Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) as Predictors of Short-Term Survival in Patients with Advanced Malignant Biliary Obstruction Treated with Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Study Outcomes
2.4. Ethical Approval
2.5. Procedure
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Statistical Analysis
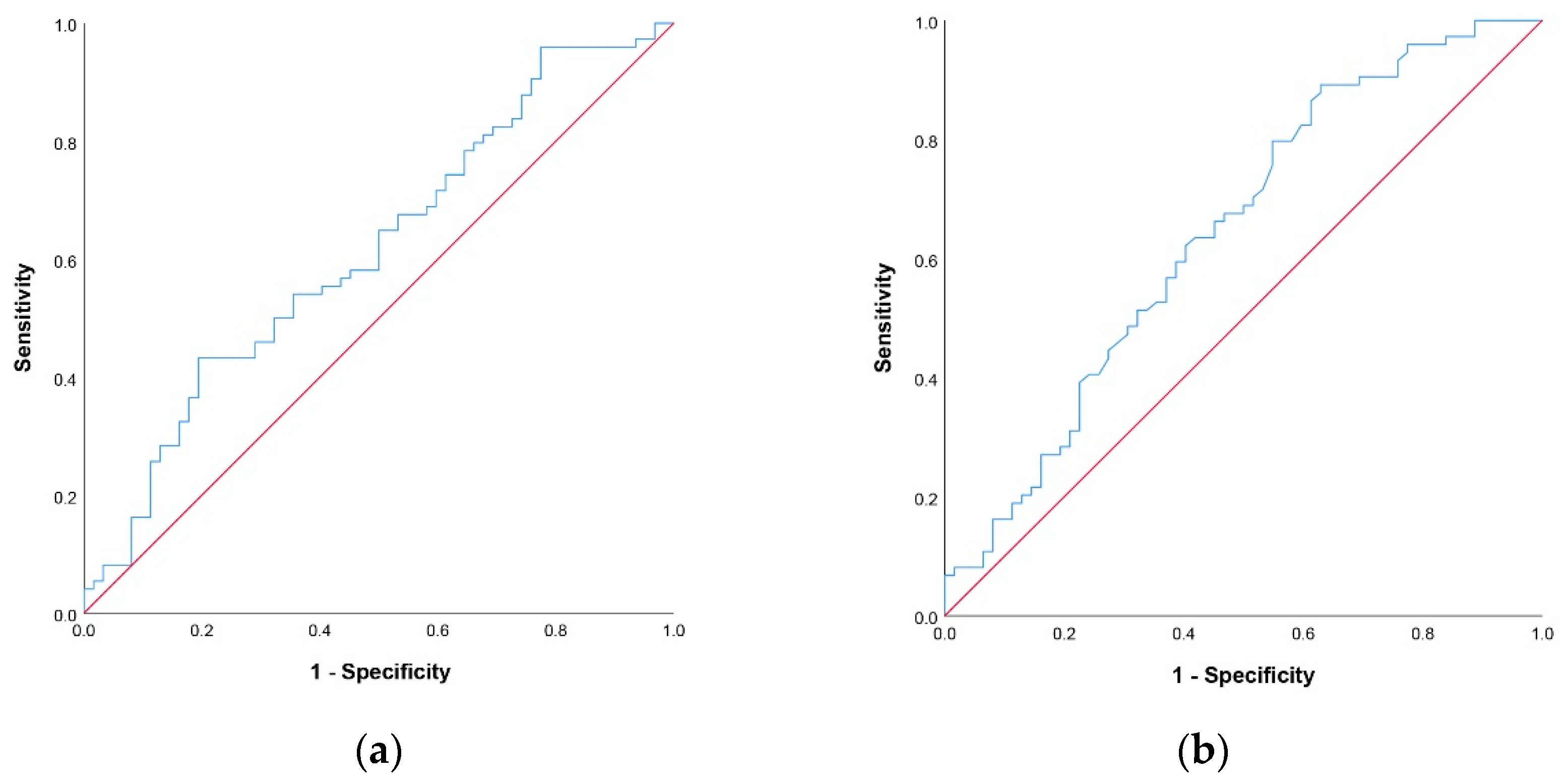
3.2.1. Cut Off-Values for NLR and PNI Scores
3.2.2. Univariate and Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis
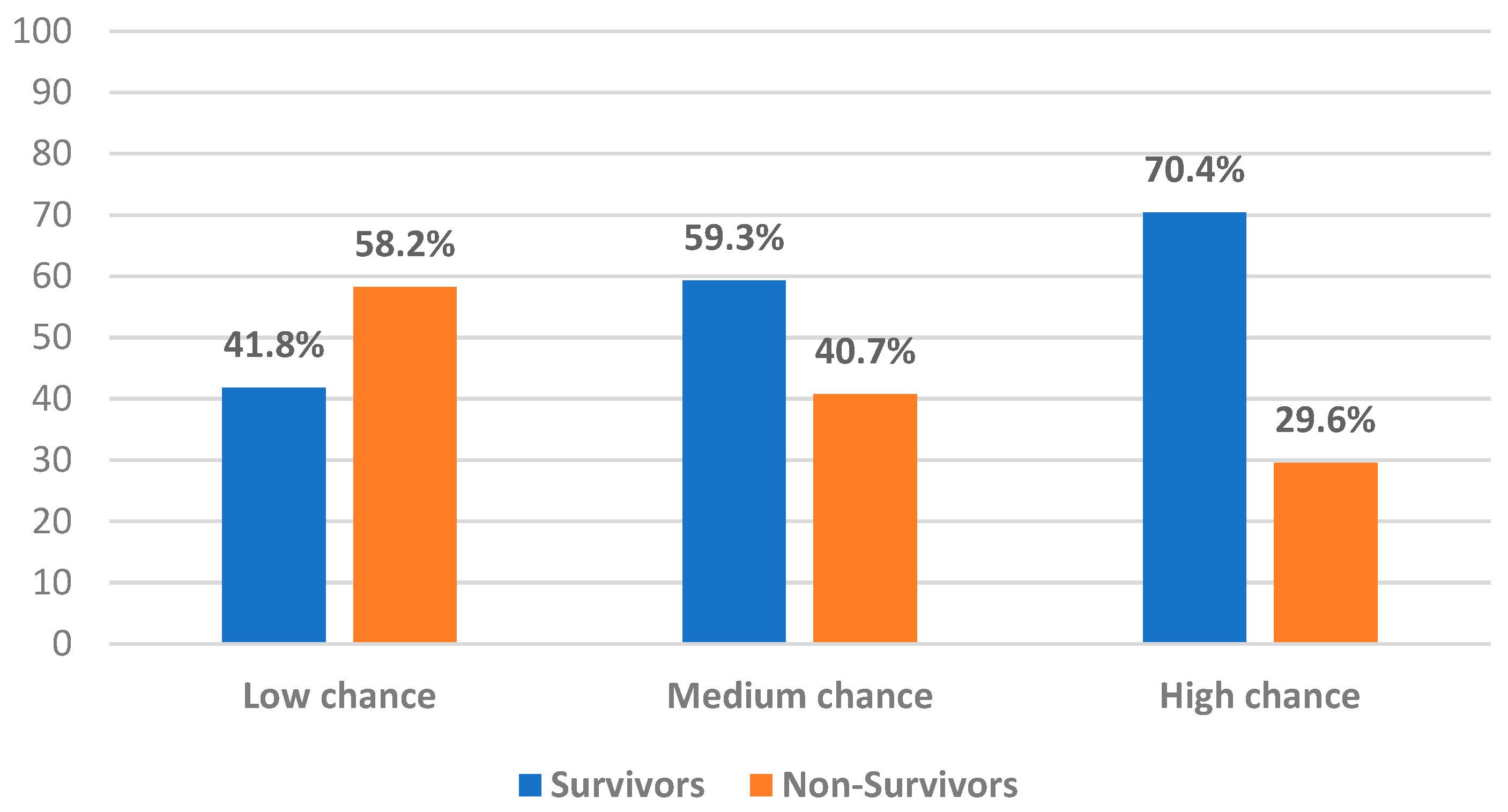
3.3. 60-Day Survival Score
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutter, C.M.; Ryu, R.K. Percutaneous Management of Malignant Biliary Obstruction. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 18, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Delden, O.M.; Laméris, J.S. Percutaneous drainage and stenting for palliation of malignant bile duct obstruction. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 18, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L.Z.C.T.; Singh, R.; Loong, C.K.; de Moura, E.G.H. Malignant Biliary Obstruction: Evidence for Best Practice. Gastroenterol. Res. Pr. 2016, 2016, 3296801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; van der Leij, C.; Katoh, M.; Benten, D.; Hendriks, B.M.F.; Hatzidakis, A. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography, Biliary Drainage and Stenting. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.A.F.; Rosendo, E.; Sousa, L.; Lopes, A.R.; Leão, I.; Queirós, R.; Marote, S.; Sousa, M.J. Complications of Biliary Drainage in Patients with Malignant Biliary Obstruction. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2020, 52, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, B.R.; Birg, A. Malignant biliary obstruction: From palliation to treatment. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 8, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyna, T.; Neuhaus, H. Self-expandable metal stents in malignant biliary obstruction: Back to the roots with uncovered stents as the “new” standard? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, N.S.; Barkun, J.S.; Barkun, A.N. Palliation of malignant biliary obstruction: A prospective trial examining impact on quality of life. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 56, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Mak, M.P.; Marques, D.F.; Capareli, F.; Carnevale, F.C.; Moreira, A.M.; Ribeiro, U.; Cecconello, I.; Hoff, P.M. Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies: Prognostic Factors and Clinical Outcomes. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2013, 44, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moole, H.; Dharmapuri, S.; Duvvuri, A.; Dharmapuri, S.; Boddireddy, R.; Moole, V.; Yedama, P.; Bondalapati, N.; Uppu, A.; Yerasi, C. Endoscopic versus Percutaneous Biliary Drainage in Palliation of Advanced Malignant Hilar Obstruction: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2016, 4726078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Qi, Q.; Sun, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z. Prognostic nutritional index predicts survival and correlates with systemic inflammatory response in advanced pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbauer, S.L.; Pantuck, A.J.; de Martino, M.; Lucca, I.; Haitel, A.; Shariat, S.F.; Belldegrun, A.S.; Klatte, T. The preoperative prognostic nutritional index is an independent predictor of survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2015, 33, 68.e1–68.