Genetic and Small-Molecule Modulation of Stat3 in a Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TNBS Models of CD
2.2. Immunohistochemical and TUNEL Analysis
2.3. Measurements of Y705-Phosphorylated (pY) STAT3 and Total STAT3 Using Luminex Bead-Based Assays
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
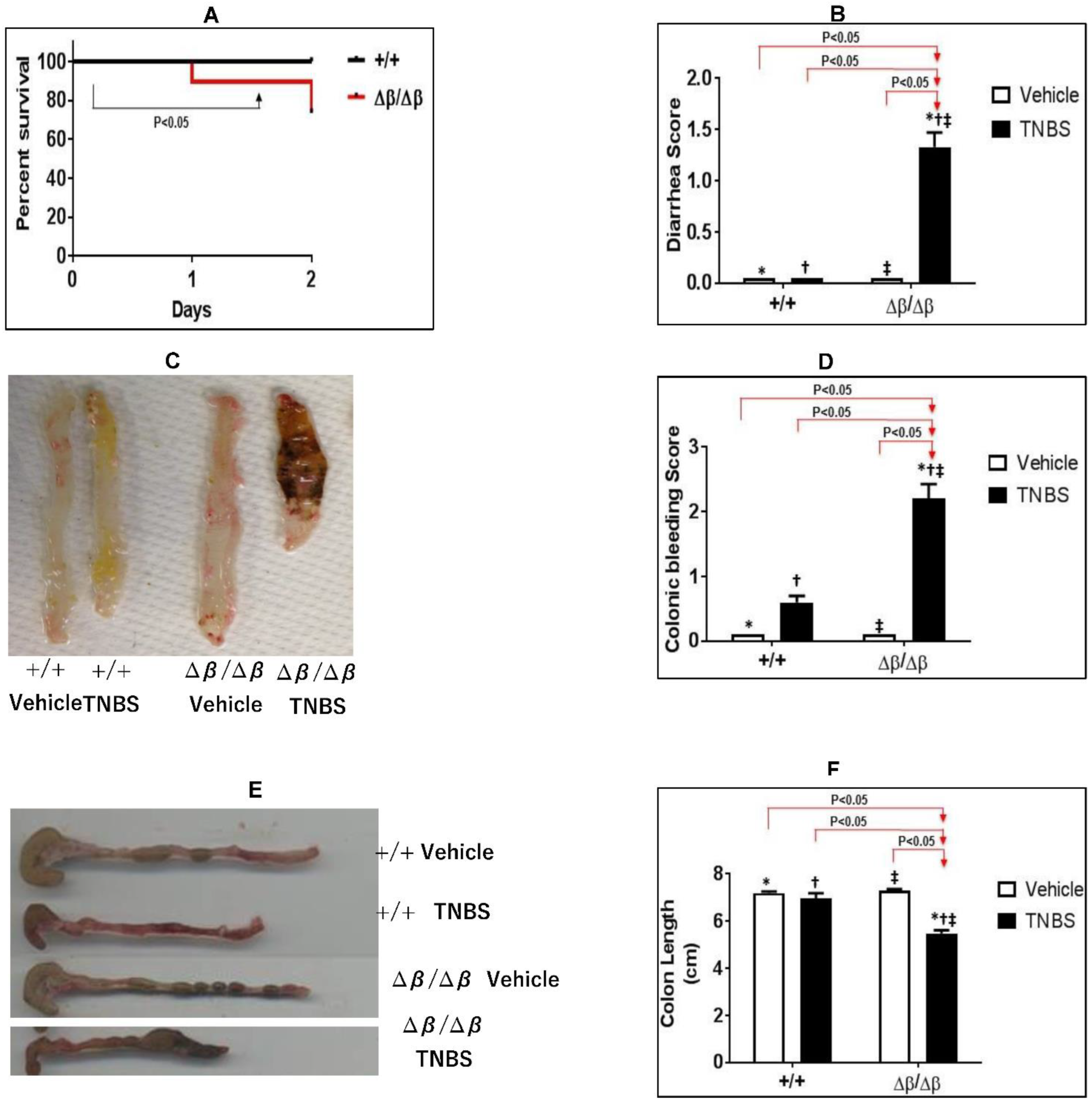
3.1. Effect of STAT3β Deletion on TNBS-Induced CD in Mice
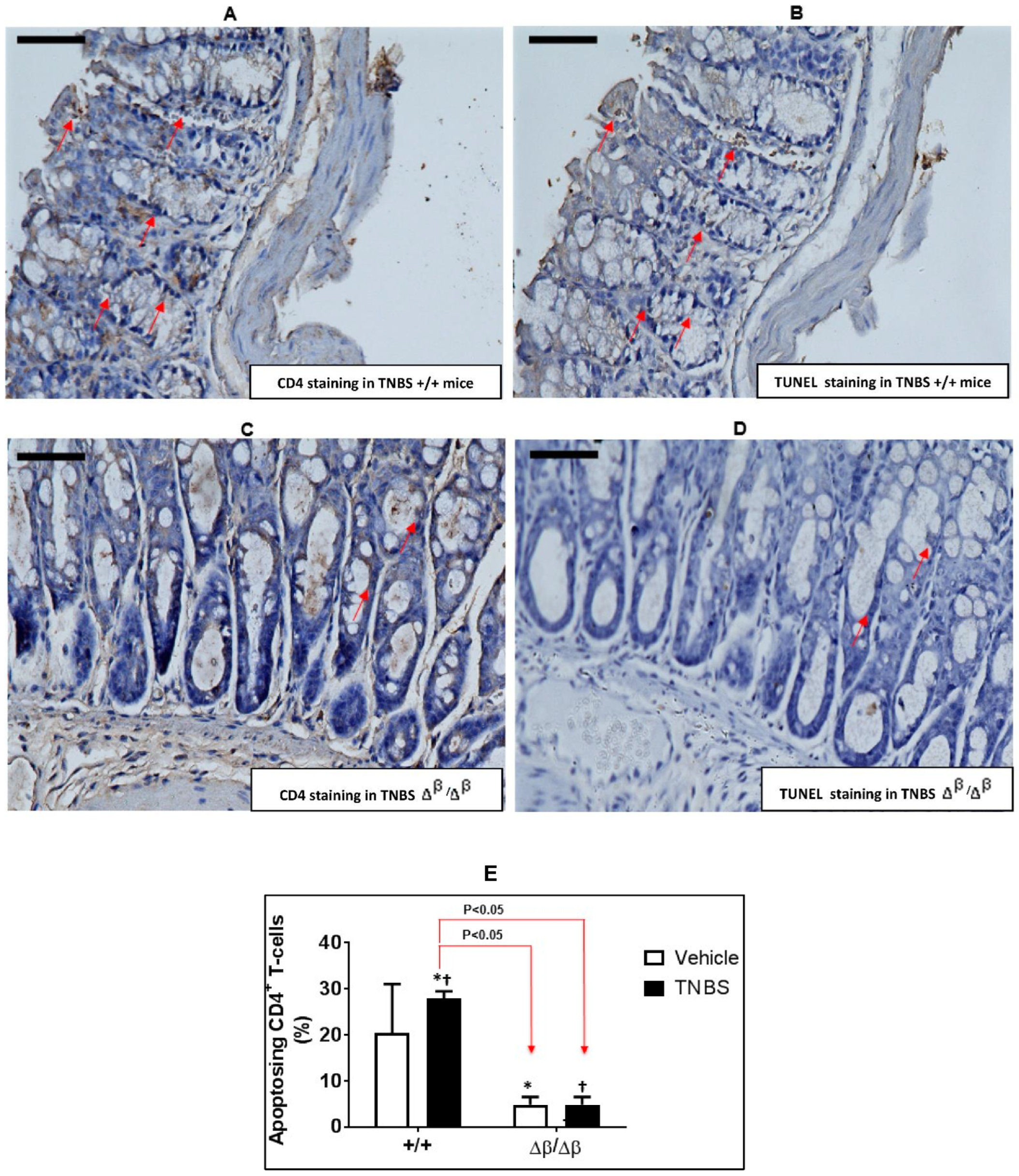
3.2. Effect of TNBS-Induced CD on Apoptosis of CD4+ Cells in Colons of +/+ and ∆β/∆β Mice
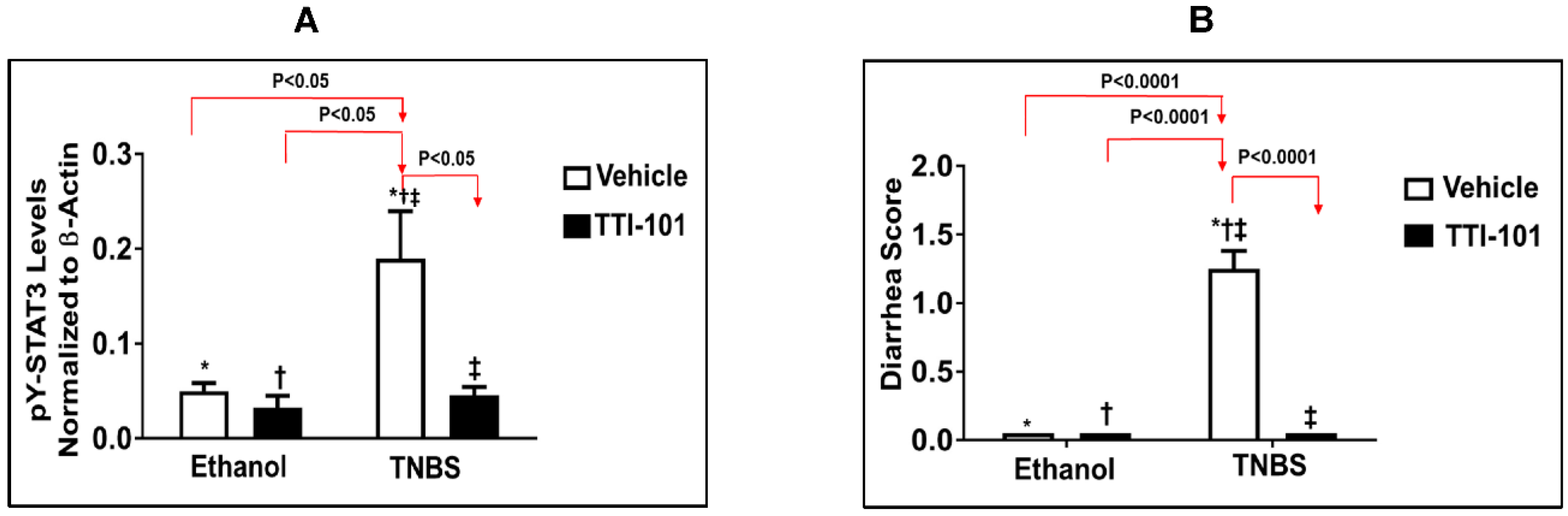
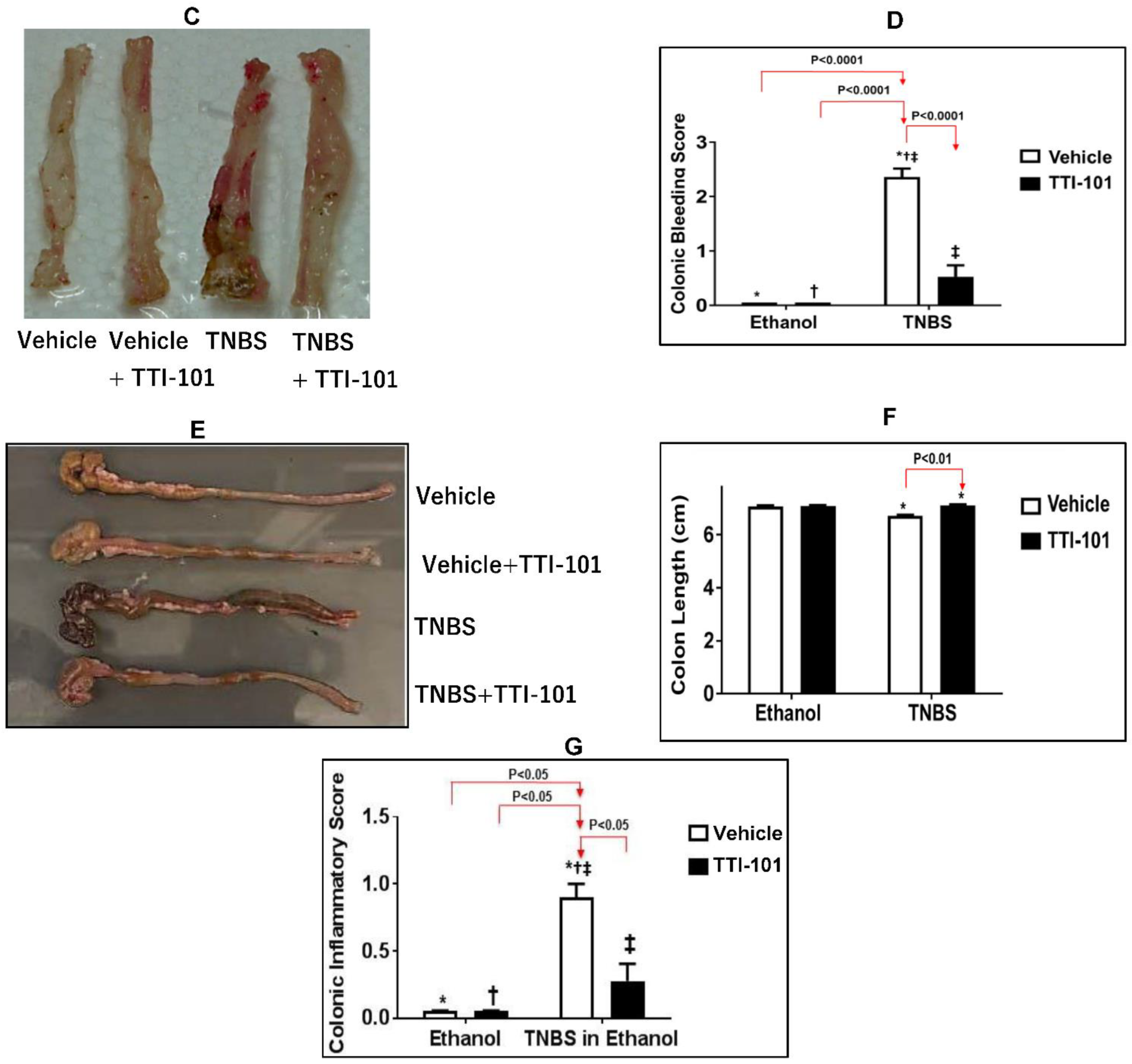
3.3. Effects of TTI-101 Treatment on TNBS-Induced CD
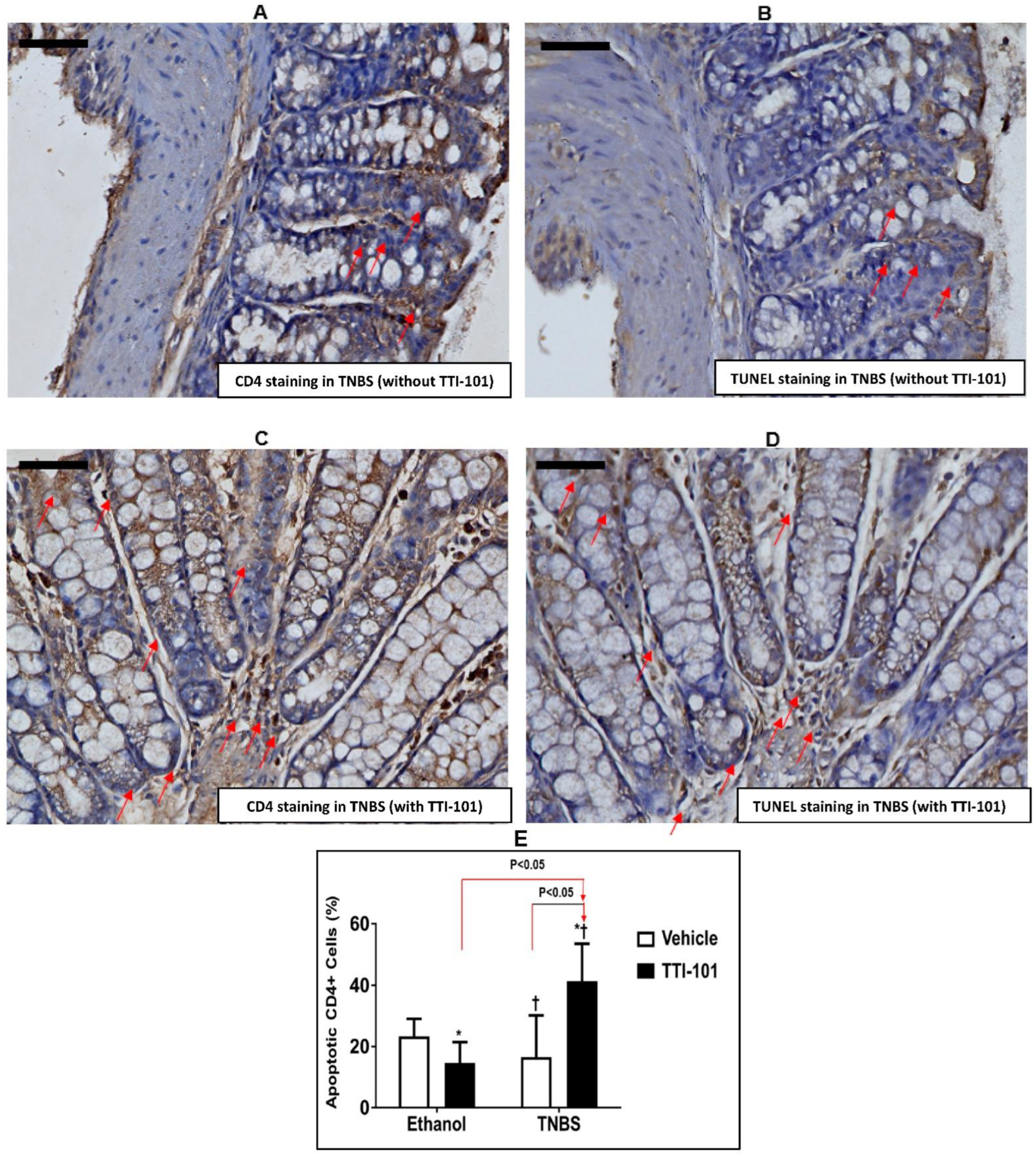
3.4. Effect of TTI-101 Treatment on Apoptosis of CD4+ Cells
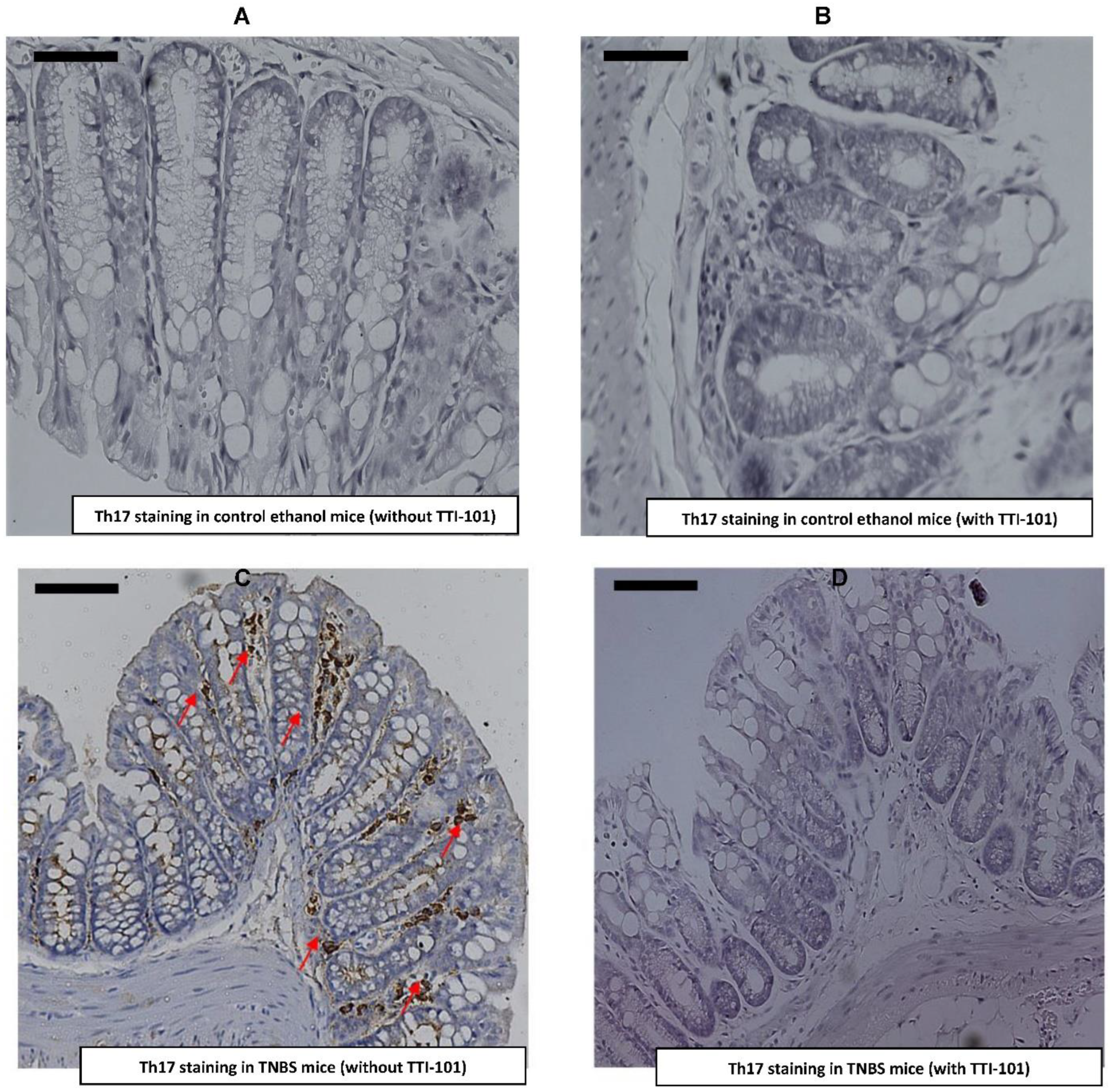
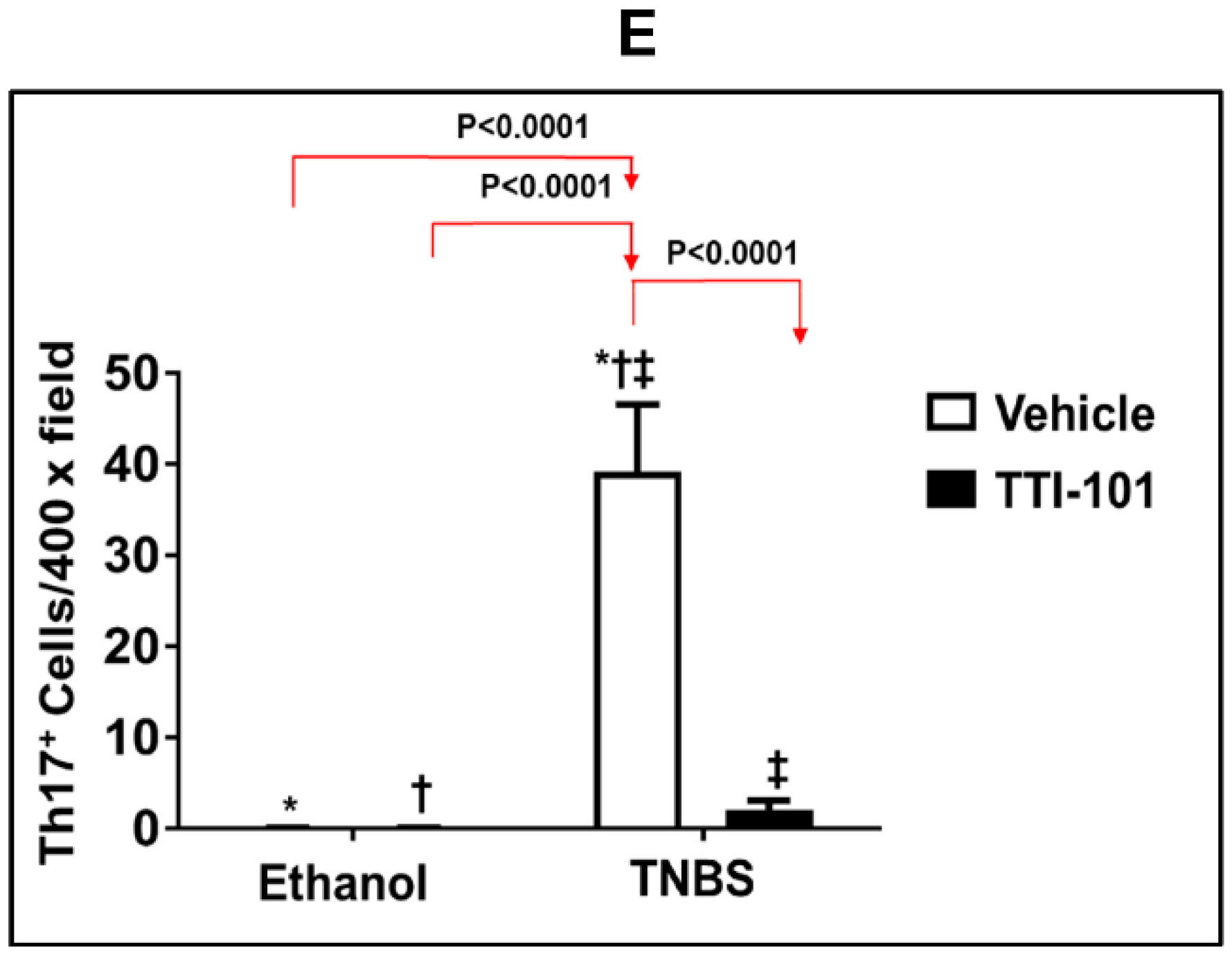
3.5. Effect of TTI-101 Treatment on Colonic Th17 Cell Infiltration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2012, 380, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, F.; Khalil, H. Crohn’s disease. A clinical update. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalla, R.; Ventham, N.T.; Satsangi, J.; Arnott, I.D. Crohn’s disease. BMJ 2014, 349, g6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juckett, G.; Trivedi, R. Evaluation of chronic diarrhea. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 84, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E. From symptom to diagnosis: Clinical distinctions among various forms of intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America. The Facts about Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Available online: https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/sites/default/files/2019-02/Updated%20IBD%20Factbook.