Eryptosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Possible Relationship with Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrollment and Blood Collection
2.2. Eryptosis Evaluation
2.3. Oxidative Stress Detection
2.3.1. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Detection
2.3.2. Copper/Zinc Superoxide Dismutase (Cu/ZnSOD) ELISA Detection
2.4. Inflammation Evaluation: IL-6 Detection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
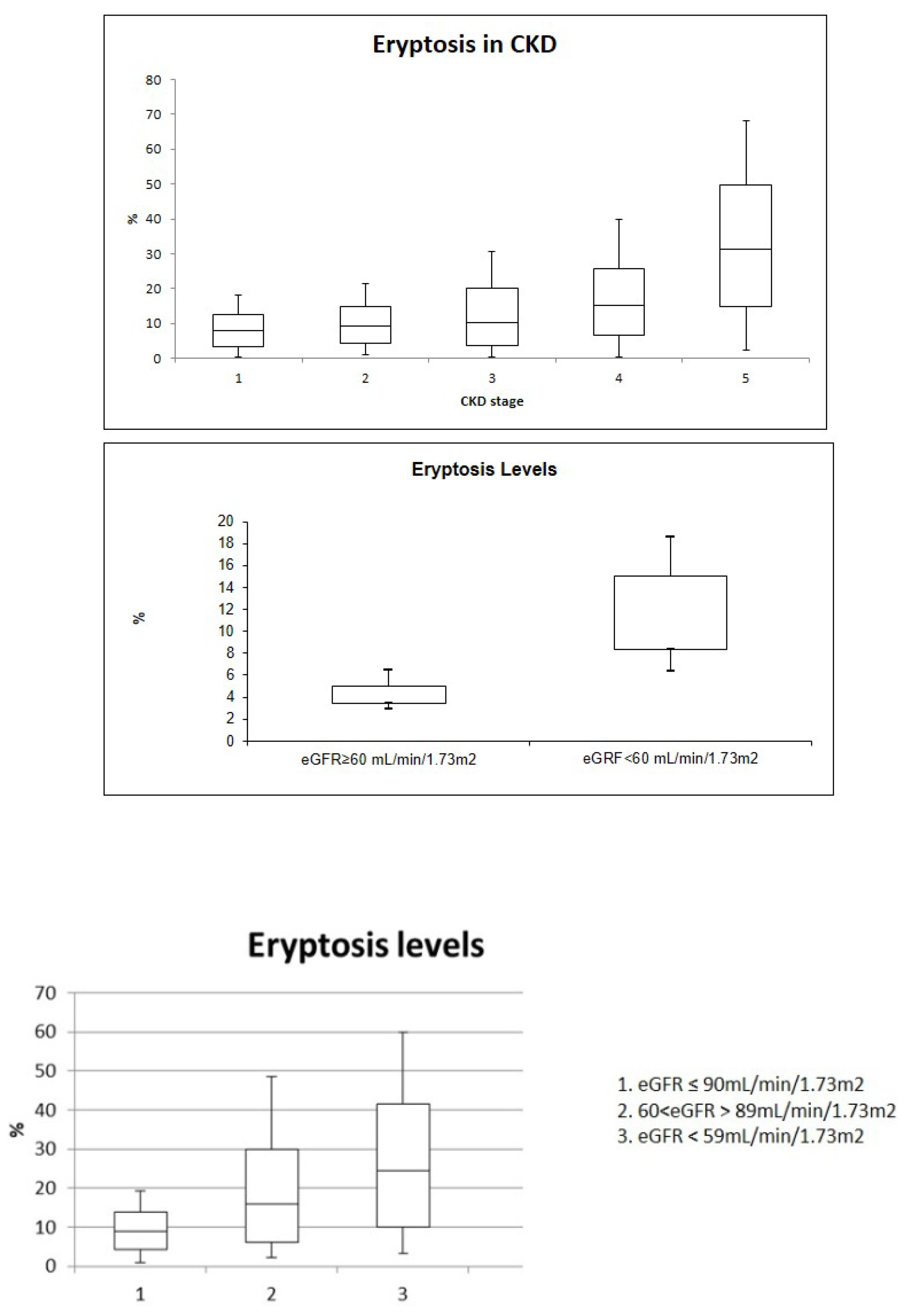
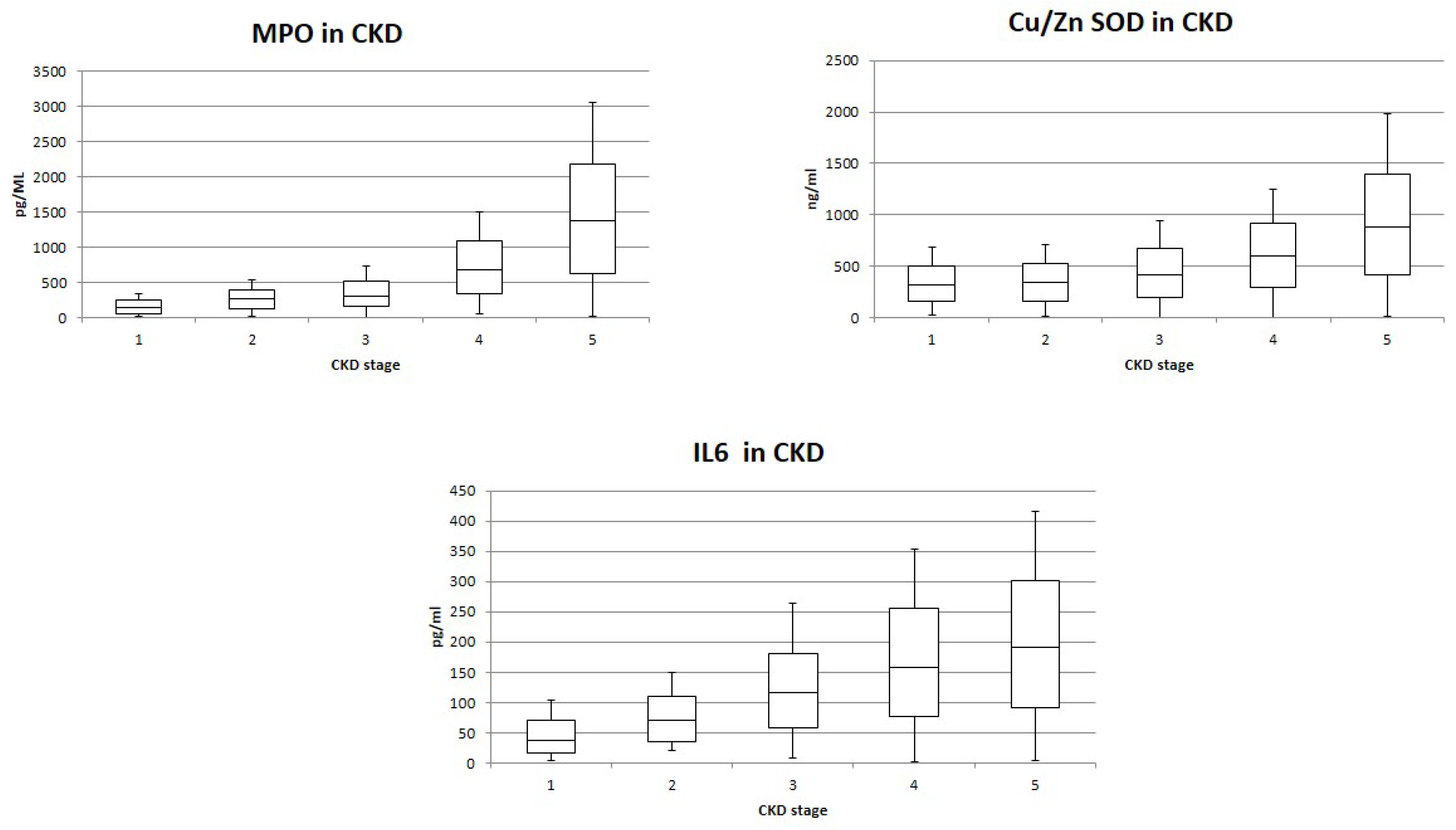
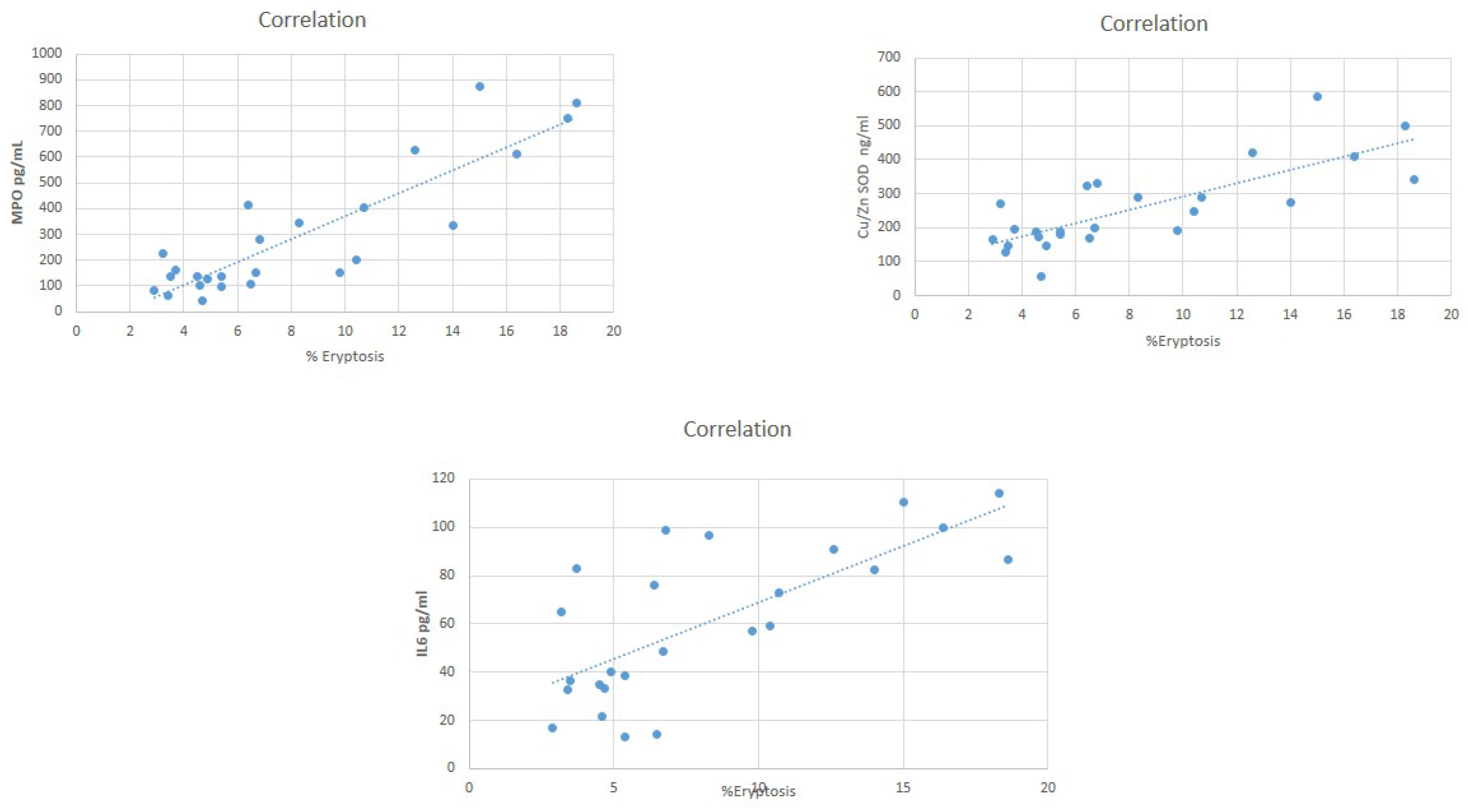
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, F.; Quadri, S.M. Mechanisms and significance of eryptosis, the suicidal death of erythrocytes. Blood Purif. 2012, 33, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.; Huber, S.M.; Szabo, I.; Gulbins, E. Plasma membrane ion channels in suicidal cell death. Arch. Biochem. Biophysl. 2007, 462, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Föller, M.; Lang, F. Ion Transport in Eryptosis, the Suicidal Death ofErythrocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Lang, E.; Fller, M. Physiology and pathophysiology of eryptosis. Trans. Med. Hemotherapy 2012, 39, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, M.; Sirolli, V.; Reale, M.; Arduini, A. Involvement of phosphatidylserine exposure in the recognition and phagocytosis of uremic erythrocytes. Am. J. Kid. Dis. 2001, 37, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, N.B.; Steiner, T.M.; Kuntsevich, V.; Virzì, G.M.; Azevedo, M.; Nakao, L.S.; Barreto, F.C.; Ronco, C.; Thijssen, A.; Kotanko, P.; et al. Uremic toxicity-induced eryptosis and monocyte modulation: The erythrophagocytosis as a novel pathway to renal anemia. Blood Purif. 2016, 41, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomini, M.; Sirolli, V.; Settefrati, N.; Dottori, S.; Di Liberato, L.; Arduini, A. Increased erythrocyte phosphatidylserine exposure in chronic renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Abed, M.; Voelkl, J.; Lang, F. Triggering of suicidal erythrocyte death by uremic toxin indoxyl sulphate. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Langer, H.; Abed, M.; Voelkl, J.; Lang, F. The uremic toxin acrolein promotes suicidal erythrocyte death. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 37, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ji, S.; Dong, W.; Qi, Y.; Song, W.; Cui, D.; Shi, J. Indolic uremic solutes enhance procoagulant activity of red blood cells through phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticle release. Toxins 2015, 7, 4390–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Yin, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Guo, M.; Wang, X. What Should Be Responsible for Eryptosis in Chronic Kidney Disease? Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2022, 47, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gok, M.G.; Paydas, S.; Boral, B.; Onan, E.; Kaya, B. Evaluation of eryptosis inpatients with chronic kidney disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Milan Manani, S.; Clementi, A.; Castegnaro, S.; Brocca, A.; Riello, C.; de Cal, M.; Giuliani, A.; Battaglia, G.G.; Crepaldi, C.; et al. Eryptosis Is Altered in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Blood Purif. 2019, 48, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabe, J.E.; Echegoyen, L.A.; Pastrana, B.; Martinez-Maldonado, M. Mechanism of inhibition of glycolysis by vanadate. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9555–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Mattiotti, M.; Clementi, A.; Milan Manani, S.; Battaglia, G.G.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. In Vitro Induction of Eryptosis by Uremic Toxins and Inflammation Mediators in Healthy Red Blood Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terawaki, H.; Yoshimura, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Matsuyama, Y.; Negawa, T.; Yamada, K.; Matsushima, M.; Nakayama, M.; Hosoya, T.; Era, S. Oxidative stress is enhanced in correlation with renal dysfunction: Examination with the redox state of albumin. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Canaud, B.; Eckardt, K.U.; Stenvinkel, P.; Wanner, C.; Zoccali, C. Oxidative stress in end-stage renal disease: An emerging threat to patient outcome. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2003, 18, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodosek, H.; Bevc, S.; Ekart, R.; Hojs, R. Oxidative stress markers in chronic kidney disease with emphasis on diabetic nephropathy. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Salinas, J.V.; Muñoz-Reyes, E.G.; Guerrero-Romero, J.F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Bracho-Riquelme, R.L.; Carrera-Gracia, M.A.; Quintanar-Escorza, M.A. Eryptosis and oxidative damage in type 2 diabetic mellitus patients with chronic kidney disease. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011, 357, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekki, K.; Taleb, W.; Bouzidi, N.; Kaddous, A.; Bouchenak, M. Effect of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis on redox status in chronic renal failure patients: A comparative study. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozoni, S.S.; Dias, G.F.; Bohnen, G.; Grobe, N.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Kotanko, P.; Moreno-Amaral, A.N. Uremia and Hypoxia Independently Induce Eryptosis and Erythrocyte Redox Imbalance. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sudnitsyna, J.; Skverchinskaya, E.; Dobrylko, I.; Nikitina, E.; Gambaryan, S.; Mindukshev, I. Microvesicle Formation Induced by Oxidative Stress in Human Erythrocytes. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tbahriti, H.F.; Meknassi, D.; Moussaoui, R.; Messaoudi, A.; Zemour, L.; Kaddous, A.; Bouchenak, M.; Mekki, K. Inflammatory status in chronic renal failure: The role of homocysteinemia and pro-inflammatory cytokines. World J. Nephrol. 2013, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Male/Female | 14 M/11 F |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 57 ± 17 |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 7/25 |
