Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Difficult Issue of Subclinical GCA in Patients with Apparently Isolated PMR
3. Are There Clinical Predictive Factors of GCA in PMR Patients?
4. PMR and GCA Pathogenesis: Clues to Identified Specifics Disease Biomarkers
4.1. Elevation of Acute Phase Reactant
4.2. Vascular Remodelling Markers
5. The Role of Imaging in Identifying GCA
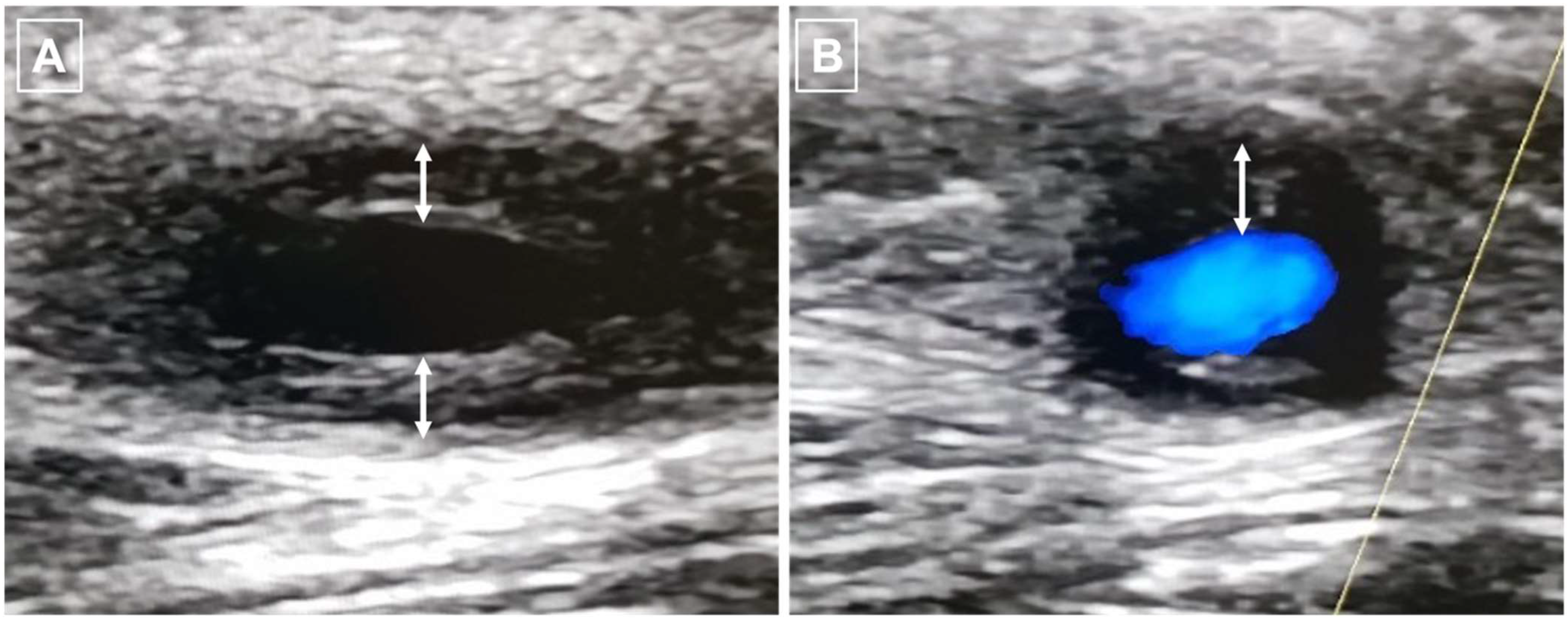
5.1. Ultrasound (US) Imaging
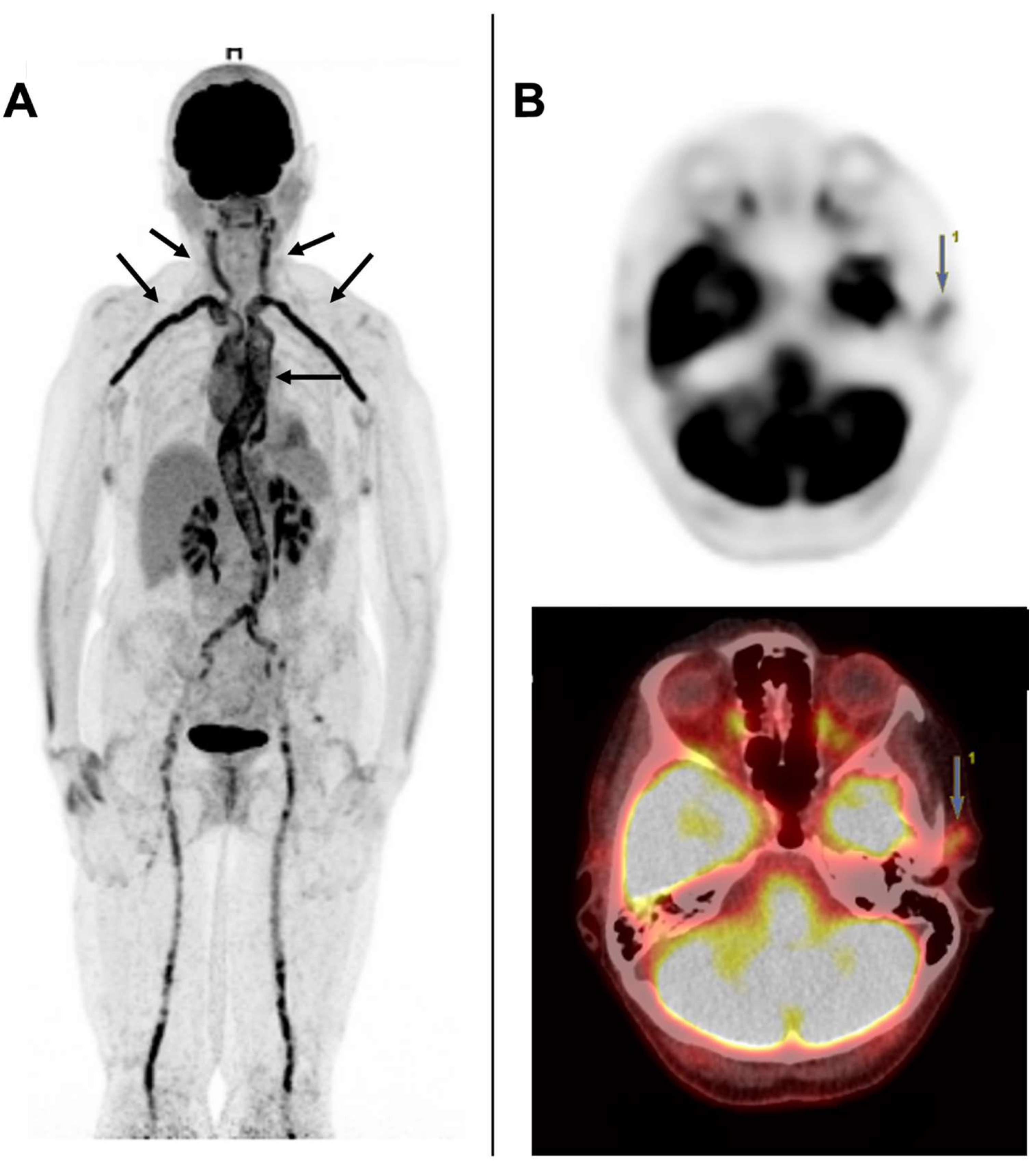
5.2. [18F] FDG-PET/CT
5.3. MRI and CTA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-Gay, M.A.; Matteson, E.L.; Castañeda, S. Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Lancet 2017, 390, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camellino, D.; Giusti, A.; Girasole, G.; Bianchi, G.; Dejaco, C. Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Drugs Aging 2019, 36, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttgereit, F.; Dejaco, C.; Matteson, E.L.; Dasgupta, B. Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2016, 315, 2442–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Ramiro, S.; Duftner, C.; Besson, F.L.; Bley, T.A.; Blockmans, D.; Brouwer, E.; Cimmino, M.A.; Clark, E.; Dasgupta, B.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Use of Imaging in Large Vessel Vasculitis in Clinical Practice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maz, M.; Chung, S.A.; Abril, A.; Langford, C.A.; Gorelik, M.; Guyatt, G.; Archer, A.M.; Conn, D.L.; Full, K.A.; Grayson, P.C.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmich, B.; Agueda, A.; Monti, S.; Buttgereit, F.; De Boysson, H.; Brouwer, E.; Cassie, R.; Cid, M.C.; Dasgupta, B.; Dejaco, C.; et al. 2018 Update of the EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Large Vessel Vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, A.; Martinez-Taboada, V.; Stanson, A.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Disease Pattern in Cranial and Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, D.; Karabayas, M.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Goel, R.; Goodyear, C.S.; Grayson, P.C.; McAdoo, S.P.; Mason, J.C.; Owen, C.; et al. Large-Vessel Vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2022, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Duftner, C.; Buttgereit, F.; Matteson, E.L.; Dasgupta, B. The Spectrum of Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Revisiting the Concept of the Disease. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, F.; Kermani, T.A.; Crowson, C.S.; Green, A.B.; Salvarani, C.; Matteson, E.L.; Warrington, K.J. Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis: A Cohort Study. Rheumatology 2014, 54, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, M.J.; Matteson, E.L.; Warrington, K.J. Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis: Diagnosis, Monitoring and Management. Rheumatology 2018, 57, ii32–ii42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermani, T.A.; Warrington, K.; Crowson, C.S.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Hunder, G.G.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L. Large-Vessel Involvement in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study of the Incidence-Trends and Prognosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boysson, H.; Daumas, A.; Vautier, M.; Parienti, J.