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- Freeman, H.J. Colorectal cancer risk in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1810–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpaz, N.; Ward, S.C.; Mescoli, C.; Itzkowitz, S.H.; Polydorides, A.D. Precancerous lesions in inflammatory bowel disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latella, G.; Papi, C. Crucial steps in the natural history of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3790–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secher, T.; Gaillot, O.; Ryffel, B.; Chamaillard, M. Remote control of intestinal tumorigenesis by innate immunity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1749–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, S.A.; Arce, M.; Khaja, A.; Fernandez, M.; Naser, N.; Elwasila, S.; Thanigachalam, S. Role of ATG16L, NOD2 and IL23R in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, B.; Gardet, A.; Xavier, R.J. Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2011, 474, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugot, J.P.; Chamaillard, M.; Zouali, H.; Lesage, S.; Cezard, J.P.; Belaiche, J.; Almer, S.; Tysk, C.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gassull, M.; et al. Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 2001, 411, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weersma, R.K.; Stokkers, P.C.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; van Hogezand, R.A.; Verspaget, H.W.; de Jong, D.J.; van der Woude, C.J.; Oldenburg, B.; Linskens, R.K.; Festen, E.A.; et al. Molecular prediction of disease risk and severity in a large Dutch Crohn’s disease cohort. Gut 2009, 58, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampe, J.; Franke, A.; Rosenstiel, P.; Till, A.; Teuber, M.; Huse, K.; Albrecht, M.; Mayr, G.; De La Vega, F.M.; Briggs, J.; et al. A genome-wide association scan of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for Crohn disease in ATG16L1. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, M.; Barrett, J.C.; Prescott, N.J.; Tremelling, M.; Anderson, C.A.; Fisher, S.A.; Roberts, R.G.; Nimmo, E.R.; Cummings, F.R.; Soars, D.; et al. Sequence variants in the autophagy gene IRGM and multiple other replicating loci contribute to Crohn’s disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, S.; Bultron, G.; Depaolo, R.W. Genetic variants associated with Crohn’s disease. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2013, 6, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Limbergen, J.; Wilson, D.C.; Satsangi, J. The genetics of Crohn’s disease. Annu. Rev. Genomics. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Clausen, B.E.; Kaisho, T.; Tsujimura, T.; Terada, N.; Forster, I.; Akira, S. Enhanced Th1 activity and development of chronic enterocolitis in mice devoid of Stat3 in macrophages and neutrophils. Immunity 1999, 10, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, R.; Mudter, J.; Finotto, S.; Mullberg, J.; Jostock, T.; Wirtz, S.; Schutz, M.; Bartsch, B.; Holtmann, M.; Becker, C.; et al. Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: Evidence in crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Yoshizaki, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Ito, H. IL-6 is required for the development of Th1 cell-mediated murine colitis. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4878–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Hanada, T.; Mitsuyama, K.; Yoshida, T.; Kamizono, S.; Hoshino, T.; Kubo, M.; Yamashita, A.; Okabe, M.; Takeda, K.; et al. CIS3/SOCS3/SSI3 plays a negative regulatory role in STAT3 activation and intestinal inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickert, G.; Neufert, C.; Leppkes, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wittkopf, N.; Warntjen, M.; Lehr, H.