| Hypertension | 8/25 |
| Nephroangiosclerosis | 3/25 |
| Polycystic kidney disease | 2/25 |
| Other causes | 3/25 |
| Unknown causes | 2/25 |
| Chronic Kidney Disease Stages | eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | Hb, g/dL | Hct, % | Fe, µg/dL | Ferritin, ng/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 95 ± 5 | 12.2 ± 0.9 | 37.8± 0.8 | 75 ± 7 | 152 ± 10 |
| G2 | 74 ±8 | 11.7 ± 1.4 | 37.2 ± 1.0 | 71 ± 8 | 133 ± 12 |
| G3 | 50 ± 6 | 11.4 ± 1.5 | 35.6 ± 1.3 | 64 ± 12 | 119 ± 15 |
| G4 | 24 ± 4 | 11.1 ± 1.4 | 35.1 ± 1.1 | 40 ± 7 | 122 ± 12 |
| G5 | 13 ± 2 | 10.4 ± 1.8 | 33.8 ± 2.0 | 34 ± 6 | 116 ± 17 |
| Correlation Values | |
|---|---|
| Eryptosis/eGFR | −0.76 |
| Eryptosis/Hb | −0.49 |
| Eryptosis/Hct | −0.64 |
| Eryptosis/Fe | −0.75 |
| Eryptosis/ferritin | −0.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clementi, A.; Virzì, G.M.; Milan Manani, S.; Battaglia, G.G.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. Eryptosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Possible Relationship with Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237167
Clementi A, Virzì GM, Milan Manani S, Battaglia GG, Ronco C, Zanella M. Eryptosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Possible Relationship with Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237167
Chicago/Turabian StyleClementi, Anna, Grazia Maria Virzì, Sabrina Milan Manani, Giovanni Giorgio Battaglia, Claudio Ronco, and Monica Zanella. 2022. "Eryptosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Possible Relationship with Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237167
APA StyleClementi, A., Virzì, G. M., Milan Manani, S., Battaglia, G. G., Ronco, C., & Zanella, M. (2022). Eryptosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Possible Relationship with Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7167. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237167