-J.; Liozon, E.; Lambert, M.; Samson, M.; Ebbo, M.; Dumont, A.; Sultan, A.; et al. Large-Vessel Involvement and Aortic Dilation in Giant-Cell Arteritis. A Multicenter Study of 549 Patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espitia, O.; Néel, A.; Leux, C.; Connault, J.; Espitia-Thibault, A.; Ponge, T.; Dupas, B.; Barrier, J.H.; Hamidou, M.A.; Agard, C. Giant Cell Arteritis with or without Aortitis at Diagnosis. A Retrospective Study of 22 Patients with Longterm Follow-up. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Rodriguez, T.R.V.; Lopez-Diaz, M.J.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Martin, J.; Llorca, J. Epidemiology of Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmig, A.K.; Gozzoli, D.; Werlen, L.; Ewald, H.; Aschwanden, M.; Blockmans, D.; Brouwer, E.; Buchanan, R.R.; Camellino, D.; Campochiaro, C.; et al. Subclinical Giant Cell Arteritis in New Onset Polymyalgia Rheumatica A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 55, 152017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Amor-Dorado, J.C.; Llorca, J. Giant Cell Arteritis without Clinically Evident Vascular Involvement in a Defined Population. Arthritis Care Res. 2004, 51, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.A.; Gromnica-Ihle, E. Incidence of Temporal Arteritis in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Prospective Study Using Colour Doppler Ultrasonography of the Temporal Arteries. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamrin, B.; Jonsson, N.; Landberg, T. Involvement of Large Vessels in Polymyalgia Arteritica. Lancet 1965, 285, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, B.; Malmvall, B.-E. The Epidemiology of Giant Cell Arteritis Including Temporal Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Incidences of Different Clinical Presentations and Eye Complications. Arthritis Rheum. 1981, 24, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myklebust, G.; Gran, J.T. A Prospective Study of 287 Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Temporal Arteritis: Clinical and Laboratory Manifestations at Onset of Disease and at the Time of Diagnosis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauchald, P.; Rygvold, O.; Øystese, B. Temporal Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Clinical and Biopsy Findings. Ann. Intern. Med. 1972, 77, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzén, P.; Sutinen, S.; Von Knorring, J. Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica in a Region of Finland: An Epidemiologic, Clinical and Pathologic Study, 1984–1988. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Peña, D.; Martínez-Rodríguez, I.; Loricera, J.; Banzo, I.; Calderón-Goercke, M.; Calvo-Río, V.; González-Vela, C.; Corrales, A.; Castañeda, S.; Blanco, R.; et al. Predictors of Positive 18F-FDG PET/CT-Scan for Large Vessel Vasculitis in Patients with Persistent Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 48, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosig, F.; Czech, N.; Mehl, C.; Henze, E.; Zeuner, R.A.; Kneba, M.; Schröder, J.O. Correlation between 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Accumulation in Large