Abstract
(1) Background: To assess the time trend in the prevalence of chronic neck pain (CNP), chronic low back pain (CLBP), and migraine or frequent headache (MFH) among people with diabetes in Spain from 2014 to 2020, this study identified sex differences and compared the prevalence of these pain sites between people with diabetes and age–sex-matched non-diabetic subjects. (2) Methods: The study design included a cross-sectional and a case–control study. The data were obtained from the European Health Interview Surveys for Spain conducted in 2014 and 2020. The presence of diabetes, CNP, CLBP, and MFH was self-reported. Study covariates included sociodemographic characteristics, comorbidities, lifestyles, and pain-related variables. (3) Results: Among people with diabetes, the prevalence of CNP, CLBP, and MFH did not improve from 2014 to 2020. Women with diabetes had a significantly higher prevalence of all the pain sites analyzed than men with diabetes. After matching by sex and age, the prevalence of CNP (26.0% vs. 21.1%; p < 0.001), CLBP (31.2% vs. 25.0%; p < 0.001), and MFH (7.7% vs. 6.5%; p = 0.028) was higher for people with diabetes than for those without diabetes. Self-reported mental disease was independently associated with reporting the three pain sites analyzed in people with diabetes. (4) Conclusions: The prevalence of CNP, CLBP, and MFH has remained stable over time. Remarkable sex differences were found, with a higher prevalence among women than men with diabetes. Diabetes was associated with reporting in all the pain sites analyzed. Self-reported mental disease was associated with reporting CNP, CLBP, and MFH.
1. Introduction
Worldwide, diabetes, neck pain (NP), low back pain (LBP), and migraine are major public health problems affecting both sexes and middle and older age groups [1,2,3,4,5].
Previous studies have suggested that diabetes is associated with a higher risk of suffering from these three pains; however, thus far, no conclusive results have been obtained [6,7,8,9].
For NP and LBP, a recent meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies concluded that diabetes was a risk factor for both pain sites, with an adjusted odds ratio (OR) of 1.24 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.05–1.47) for NP and 1.35 (95% CI 1.20–1.52) for LBP [6].
Population studies conducted in our country have confirmed these associations [10,11,12]. People with diabetes not only seem to have more frequent pain but also more severe levels of pain [10,11,12].
Among the possible causes that can explain the association of spinal pain (NP and/or LBP) with diabetes are that people with diabetes have an increased risk of cartilage inflammation, loss of muscle strength, spinal stenosis, and degenerative intervertebral disc (IVD) disease [6,7,8,13,14]. The arguments for a spurious association between spinal pain and diabetes include the confounding effect of obesity, depression, and sedentarism, conditions more frequent among people with diabetes than without [6,7,8].
Diabetes has also been found to co-occur with migraine [9]. Previous investigations on the association of diabetes with migraine have found that diabetes is either a risk, a protective factor, or that there is no association [9,15,16]. Different settings (hospitals, primary care centers, population surveys), sampling methods, pain definitions, study populations, sample sizes, and statistical methods can explain the lack of conclusive results [9,15,16].
Diabetes may be relevant in migraine pathophysiology because people with diabetes show changes in nerve conduction, vascular reactivity, and an elevated level of inflammatory markers [15,17]. However, as for spinal pains, the confounding effects of obesity, mental health, and unhealthy lifestyles must be considered when examining the relationship between diabetes and migraine [9,17,18,19].
A higher prevalence of NP, LBP, and migraine among women than men is a constant finding in the presence of diabetes [5,8,10,11,15,20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
The underlying mechanism that could explain these differences remains unknown, but several reasons could be suggested, such as the increase in the inflammatory response caused by estrogen or the rapid spine degeneration in women after menopause [20,23].
Investigating the association of diabetes with NP, LBP, and migraine is, therefore, important to improving the prevention and treatment and to implementing public health policies to reduce the health and economic burden derived from these conditions. The Spanish healthcare system offers universal coverage to residents and is free of charge. All health services are provided, including physical therapy for chronic pain.
The aims of this investigation were as follows: (i) to assess the time trend in the prevalence of chronic neck pain (CNP), chronic low back pain (CLBP), and migraine or frequent headache (MFH) among people with diabetes in Spain from 2014 to 2020; (ii) to identify sex differences in the prevalence of these pain sites between men and women with diabetes; (iii) to compare the prevalence of these pain sites between people with diabetes and age–sex-matched non-diabetic subjects; and (iv) to identify which sociodemographic and clinical variables were associated with reporting these pains in people with diabetes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
The study design included a cross-sectional and a retrospective observational case–control study. The data were obtained from the European Health Interview Surveys for Spain (EHISSs) conducted in 2014 (EHISS2014) and 2020 (EHISS2020). The European Health Interview Survey was started in 2008, promoted by the European Commission, with the objective of providing comparable reliable data on health status, health determinants, and healthcare uses from population surveys for all European Union member states [27].
EHISSs provide a representative sample of adults aged ≥ 15 years residing in households in Spain. Information was collected through a home-based personal interview from January to December 2014 for the EHISS2014. The EHISS2020 was initially intended to be conducted from July 2019 to July 2020 using the same methodology as the EHISS2014, but due to the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown period in Spain, from March 2020 until July 2020, interviews were conducted by telephone [28,29].
All the variables used in this investigation were collected with questions identically worded in both surveys. A detailed description of the methodology, questionnaires, and non-response data for the EHISS2014 and EHISS2020 can be found on the website of the Spanish National Statistics Institute (SNSI) [28].
