteritis Presenting With Apparently Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Study of a Series of 100 Patients. Medicine 2007, 86, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, J.; Estrada, P.; López-Vives, L.; Ricse, M.; Zacarías, A.; Heredia, S.; Gómez-Vaquero, C.; Nolla, J.M. Prevalence of Ischemic Complications in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis Presenting with Apparently Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liozon, E.; de Boysson, H.; Dalmay, F.; Gondran, G.; Bezanahary, H.; Fauchais, A.-L.; Ly, K.-H. Development of Giant Cell Arteritis after Treating Polymyalgia or Peripheral Arthritis: A Retrospective Case-control Study. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Valverde, V.; Sarabia, J.M.; González-Gay, M.A.; Figueroa, M.; Armona, J.; Blanco, R.; Fernández-Sueiro, J.L.; Martínez-Taboada, V.M. Risk Factors and Predictive Models of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Am. J. Med. 1997, 102, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, C.; Barshack, I.; Koren-Morag, N.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Bornstein, G. Baseline Clinical Predictors of an Ultimate Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis in Patients Referred to Temporal Artery Biopsy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimmino, M.A.; Zampogna, G.; Parodi, M. Is FDG-PET Useful in the Evaluation of Steroid-Resistant PMR Patients? Rheumatology 2008, 47, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haworth, S.; Ridgeway, J.; Stewart, I.; Dyer, P.A.; Pepper, L.; Ollier, W. Polymyalgia Rheumatica Is Associated with Both HLA-DRB1*0401 and DRB1*0404. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labbe, P.; Flipo, R.; Fajardy, I.; Hachulla, E.; Houvenagel, E.; Hatron, P.; Duquesnoy, B.; Danze, P. HLA DRB1 polymorphism in rhizomelic pseudo-polyarthritis and horton disease. Rev. Med. Interne 1995, 16, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma-Krupa, W.; Jeon, M.-S.; Spoerl, S.; Tedder, T.F.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Activation of Arterial Wall Dendritic Cells and Breakdown of Self-Tolerance in Giant Cell Arteritis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Geest, K.S.M.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Rutgers, A.; Horst, G.; Bijzet, J.; Arends, S.; Roffel, M.P.; Boots, A.M.H.; Brouwer, E. Serum Markers Associated with Disease Activity in Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samson, M.; Ly, K.H.; Tournier, B.; Janikashvili, N.; Trad, M.; Ciudad, M.; Gautheron, A.; Devilliers, H.; Quipourt, V.; Maurier, F.; et al. Involvement and Prognosis Value of CD8 + T Cells in Giant Cell Arteritis. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 72, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, N.E.; Ms, J.W.F.; Wagner, A.D.; Hunder, G.G.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Correlation of Interleukin-6 Production and Disease Activity in Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, M.; Audia, S.; Fraszczak, J.; Trad, M.; Ornetti, P.; Lakomy, D.; Ciudad, M.; Leguy, V.; Berthier, S.; Vinit, J.; et al. Th1 and Th17 Lymphocytes Expressing CD161 Are Implicated in Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica Pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3788–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, M.; Corbera-Bellalta, M.; Audia, S.; Planas-Rigol, E.; Martin, L.; Cid, M.C.; Bonnotte, B. Recent Advances in our Understanding of Giant Cell Arteritis Pathogenesis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiemy, W.F.; Zhang, A.; Boots, A.M.H.; Heeringa, P.; Sandovici, M.; Diepstra, A.; Hein, S.; Dasgupta, B.; Brouwer, E.; van der Geest, K.S. Expression of Interleukin-6 in Synovial Tissue of Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sleen, Y.; Therkildsen, P.; Nielsen, B.D.; van der Geest, K.S.M.; Hansen, I.; Heeringa, P.; Posthumus, M.D.; Sandovici, M.; Toonen, E.J.M.; Zijlstra, J.; et al. Angiopoietin-2/-1 Ratios and MMP-3 Levels as an Early Warning Sign for the Presence of Giant Cell Arteritis in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, S.; Nunokawa, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Kamei, S.; Yokogawa, N.; Takizawa, Y.; Shimada, K.; Sugii, S.; Setoguchi, K. MMP-3 can Distinguish Isolated PMR from PMR with GCA: A Retrospective Study Regarding PMR and GCA in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sleen, Y.; Boots, A.M.H.