Vessels and Serological Markers of Inflammation in Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Quantitative PET Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamifar, A.; Ellingsen, T.; Hess, S.; Gerke, O.; Larsen, R.H.; Farahani, Z.A.; Hansen, P.S.; Hansen, I.M.J.; Petersen, H.; Marcussen, N.; et al. The Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients With Clinical Suspicion of Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteri-tis: A Prospective, Observational, and Cross-Sectional Study. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Kubota, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Minaminoto, R.; Morooka, M.; Ito, K.; Kano, T.; Kaneko, H.; Takashima, H.; Mimoiri, A. Whole-Body Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Patients with Active Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Evidence for Distinctive Bursitis and Large-Vessel Vasculitis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 22, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blockmans, D.; De Ceuninck, L.; Vanderschueren, S.; Knockaert, D.; Mortelmans, L.; Bobbaers, H. Repetitive 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Prospective Study in 35 Patients. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Font, C.; García-Martínez, A.; Espígol-Frigolé, G.; Sanmartí, R.; Cañete, J.D.; Grau, J.M.; Cid, M.C. Development of Ischemic Complications in Patients With Giant Cell Arteritis Presenting With Apparently Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Study of a Series of 100 Patients. Medicine 2007, 86, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, J.; Estrada, P.; López-Vives, L.; Ricse, M.; Zacarías, A.; Heredia, S.; Gómez-Vaquero, C.; Nolla, J.M. Prevalence of Ischemic Complications in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis Presenting with Apparently Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liozon, E.; de Boysson, H.; Dalmay, F.; Gondran, G.; Bezanahary, H.; Fauchais, A.-L.; Ly, K.-H. Development of Giant Cell Arteritis after Treating Polymyalgia or Peripheral Arthritis: A Retrospective Case-control Study. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Valverde, V.; Sarabia, J.M.; González-Gay, M.A.; Figueroa, M.; Armona, J.; Blanco, R.; Fernández-Sueiro, J.L.; Martínez-Taboada, V.M. Risk Factors and Predictive Models of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Am. J. Med. 1997, 102, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, C.; Barshack, I.; Koren-Morag, N.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Bornstein, G. Baseline Clinical Predictors of an Ultimate Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis in Patients Referred to Temporal Artery Biopsy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimmino, M.A.; Zampogna, G.; Parodi, M. Is FDG-PET Useful in the Evaluation of Steroid-Resistant PMR Patients? Rheumatology 2008, 47, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haworth, S.; Ridgeway, J.; Stewart, I.; Dyer, P.A.; Pepper, L.; Ollier, W. Polymyalgia Rheumatica Is Associated with Both HLA-DRB1*0401 and DRB1*0404. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Labbe, P.; Flipo, R.; Fajardy, I.; Hachulla, E.; Houvenagel, E.; Hatron, P.; Duquesnoy, B.; Danze, P. HLA DRB1 polymorphism in rhizomelic pseudo-polyarthritis and horton disease. Rev. Med. Interne 1995, 16, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma-Krupa, W.; Jeon, M.