Applicability of Actigraphy for Assessing Sleep Behaviour in Children with Palliative Care Needs Benchmarked against the Gold Standard Polysomnography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Actigraphy
2.3. Polysomnography (PSG)
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
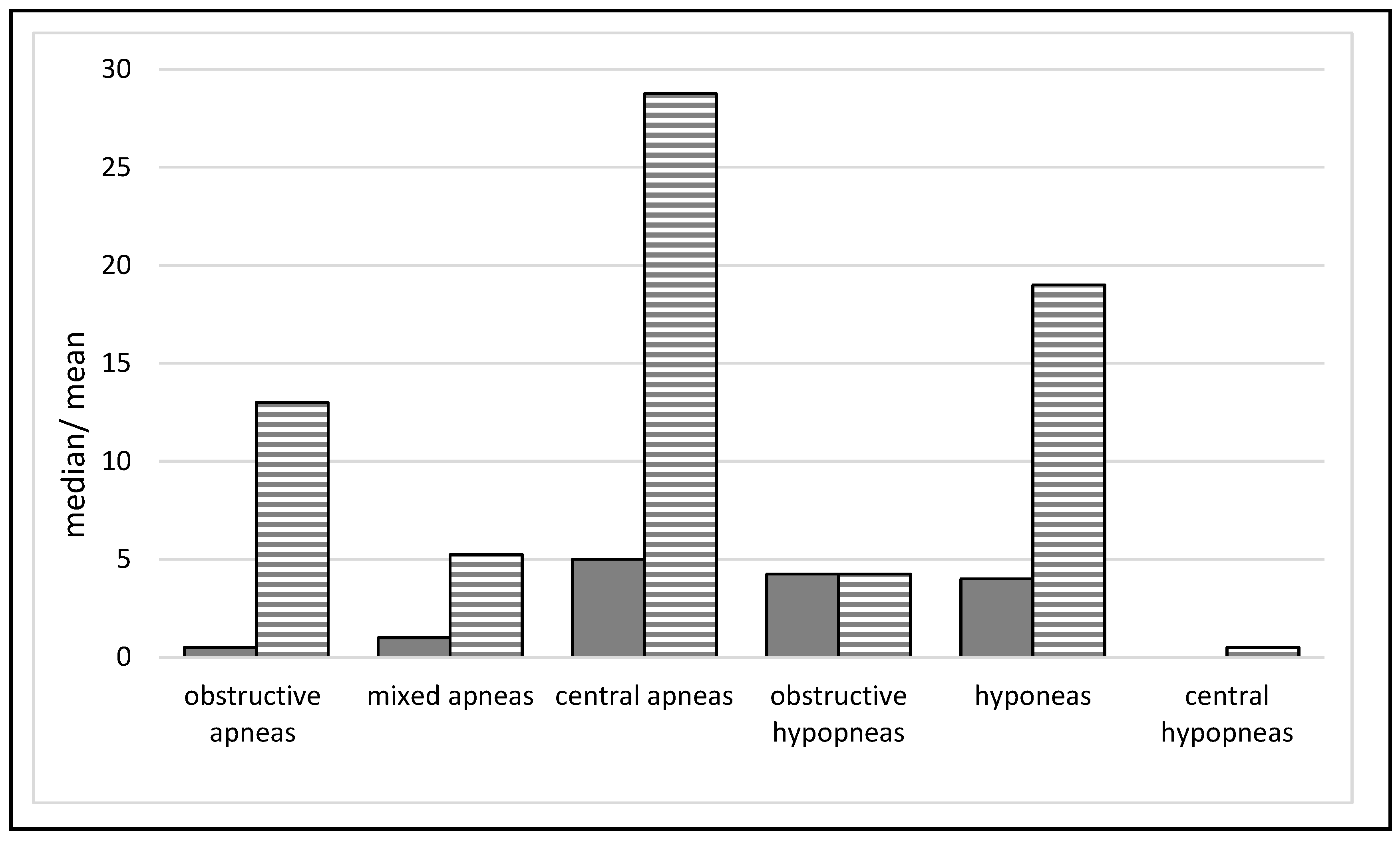
3.1. Polysomnography (PSG)
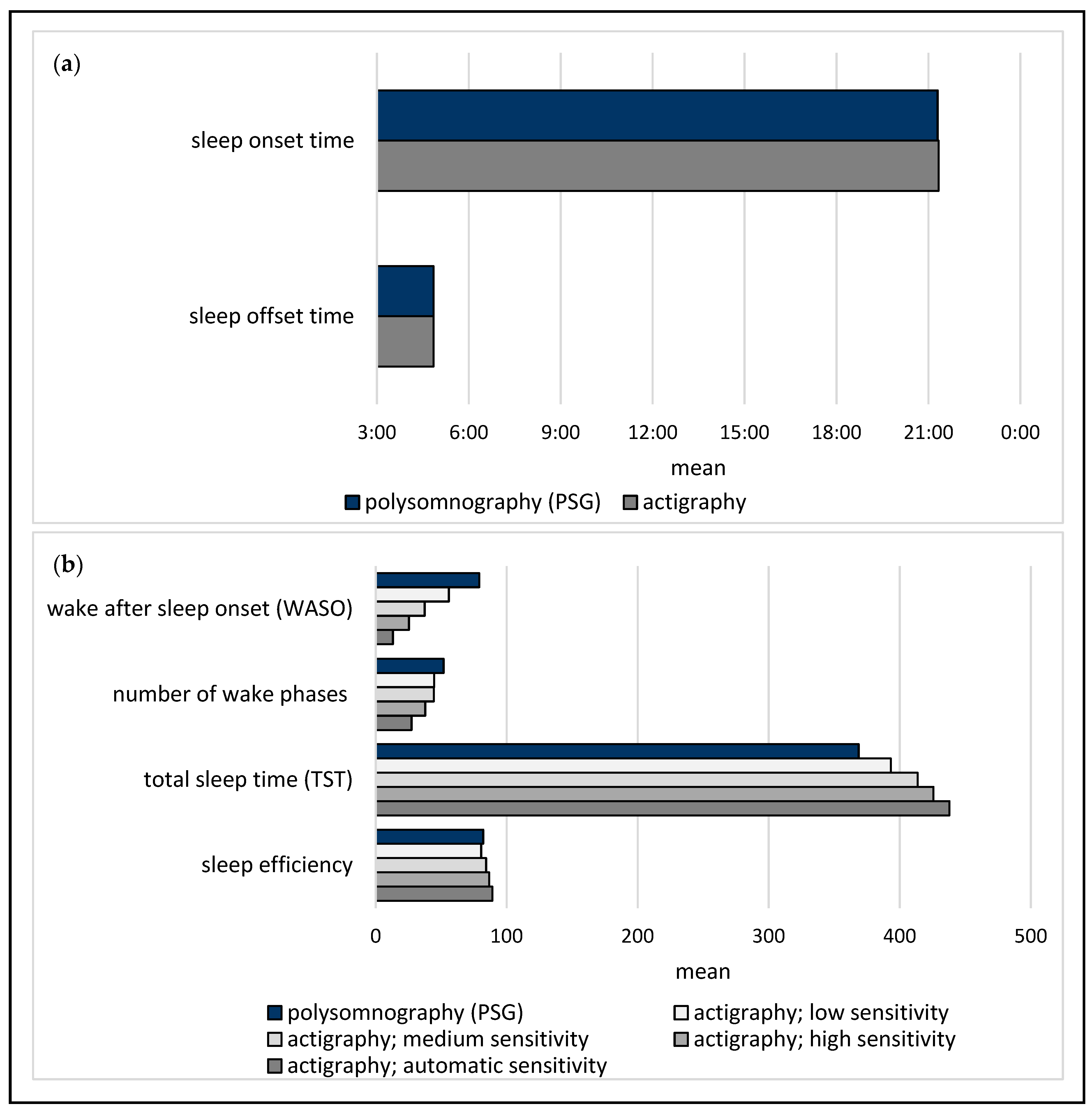
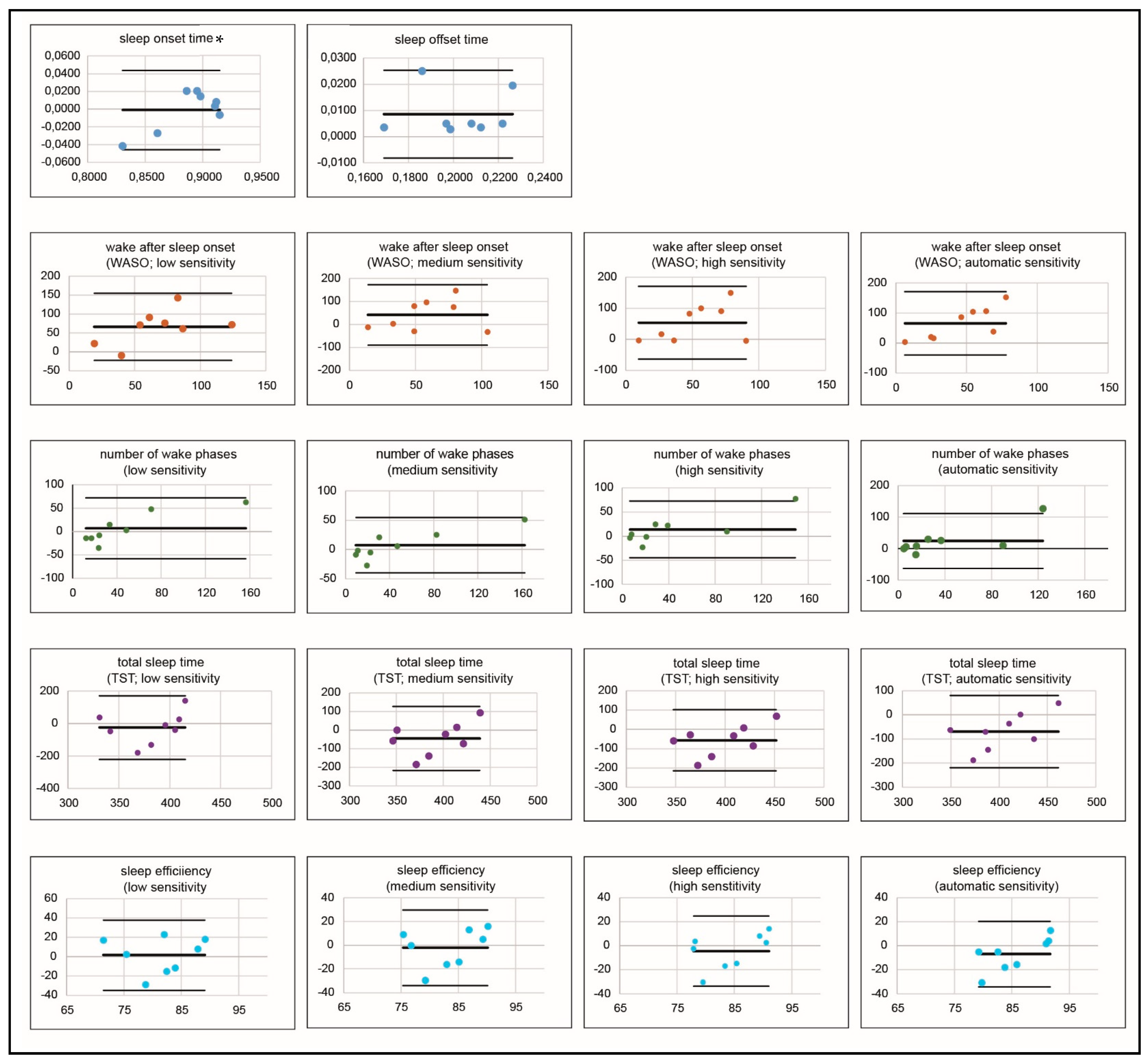
3.2. Polysomnography (PSG) Compared to Actigraphy
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoell, J.I.; Weber, H.; Warfsmann, J.; Trocan, L.; Gagnon, G.; Danneberg, M.; Balzer, S.; Keller, T.; Janßen, G.; Kuhlen, M. Facing the large variety of life-limiting conditions in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwantes, S.; O’Brien, H.W. Pediatric palliative care for children with complex chronic medical conditions. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 61, 797–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, R.; Siden, H.; Cadell, S.; Davies, B.; Andrews, G.; Feichtinger, L.; Singh, M. Charting the territory: Symptoms and functional assessment in children with progressive, non-curable conditions. Arch. Dis. Child 2014, 99, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feudtner, C.; Nye, R.; Hill, D.L.; Hall, M.; Hinds, P.; Johnston, E.E.; Friebert, S.; Hays, R.; Kang, T.I.; Wolfe, J. Polysymptomatology in pediatric patients receiving palliative care based on parent-reported data. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2119730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benini, F.; Bellentani, M.; Reali, L.; Lazzarin, P.; Zen, L.d.; Pellegatta, F.; Aprile, P.L.; Scaccabarozzi, G. An estimation of the number of children requiring pediatric palliative care in italy. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, L.K.; Bluebond-Langner, M.; Ling, J. Advances and challenges in european paediatric palliative care. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verberne, L.M.; Fahner, J.C.; Sondaal, S.F.V.; Schouten-van Meeteren, A.Y.N.; Kruiff, C.C.d.; van Delden, J.J.M.; Kars, M.C. Anticipating the future of the child and family in pediatric palliative care: A qualitative study into the perspectives of parents and healthcare professionals. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 180, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, C. National Policy: Palliative Care for Children with Life-Limiting Conditions in Ireland; DoH: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, F.; Abu-Saad Huijer, H.; Benini, F.; Kuttner, L.; Wood, C.; Feraris, P.C.; Zernikow, B. Impacct: Standards of paediatric palliative care. Schmerz 2008, 22, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Brenner, M.; Hauer, J.; Molloy, E.; McDonald, D. Severe neurological impairment: A delphi consensus-based definition. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 29, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauer, J.M.; Wolfe, J. Supportive and palliative care of children with metabolic and neurological diseases. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2014, 8, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.Y.; Lee, W.T.; Lee, C.C.; Jeng, S.F.; Weng, W.C. Agreement between actigraphy and diary-recorded measures of sleep in children with epilepsy. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2018, 50, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard-Tremblay, E.; Constantin, E.; Gruber, R.; Brouillette, R.T.; Shevell, M. Sleep in children with cerebral palsy: A review. J. Child Neurol. 2011, 26, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleyias, J.; Manley, P.; Kothare, S.V. Sleep disorders in children with cancer. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 19, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stores, G. Children’s sleep disorders: Modern approaches, developmental effects, and children at special risk. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1999, 41, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mindell, J.; Millet, G.C.; Ofer, D.; Beck, S.E.; Mason, T.B.A.; Brooks, L.J.; Traylor, J.; Marcus, C.L. Pediatric polysomnography: The patient and family perspective. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2011, 7, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Spence, D.; Bahammam, A. Polysomnography: An Overview; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Combs, D.; Goodwin, J.L.; Quan, S.F.; Morgan, W.J.; Hsu, C.-H.; Edgin, J.O.; Parthasarathy, S. Mother knows best? Comparing child report and parent report of sleep parameters with polysomnography. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, M.; Whittingham, K.; Edwards, P.; Boyd, R.N. Psychometric properties of parent and child reported sleep assessment tools in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, J.E.; Freeman, R.D. Melatonin therapy for circadian rhythm sleep disorders in children with multiple disabilities: What have we learned in the last decade? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2004, 46, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.T.; McCrae, C.S.; Cheung, J.; Martin, J.L.; Harrod, C.G.; Heald, J.L.; Carden, K.A. Use of actigraphy for the evaluation of sleep disorders and circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders: An american academy of sleep medicine clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, J.G.; Becker-Carus, C.; Büttner-Teleaga, A.; Cassel, W.; Danker-Hopfe, H.; Dück, A.; Frohn, C.; Hein, H.; Penzel, T.; Rodenbeck, A.; et al. The role of actigraphy in sleep medicine. Somnologie 2021, 25, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbensen, A.J.; Hoffman, E.K.; Stansberry, E.; Shaffer, R. Convergent validity of actigraphy with polysomnography and parent reports when measuring sleep in children with down syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2018, 62, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, L.J.; Hiruma, L.S.; Avis, K.; Montgomery-Downs, H.; Valentin, J. Comparison of a commercial accelerometer with polysomnography and actigraphy in children and adolescents. Sleep 2015, 38, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz-Kodat, E.; Reynaud, E.; Geoffray, M.-M.; Limousin, N.; Franco, P.; Bourgin, P.; Schroder, C.M. Validity of actigraphy compared to polysomnography for sleep assessment in children with autism spectrum disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.E.; Bichell, T.J.; Surdyka, K.; Malow, B.A. Sleep in children and adolescents with angelman syndrome: Association with parent sleep and stress. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2012, 56, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkart, S.; Beets Michael, W.; Armstrong, B.; Hunt Ethan, T.; Dugger, R.; von Klinggraeff, L.; Jones, A.; Brown David, E.; Weaver, R.G. Comparison of multichannel and single-channel wrist-based devices with polysomnography to measure sleep in children and adolescents. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Licis, A.; Boyd, J.; Hoyt, C.R.; Ju, Y.-E.S. Validation of actigraphy for sleep measurement in children with cerebral palsy. Sleep Med. 2022, 90, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaka, Y.; Sadeh, A.; Bradbury, L.; Massicotte, C.; Zak, M.; Go, C.; Shorer, Z.; Weiss, S.K. Validation of actigraphy with continuous video-electroencephalography in children with epilepsy. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niel, K.; LaRosa, K.N.; Klages, K.L.; Merchant, T.E.; Wise, M.S.; Witcraft, S.M.; Hancock, D.; Caples, M.; Mandrell, B.N.; Crabtree, V.M. Actigraphy versus polysomnography to measure sleep in youth treated for craniopharyngioma. Behav. Sleep Med. 2019, 18, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueck, A.; Reis, O.; Bastian, M.; van Treeck, L.; Weirich, S.; Haessler, F.; Fiedler, A.; Koelch, M.; Berger, C. Feasibility of a complex setting for assessing sleep and circadian rhythmicity in a fragile x cohort. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, S.; Bruni, O.; Aricò, D.; Elia, M.; Ferri, R. Polysomnographic assessment of sleep disturbances in children with developmental disabilities and seizures. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 31, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, D.W.; Farabi, S.S. Physiology of sleep. Diabetes Spectr. 2016, 29, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tétreault, É.; Bélanger, M.