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Zhou, T.; Fang, W.; Xue, C.; Hu, Z.; Qin, T.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts overall survival of small-cell lung cancer patients. Tumor Biol. 2014, 36, 3389–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, M.; Fujii, T.; Kodera, Y.; Nagai, S.; Takeda, S.; Nakao, A. Nutritional predictors of postoperative outcome in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2010, 98, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migita, K.; Takayama, T.; Saeki, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Wakatsuki, K.; Enomoto, K.; Tanaka, T.; Ito, M.; Kurumatani, N.; Nakajima, Y. The Prognostic Nutritional Index Predicts Long-term Outcomes of Gastric Cancer Patients Independent of Tumor Stage. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Hiro, J.; Uchida, K.; Kusunoki, M. Prognostic Nutritional Index Predicts Postoperative Outcome in Colorectal Cancer. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 2688–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Usami, N.; Fukumoto, K.; Mizuno, T.; Kuroda, H.; Sakakura, N.; Yokoi, K.; Sakao, Y. The Significance of the Prognostic Nutritional Index in Patients with Completely Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozoe, T.; Kimura, Y.; Ishida, M.; Saeki, H.; Korenaga, D.; Sugimachi, K. Correlation of pre-operative nutritional condition with post-operative complications in surgical treatment for oesophageal carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 28, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; North, B.V.; Sharma, R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: The prognostic nutritional index (PNI). Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.-B.; Tian, T.; Tian, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-J. Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, J.; Shao, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X. The elevated NLR, PLR and PLT may predict the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68837–68846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieto, E.; Galizia, G.; Auricchio, A.; Cardella, F.; Mabilia, A.; Basile, N.; Del Sorbo, G.; Castellano, P.; Romano, C.; Orditura, M.; et al. Preoperative Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Lymphocyte to Monocyte Ratio are Prognostic Factors in Gastric Cancers Undergoing Surgery. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2017, 21, 1764–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Gu, L.; Pei, H.; Kuai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, Z. Prognostic value of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Clinics 2015, 70, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-J.; Hu, Z.-G.; Shi, W.-X.; Deng, T.; He, S.-Q.; Yuan, S.