-S.; Spoerl, S.; Tedder, T.F.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Activation of Arterial Wall Dendritic Cells and Breakdown of Self-Tolerance in Giant Cell Arteritis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Geest, K.S.M.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Rutgers, A.; Horst, G.; Bijzet, J.; Arends, S.; Roffel, M.P.; Boots, A.M.H.; Brouwer, E. Serum Markers Associated with Disease Activity in Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, M.; Ly, K.H.; Tournier, B.; Janikashvili, N.; Trad, M.; Ciudad, M.; Gautheron, A.; Devilliers, H.; Quipourt, V.; Maurier, F.; et al. Involvement and Prognosis Value of CD8 + T Cells in Giant Cell Arteritis. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 72, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, N.E.; Ms, J.W.F.; Wagner, A.D.; Hunder, G.G.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Correlation of Interleukin-6 Production and Disease Activity in Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, M.; Audia, S.; Fraszczak, J.; Trad, M.; Ornetti, P.; Lakomy, D.; Ciudad, M.; Leguy, V.; Berthier, S.; Vinit, J.; et al. Th1 and Th17 Lymphocytes Expressing CD161 Are Implicated in Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica Pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3788–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, M.; Corbera-Bellalta, M.; Audia, S.; Planas-Rigol, E.; Martin, L.; Cid, M.C.; Bonnotte, B. Recent Advances in our Understanding of Giant Cell Arteritis Pathogenesis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiemy, W.F.; Zhang, A.; Boots, A.M.H.; Heeringa, P.; Sandovici, M.; Diepstra, A.; Hein, S.; Dasgupta, B.; Brouwer, E.; van der Geest, K.S. Expression of Interleukin-6 in Synovial Tissue of Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sleen, Y.; Therkildsen, P.; Nielsen, B.D.; van der Geest, K.S.M.; Hansen, I.; Heeringa, P.; Posthumus, M.D.; Sandovici, M.; Toonen, E.J.M.; Zijlstra, J.; et al. Angiopoietin-2/-1 Ratios and MMP-3 Levels as an Early Warning Sign for the Presence of Giant Cell Arteritis in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, S.; Nunokawa, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Kamei, S.; Yokogawa, N.; Takizawa, Y.; Shimada, K.; Sugii, S.; Setoguchi, K. MMP-3 can Distinguish Isolated PMR from PMR with GCA: A Retrospective Study Regarding PMR and GCA in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sleen, Y.; Boots, A.M.H.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Bijzet, J.; Sandovici, M.; Van Der Geest, K.S.M.; Brouwer, E. High Angiopoietin-2 Levels Associate with Arterial Inflammation and Long-Term Glucocorticoid Requirement in Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Rheumatology 2019, 59, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Rivas, M.J.; Rodriguez-Ledo, P.; Llorca, J. Epidemiology of Biopsy Proven Giant Cell Arteritis in Northwestern Spain: Trend over an 18 Year Period. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gay, M.A.; García-Porrúa, C.; Vázquez-Caruncho, M. Polymyalgia Rheumatica in Biopsy Proven Giant Cell Arteritis Does Not Constitute a Different Subset but Differs from Isolated Polymyalgia Rheumatica. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 1750–1755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Segarra, M.; Vilardell, C.; Sánchez, M.; García-Martínez, A.; Esteban, M.-J.; Grau, J.M.; Urbano-Márquez, A.; Colomer, D.; Kleinman, H.K.; et al. Elevated Production of Interleukin-6 Is Associated With a Lower Incidence of Disease-Related Ischemic Events in Patients With Giant-Cell Arteritis: Angiogenic Activity of Interleukin-6 as a Potential Protective Mechanism. Circulation 2003, 107, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Maeda, T.; Zhang, H.; Berry, G.J.; Zeisbrich, M.; Brockett, R.; Greenstein, A.E.; Tian, L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. MMP (Matrix Metalloprotease)-9–Producing Monocytes Enable T Cells to Invade the Vessel Wall and Cause Vasculitis. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duftner, C.; Dejaco, C.; Sepriano, A.; Falzon, L.; Schmidt, W.A.; Ramiro, S. Imaging in Diagnosis, Outcome Prediction and Monitoring of Large Vessel Vasculitis: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis Informing the EULAR Recommendations. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, T.; Durand-Bailloud, B.; Soudry-Faure, A.; Greigert, H.; Drouet, C.; Devilliers, H.; Ramon, A.; Bejot, Y.; Martin, L.; Creuzot-Garcher, C.; et al. PET/CT of Cranial Arteries for a Sensitive Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis. Rheumatology 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammel, A.M.; Hsiao, E.; Schembri, G.; Nguyen, K.; Brewer, J.; Schrieber, L.; Janssen, B.; Youssef, P.; Fraser, C.; Bailey, E.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography of the Head, Neck, and Chest for Giant Cell Arteritis: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Cross-Sectional Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-J.; Li, M.-X.; Zhang, P.; Qin, H.-Q.; Guo, Z.-N.; Yang, Y. Validity of High Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detecting Giant Cell Arteritis: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3541–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Haugeberg, G.; Hetland, H.; Soldal, D.M.; Bie, R.; Myklebust, G. Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasonography of Temporal Arteries and Large Vessels in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Consecutive Case Series. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lariviere, D.; Benali, K.; Coustet, B.; Pasi, N.; Hyafil, F.; Klein, I.; Chauchard, M.; Alexandra, J.-F.; Goulenok, T.; Dossier, A.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography Angiography for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A Real-Life Prospective Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-González, S.; Depetris, M.; García-Martínez, A.; Espígol-Frigolé, G.; Tavera-Bahillo, I.; Corbera-Bellata, M.; Planas-Rigol, E.; Alba, M.A.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Grau, J.M.