2.2. Study Population and Matching Method
We included participants aged 18 years or over. To identify those persons interviewed with and without diabetes, we used the question: “Has your doctor told you that you are suffering from diabetes?” Those with an affirmative answer were considered “cases” for study purposes. For each “case”, we selected a person interviewed in the same EHISS with the identical sex, age, and region of residence who had answered “no” to the previous questions. This participant was defined as a matched “control”. In the database, if we found more than one possible matched control for a case, the control was selected randomly. Of the 1945 participants of the EHISS2014 with diabetes, 1871 could be matched (96.20%); the equivalent figures for the EHISS2020 were 2150 and 2049 (95.30%).
2.3. Study Variables
The dependent study variables were the self-reported presence of “CNP”, “CLBP”, and “MFH”. The questions and possible answers used to classify participants in the EHISS2014 and EHISS2020, based on being affected by these pains, are detailed in Supplementary Table S1. The variable “spinal pain” included those participants who answered affirmatively to one or both questions regarding back pain (CNP and/or CLBP). The variable “any pain site” included those who reported suffering in one or more of any of the three pain sites studied. According to the EHISS definitions, a pain is considered chronic if it lasts for at least six months [28].
Study covariates included sociodemographic characteristics, such as age, sex, educational level, and living with a partner. Pain-related variables collected were pain intensity in the last four weeks and consumption of pain medication in the last two weeks.
To assess the health status of the participants, self-rated health over the last year and the presence of the following chronic conditions were analyzed: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart diseases (heart failure and/or coronary disease), stroke, cancer, mental disease (anxiety and/or depression), and high blood pressure. Lifestyle variables included sedentary lifestyle, alcohol consumption, active smoking, and body mass index (<25, 25–29.9, and ≥30) (Table S1).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The prevalence of CNP, CLBP, and MFH was estimated according to study variables for people with and without diabetes. As descriptive statistics, we provide means with standard deviations for quantitative variables and absolute numbers with relative frequencies expressed as percentages for qualitative variables. To compare quantitative and qualitative variables, we used the Student t-test and the chi-square test, respectively. When comparisons were conducted for cases vs. matched controls, paired Student t-tests, and the McNemar test were applied.
Logistic regression models were constructed to identify which study variables were independently associated with reporting CNP, CLBP, and MFH among participants with diabetes. The recommendation of Hosmer et al. was used for model construction [30]. The following steps were followed: (i) bivariate analysis of each independent study variable; (ii) selection of those variables with a significant association (p < 0.10) in the bivariate analysis and those considered important in previous research; (iii) checking the contribution of each variable included in the model using the Wald statistic; (iv) using the likelihood ratio to compare successive models as variables were included and excluded; (v) once the final model was obtained, checking the linearity between variables and two-way interactions. The results of the multivariable models are presented as adjusted odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
The statistical software used was STATA 14.0 (StataCorp. 2015. Stata Statistical Software: Release 14. StataCorp LP.: College Station, TX, USA).
2.5. Ethical Aspects
The databases of the EHISS2014 and EHISS2020 can be freely downloaded from the website of the Spanish Ministry of Health [31]. According to Spanish law, for free and public access to anonymous data collected by the health authorities, the approval of an ethics committee is waived.
3. Results
The total number of individuals with self-reported diabetes analyzed was 3920 (1871 in the EHISS2014 and 2049 in the EHISS2020). The distribution of the study population by study variables according to the year of survey is shown in Table 1. In both surveys, the mean ages were significantly higher among people with diabetes than among participants without this condition (68.61 years vs. 51.71 years, p < 0.001, in the EHISS2014; and 70.23 years vs. 53.84 years, p < 0.001, in the EHISS2020), and women were slightly over-represented in the sample.

Table 1.
Distribution according to study variables of people with self-reported diabetes included in the European Health Interview Surveys for Spain (EHISSs) conducted in 2014 and 2020.
The crude prevalence of CNP (27.9% vs. 24.3; p = 0.010), CLBP (33% vs. 29.4; p = 0.013), spinal pain (39.4% vs. 34.5%; p = 0.001), MFH (8.6% vs. 6.9%; p = 0.043), and “any pain site” (41.9% vs. 36.8%; p = 0.001) decreased from 2014 to 2020. Additionally, the intensity of pain in the last four weeks was significantly lower in 2020 (Table 1).
3.1. Sex Differences in the Prevalence of Pain between Men and Women with Diabetes
Shown in Figure 1 is the prevalence of CNP, CLBP, spinal pain, MFH, and “any pain site” according to sex among people with diabetes included in the EHISSs conducted in 2014 and 2020. As can be seen in the figure, women with diabetes had a significantly higher prevalence of all the pain sites analyzed than men with diabetes in both surveys (all p < 0.001). It is remarkable that around half of the women with diabetes reported at least one pain (51.6% in the EHISS2014 and 46.9% in the EHISS2014), with men showing a 20% lower prevalence. MHF was the pain with the lowest figures for women and men with diabetes in both surveys, with 12.5% and 10.1% for women and 4.3% and 3.7% for men in 2014 and 2020, respectively. However, this type of pain was almost three-fold higher among women. CLBP was reported by 40% of women and 25.3% of men in 2014, and by 36.6% of women and 22.1% of men in 2020. Even though this was the most frequent pain site, the proportional difference between both sexes was the lowest (58% in 2014 and 66% in 2020). The prevalence of CNP was twice as high among women with diabetes in 2014 (36.6% vs. 18.3%) and 2020 (32.1% vs. 16.3%) when compared to men with diabetes (both p < 0.001).
