Comparison of Clinical Manifestations and Pathology between Kimura Disease and IgG4-Related Disease: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
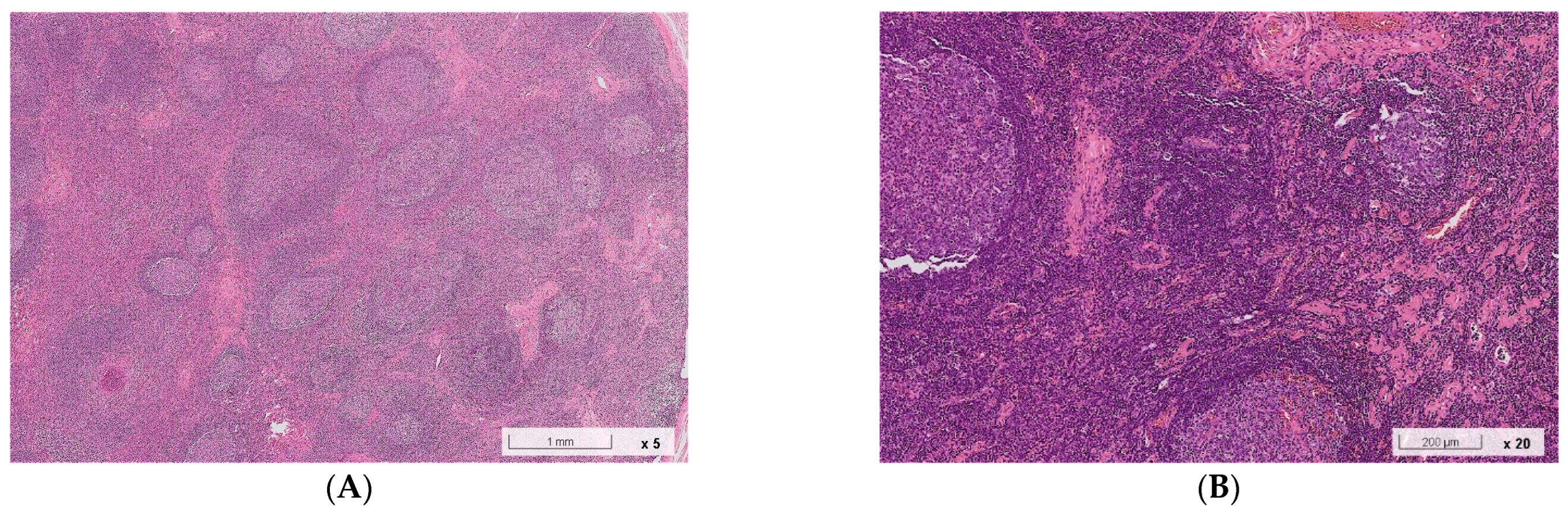
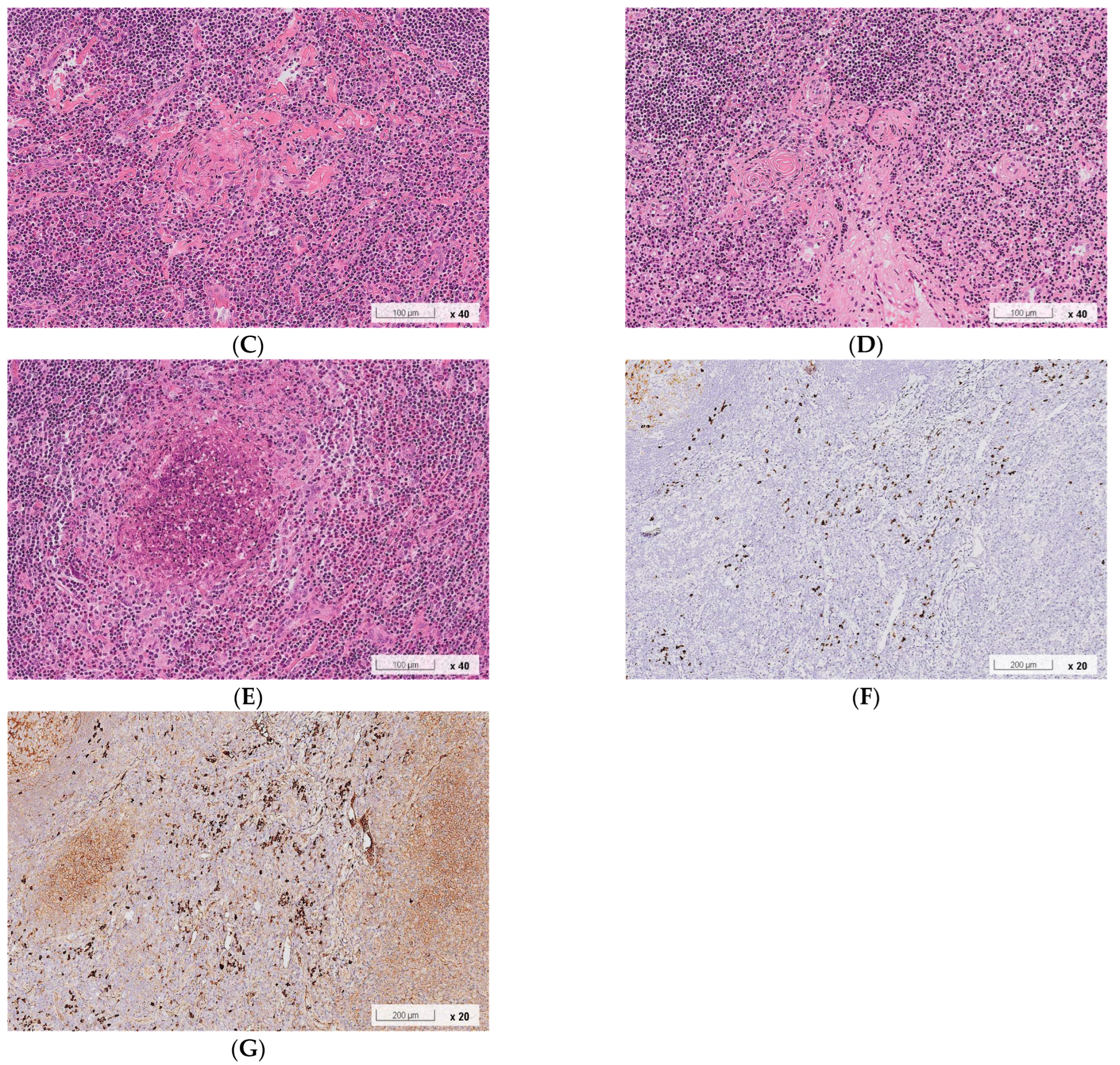
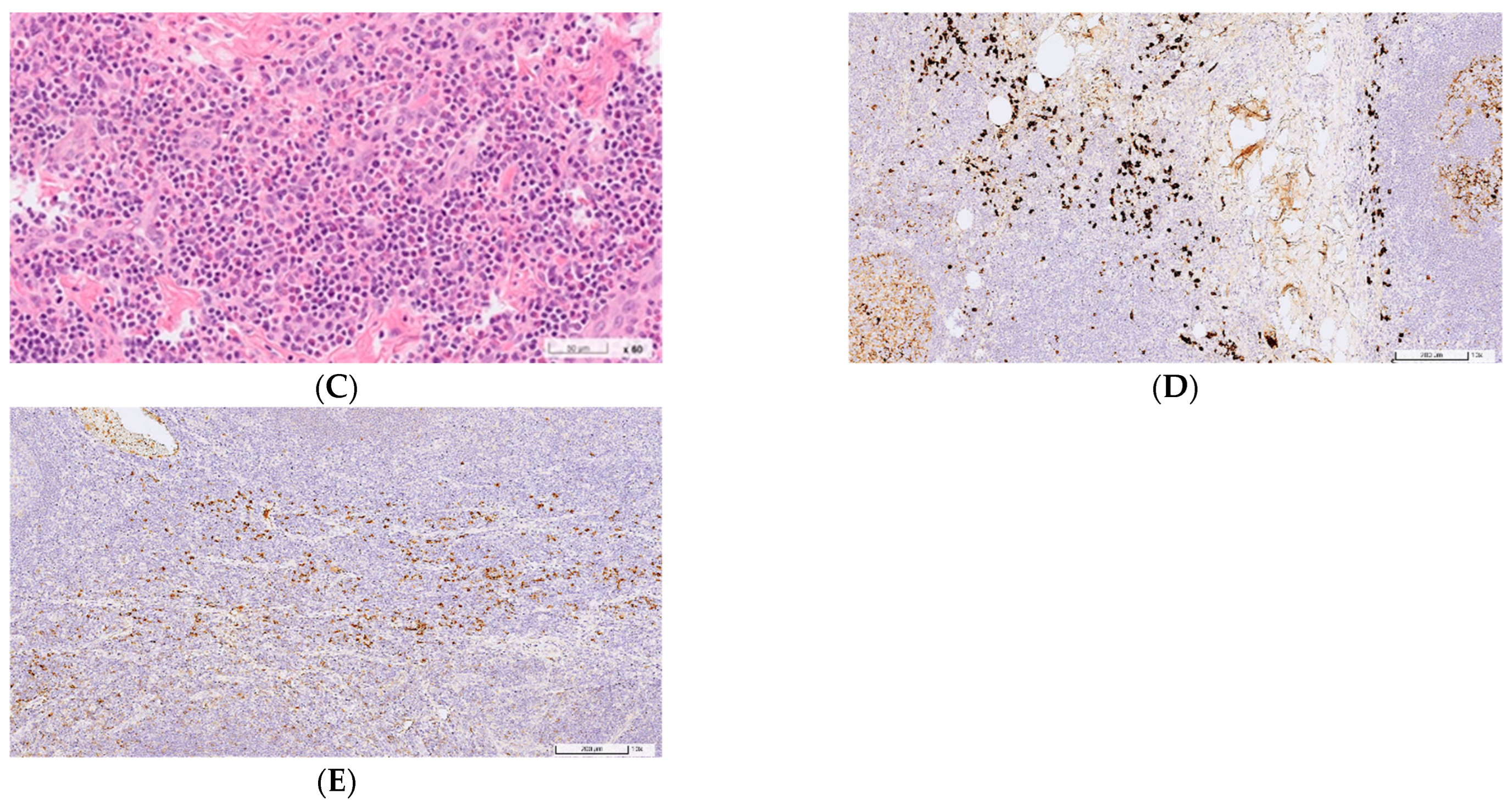
2.1. Case 1
2.2. Case 2
3. Discussion
| Kimura Disease (KD) | IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4RD) | Case 1 | Case 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Distribution | 10–80 [3,4,7,12,17] | 20–80 [10,12,17,19] | 38 | 36 |
| Median years | 30–40 [3,4,7,12,17] | 50–60 [10,12,17,18,19,20] | N/A | N/A |
| Male predominance | Strong (80%) [3,4,7,12,17] | Slight (60%) [10,12,16,18,19,20] | Male | Male |
| Head and neck predominance | Strong (80%) [4,7,12] | Slight (54%) [10,12,18,21] | Postauricular region | Postauricular region |
| Peripheral blood eosinophilia | Frequently (80%) [4,7,8,12,17] | Occasionally (20%) [12,16,17,19,20,25] | N/A 5.8% | 24.0%19.3% |
| Serum IgE elevation (>100 kU/L) | Frequently (82%) [3,4,7,12,17] | Rarely (8%) [12,17] | N/A713 | N/A |
| Serum IgG4 elevation (>135 mg/dL) | Occasionally (11%) [3,7,12,17] | Frequently (82%) [10,12,17,19] | N/A193 | N/A215 |
| Histological features | ||||
| Lymphoplasmacytic infiltration | Almost always (98%) [7,12,17] | Almost always (95%) [12,17,22] | Positive | Positive |
| Lymphoid follicular hyperplasia | Almost always (95%) [12,17] | Almost always (92%) [12,17] | Positive | Positive |
| Eosinophil infiltration | Almost always (100%) [7,12] | Sometimes (49%) [12,19,22] | Positive | Positive |
| Eosinophilic abscess | Frequently (74%) [12,17] | Rarely (1%) [12,17] | Positive | Negative |
| Proliferation of postcapillary venules | Frequently (82%) [7,12] | Sometimes (55%) [12] | Positive | Positive |
| Stromal fibrosis | Frequently (80%) [7,12,17] | Frequently (82%) [12] | Positive | Positive |
| Storiform fibrosis | Rarely (6%) [7,12,17] | Sometimes present (49%) [10,12,17,22] | Negative | Negative |
| Obliterative phlebitis | Rarely (1%) [7,12] | Occasionally present (22%) [10,12,19,22] | Negative | Negative |
| IgG4 (+) plasma cell ≥ 50/HPF | Occasionally (36%) [7,12] | Almost always (100%) [12,17,19] | Positive | Positive |