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography Assessment of Large Vessel Inflammation in Patients with Newly Diagnosed, Biopsy-Proven Giant Cell Arteritis: A Prospective, Case–Control Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, B.; Mariano-Goulart, D.; Bourdon, A.; Benkiran, M.; Vauchot, F.; De Verbizier, D.; Ben Bouallègue, F. Diagnostic Performance of 18F-FDG PET-CT for Large Vessel Involvement Assessment in Patients with Suspected Giant Cell Arteritis and Negative Temporal Artery Biopsy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2019, 33, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinagel, M.; Chatelus, E.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; Sibilia, J.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Chasset, F.; Arnaud, L. Diagnostic Performance of Temporal Artery Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 18, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Haugeberg, G.; Lindland, A.; Myklebust, G. The Fast-Track Ultrasound Clinic for Early Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis Significantly Reduces Permanent Visual Impairment: Towards a More Effective Strategy to Improve Clinical Outcome in Giant Cell Arteritis? Rheumatology 2016, 55, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, W.A. Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Management of Giant Cell Arteritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, ii22–ii31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrysidis, S.; Duftner, C.; Dejaco, C.; Schäfer, V.S.; Ramiro, S.; Carrara, G.; Scirè, C.A.; Hocevar, A.; Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Iagnocco, A.; et al. Definitions and Reliability Assessment of Elementary Ultrasound Lesions in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Study from the OMERACT Large Vessel Vasculitis Ultrasound Working Group. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prearo, I.; Dekorsy, F.J.; Brendel, M.; Lottspeich, C.; Dechant, C.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U.; Czihal, M. Diagnostic Yield of Axillary Artery Ultrasound in Addition to Temporal Artery Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaversen, A.C.B.; Brekke, L.K.; Kermani, T.A.; Molberg, Ø.; Diamantopoulos, A.P. Extended Ultrasound Examination Identifies More Large Vessel Involvement in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis. Rheumatology 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysidis, S.; Terslev, L.; Christensen, R.; Fredberg, U.; Larsen, K.; Lorenzen, T.; Døhn, U.M.; Diamantopoulos, A.P. Vascular Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A Reliability and Agreement Study Based on a Standardised Training Programme. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, V.S.; Chrysidis, S.; Dejaco, C.; Duftner, C.; Iagnocco, A.; Bruyn, G.A.; Carrara, G.; D’Agostino, M.A.; De Miguel, E.; Diamantopoulos, A.P.; et al. Assessing Vasculitis in Giant Cell Arteritis by Ultrasound: Results of OMERACT Patient-based Reliability Exercises. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqmani, R.; Lee, E.; Singh, S.; Gillett, M.; Schmidt, W.A.; Bradburn, M.; Dasgupta, B.; Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Forrester-Barker, W.; Hamilton, W.; et al. The Role of Ultrasound Compared to Biopsy of Temporal Arteries in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis (TABUL): A Diagnostic Accuracy and Cost-Effectiveness Study. Health Technol. Assess. 