-A.; Hirth, S.; Weigmann, B.; Wirtz, S.; et al. STAT3 links IL-22 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells to mucosal wound healing. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, R.; Neurath, M.F. Signaling molecules: The pathogenic role of the IL-6/STAT-3 trans signaling pathway in intestinal inflammation and in colonic cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, T.S.; Sanders, L.K.; Nathans, D. Cooperative transcriptional activity of Jun and Stat3 beta, a short form of Stat3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9097–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; White, S.M.; Schaefer, T.S.; Ball, E.D.; Dyer, K.F.; Tweardy, D.J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor activation of Stat3 alpha and Stat3 beta in immature normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Blood 1996, 88, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldenhoven, E.; van Dijk, T.B.; Solari, R.; Armstrong, J.; Raaijmakers, J.A.; Lammers, J.W.; Koenderman, L.; de Groot, R.P. STAT3beta, a splice variant of transcription factor STAT3, is a dominant negative regulator of transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13221–13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Noguchi, K.; Shi, W.; Tanaka, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Yoshida, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat3 gene leads to early embryonic lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3801–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritano, D.; Sugrue, M.L.; Tininini, S.; Dewilde, S.; Strobl, B.; Fu, X.; Murray-Tait, V.; Chiarle, R.; Poli, V. The STAT3 isoforms alpha and beta have unique and specific functions. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Huso, D.L.; Nathans, D.; Desiderio, S. Specific ablation of Stat3beta distorts the pattern of Stat3-responsive gene expression and impairs recovery from endotoxic shock. Cell 2002, 108, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alten, J.A.; Moran, A.; Tsimelzon, A.I.; Mastrangelo, M.A.