-G. Prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2807–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, Y.; Takashi, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Ohtsuka, M. The prognostic impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) in patients with distal bile duct cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaller, R.; Arbănași, E.M.; Mureșan, A.V.; Voidăzan, S.; Arbănași, E.M.; Horváth, E.; Suciu, B.A.; Hosu, I.; Halmaciu, I.; Brinzaniuc, K.; et al. The Predictive Value of Systemic Inflammatory Markers, the Prognostic Nutritional Index, and Measured Vessels’ Diameters in Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation Failure. Life 2022, 12, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureșan, A.V.; Russu, E.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Hosu, I.; Arbănași, E.M.; Voidăzan, S.T. The Predictive Value of NLR, MLR, and PLR in the Outcome of End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, R.; Russu, E.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Arbănași, E.M.; Melinte, R.M.; Coșarcă, C.M.; Cocuz, I.G.; Sabău, A.H.; Tinca, A.C.; et al. Carotid Plaque Features and Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of Restenosis and Mortality Following Carotid Endarterectomy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russu, E.; Mureșan, A.V.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Hosu, I.; Voidăzan, S.; Arbănași, E.M.; Coșarcă, C.M. The Predictive Role of NLR and PLR in Outcome and Patency of Lower Limb Revascularization in Patients with Femoropopliteal Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Mi, X.; Shao, M.; Liu, L. The prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with platinum-based chemotherapeutics. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippiadis, D.K.; Binkert, C.; Pellerin, O.; Hoffmann, R.T.; Krajina, A.; Pereira, P.L. Cirse Quality Assurance Document and Standards for Classification of Complications: The Cirse Classification System. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ding, T.; Pan, W.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, L. Increased intratumoral regulatory T cells are related to intratumoral macrophages and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikos, T.A.; Donnenberg, A.D.; Landreneau, R.J.; Luketich, J.D.; Donnenberg, V.S. Lung T-cell subset composition at the time of surgical resection is a prognostic indicator in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravasco, P. Nutrition in Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, N. The Significant Value of Preoperative Prognostic Nutritional Index for Survival in Pancreatic Cancers. Pancreas 2018, 47, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Pang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Man, Z.; Yang, S.; et al. Nutritional prognostic scores in patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma treated by percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting combined with 125I seed intracavitary irradiation. Medicine 2018, 97, e11000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, M.; Filippi, R.; Vivaldi, C.; Caputo, F.; Leone, F.; Salani, F.; Cerma, K.; Aglietta, M.; Fornaro, L.; Sperti, E.; et al. The prognostic nutritional index predicts survival and response to first-line chemotherapy in advanced biliary cancer. Liver Int. 2019, 40, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; Mcnamara, M.G.; Šeruga, B.