2016, 20, 1–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammel, A.M.; Hsiao, E.; Schrieber, L.; Janssen, B.; Youssef, P.; Fraser, C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Dunn, H.; Bailey, D.L.; Roach, P.; et al. Fluorine-18 Fluoro-2-Deoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Uptake in the Superficial Temporal and Vertebral Arteries in Biopsy Positive Giant Cell Arteritis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 23, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.D.; Hansen, I.T.; Kramer, S.; Haraldsen, A.; Hjorthaug, K.; Bogsrud, T.V.; Ejlersen, J.A.; Stolle, L.B.; Keller, K.K.; Therkildsen, P.; et al. Simple Dichotomous Assessment of Cranial Artery Inflammation by Conventional 18F-FDG PET/CT Shows High Accuracy for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: A case-control study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.D.; Gormsen, L.C.; Hansen, I.T.; Keller, K.K.; Therkildsen, P.; Hauge, E.-M. Three Days of High-Dose Glucocorticoid Treatment Attenuates Large-Vessel 18F-FDG Uptake in Large-Vessel Giant Cell Arteritis but with a Limited Impact on Diagnostic Accuracy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imfeld, S.; Aschwanden, M.; Rottenburger, C.; Schegk, E.; Berger, C.T.; Staub, D.; Daikeler, T. [18F] FDG Positron Emission Tomography and Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: Congruent or Complementary Imaging Methods? Rheumatology 2020, 59, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Geest, K.S.M.; van Sleen, Y.; Nienhuis, P.; Sandovici, M.; Westerdijk, N.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Brouwer, E.; Slart, R.H.J.A. Comparison and Validation of FDG-PET/CT Scores for Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Rheumatology 2021, 61, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Geest, K.S.M.; Sandovici, M.; Nienhuis, P.H.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Heeringa, P.; Brouwer, E.; Jiemy, W.F. Novel PET Imaging of Inflammatory Targets and Cells for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 902155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Régent, C.; Ben Hassen, W.; Seners, P.; Oppenheim, C.; Régent, A. 3D T1-Weighted Black-Blood Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S124), 95–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poillon, G.; Collin, A.; Benhamou, Y.; Clavel, G.; Savatovsky, J.; Pinson, C.; Zuber, K.; Charbonneau, F.; Vignal, C.; Picard, H.; et al. Increased Diagnostic Accuracy of Giant Cell Arteritis Using Three-Dimensional Fat-Saturated Contrast-Enhanced Vessel-wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3 T. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, A.; Jernberg, E.T.; Bardi, M.; Geiger, J.; Lohne, F.; Schmidt, W.A.; Myklebust, G.; Diamantopoulos, A.P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compared to Ultrasonography in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, P.E.; Aho-Glélé, S.; Ornetti, P.; Chevallier, O.; Devilliers, H.; Ricolfi, F.; Bonnotte, B.; Loffroy, R.; Samson, M. CT Analysis of the Aorta in Giant-Cell Arteritis: A Case-Control Study. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3676–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomarker | Study Design | Population | AUC | Threshold | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESR | Prospective 2 international cohorts (Aarhus, UMCG) | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | Aarhus: 0.82 UMCG: 0.77 | Aarhus: 60 mm/h UMCG: 91 mm/h | [45] |