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Bijzet, J.; Sandovici, M.; Van Der Geest, K.S.M.; Brouwer, E. High Angiopoietin-2 Levels Associate with Arterial Inflammation and Long-Term Glucocorticoid Requirement in Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Rheumatology 2019, 59, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Rivas, M.J.; Rodriguez-Ledo, P.; Llorca, J. Epidemiology of Biopsy Proven Giant Cell Arteritis in Northwestern Spain: Trend over an 18 Year Period. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Gay, M.A.; García-Porrúa, C.; Vázquez-Caruncho, M. Polymyalgia Rheumatica in Biopsy Proven Giant Cell Arteritis Does Not Constitute a Different Subset but Differs from Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 1750–1755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Segarra, M.; Vilardell, C.; Sánchez, M.; García-Martínez, A.; Esteban, M.-J.; Grau, J.M.; Urbano-Márquez, A.; Colomer, D.; Kleinman, H.K.; et al. Elevated Production of Interleukin-6 Is Associated With a Lower Incidence of Disease-Related Ischemic Events in Patients With Giant-Cell Arteritis: Angiogenic Activity of Interleukin-6 as a Potential Protective Mechanism. Circulation 2003, 107, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Maeda, T.; Zhang, H.; Berry, G.J.; Zeisbrich, M.; Brockett, R.; Greenstein, A.E.; Tian, L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. MMP (Matrix Metalloprotease)-9–Producing Monocytes Enable T Cells to Invade the Vessel Wall and Cause Vasculitis. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duftner, C.; Dejaco, C.; Sepriano, A.; Falzon, L.; Schmidt, W.A.; Ramiro, S. Imaging in Diagnosis, Outcome Prediction and Monitoring of Large Vessel Vasculitis: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis Informing the EULAR Recommendations. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thibault, T.; Durand-Bailloud, B.; Soudry-Faure, A.; Greigert, H.; Drouet, C.; Devilliers, H.; Ramon, A.; Bejot, Y.; Martin, L.; Creuzot-Garcher, C.; et al. PET/CT of Cranial Arteries for a Sensitive Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis. Rheumatology 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammel, A.M.; Hsiao, E.; Schembri, G.; Nguyen, K.; Brewer, J.; Schrieber, L.; Janssen, B.; Youssef, P.; Fraser, C.; Bailey, E.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography of the Head, Neck, and Chest for Giant Cell Arteritis: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Cross-Sectional Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-J.; Li, M.-X.; Zhang, P.; Qin, H.-Q.; Guo, Z.-N.; Yang, Y. Validity of High Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detecting Giant Cell Arteritis: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3541–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Haugeberg, G.; Hetland, H.; Soldal, D.M.; Bie, R.; Myklebust, G. Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasonography of Temporal Arteries and Large Vessels in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Consecutive Case Series. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lariviere, D.; Benali, K.; Coustet, B.; Pasi, N.; Hyafil, F.; Klein, I.; Chauchard, M.; Alexandra, J.-F.; Goulenok, T.; Dossier, A.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography Angiography for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A Real-Life Prospective Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-González, S.; Depetris, M.; García-Martínez, A.; Espígol-Frigolé, G.; Tavera-Bahillo, I.; Corbera-Bellata, M.; Planas-Rigol, E.; Alba, M.A.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Grau, J.M.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography Assessment of Large Vessel Inflammation in Patients with Newly Diagnosed, Biopsy-Proven Giant Cell Arteritis: A Prospective, Case–Control Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hay, B.; Mariano-Goulart, D.; Bourdon, A.; Benkiran, M.; Vauchot, F.; De Verbizier, D.; Ben Bouallègue, F. Diagnostic Performance of 18F-FDG PET-CT for Large Vessel Involvement Assessment in Patients with Suspected Giant Cell Arteritis and Negative Temporal Artery Biopsy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2019, 33, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinagel, M.; Chatelus, E.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; Sibilia, J.