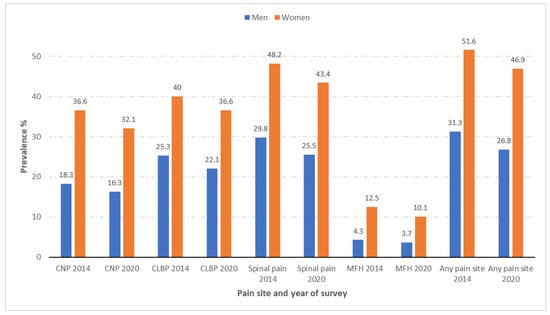
Figure 1.
Prevalence of chronic neck pain (CNP), chronic low back pain (CLBP), spinal pain, and migraine or frequent headache (MFH), and any pain site according to sex among people with self-reported diabetes included in the European Health Interview Surveys for Spain (EHISSs) conducted in 2014 and 2020.
The prevalence of all the types of pain described was significantly higher in women than in men in both the EHISS2014 and the EHISS2020.
3.2. Differences in the Prevalence of Pain between People with Diabetes and Age–Sex-Matched Non-Diabetic Subjects
The comparison of the prevalence of CNP, CLBP, and MFH between subjects with diabetes and sex–age-matched subjects without diabetes according to sociodemographic variables and pain characteristics can be seen in Table 2. Once the two surveys were joined, the prevalence of CNP (26.0% vs. 21.1%; p < 0.001), CLBP (31.2% vs. 25.0%; p < 0.001), and MFH (7.7% vs. 6.5%; p = 0.028) was significantly higher for people with diabetes than among age–sex-matched non-diabetic participants. The frequency of the three pain sites was significantly higher among people with diabetes than among controls without diabetes when the populations were stratified by sex, age, educational level, and living with partner.

Table 2.
Prevalence of chronic neck pain, chronic low back pain, and migraine or frequent headache among subjects with diabetes and sex–age-matched subjects without diabetes according to sociodemographic variables and pain characteristics.
The prevalence of pain sites according to clinical variables and lifestyles among subjects with diabetes and matched controls is shown in Table 3. For all the categories of the variables shown in Table 3, the prevalence of CNP, CLBP, and MFH was always significantly higher among people with diabetes than among their matched controls without diabetes.

Table 3.
Prevalence of chronic neck pain, chronic low back pain, and migraine or frequent headache among subjects with diabetes and sex–age-matched subjects without diabetes according to clinical variables and lifestyles.
3.3. Variables Associated with CNP, CLBP, and MFH in People with Diabetes
Among people with diabetes, the frequency of self-reported CNP and CLBP increased with age, whereas for MFH, the highest prevalence was observed in the youngest age group. For the three pain sites analyzed, lower educational level and use of pain medications were associated with a significantly higher prevalence (Table 2).
As can be seen in Table 3, in the diabetes population, a remarkably high prevalence of CNP was found for those with concomitant mental disease (47.1%), COPD (42.8%), fair/poor/very poor self-rated health (34.4%), and BMI ≥ 30 (30.3%). On the other hand, the lowest frequencies were reported for those with “very good/good” self-reported health (11.7%) and those who do not have a sedentary lifestyle (19.5%). Among people with diabetes and CLBP, the highest prevalence was observed among those with a mental disease (54.6%), COPD (49.5%), and heart disease (44.8%), and the lowest was observed in those with “very good/good” self-reported health (13.7%). Finally, for MFH, mental disease (20,6%), COPD (14.5%), and cancer (13.3.8%) were the chronic conditions associated with the highest prevalence, and “very good/good” self-reported health (2.8%) was associated with the lowest prevalence.
The results of the multivariable logistic regression model for identifying variables independently associated with each of the three pain sites analyzed are shown in Table 4. After adjusting for possible confounders, women with diabetes had a significantly higher risk of reporting CNP (OR 1.78; 95% CI 1.47–2.16), CLBP (OR 1.19; 95% CI 1.01–1.48), and MFH (OR 2.12; 95% CI 56–2.82) than men with diabetes.

Table 4.
Factors associated with suffering from chronic neck pain, chronic low back pain, and migraine or frequent headache among people with diabetes. Results of multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Furthermore, “fair/poor/very poor” self-reported health, mental disorder, and use of pain medication were variables associated with the three pain sites.
The predictors of CNP also included COPD, concomitant CLBP, and concomitant MFH. Older age, COPD, higher BMI, and concomitant CNP or MFH increased the probability of reporting CLBP. In addition to the variables previously mentioned, concomitant CNP and CLBP were associated with MFH.
Finally, as can be seen in Table 4, the multivariable analysis showed no significant change in the prevalence of CNP, CLBP, or MFH from 2014 to 2020.
4. Discussion
The main results of our investigation are as follows: (1) no improvement was observed in the prevalence of pain among men and women with diabetes from the previous survey conducted six years before; (2) important sex differences in the prevalence of these pains were found, with a higher prevalence and severity among women than men with diabetes; (3) the prevalence of “any pain site” was very high among people with diabetes, and women and men with diabetes had a significantly higher prevalence of all pain sites than age-matched individuals without diabetes; (4) among women with diabetes, worse self-reported health and self-reported mental disease were associated with reporting the three pain sites analyzed after multivariable adjustment.
