Comparison of COVID-19 and RSV Infection Courses in Infants and Children under 36 Months Hospitalized in Paediatric Department in Fall and Winter Season 2021/2022
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Group Characteristics and Baseline Clinical Features
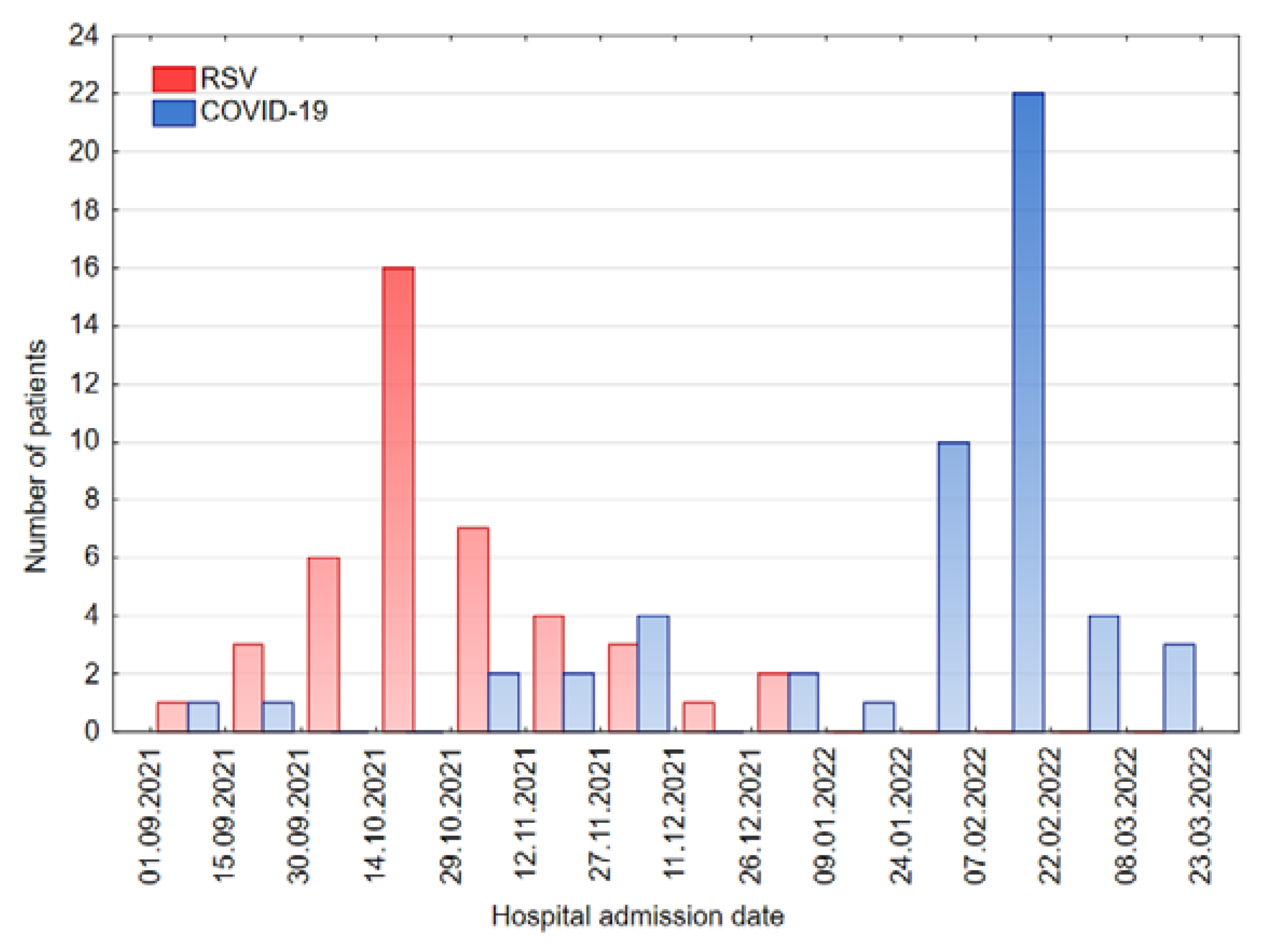
3.2. Hospital Admission in the Present and Previous Seasons
3.3. Frequency of Symptoms Presented by Patients with COVID-19 and RSV Infection during the Whole Hospital Stay
3.4. Laboratory Findings
3.5. Methods of Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Child Mortality and COVID-19. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-survival/covid-19/ (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Arora, A. COVID-19 Confirmed Cases and Deaths. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/resources/covid-19-confirmed-cases-and-deaths-dashboard/ (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- Ludvigsson, J.F. Systematic Review of COVID-19 in Children Shows Milder Cases and a Better Prognosis than Adults. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebach, M.K.; Piedimonte, G.; Ley, S.H. COVID-19 in Childhood: Transmission, Clinical Presentation, Complications and Risk Factors. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, L.; Van Paemel, R.; Haerynck, F. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Related to COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2019–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, R.T.; Bont, L.J.; Zar, H.; Polack, F.P.; Park, C.; Claxton, A.; Borok, G.; Butylkova, Y.; Wegzyn, C. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospitalization and Mortality: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Disease Burden Estimates of Acute Lower Respiratory Infections Due to Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Young Children in 2015: A Systematic Review and Modelling Study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan Ozdemir, S.; Soysal, B.; Calkavur, S.; Gökmen Yıldırım, T.; Kıymet, E.; Kalkanlı, O.; Çolak, R.; Devrim, İ. Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection More Dangerous than COVID 19 in the Neonatal Period? J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 4398–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Ruebsteck, E.; Eifinger, F.; Klein, F.; Oberthuer, A.; van Koningsbruggen-Rietschel, S.; Huenseler, C.; Weber, L.T. Morbidity of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infections: RSV Compared with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infections in Children Aged 0–4 Years in Cologne, Germany. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, jiac052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobak, E.; Machura, E.; Wrzask, M.; Krakowczyk, H.; Mielczarek, M. RSV infection course in infants and young children during hospitalization. Przegl. Lek. 2011, 68, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Coma, E.; Vila, J.; Méndez-Boo, L.; Antón, A.; Mora, N.; Fina, F.; Fàbregas, M.; Medina, M. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections in Young Children Presenting to Primary Care in Catalonia during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Pediatric. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, M.; Tsuzuki, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Iwamoto, N. Resurgence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic, Tokyo, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2969–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, P.; Sagoschen, I.; Weise, K.; Plachter, B.; Münzel, T.; Gori, T.; Vosseler, M. Influenza and RSV Incidence during COVID-19 Pandemic-an Observational Study from in-Hospital Point-of-Care Testing. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 210, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.J. Changes in Influenza and Other Respiratory Virus Activity during the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, 2020–2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, K.J.; Whitaker, M.; Agathis, N.T.; Anglin, O.; Milucky, J.; Patel, K.; Pham, H.; Kirley, P.D.; Kawasaki, B.; Meek, J.; et al. Hospitalization of Infants and Children Aged 0–4 Years with Laboratory-Confirmed COVID-19—COVID-NET, 14 States, March 2020–February 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, S.; Brendish, N.J.; Clark, T.W. SARS-CoV-2 Has Displaced Other Seasonal Respiratory Viruses: Results from a Prospective Cohort Study. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, P.A. SARS-CoV-2 and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Coinfection in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, e164–e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, L.; Gheiasi, S.F.; Taher, M.; Basirinezhad, M.H.; Shaikh, Z.A.; Dehghan Nayeri, N. Clinical Features of COVID-19 in Newborns, Infants, and Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Compr. Child Adolesc. Nurs. 2022, 45, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.E.; Asfour, A.; Sewell, T.B.; Hooe, B.; Pryce, P.; Earley, C.; Shen, M.Y.; Kerner-Rossi, M.; Thakur, K.T.; Vargas, W.S.; et al. Neurological Issues in Children with COVID-19. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 743, 135567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafstrom, C.E. Neurological Effects of COVID-19 in Infants and Children. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozan, L.; Shusterman, E.; Ablin, J.; Mitelpunkt, A.; Weiss-Meilik, A.; Adler, A.; Choshen, G.; Kehat, O. Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in COVID-19 Compared with Influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19—Guidance for Management of Children Admitted to Hospital and for Treatment of Non-Hospitalised Children at Risk of Severe Disease. Available online: https://www.rcpch.ac.uk/resources/covid-19-management-children-hospital-and-non-hospitalised (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- COVID-19 Rapid Guideline: Managing COVID-19. Available online: https://app.magicapp.org/#/guideline/L4Qb5n/section/EgaGN7 (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Simões, E.A.F.; Bont, L.; Manzoni, P.; Fauroux, B.; Paes, B.; Figueras-Aloy, J.; Checchia, P.A.; Carbonell-Estrany, X. Past, Present and Future Approaches to the Prevention and Treatment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2018, 7, 87–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.K.; Seales, S.; Budzik, C. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis in Children. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 95, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farley, R.; Spurling, G.K.P.; Eriksson, L.; Del Mar, C.B. Antibiotics for Bronchiolitis in Children under Two Years of Age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 10, CD005189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkonen, H.; Waris, M.; Ruohola, A.; Ruuskanen, O.; Heikkinen, T. Recurrent Wheezing after Respiratory Syncytial Virus or Non-Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis in Infancy: A 3-Year Follow-Up. Allergy 2009, 64, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jartti, T.; Bønnelykke, K.; Elenius, V.; Feleszko, W. Role of Viruses in Asthma. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanov, I.M.; Spiridonova, E.; Bobkova, P.; Gamirova, A.; Shikhaleva, A.; Andreeva, M.; Blyuss, O.; El-Taravi, Y.; DunnGalvin, A.; Comberiati, P.; et al. Risk Factors for Post-COVID-19 Condition in Previously Hospitalised Children Using the ISARIC Global Follow-up Protocol: A Prospective Cohort Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, J.A.; Burns, J.P. Epidemiology of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Step Closer to Understanding Who, Where, and When. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Tenforde, M.W.; Friedman, K.G.; Newhams, M.; Rose, E.B.; Dapul, H.; Soma, V.L.; Maddux, A.B.; Mourani, P.M.; Bowens, C.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of US Children and Adolescents with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Compared with Severe Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2021, 325, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Baseline Clinical Features | COVID-19 | RSV Infection | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| cough | 20 38.50% | 40 93.20% | 0.000 |
| rhinitis | 11 21.15% | 31 72.09% | 0.000 |
| fever | 40 76.92% | 16 37.21% | 0.003 |
| dyspnea | 10 19.23% | 33 76.74% | 0.000 |
| weakness | 15 28.85% | 13 30.23% | 0.882 |
| lack of appetite | 23 44.23% | 18 41.86% | 0.816 |
| vomiting or diarrhea | 12 23.08% | 5 11.63% | 0.552 |
| seizures | 7 13.46% | 0 0.00% | 0.035 |
| auscultatory changes | 11 21.15% | 40 93.02% | 0.000 |
| wheezes | 2 3.85% | 29 67.44% | 0.000 |
| crackles | 2 3.85% | 28 65.12% | 0.000 |
| rhonchi | 10 19.23% | 18 41.86% | 0.122 |
| stridor | 5 9.62% | 0 0.00% | 0.100 |
| Fall and Winter Season | Number of RSV-Diagnosed Patients |
|---|---|
| 2021/2022 | 43 |
| 2020/2021 | 0 |
| 2019/2020 | 56 |
| 2018/2019 | 35 |
| Treatment Methods | COVID-19 | RSV Infection | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| bronchodilator therapy | 3 5.77% | 38 88.37% | 0.000 |
| inhaled steroid therapy in admission | 8 15.38% | 14 32.56% | 0.083 |
| inhaled steroid therapy in total | 12 23.08% | 26 60.47% | 0.000 |
| systemic steroid therapy | 6 11.54% | 11 25.58% | 0.065 |
| passive oxygen therapy | 4 7.69% | 21 48.84% | 0.000 |
| high flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy | 1 1.92% | 4 9.30% | 0.254 |
| antibiotic therapy in admission | 1 1.92% | 6 13.95% | 0.065 |
| antibiotic therapy in total | 6 11.54% | 19 44.19% | 0.001 |
| supportive care only | 33 63.46% | 1 2.33% | 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fedorczak, A.; Zielińska, N.; Nosek-Wasilewska, P.; Mikołajczyk, K.; Lisiak, J.; Zeman, K.; Tkaczyk, M. Comparison of COVID-19 and RSV Infection Courses in Infants and Children under 36 Months Hospitalized in Paediatric Department in Fall and Winter Season 2021/2022. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237088
Fedorczak A, Zielińska N, Nosek-Wasilewska P, Mikołajczyk K, Lisiak J, Zeman K, Tkaczyk M. Comparison of COVID-19 and RSV Infection Courses in Infants and Children under 36 Months Hospitalized in Paediatric Department in Fall and Winter Season 2021/2022. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237088
Chicago/Turabian StyleFedorczak, Anna, Natalia Zielińska, Paulina Nosek-Wasilewska, Katarzyna Mikołajczyk, Joanna Lisiak, Krzysztof Zeman, and Marcin Tkaczyk. 2022. "Comparison of COVID-19 and RSV Infection Courses in Infants and Children under 36 Months Hospitalized in Paediatric Department in Fall and Winter Season 2021/2022" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237088
APA StyleFedorczak, A., Zielińska, N., Nosek-Wasilewska, P., Mikołajczyk, K., Lisiak, J., Zeman, K., & Tkaczyk, M. (2022). Comparison of COVID-19 and RSV Infection Courses in Infants and Children under 36 Months Hospitalized in Paediatric Department in Fall and Winter Season 2021/2022. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237088