| IgG4/IgG (+) plasma cell ratio ≥ 40% | Occasionally (39%) [7,12] | Almost always (100%) [12,17,19] | Positive | Positive |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Allergic disease | Occasionally (15%) [4,7,12,17] | Sometimes (46%) [12,16,17,18,19,25] | Allergic urticaria | Negative |
| Nephropathy | Occasionally (14%) [4,7,8,17] | Occasionally (12%) [10,18] | Negative | Negative |
| Malignancy | No report | Rare (1.2%) [18] | Negative | Negative |
| Recurrence | Sometimes (25%) [4,7] | Sometimes (38%) [18,20,25] | Negative | Negative |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimm, H.T.; Szeto, C. Eosinophilic hyperplastic lymphogranuloma, comparison with Mikulicz’s disease. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 1937, 23, 699–700. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, T.; Yoshimura, S.; Ishikawa, E. On the unusual granulation combined with hyperplastic changes of lymphatic tissue. Trans. Soc. Pathol. Jpn. 1948, 37, 179–180. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Mo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Clinical, Pathological, Laboratory Characteristics, and Treatment Regimens of Kimura Disease and Their Relationships With Tumor Size and Recurrence. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 720144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakehi, E.; Kotani, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Fukuyasu, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Sakurai, S.; Hirotani, A.; Simizu, K.; Fujita, R.; Shoji, K.; et al. Kimura’s disease: Effects of age on clinical presentation. QJM Int. J. Med. 2020, 113, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Sun, G.; Cao, Y.; Gao, N.; Qi, W. Clinical analysis of Kimura’s disease in 24 cases from China. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, K.; Itami, S.; Hatano, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Takayasu, S. In vivo expression of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 and IFN-gamma mRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and effect of cyclosporin A in a patient with Kimura’s disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 137, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottler, D.; Barète, S.; Quéreux, G.; Ingen-Housz-Oro, S.; Fraitag, S.; Ortonne, N.; Deschamps, L.; Rybojad, M.; Flageul, B.; Crickx, B.; et