4.1. Time Trends in the Prevalence of Pains among People with Diabetes
Population-based studies have reported that the incidence rate of spinal pain is decreasing. According to the Global Burden of Disease (GBD), in Spain, the age-standardized incidence rate of LBP showed a downward trend from 1990 to 2019, with an estimated annual percentage change (EAPCs) of −0.84% (95% CI, −0.96 to −0.72) among men and −0.15 (95% CI, −0.21 to −0.09) among women [3]. For both sexes, NP decreased by −0.3% (95% CI, −0.43 to −0.18) [32]. The equivalent figures for migraine were −0.098% for men and −0.12% for women [33].
In the USA, analysis of the National Health Interview Survey showed that the overall age-adjusted prevalence of migraine or severe headache in US adults remained remarkably stable from 2005 to 2018 [25]. In Spain, studies conducted with health surveys reported that the prevalence of NP and LBP increased from 2008/9 to 2011/12 (7.86 vs. 8.56% and 5.18 vs. 5.44%, respectively), and the prevalence of migraine also rose in the first decade of the 21st century (2003–2012) [34,35].
Regarding the trends among people with diabetes in Spain, a very recent report using the Spanish National Survey for 2017 found that the prevalence of NP and LPB was very similar to that found in our investigation, confirming the lack of improvement over time [10].
Even if effective strategies and improvements in therapies exist to reduce the incidence and alleviate spinal pain and migraine, many people who are affected, including those with diabetes, do not seem to be benefiting from this knowledge [10,25,32,33,35].
4.2. Sex Differences in the Prevalence of Pains among People with Diabetes
A remarkable result of our investigation was the higher prevalence of all pain sites among women than men with diabetes. The figures were around twice as high for spinal pain and almost three-fold for MFH. This significantly higher presence of self-reported pain among women was frequently found in previous studies conducted in Spain and other countries [8,10,11,12,16,24,36,37].
Different authors have suggested possible reasons to explain these sex differences in people with diabetes [8,12,24]. Glycemic control is poorer in women than in men with diabetes; therefore, low-grade systemic inflammation may be more severe in women than in their male counterparts. Additionally, depressive symptoms related to diabetes are more frequent among women than men, which could also contribute to the sex-related differences found [8,12,24].
In the general population, it has been seen that women have a greater awareness of the symptoms and signs of pain and perform more housework in non-ergonomic positions [5]. Additionally, female sex hormones, such as estrogen, have been associated with an increase in the inflammatory response, which may result in greater spine degeneration [20,23]. Finally, healthcare provider bias regarding chronic pain has been reported, as women seem to be diagnosed later, with more severe pain, and treated less effectively than men [38].
4.3. Differences in the Prevalence of Pains between People with Diabetes and Matched Controls
In our investigation, the prevalence of the three pain sites studied was high among people with diabetes and significantly higher than among matched controls without diabetes. Comparing the prevalence estimations with other studies is difficult because the questions used to collect pain information, the settings, the methodology, and the study populations usually differ between investigations [6,8,9,10,11,12,16,24,26,36,39,40]. However, spinal pain has been reported to be more prevalent among people with diabetes than the general population in previous investigations [6,8,10,11,12,24,39,40,41]. Pozzobon et al. conducted a meta-analysis of 11 observational studies, including cohort, case–control, cross-sectional, and twin control studies, and confirmed the association of diabetes with NP and LBP [6].
In our population, CNP was reported by 27.9% and 24.3% of people with diabetes in 2014 and 2020, and after matching with subjects without diabetes by year of survey, age, and sex, CNP was 4.9% higher (p < 0.001).
Among a total of 21,889 participants with diabetes included in the UK Biobank cohort, 21.1% of the participants with diabetes had neck and shoulder pain [41]. Analysis of this database found that type 2 diabetes was associated with neck/shoulder pain (adjusted OR 1.14, 95% CI 1.10–1.18) [41].
Molsted et al. compared the self-reported presence of neck and shoulder pain among 951 patients with T2DM and 2923 matched subjects without diabetes using the question: “Have you been bothered by pain in the shoulder and neck over the last 14 days?” The three possible answers were “Yes, very bothered”, “Yes, bothered a little”, or “No”. The percentages of people with T2DM who reported being “very bothered” or “a little bothered” were 52% and 31% (p < 0.001) [24].
In our country, cross-sectional analysis of 2096 twins showed that T2DM was associated with CNP (unadjusted OR 1.35; 95% CI 1.02 to 1.79; adjusted OR 1.37; 95% CI 1.01 to 1.85) [12].
As found for CNP, the prevalence of CLBP after matching was significantly higher among those with diabetes than among matched controls (31.2% vs. 25.0%; p < 0.001). Data from the United States, using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for the period between 2010–2011, reported that the prevalence of CLBP was 19.8% among people with diabetes aged 20–69 years and 12.9% in adults without diabetes (p < 0.001) [39]. In Portugal, a national cross-sectional study using self-reported data, conducted from 2011 to 2013, also found a significantly higher prevalence of CLBP of 18.6% among those with diabetes, compared to 6.8% among those without the condition [36]. The lower rates compared to our results can be explained by the younger age groups analyzed in the USA study and the shorter time periods for pain recall considered in both investigations (3 months vs. 12 months) [36,39]. In the UK Biobank cohort, the prevalence of LBP pain was 32.6%, slightly higher than in our results [41]. In Denmark, the prevalence of LBP in the last 14 days among people with diabetes was 60%, with only 30% of age-, sex-, and region-matched subjects without diabetes reporting this pain [24].