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Aneja, P.; Ocaña, A.; Leibowitz-Amit, R.; Sonpavde, G.; Knox, J.J.; Tran, B.; et al. Prognostic Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bald, T.; Quast, T.; Landsberg, J.; Rogava, M.; Glodde, N.; Lopez-Ramos, D.; Kohlmeyer, J.; Riesenberg, S.; van den Boorn-Konijnenberg, D.; Hömig-Hölzel, C.; et al. Ultraviolet-radiation-induced inflammation promotes angiotropism and metastasis in melanoma. Nature 2014, 507, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakos, C.I.; Charles, K.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e493–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxburgh, C.S.D.; McMillan, D.C. Cancer and systemic inflammation: Treat the tumour and treat the host. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Heij, L.R.; Czigany, Z.; Dahl, E.; Dulk, M.D.; Lang, S.A.; Ulmer, T.F.; Neumann, U.P.; Bednarsch, J. The prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W. Preoperative risk grade predicts the long-term prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A retrospective cohort analysis. BMC Surg. 2021, 21, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, N.; Okuda, T.; Sakagami, J.; Harada, T.; Ohara, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Sakai, H.; Oka, K.; Hara, T.; Tsuji, T.; et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts prognosis in unresectable pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brountzos, E.N.; Ptochis, N.; Panagiotou, I.; Malagari, K.; Tzavara, C.; Kelekis, D. A Survival Analysis of Patients with Malignant Biliary Strictures Treated by Percutaneous Metallic Stenting. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 30, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahinli, H.; Özet, A. Prognostic and predictive factors in cancer patients with obstructive jaundice treated by percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage: A single-center experience. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Li, W.T.; Peng, W.J.; Li, G.D.; He, X.H.; Xu, L.C. Clinical outcomes and prediction of survival following percutaneous biliary drainage for malignant obstructive jaundice. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Furuse, J.; Yoshino, M.; Konishi, M.; Kawano, N.; Kinoshita, T.; Ryu, M. Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage for the Treatment of Obstructive Jaundice Caused by Metastases from Nonbiliary and Nonpancreatic Cancers. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 26, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Niemelä, J.; Kallio, R.; Ohtonen, P.; Perälä, J.; Saarnio, J.; Syrjälä, H. Is Palliative Percutaneous Drainage for Malignant Biliary Obstruction Useful? World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 2980–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, A.M.; Annam, A.; Brody, L.; Gunn, A.J.; Himes, E.A.; Patel, S.; Tam, A.L.; Dariushnia, S.R. Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Standards for Percutaneous Cholecystostomy and Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Interventions. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quencer, K.B.; Tadros, A.S.; Marashi, K.B.; Cizman, Z.; Reiner, E.; O’Hara, R.; Oklu, R. Bleeding after Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage: Incidence, Causes and Treatments. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, J.; Mytton, J.; Evison, F.; Mangat, K.S.; Patel, P.; Trudgill, N. The outcomes of biliary drainage by percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography for the palliation of malignant biliary obstruction in England between 2001 and 2014: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuqan, W.; Innabi, A.; Alawneh, A.; Abu Farsakh, F.; Al-Khatib, M. Prediction of survival following percutaneous biliary drainage for malignant biliary obstruction. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2017, 5, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, A.; Ishii, H.; Ozaka, M.; Matsusaka, S.; Chin, K.; Mizunuma, N.; Yukisawa, S.; Matsueda, K.; Furuse, J. Clinical Outcome of Biliary Drainage for Obstructive Jaundice Caused by Colorectal and Gastric Cancers. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 42, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, R.H.; Ulrich, R.; Hsu, M.; Moskowitz, C.; Reidy-Lagunes, D.; Covey, A.M.; Brody, L.A.; Robson, P.M.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Solomon, S.B.; et al. Outcomes of Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Biliary Drainage to Reduce Bilirubin for Administration of Chemotherapy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.L.; Sudheendra, D.; Dagli, M.; Mondschein, J.I.; Stavropoulos, S.W.; Shlansky-Goldberg, R.D.; Trerotola, S.O.; Teitelbaum, U.; Mick, R.; Soulen, M.C. Percutaneous biliary drainage effectively lowers serum bilirubin to permit chemotherapy treatment. Abdom. Radiol. 2016, 41, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.-F.; Lu, J.; Zhu, H.-D.; Guo, J.-H.; Huang, M.; Ji, J.-S.; Lv, W.-F.; Li, Y.-L.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Early Warning Models to Estimate the 30-Day Mortality Risk After Stent Placement for Patients with Malignant Biliary Obstruction. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Total | 60-Day Survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Survivors | Survivors | p | ||
| n = 136 | n = 62 | n = 74 | ||
| Gender, male, n (%) | 72 (52.9) | 35 (56.5) | 37 (50.0) | 0.453 |
| Age, mean ± sd | 65.7 ± 11.7 | 67.9 ± 11.4 | 63.9 ± 11.7 | 0.047 |
| Diagnosis, n (%) | ||||
| Klatskin tumor | 29 (21.3) | 11 (17.7) | 18 (24.3) | |
| Periampullary tumor | 13 (9.6) | 5 (8.1) | 8 (10.8) | |
| Liver hilum metastasis | 25 (18.4) | 10 (16.1) | 15 (20.3) | |
| Pancreatic cancer | 37 (27.2) | 21 (33.9) | 16 (21.6) | 0.685 |
| Gallbladder carcinoma | 11 (8.1) | 6 (9.7) | 5 (6.8) | |
| Primary liver tumor (HCC, CCC) | 11 (8.1) | 4 (6.5) | 7 (9.5) | |
| Gastric adenocarcinoma | 10 (7.4) | 5 (8.1) | 5 (6.8) | |
| Level of obstruction, n (%) | ||||
| Proximal | 84 (61.8) | 33 (53.2) | 51 (68.9) | 0.061 |
| Distal | 52 (38.2) | 29 (46.8) | 23 (31.1) | |
| PTBD access site, n (%), | 0.085 | |||
| Right lobe | 100 (73.5) | 50 (80.6) | 50 (67.6) | |
| Left lobe | 36 (26.5) | 12 (19.4) | 24 (32.4) | |
| Complications, n (%) | 13 (9.6) | 6 (9.7) | 7 (9.5) | 0.966 |
| Liver metastasis, n (%) | 53 (39.0) | 25 (40.3) | 28 (37.8) | 0.767 |
| Further treatment, n (%) | 49 (36) | 1 (1.6) | 48 (64.9) | 0.001 |
| Chemotherapy | 45 (33.1) | 1 (1.6) | 44 (59.5) | |
| Chemotherapy and SBRT | 4 (2.9) | 4 (5.4) | ||
| Preprocedural total bilirubin median (25th–75th percentile) | 351.0 (287.5–466.0) | 366.7 (297.9–462.0) | 345.0 (286.9–474.4) | 0.795 |