al. Retrospective Multicentric Study of 25 Kimura Disease Patients: Emphasis on Therapeutics and Shared Features with Cutaneous IgG4-Related Disease. Dermatology 2015, 231, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, Y.; Furusu, A.; Nishino, T.; Ichinose, H.; Ohnita, A.; Iwasaki, K.; Taguchi, T.; Kohno, S. Membranous nephropathy and Kimura’s disease man-ifesting a hip mass. A case report with literature review. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, H.; Okazaki, K.; Kawa, S.; Takahashi, H.; Goto, H.; Matsui, S.; Ishizaka, N.; Akamizu, T.; Sato, Y.; Kawano, M. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Perugino, C.A.; Naden, R.; Choi, H.K.; Stone, J.H. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: An analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, T.; Miyanaga, T.; Tago, O.; Udagawa, M.; Kamiyama, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Ishikawa, O. Isolated cutaneous manifestation of IgG4-related disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ng, C.S.; Yin, W. A comparative study of Kimura’s disease and IgG4-related disease: Similarities, differences and overlapping features. Histopathology 2021, 79, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Fang, Z.; Kong, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z. Kimura’s disease or IgG4-related disease? A case-based review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 34, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Naden, F.R.P.; Chari, S.; Choi, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Dicaire, J.; Hart, P.A.; Inoue, M.D.; Khosroshahi, A.; Kubota, K.; et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.; Verhagen, J.; Blaser, K.; Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Mechanisms of immune suppression by interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta: The role of T regulatory cells. Immunology 2006, 117, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, D.; Xia, C.; et al. Salivary gland involvement disparities in clinical characteristics of IgG4-related disease: A retrospective study of 428 patients. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-X.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Sun, Z.-P.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, G.