Several causes may explain the association between diabetes and spinal pain [7,8,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. Hyperglycemia and altered fat metabolism that are commonly present in diabetes can negatively affect intervertebral discs (IVDs), causing alterations in the structural composition, which may result in an increased risk of disc prolapse and back pain [42,43]. Animal experiments have found that diabetic rats have an elevated advanced glycation end product concentration and, consequently, lower values of glycosaminoglycan and water contents in discs [42]. This reduces the shock-absorbing properties of the IVDs, making them more susceptible to mechanical damage [42]. Microangiopathy caused by diabetes also causes a lower flow of oxygen and nutrients to the IVDs [44]. All these changes alter the biomechanics of the spine and contribute to spinal pain [7,42,43,44].
Some studies have suggested that dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors may increase pain in the joints [45].
Unlike the findings found for spinal pain, the association between migraine and diabetes is controversial [9,15,16,37]. In our study population, people with diabetes reported MFH in a small but significantly higher proportion than matched non-diabetic subjects (7.7% vs. 6.5%; p = 0.028). In a previous study conducted in Spain, after multivariable adjustment, diabetes was not associated with a higher risk of migraine (adj. OR 1.06; 95% CI 0.89–1.25) [16].
Previous studies have reported the prevalence of migraine to be similar or higher among people with diabetes, and others found an inverse relationship between diabetes and migraine [9,15,16,37].
The relationship of diabetes with migraine seems to be inversely related to age, with a higher prevalence being found among younger subjects, decreasing with age. This trend was also seen in our population (Table 2) [15,16].
Despite the contradictory results that exist concerning the relationship between diabetes and migraine, diabetes may be relevant in migraine pathophysiology, considering that diabetic patients display changes in vascular reactivity and nerve conduction [15]. Possible mechanisms involved have been suggested [15]. Several pro-inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, IL-1b, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α, are elevated in migraine and diabetes. Furthermore, the sympathetic nervous system and autonomic dysfunction found in people with diabetes may also explain the relationship between migraine and DM [15]. However, further studies should clarify this issue.
4.4. Variables Associated with Pains among People with Diabetes
Besides being a woman, four study variables were associated with a higher prevalence of NP, CLBP, and MFH. These were bad self-reported health, self-reported mental disease, use of pain medication, and the presence of concomitant pain in any other site.
The relationship of worse self-rated health with any of the pain localizations analyzed was expected, as all these pains have important effects on the quality of life of people with diabetes and have been described before by other authors [10,11,15,16,24,46].
The association between mental diseases and spinal pain or migraine has been previously reported in the general population and among people with diabetes [8,10,16,26,34,35,47,48]. It is well known that diabetes has deleterious effects on mental health and suffering from depression and anxiety is a known risk factor associated with the transition from acute to chronic back pain [47,48].
The frequent use of pain medication has been reported among DM sufferers [10,11,16,46]. In our study population, almost half of the persons interviewed had consumed pain medication in the last two weeks. In the US, 78% of people with diabetes and chronic pain reported that they used pain medication on either a regular or an occasional basis [46].
We agree with other authors in that, among people with diabetes, the highest ORs were found for reporting pain in one site and the presence of pain in any other site [10,11,16,40,41,49]. It has been found that a higher number of pain sites results in multiple stimuli to the brain; therefore, the brain chemistry is altered, meaning that it is more likely that the pain becomes chronic [2].
Among people with diabetes, the multivariable model for LBP showed a significant association with a higher BMI, which has been previously reported in studies conducted in populations with diabetes [24,39,46,50,51,52]. Molsted et al. found that, in people with diabetes of both sexes, BMI was associated with a higher prevalence of LBP [24]. Data from the Nord-Trøndelag health study confirmed that BMI was strongly associated with both diabetes and low back pain [51,52].
4.5. Recommendations and Future Investigations
Even if CLBP, CNP, and MH have different etiologies, risk factors, and treatments, there are many actions that could be implemented to reduce the incidence, disability, and loss of quality of life caused by these pains [8,10,11,12,16,24,26,37,39,40,43,46,50,51,52]. Among possible interventions are screening for pain in patients with diabetes in clinical settings, creating specialized pain units, providing health education for patients and families regarding nonpharmacological treatments, and assessing occupational risk factors. Given the importance of mental health on pain in people with diabetes, the presence of depression and anxiety should be assessed on a regular basis [12]. Regarding lifestyles, exercise therapy and weight reduction should be recommended to patients with diabetes to lower their risk of spinal pain [12,15]. Among people with diabetes, physical exercise can reduce muscle mass loss, negative structural changes in the IVDs, and fat infiltration in the paraspinal muscles [53]. In people with diabetes, improvement in lifestyle can reduce the frequency of migraine attacks, probably by affecting peripheral and central mechanisms [15]. Future research should include longitudinal studies to obtain causal evidence of the associations found in cross-sectional studies and to find explanations for the sex-related differences in the association of diabetes with spinal pain and MFH.
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
The main strength of this study is the use of two large national health surveys that provide a representative sample of the Spanish population, providing data on sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle variables that are not usually recorded in clinical records. We analyzed the data of almost four thousand individuals with self-reported diabetes who were randomly selected from the Spanish general population, and not from health services, therefore, increasing the external validity of our results. Furthermore, we used a matched design to compare people with and without diabetes, avoiding the confounding effect of age and sex.
However, there are relevant limitations that should be considered. First, with the cross-sectional design that was used, the causality issue cannot be properly addressed. Second, in the multivariable analyses, many potential confounding factors were included, but the possibility of residual confounding factors cannot be ruled out. Third, even if the questions used for self-reported CNP, CLBP, and MFH were formulated using worldwide definitions of these conditions, these questions have not been validated in the EHISS.