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Poli, V.; Tweardy, D.J. Prevention of hypovolemic circulatory collapse by IL-6 activated Stat3. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; Tsimelzon, A.I.; Mastrangelo, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Yu, B.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Poli, V.; Tweardy, D.J. Prevention of trauma/hemorrhagic shock-induced lung apoptosis by IL-6-mediated activation of Stat3. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2009, 2, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.; Akcan Arikan, A.; Mastrangelo, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Yu, B.; Poli, V.; Tweardy, D.J. Prevention of trauma and hemorrhagic shock-mediated liver apoptosis by activation of stat3alpha. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2008, 1, 213–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, E.; Margonis, G.A.; Angelou, A.; Pikouli, A.; Argiri, P.; Karavokyros, I.; Papalois, A.; Pikoulis, E. The TNBS-induced colitis animal model: An overview. Ann. Med. Surg. 2016, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiffele, F.; Fuss, I.J. Induction of TNBS colitis in mice. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2002, 49, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morampudi, V.; Bhinder, G.; Wu, X.; Dai, C.; Sham, H.P.; Vallance, B.A.; Jacobson, K. DNBS/TNBS colitis models: Providing insights into inflammatory bowel disease and effects of dietary fat. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 84, e51297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazel, K.; O’Connor, A. Emerging treatments for inflammatory bowel disease. Ther. Adv. Chronic. Dis. 2020, 11, 