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Chasset, F.; Arnaud, L. Diagnostic Performance of Temporal Artery Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 18, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Haugeberg, G.; Lindland, A.; Myklebust, G. The Fast-Track Ultrasound Clinic for Early Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis Significantly Reduces Permanent Visual Impairment: Towards a More Effective Strategy to Improve Clinical Outcome in Giant Cell Arteritis? Rheumatology 2016, 55, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, W.A. Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Management of Giant Cell Arteritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, ii22–ii31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chrysidis, S.; Duftner, C.; Dejaco, C.; Schäfer, V.S.; Ramiro, S.; Carrara, G.; Scirè, C.A.; Hocevar, A.; Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Iagnocco, A.; et al. Definitions and Reliability Assessment of Elementary Ultrasound Lesions in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Study from the OMERACT Large Vessel Vasculitis Ultrasound Working Group. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prearo, I.; Dekorsy, F.J.; Brendel, M.; Lottspeich, C.; Dechant, C.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U.; Czihal, M. Diagnostic Yield of Axillary Artery Ultrasound in Addition to Temporal Artery Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaversen, A.C.B.; Brekke, L.K.; Kermani, T.A.; Molberg, Ø.; Diamantopoulos, A.P. Extended Ultrasound Examination Identifies More Large Vessel Involvement in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis. Rheumatology 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysidis, S.; Terslev, L.; Christensen, R.; Fredberg, U.; Larsen, K.; Lorenzen, T.; Døhn, U.M.; Diamantopoulos, A.P. Vascular Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A Reliability and Agreement Study Based on a Standardised Training Programme. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, V.S.; Chrysidis, S.; Dejaco, C.; Duftner, C.; Iagnocco, A.; Bruyn, G.A.; Carrara, G.; D’Agostino, M.A.; De Miguel, E.; Diamantopoulos, A.P.; et al. Assessing Vasculitis in Giant Cell Arteritis by Ultrasound: Results of OMERACT Patient-based Reliability Exercises. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqmani, R.; Lee, E.; Singh, S.; Gillett, M.; Schmidt, W.A.; Bradburn, M.; Dasgupta, B.; Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Forrester-Barker, W.; Hamilton, W.; et al. The Role of Ultrasound Compared to Biopsy of Temporal Arteries in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis (TABUL): A Diagnostic Accuracy and Cost-Effectiveness Study. Health Technol. Assess. 2016, 20, 1–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sammel, A.M.; Hsiao, E.; Schrieber, L.; Janssen, B.; Youssef, P.; Fraser, C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Dunn, H.; Bailey, D.L.; Roach, P.; et al. Fluorine-18 Fluoro-2-Deoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Uptake in the Superficial Temporal and Vertebral Arteries in Biopsy Positive Giant Cell Arteritis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 23, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.D.; Hansen, I.T.; Kramer, S.; Haraldsen, A.; Hjorthaug, K.; Bogsrud, T.V.; Ejlersen, J.A.; Stolle, L.B.; Keller, K.K.; Therkildsen, P.; et al. Simple Dichotomous Assessment of Cranial Artery Inflammation by Conventional 18F-FDG PET/CT Shows High Accuracy for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A case-control study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.D.; Gormsen, L.C.; Hansen, I.T.; Keller, K.K.; Therkildsen, P.; Hauge, E.-M. Three Days of High-Dose Glucocorticoid Treatment Attenuates Large-Vessel 18F-FDG Uptake in Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis but with a Limited Impact on Diagnostic Accuracy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imfeld, S.; Aschwanden, M.; Rottenburger, C.; Schegk, E.; Berger, C.T.; Staub, D.; Daikeler, T. [18F] FDG Positron Emission Tomography and Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: Congruent or Complementary Imaging Methods? Rheumatology 2020, 59, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Geest, K.S.M.; van Sleen, Y.; Nienhuis, P.; Sandovici, M.; Westerdijk, N.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Brouwer, E.; Slart, R.H.J.A. Comparison and Validation of FDG-PET/CT Scores for Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Rheumatology 2021, 61, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Geest, K.S.M.; Sandovici, M.; Nienhuis, P.H.