Fourth, the validity of self-reported diabetes has not been evaluated in the EHISS. However, in a previous study conducted in our country, self-reported diabetes showed a sensitivity of over 70% and a specificity of over 95% when compared with medical records [54]. Self-reporting has been used as a valid method to determine diabetes status in Spain and different countries [6,9,10,11,16,25,39,55,56,57,58,59,60].
Fifth, important information on diabetes is not available in the EHISS, including the diabetes type, duration, pharmacological treatments, disabilities, and chronic complications. Given the epidemiology of diabetes in Spain, it is expected that over 96% of individuals with self-reported diabetes have type 2 [61]. This information was also lacking for the pain sites studied. Previous studies have suggested that people with diabetes taking metformin may be less likely to report back, neck, and multisite musculoskeletal pain than those not taking this medication [41]. Sixth, the validity of information obtained during interviews may be affected by recall errors or socially desirable responses, i.e., the tendency of respondents to reply in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others. Finally, the initial response rates for the EHISS 2014 and EHISS2020 were 61% and 59%, respectively, and thus the existence of a non-response bias must be considered [28]. Regarding this point, the EHISS2020 data collection method was affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, and thus the possible effect of the pandemic itself and the change in collection method on our results is unpredictable [29].
5. Conclusions
The prevalence of CNP, CLBP, and MFH among men and women with diabetes has remained stable over time. Remarkable sex differences were found, with a higher prevalence and severity among women than men with diabetes. The prevalence of all pains studied was very high among people with diabetes, and women and men with diabetes had a significantly higher prevalence of all pain sites analyzed than age-matched individuals without diabetes. Among women with diabetes, worse self-reported health and self-reported mental disease were associated with reporting the three pain sites analyzed after multivariable adjustment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm11236953/s1, Table S1: Definition of variables according to the questions included in the European Health Interview Surveys in Spain conducted in years 2014 and 2020.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.J.-G. and N.P.-F.; Methodology, J.J.Z.-L. and A.L.-d.-A.; Validation, D.C.-A.; Data curation, N.C.-C. and C.N.; Formal analysis, J.d.M.-D.; Funding: A.L.-d.-A. and R.J.-G.; Writing—original draft, R.J.-G. and N.P.-F.; Writing—review and editing, J.J.Z.-L., D.C.-A., C.N., A.L.-d.-A., N.C.-C. and J.d.M.-D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is a part of the research funded by the: FIS (Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias—Health Research Fund, Instituto de Salud Carlos III) and co-financed by the European Union through the Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER, “Una manera de hacer Europa”): grant no. PI20/00118, by the Universidad Complutense de Madrid. Grupo de Investigación en Epidemiología de las Enfermedades Crónicas de Alta Prevalencia en España (970970) and the Convenio V-PRICIT de la Comunidad de Madrid y la Universidad Complutense de Madrid (“Programa de Excelencia para el Profesorado Universitario” INV.AY.20.2021.1E126).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
According to the contract signed with the Spanish Ministry of Health and Social Services, which provided access to the databases from the Spanish National Health Survey and European Health Survey for Spain, we cannot share the databases with any other investigator, and we have to destroy the databases once the investigation has concluded. Consequently, we cannot upload the databases to any public repository. However, any investigator can apply for access to the databases by filling out the questionnaire available at http://www.msssi.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/estadisticas/estMinisterio/SolicitudSNHSdocs/Formulario_Peticion_Datos_SNHS.pdf. (accessed on 14 September 2022). All other relevant data are included in the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Safiri, S.; Karamzad, N.; Kaufman, J.S.; Bell, A.W.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Collins, G.; Kolahi, A.A. Prevalence, Deaths and Disability-Adjusted-Life-Years (DALYs) Due to Type 2 Diabetes and Its Attributable Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990-2019: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 838027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Pourfathi, H.; Eagan, A.; Mansournia, M.A.; Khodayari, M.T.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Kaufman, J.; Collins, G.; Dai, H.; Bragazzi, N.L.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine in 204 countries and territories, 1990 to 2019. Pain 2022, 163, e293–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ye, H.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Ye, J.; Liao, M.; Chen, X. Epidemiological trends of low back pain at the global, regional, and national levels. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, L. Incidence trend of five common musculoskeletal disorders from 1990 to 2017 at the global, regional and national level: Results from the global burden of disease study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.J.; Stovner, L.J.; Jensen, R.; Uluduz, D.; Katsarava, Z. Lifting The Burden: The Global Campaign against Headache. Migraine remains second among the world’s causes of disability, and first among young women: Findings from GBD2019. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzobon, D.; Ferreira, P.H.; Dario, A.B.; Almeida, L.; Vesentini, G.; Harmer, A.R.; Ferreira, M.L. Is there an association between diabetes and neck and back pain? A systematic review with meta-analyses. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, S.; Akhter, Z.; Sukaina, M.; Sohail, F.; Nasir, F. Association of Diabetes With Lower Back Pain: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, L.; Rathmann, W.; Koyanagi, A.; Haro, J.M.; Kostev, K. Association between type 2 diabetes and chronic low back pain in general practices in Germany. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, M.; Maleki, F.; Khoramdad, M.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Kolahi, A.A.; Safiri, S. A systematic literature review of observational studies of the bilateral association between diabetes and migraine. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Florencio, L.; Lopez-de-Andres, A.