-È.; Bernier, A.; Carrier, J. Actigraphy data in pediatric research: The role of sleep diaries. Sleep Med. 2018, 47, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.E.; Harding, S.M.; Marcus, C.; Vaughn, B.V. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, Version 2.2; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2012; Volume 176, p. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding bland altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maganti, R.; Sheth, R.D.; Hermann, B.P.; Weber, S.; Gidal, B.E.; Fine, J. Sleep architecture in children with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, S.; Bruni, O.; Leuzzi, V.; Elia, M.; Verrillo, E.; Ferri, R. Sleep polygraphy in angelman syndrome. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrillo, E.; Bruni, O.; Franco, P.; Ferri, R.; Thiriez, G.; Pavone, M.; Petrone, A.; Paglietti, M.G.; Crinò, A.; Cutrera, R. Analysis of nrem sleep in children with prader–willi syndrome and the effect of growth hormone treatment. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, C.; Forbat, L.; Anderson, G.; Gibson, F.; Hain, R. Challenging symptom profiles of life-limiting conditions in children: A survey of care professionals and families. Palliat. Med. 2011, 25, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siden, H.; Steele, R. Charting the territory: Children and families living with progressive life-threatening conditions. Paediatr. Child Health 2015, 20, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pawliuk, C.; Widger, K.; Dewan, T.; Brander, G.; Brown, H.L.; Hermansen, A.-M.; Gregoire, M.-C.; Steele, R.; Siden, H.H. Scoping review of symptoms in children with rare, progressive, life-threatening disorders. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2019, 10, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sateia, M.J. International classification of sleep disorders. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, D.M.; Mitchell, J.J. Pathophysiology, evaluation, and management of sleep disorders in the mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122s, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinard, J.M.; Azabou, E.; Essid, N.; Quijano-Roy, S.; Haddad, S.; Cheliout-Heraut, F. Sleep-disordered breathing in children with congenital muscular dystrophies. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraleda-Cibrian, M.; Edwards, S.P.; Kasten, S.J.; Buchman, S.R.; Berger, M.; O’Brien, L.M. Obstructive sleep apnea pretreatment and posttreatment in symptomatic children with congenital craniofacial malformations. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.A.; Fennell, E.B.; Carney, P.R. Daytime behavior and sleep disturbance in childhood epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2004, 5, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namisango, E.; Bristowe, K.; Allsop, M.J.; Murtagh, F.E.M.; Abas, M.; Higginson, I.J.; Downing, J.; Harding, R. Symptoms and concerns among children and young people with life-limiting and life-threatening conditions: A systematic review highlighting meaningful health outcomes. Patient 2019, 12, 15–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tietze, A.L.; Zernikow, B.; Michel, E.; Blankenburg, M. Sleep disturbances in children, adolescents, and young adults with severe psychomotor impairment: Impact on parental quality of life and sleep. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licheni, S.H.; McMahon, J.M.; Schneider, A.L.; Davey, M.J.; Scheffer, I.E. Sleep problems in dravet syndrome: A modifiable comorbidity. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knupp, K.G.; Scarbro, S.; Wilkening, G.; Juarez-Colunga, E.; Kempe, A.; Dempsey, A. Parental perception of comorbidities in children with dravet syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 76, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.M.; Graef, D.M.; Ehrentraut, J.H.; Tynes, B.L.; Crabtree, V.M. Sleep and pain in pediatric illness: A conceptual review. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.M.; Ryther, R.C.; Jennesson, M.; Geffrey, A.L.; Bruno, P.L.; Anagnos, C.J.; Shoeb, A.H.; Thibert, R.L.; Thiele, E.A. Impact of pediatric epilepsy on sleep patterns and behaviors in children and parents. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.M.; Szymusiak, R. Neurobiology of arousal and sleep: Updates and insights into neurological disorders. Curr. Sleep Med. Rep. 2015, 1, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, L.A.; Wager, J.; Blankenburg, M.; Zernikow, B. The unfavorable alliance of pain and poor sleep in children with life-limiting conditions and severe psychomotor impairment. Children 2018, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, D. Environmental noise and sleep disturbances: A threat to health? Sleep Sci. 2014, 7, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, L.A.; Zernikow, B.; Stening, K.; Wager, J. Insights into the frequency and distinguishing features of sleep disorders in pediatric palliative care incorporating a systematic sleep protocol. Children 2021, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.A.; Gregoire, M.C. Challenging neurological symptoms in paediatric palliative care: An approach to symptom evaluation and management in children with neurological impairment. Paediatr. Child Health 2015, 20, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, J.F.; Koch, S.A.; Bolden, L.B.; Thompson, M.D. Neuropsychological consequences of sleep disturbance in children with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 57, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toon, E.; Davey, M.J.; Hollis, S.L.; Nixon, G.M.; Horne, R.S.; Biggs, S.N. Comparison of commercial wrist-based and smartphone accelerometers, actigraphy, and psg in a clinical cohort of children and adolescents. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.-J.; Zhong, W.-H.; Liu, Y.-X.; Miao, H.-Z.; Li, Y.-C.; Ji, M.-H. Sample size for assessing agreement between two methods of measurement by Bland-Altman method. Int. J. Biostat. 2016, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medcalc, Version 2.121; Software Ltd.: Ostend, Belgium, 2022.
| Underlying Disease | Grouped (ICD-10 Code) | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Epileptic encephalopathy | disorder of the brain, unspecified (Q93.9) | 1 (12.5) |
| Cerebral leukodystrophy | metabolic disorders (E70–E90) | 1 (12.5) |
| Superior multisystem disease with foreground involvement of the central nervous system | congenital malformation of the brain, unspecified (Q04.9) | 2 (25) |
| Joubert syndrome | ||
| Arnold Chiari malformation type 2 | other specified disorders of the brain (Q93.8) | 1 (12.5) |
| congenital malformation of the brain, unspecified (Q04.9) | 1 (12.5) | |
| Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy | other disturbances of the cerebral status of newborns (P91) | 1 (12.5) |
| Trisomy 18 | other specified congenital malformation syndromes affecting multiple systems (Q87) | 1 (12.5) |
| Duchenne muscular dystrophy | primary disorders of muscles (G71) | 1 (12.5) |
| care level 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 (0) | |
| 2 | 1 (12.5) | |
| 3 | 2 (25) | |
| 4 | 1 (12.5) | |
| 5 | 4 (50) | |
| born preterm | ||
| Yes | 3 (37.5) | |
| No | 5 (62.5) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubek, L.A.; Kutz, P.; Roll, C.; Zernikow, B.; Wager, J. Applicability of Actigraphy for Assessing Sleep Behaviour in Children with Palliative Care Needs Benchmarked against the Gold Standard Polysomnography. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237107
Kubek LA, Kutz P, Roll C, Zernikow B, Wager J. Applicability of Actigraphy for Assessing Sleep Behaviour in Children with Palliative Care Needs Benchmarked against the Gold Standard Polysomnography. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237107
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubek, Larissa Alice, Patrizia Kutz, Claudia Roll, Boris Zernikow, and Julia Wager. 2022. "Applicability of Actigraphy for Assessing Sleep Behaviour in Children with Palliative Care Needs Benchmarked against the Gold Standard Polysomnography" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237107
APA StyleKubek, L. A., Kutz, P., Roll, C., Zernikow, B., & Wager, J. (2022). Applicability of Actigraphy for Assessing Sleep Behaviour in Children with Palliative Care Needs Benchmarked against the Gold Standard Polysomnography. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237107