2040622319899297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.H.; Yoo, W.; Stevenson, H.L.; Deshpande, D.; Shen, H.; Gagea, M.; Yoo, S.Y.; Wang, J.; Eckols, T.K.; Bharadwaj, U.; et al. Multifunctional Effects of a Small-Molecule STAT3 Inhibitor on NASH and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5537–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redell, M.S.; Ruiz, M.J.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Tweardy, D.J. Stat3 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia: Ligand-dependent and -independent activation and induction of apoptosis by a novel small-molecule Stat3 inhibitor. Blood 2011, 117, 5701–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, B.; Landis, M.D.; Tweardy, D.J.; Chang, J.C.; Dobrolecki, L.E.; Wu, M.F.; Zhang, X.; Westbrook, T.F.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Liu, D.; et al. Selective small molecule Stat3 inhibitor reduces breast cancer tumor-initiating cells and improves recurrence free survival in a human-xenograft model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Eckols, T.K.; Xu, X.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Adachi, M.; Song, Y.; Mo, Q.; Lai, S.Y.; Tweardy, D.J. Small-molecule inhibition of STAT3 in radioresistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26307–26330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavino, A.C.; Nahmod, K.; Bharadwaj, U.; Makedonas, G.; Tweardy, D.J. STAT3 inhibition prevents lung inflammation, remodeling, and accumulation of Th2 and Th17 cells in a murine asthma model. Allergy 2016, 71, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, K.A.; Dong, J.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Y.; Schor, N.; Tweardy, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Mitch, W.E. Inhibition of Stat3 activation suppresses caspase-3 and the ubiquitin-proteasome system, leading to preservation of muscle mass in cancer cachexia. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11177–11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.; Okhuysen, P.C.; Chappell, C.L.; Weinstock, J.V.; Lewis, D.E.; Actor, J.K.; White, A.C., Jr. Substance P expression correlates with severity of diarrhea in cryptosporidiosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, M.; Garza, M.A.; Xie, M.; Weinstock, J.; Xiang, Q.; Robinson, P. Substance P is associated with heart enlargement and apoptosis in murine dilated cardiomyopathy induced by Taenia crassiceps infection. J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Jiang, X.; Tweardy, B.J.; Tweardy, D.J. Chemical probes that competitively and selectively inhibit Stat3 activation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; Dong, Y.; Tweardy, D.J.; Garibotto, G.; Mitch, W.E. Stat3 Activation Links a C/EBPdelta to Myostatin Pathway to Stimulate Loss of Muscle Mass. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hox, V.; O’Connell, M.P.; Lyons, J.J.; Sackstein, P.; Dimaggio, T.; Jones, N.; Nelson, C.; Boehm, M.; Holland, S.M.; Freeman, A.F.; et al. Diminution of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling inhibits vascular permeability and anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasembeli, M.M.; Bharadwaj, U.; Robinson, P.; Tweardy, D.J. Contribution of STAT3 to Inflammatory and Fibrotic Diseases and Prospects for its Targeting for Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.M.; Bharadwaj, U.; Eckols, T.K.; Kolosov, M.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Fridley, C.; Siller, R.; Tweardy, D.J. Small-molecule targeting of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 to treat non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettner, N.M.