| Postprocedural total bilirubin median (25th–75th percentile) | 194.1 (81.4–282.7) | 219.2 (116.8–317.4) | 146.0 (68.0–244.8) | 0.010 |
| Absolute neutrophil count (109/L), median (25th–75th percentile) | 5.8 (4.3–7.9) | 6.4 (5.0–8.9) | 5.2 (3.8–7.0) | 0.003 |
| Absolute lymphocyte count(109/L), median (25th–75th percentile) | 1.2 (0.9–1.5) | 1.2 (0.8–1.6) | 1.2 (0.9–1.5) | 0.993 |
| Serum albumin, mean ± sd | 32.3 ± 5.6 | 30.6 ± 5.8 | 33.7 ± 5.0 | 0.001 |
| PNI, median (25th–75th percentile) | 38.3 (34.0–43.5) | 36.2 (32.0–41.6) | 40.2 (35.5–45.5) | 0.004 |
| NLR, median (25th–75th percentile) | 4.7 (3.2–7.8) | 5.3 (3.6–10.1) | 4.0 (2.9–6.6) | 0.021 |
| Variable | OR | 95% CI for OR | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | |||
| Gender | 1.296 | 0.658–2.554 | 0.453 |
| Age | 0.970 | 0.941–1.000 | 0.049 |
| Liver metastasis | 0.858 | 0.426–1.726 | 0.767 |
| Level of obstruction | 0.513 | 0.255–1.034 | 0.062 |
| PTBD access site | 2.000 | 0.902–4.434 | 0.088 |
| Preprocedural total bilirubin | 1.000 | 0.998–1.002 | 0.955 |
| Postprocedural total bilirubin | 0.998 | 0.996–1.000 | 0.087 |
| Absolute neutrophil count | 0.895 | 0.812–0.987 | 0.026 |
| Absolute lymphocyte count | 1.225 | 0.839–1.790 | 0.293 |
| Serum albumin level | 1.116 | 1.042–1.195 | 0.002 |
| NLR ≤ 3 | 0.429 | 0.180–1.022 | 0.056 |
| PNI ≥ 36.7 | 2.230 | 1.115–4.462 | 0.023 |
| Multivariate | |||
| Level of obstruction | 0.437 | 0.209–0.911 | 0.027 |
| PNI ≥ 36.7 | 2.562 | 1.243–5.279 | 0.011 |
| Values | Point | Event | 60-Day Survival Score | Survival Chance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLR > 3 | 0 | NLR > 3 and PNI < 36.7 | 0 | Low chance |
| NLR ≤ 3 | 1 | NLR > 3 and PNI ≥ 36.7 | 1 | Medium chance |
| PNI < 36.7 | 0 | NLR ≤ 3 and PNI < 36.7 | 1 | Medium chance |
| PNI ≥ 36.7 | 1 | NLR ≤ 3 and PNI ≥ 36.7 | 2 | High chance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakosek, M.; Bulatovic, D.; Pavlovic, V.; Filipovic, A.; Igic, A.; Galun, D.; Jovanovic, D.; Sisevic, J.; Masulovic, D. Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) as Predictors of Short-Term Survival in Patients with Advanced Malignant Biliary Obstruction Treated with Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237055
Zakosek M, Bulatovic D, Pavlovic V, Filipovic A, Igic A, Galun D, Jovanovic D, Sisevic J, Masulovic D. Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) as Predictors of Short-Term Survival in Patients with Advanced Malignant Biliary Obstruction Treated with Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237055
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakosek, Milos, Dusan Bulatovic, Vedrana Pavlovic, Aleksandar Filipovic, Aleksa Igic, Danijel Galun, Darko Jovanovic, Jelena Sisevic, and Dragan Masulovic. 2022. "Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) as Predictors of Short-Term Survival in Patients with Advanced Malignant Biliary Obstruction Treated with Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237055
APA StyleZakosek, M., Bulatovic, D., Pavlovic, V., Filipovic, A., Igic, A., Galun, D., Jovanovic, D., Sisevic, J., & Masulovic, D. (2022). Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) as Predictors of Short-Term Survival in Patients with Advanced Malignant Biliary Obstruction Treated with Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237055