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Heeringa, P.; Brouwer, E.; Jiemy, W.F. Novel PET Imaging of Inflammatory Targets and Cells for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 902155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Régent, C.; Ben Hassen, W.; Seners, P.; Oppenheim, C.; Régent, A. 3D T1-Weighted Black-Blood Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S124), 95–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poillon, G.; Collin, A.; Benhamou, Y.; Clavel, G.; Savatovsky, J.; Pinson, C.; Zuber, K.; Charbonneau, F.; Vignal, C.; Picard, H.; et al. Increased Diagnostic Accuracy of Giant Cell Arteritis Using Three-Dimensional Fat-Saturated Contrast-Enhanced Vessel-wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3 T. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, A.; Jernberg, E.T.; Bardi, M.; Geiger, J.; Lohne, F.; Schmidt, W.A.; Myklebust, G.; Diamantopoulos, A.P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compared to Ultrasonography in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, P.E.; Aho-Glélé, S.; Ornetti, P.; Chevallier, O.; Devilliers, H.; Ricolfi, F.; Bonnotte, B.; Loffroy, R.; Samson, M. CT Analysis of the Aorta in Giant-Cell Arteritis: A Case-Control Study. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3676–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomarker | Study Design | Population | AUC | Threshold | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESR | Prospective 2 international cohorts (Aarhus, UMCG) | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | Aarhus: 0.82 UMCG: 0.77 | Aarhus: 60 mm/h UMCG: 91 mm/h | [45] |
| Retrospective | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | NR | NR | [46] | |
| Angiopoietin 2 | Prospective UMCG cohort | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | 0.90 | 3124 pg/mL | [47] |
| Angiopoietin 2/Angiopoeitin 1 ratio | Prospective 2 international cohorts (Aarhus, UMCG) | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | Aarhus: 0.78 UMCG: 0.88 | Aarhus: 0.048 UMCG: 0.051 | [45] |
| MMP-3 | Prospective 2 international cohorts (Aarhus, UMCG) | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | Aarhus: 0.81 UMCG: 0.82 | Aarhus: 23 ng/mL UMCG: 14 ng/mL | [45] |
| Retrospective | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | 0.81 | 140 ng/mL | [46] |
| C-GCA | LV-GCA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US | [18F] FDG-PET/CT | MRI | US | [18F] FDG-PET/CT | CTA | ||
| Features | Halo sign Compression sign Stenose Occlusion | Vascular uptake Vascular occlusion and stenosis | Mural thickening Enhancement of cranial arteries | Halo sign Stenose Occlusion | Vascular uptake Vascular occlusion and stenosis | Mural thickening Arteries enhancement | |
| Diagnostic accuracy | Compared to clinical diagnosis | Se: 77% Spe: 96% [52] | Se: 71-73.3% Spe: 91-97.2% [53,54] | Se: 75% Spe: 89% [55] | Se: 100% Spe: 91% [56] * | Se: 61-80% Spe: 79-100% [53,57,58,59] | Se:73% Spe: 78% [57] |
| Compared to TAB | Se: 68% Spe: 81% [60] | Se: 92% Spe: 85% [54] | Se: 91% Spe: 78% [55] | ||||
| Advantages | No radiation Fast track clinics Low cost High resolution Availability | Overview of involved arteries Detection of GCA/PMR mimickers (infection, neoplasia) | No radiation No iodinated contrast agents | No radiation Fast track clinics Low cost High resolution Availability | Overview of involved arteries Detection of GCA/PMR mimickers (infection, neoplasia) | Good overview of the aorta Fast acquisition | |
| Disadvantages | Trained operator (especially for large vessels assessment) | Radiation (25 mSv) High cost Completion time Decrease in sensitivity after 3 days of glucocorticoids | High cost Low availability Limited by metal devices, claustrophobia, or pacemaker | Limited value for aortitis assessment Trained operator (especially for large vessels assessment) | Radiation (25 mSv) High cost Completion time Decrease in sensitivity after 3 days of glucocorticoids | Radiation (17mSv) Iodinated contrast medium | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramon, A.; Greigert, H.; Ornetti, P.; Maillefert, J.-F.; Bonnotte, B.; Samson, M. Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412
Ramon A, Greigert H, Ornetti P, Maillefert J-F, Bonnotte B, Samson M. Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamon, André, Hélène Greigert, Paul Ornetti, Jean-Francis Maillefert, Bernard Bonnotte, and Maxime Samson. 2022. "Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412
APA StyleRamon, A., Greigert, H., Ornetti, P., Maillefert, J.-F., Bonnotte, B., & Samson, M. (2022). Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412