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Durak, M.G.; Bui, T.; Kohansal, M.; Ha, M.J.; Liu, B.; Rao, X.; Wang, J.; Yi, M.; et al. Combined Inhibition of STAT3 and DNA Repair in Palbociclib-Resistant ER-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3996–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, S. Crohn’s disease: Th1, Th17 or both? The change of a paradigm: New immunological and genetic insights implicate Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. Gut 2009, 58, 1152–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steward-Tharp, S.M.; Laurence, A.; Kanno, Y.; Kotlyar, A.; Villarino, A.V.; Sciume, G.; Kuchen, S.; Resch, W.; Wohlfert, E.A.; Jiang, K.; et al. A mouse model of HIES reveals pro- and anti-inflammatory functions of STAT3. Blood 2014, 123, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonzi, T.; Newton, I.P.; Bryce, P.J.; Di Carlo, E.; Lattanzio, G.; Tripodi, M.; Musiani, P.; Poli, V. Induced somatic inactivation of STAT3 in mice triggers the development of a fulminant form of enterocolitis. Cytokine 2004, 26, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robinson, P.; Magness, E.; Montoya, K.; Engineer, N.; Eckols, T.K.; Rodriguez, E.; Tweardy, D.J. Genetic and Small-Molecule Modulation of Stat3 in a Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237020
Robinson P, Magness E, Montoya K, Engineer N, Eckols TK, Rodriguez E, Tweardy DJ. Genetic and Small-Molecule Modulation of Stat3 in a Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237020
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobinson, Prema, Emily Magness, Kelsey Montoya, Nikita Engineer, Thomas K. Eckols, Emma Rodriguez, and David J. Tweardy. 2022. "Genetic and Small-Molecule Modulation of Stat3 in a Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237020
APA StyleRobinson, P., Magness, E., Montoya, K., Engineer, N., Eckols, T. K., Rodriguez, E., & Tweardy, D. J. (2022). Genetic and Small-Molecule Modulation of Stat3 in a Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237020