-Y. Differential diagnosis of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis and Kimura’s disease of the salivary gland: A comparative case series. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 50, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Tang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Fei, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Sex disparities in clinical characteristics and prognosis of immunoglobulin G4–related disease: A prospective study of 403 patients. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z.P.; Cai, Z.G.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.X.; Hua, H.; Li, M.; Hong, X.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related si-aladenitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Fei, Y.; Peng, L.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y. Different clinical patterns of IgG4-RD patients with and without eosinophilia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotta, M.; Mancuso, G.; Della-Torre, E. Advances in the diagnosis and management of IgG4 related disease. BMJ 2020, 369, m1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, V.; Zen, Y.; Chan, J.K.; Yi, E.E.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Klöppel, G.; Heathcote, J.G.; Khosroshahi, A.; Ferry, J.A.; et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuk, W.; Chan, J.K. Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related disease: An underdiagnosed and overdiagnosed entity. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 29, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, B.L. IgG4-related lymphadenopathy—A difficult diagnosis. Surg. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Feng, W.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y. Concurrence of IgG4-related disease and Kimura disease with pulmonary embolism and lung cancer: A case report. BMC Pulm Med. 2022, 22, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaki, Y.; Ikushima, S.; Matsui, S.; Hebisawa, A.; Ichimura, Y.; Izumi, S.; Ujita, M.; Arita, M.; Tomii, K.; Komase, Y.; et al. Comparison of clinical and pathological features of lung lesions of systemic IgG4-related disease and idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease. Histopathology. 