| Retrospective | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | NR | NR | [46] | |
| Angiopoietin 2 | Prospective UMCG cohort | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | 0.90 | 3124 pg/mL | [47] |
| Angiopoietin 2/Angiopoeitin 1 ratio | Prospective 2 international cohorts (Aarhus, UMCG) | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | Aarhus: 0.78 UMCG: 0.88 | Aarhus: 0.048 UMCG: 0.051 | [45] |
| MMP-3 | Prospective 2 international cohorts (Aarhus, UMCG) | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | Aarhus: 0.81 UMCG: 0.82 | Aarhus: 23 ng/mL UMCG: 14 ng/mL | [45] |
| Retrospective | GCA/PMR overlap versus Isolated PMR | 0.81 | 140 ng/mL | [46] |
| C-GCA | LV-GCA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US | [18F] FDG-PET/CT | MRI | US | [18F] FDG-PET/CT | CTA | ||
| Features | Halo sign Compression sign Stenose Occlusion | Vascular uptake Vascular occlusion and stenosis | Mural thickening Enhancement of cranial arteries | Halo sign Stenose Occlusion | Vascular uptake Vascular occlusion and stenosis | Mural thickening Arteries enhancement | |
| Diagnostic accuracy | Compared to clinical diagnosis | Se: 77% Spe: 96% [52] | Se: 71-73.3% Spe: 91-97.2% [53,54] | Se: 75% Spe: 89% [55] | Se: 100% Spe: 91% [56] * | Se: 61-80% Spe: 79-100% [53,57,58,59] | Se:73% Spe: 78% [57] |
| Compared to TAB | Se: 68% Spe: 81% [60] | Se: 92% Spe: 85% [54] | Se: 91% Spe: 78% [55] | ||||
| Advantages | No radiation Fast track clinics Low cost High resolution Availability | Overview of involved arteries Detection of GCA/PMR mimickers (infection, neoplasia) | No radiation No iodinated contrast agents | No radiation Fast track clinics Low cost High resolution Availability | Overview of involved arteries Detection of GCA/PMR mimickers (infection, neoplasia) | Good overview of the aorta Fast acquisition | |
| Disadvantages | Trained operator (especially for large vessels assessment) | Radiation (25 mSv) High cost Completion time Decrease in sensitivity after 3 days of glucocorticoids | High cost Low availability Limited by metal devices, claustrophobia, or pacemaker | Limited value for aortitis assessment Trained operator (especially for large vessels assessment) | Radiation (25 mSv) High cost Completion time Decrease in sensitivity after 3 days of glucocorticoids | Radiation (17mSv) Iodinated contrast medium | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramon, A.; Greigert, H.; Ornetti, P.; Maillefert, J.-F.; Bonnotte, B.; Samson, M. Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412
Ramon A, Greigert H, Ornetti P, Maillefert J-F, Bonnotte B, Samson M. Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamon, André, Hélène Greigert, Paul Ornetti, Jean-Francis Maillefert, Bernard Bonnotte, and Maxime Samson. 2022. "Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412
APA StyleRamon, A., Greigert, H., Ornetti, P., Maillefert, J.-F., Bonnotte, B., & Samson, M. (2022). Predictive Factors of Giant Cell Arteritis in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247412