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Palacios-Ceña, D.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Jimenez-Garcia, R.; Perez-Farinos, N.; Carabantes-Alarcon, D.; Martinez-Hernandez, D.; Albaladejo-Vicente, R. Is There an Association between Diabetes and Neck and Back Pain? Results of a Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Garcia, R.; Del Barrio, J.L.; Hernandez-Barrera, V.; de Miguel-Díez, J.; Jimenez-Trujillo, I.; Martinez-Huedo, M.A.; Lopez-de-Andres, A. Is there an association between diabetes and neck pain and lower back pain? Results of a population-based study. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dario, A.; Ferreira, M.; Refshauge, K.; Harmer, A.; Sánchez-Romera, J.; Pérez-Riquelme, F.; Cisneros, L.; Ordoñana, J.; Ferreira, P. Mapping the association between back pain and type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study of adult Spanish twins. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadiya, G.; Gohil, K.; Gandbhir, V.; Shakya, A.; Soni, Y. Hyperglycemia and its influence on development of lumbar degenerative disc disease. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2020, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadiya, G.; Saindane, K.; Soni, Y.; Gohil, K.; Shakya, A.; Attar, M.U. Diabetes Mellitus and the Development of Lumbar Canal Stenosis: Is There Any Relevance? Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Mancilla, E.; Al-Hassany, L.; Villalón, C.M.; Maassen Vandenbrink, A. Metabolic Aspects of Migraine: Association With Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 686398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-Andrés, A.; Luis Del Barrio, J.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; de Miguel-Díez, J.; Jimenez-Trujillo, I.; Martinez-Huedo, M.A.; Jimenez-García, R. Migraine in adults with diabetes; is there an association? Results of a population-based study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2018, 11, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casucci, G.; Villani, V.; Cologno, D.; D’Onofrio, F. Migraine and metabolism. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, S81–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.; Manack, A.; Serrano, D.; Turkel, C.; Lipton, R. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 2010, 81, 428.e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horev, A.W.I.; Lantsberg, L.; Ifergane, G. A high incidence of migraine with aura among morbidly obese women. Headache 2005, 45, 936.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetvik, K.G.; MacGregor, E.A. Sex differences in the epidemiology, clinical features, and pathophysiology of migraine. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, A.J.; Lissounov, A.; Knezevic, I.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. Pain and sex hormones: A review of current understanding. Pain Manag. 2016, 6, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazeminasab, S.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Amiri, P.; Pourfathi, H.; Araj-Khodaei, M.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Kolahi, A.A.; Safiri, S. Neck pain: Global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, D.; Bain, C.; Williams, G.; March, L.; Brooks, P.; Blyth, F.; Woolf, A.; Vos, T.; Buchbinder, R. A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain. Arthritis. Rheum. 2012, 64, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molsted, S.; Tribler, J.; Snorgaard, O. Musculoskeletal pain in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 96, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burch, R.; Rizzoli, P.; Loder, E. The prevalence and impact of migraine and severe headache in the United States: Updated age, sex, and socioeconomic-specific estimates from government health surveys. Headache 2021, 61, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Ceña, D.; Albaladejo-Vicente, R.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Lima-Florencio, L.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Jimenez-Garcia, R.; López-de-Andrés, A.; de Miguel-Diez, J.; Perez-Farinos, N. Female Gender Is Associated with a Higher Prevalence of Chronic Neck Pain, Chronic Low Back Pain, and Migraine: Results of the Spanish National Health Survey, 2017. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurostat. European Health Interview Survey (EHIS). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/microdata/european-health-interview-survey (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Europea de Salud en España. [European Health Interview Surveys for Spain]. Available online: https://www.ine.es/dyngs/INEbase/es/operacion.htm?c=Estadistica_C&cid=1254736176784&menu=metodologia&idp=1254735573175 (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Ministerio de Sanidad. European Health Survey in Spain 2020 [Encuesta Europea de Salud en España 2020]. Available online: https://www.mscbs.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/EncuestaEuropea/Enc_Eur_Salud_en_Esp_2020.htm (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Sanidad. Encuesta Europea de Salud en España. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/EncuestaEuropea/home.htm (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Shin, D.W.; Shin, J.I.; Koyanagi, A.; Jacob, L.; Smith, L.; Lee, H.; Chang, Y.; Song, T.J. Global, regional, and national neck pain burden in the general population, 1990-2019: An analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Neurol 2022, 13, 955367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Headache Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990-2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 954–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Ceña, D.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Carrasco-Garrido, P.; Jiménez-García, R.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C. Prevalence of neck and low back pain in community-dwelling adults in Spain: An updated population-based national study (2009/10-2011/12). Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Palacios-Ceña, D.; Salom-Moreno, J.; López-de-Andres, A.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Jiménez-Trujillo, I.; Jiménez-García, R.; Gallardo-Pino, C.; García-Gómez-de-las-Heras, M.S.; Carrasco-Garrido, P. Has the prevalence of migraine changed over the last decade (2003-2012)? A Spanish population-based survey. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, N.; Rodrigues, A.; Eusébio, M.; Ramiro, S.; Machado, P.; Canhão, H.; Branco, J.C. Prevalence and social burden of active chronic low back pain in the adult Portuguese population: Results from a national survey. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, F.S.; Rahmanian, M.; Namiranian, N.; Arzaghi, S.M.; Dehghan, F.; Chavoshzade, F.; Sepehri, F. Migraine and type 2 diabetes; is there any association? J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2016, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samulowitz, A.; Gremyr, I.; Eriksson, E.; Hensing, G. “Brave Men” and “Emotional Women”: A Theory-Guided Literature Review on Gender Bias in Health Care and Gendered Norms towards Patients with Chronic Pain. Pain Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 6358624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoon, A.; Bydon, M.; Kerezoudis, P.; Maloney, P.R.; Rinaldo, L.; Yeh, H.C. Chronic low-back pain in adult with diabetes: NHANES 2009-2010. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pico-Espinosa, O.J.; Skillgate, E.; Tettamanti, G.; Lager, A.; Holm, L.W. Diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidaemia as risk factors for frequent pain in the back, neck and/or shoulders/arms among adults in Stockholm 2006 to 2010 - Results from the Stockholm Public Health Cohort. Scand J. Pain 2017, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-E-Silva, A.P.; Harmer, A.R.; Ferreira, M.L.; Ferreira, P.H. The effect of the anti-diabetic drug metformin on musculoskeletal pain: A cross-sectional study with 21,889 individuals from the UK biobank. Eur. J. Pain 2021, 25, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, A.J.; Berg-Johansen, B.; Metz, L.N.; Miller, S.; La, B.; Liebenberg, E.C.; Coughlin, D.G.; Graham, J.L.; Stanhope, K.L.; Havel, P.J.; et al. Alterations in intervertebral disc composition, matrix homeostasis and biomechanical behavior in the UCD-T2DM rat model of type 2 diabetes. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldo, L.; McCutcheon, B.A.; Gilder, H.; Kerezoudis, P.; Murphy, M.; Maloney, P.; Hassoon, A.; Bydon, M. Diabetes and Back Pain: Markers of Diabetes Disease Progression Are Associated With Chronic Back Pain. Clin. Diabetes 2017, 35, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunhagen, T.; Shirazi-Adl, A.; Fairbank, J.C.; Urban, J.P. Intervertebral disk nutrition: A review of factors influencing concentrations of nutrients and metabolites. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 42, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascolo, A.; Rafaniello, C.; Sportiello, L.; Sessa, M.; Cimmaruta, D.; Rossi, F.; Capuano, A. Dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitor-induced arthritis/arthralgia: A review of clinical cases. Drug. Saf. 2016, 39, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krein, S.L.; Heisler, M.; Piette, J.D.; Makki, F.; Kerr, E.A. The effect of chronic pain on diabetes patients’ self-management. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevans, J.M.; Delitto, A.; Khoja, S.S.; Patterson, C.G.; Smith, C.N.; Schneider, M.J.; Freburger, J.K.; Greco, C.M.; Freel, J.A.; Sowa, G.A.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Transition From Acute to Chronic Low Back Pain in US Patients Seeking Primary Care. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2037371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.E.E.; Nicolson, K.P.; Smith, B.H. Chronic pain: A review of its epidemiology and associated factors in population-based studies. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e273–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strine, T.W.; Hootman, J.M. US national prevalence and correlates of low back and neck pain among adults. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 57, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eivazi MAbadi, L. Low back pain in diabetes mellitus and importance of preventive approach. Health Promot. Perspect. 2012, 2, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heuch, I.; Heuch, I.; Hagen, K.; Sørgjerd, E.P.; Åsvold, B.O.; Zwart, J.A. Does diabetes influence the probability of experiencing chronic low back pain? A population-based cohort study: The Nord-Trøndelag Health Study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, S.; Midthjell, K.; Tesfamarian, M.Y.; Grill, V. Age, overweight and physical inactivity increase the risk of latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: Results from the Nord-Trøndelag health study. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teichtahl, A.J.; Urquhart, D.M.; Wang, Y.; Wluka, A.E.; O’Sullivan, R.; Jones, G.; Cicuttini, F.M. Physical inactivity is associated with narrower lumbar intervertebral discs, high fat content of paraspinal muscles and low back pain and disability. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, J.M.; Tormo, M.J.; Egea-Caparrós, J.M.; Ortolá-Devesa, J.B.; Navarro, C. Accuracy of self-reported diabetes, hypertension and hyperlipidemia in the adult Spanish population. DINO study findings. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2009, 62, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espelt, A.; Goday, A.; Franch, J.; Borrell, C. Validity of self-reported diabetes in health interview surveys for measuring social inequalities in the prevalence of diabetes. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2012, 66, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paalanen, L.; Koponen, P.; Laatikainen, T.; Tolonen, H. Public health monitoring of hypertension, diabetes and elevated cholesterol: Comparison of different data sources. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 28, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Morita, A.; Goto, M.; Sasaki, S.; Miyachi, M.; Aiba, N.; Kato, M.; Terauchi, Y.; Noda, M.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Validity of diabetes self-reports in the Saku diabetes study. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.C.; Barros, M.B.A.; Szwarcwald, C.L.; Machado, Í.E.; Malta, D.C. Differences between self-reported and laboratory measures of diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and hypercholesterolemia. Ciên Saúde Colet. 2021, 26, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.L.; Pankow, J.S.; Heiss, G.; Selvin, E. Validity and reliability of self-reported diabetes in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, F.; Moradinazar, M.; Hamzeh, B.; Rezaeian, S. The reliability of self-reporting chronic diseases: How reliable is the result of population-based cohort studies. J. Prev. Med. Hygiene 2019, 60, E349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health. Prevalencia de Diabetes Mellitus. BDCAP. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/estadisticas/estMinisterio/SIAP/3Prev_diabetes_mellitus.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).