2017, 70, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Kanda, R.; Nawata, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kawabe, A.; Hanami, K.; Nakatsuka, K.; Saito, K.; Nakayamada, S.; Tanaka, Y. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis exhibits T cell activation and IgG4 immune response in the tissue; comparison with IgG4-related disease. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Park, S.; Slack, G.W.; Dalal, B.I.; Skinnider, B.F.; Schaeffer, D.F.; Dutz, J.P.; Law, J.K.; Donnellan, F.; Marquez, V.; et al. IgG4-related disease and lymphocyte-variant hypereosinophilic syndrome: A comparative case series. Eur J Haematol. 2017, 98, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, E.L.; Sadler, R.; Bateman, A.C.; Makuch, M.; Cargill, T.; Ferry, B.; Aalberse, R.; Barnes, E.; Rispens, T. Increases in IgE, Eosinophils, and Mast Cells Can be Used in Diagnosis and to Predict Relapse of IgG4-Related Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1444–1452.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Chang, M.-L.; Teng, W.-C.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Yu, H.-H.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Chan, T.-M. Comparison of Clinical Manifestations and Pathology between Kimura Disease and IgG4-Related Disease: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236887
Chang S-Y, Lee C-C, Chang M-L, Teng W-C, Hsiao C-Y, Yu H-H, Hsieh M-J, Chan T-M. Comparison of Clinical Manifestations and Pathology between Kimura Disease and IgG4-Related Disease: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236887
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Sing-Ya, Chih-Chun Lee, Ming-Ling Chang, Wen-Chieh Teng, Chao-Yang Hsiao, Han-Hua Yu, Meng-Ju Hsieh, and Tien-Ming Chan. 2022. "Comparison of Clinical Manifestations and Pathology between Kimura Disease and IgG4-Related Disease: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236887
APA StyleChang, S.-Y., Lee, C.-C., Chang, M.-L., Teng, W.-C., Hsiao, C.-Y., Yu, H.-H., Hsieh, M.-J., & Chan, T.-M. (2022). Comparison of Clinical Manifestations and Pathology between Kimura Disease and IgG4-Related Disease: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 6887. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236887






