Long-Term Prediction Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Antiviral Therapy: Based on Data from Korean Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design & Population
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Antiviral Therapy
3.3. HCC Development
3.4. Model Development
3.5. Derivation of the ACCESS-HCC Score for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
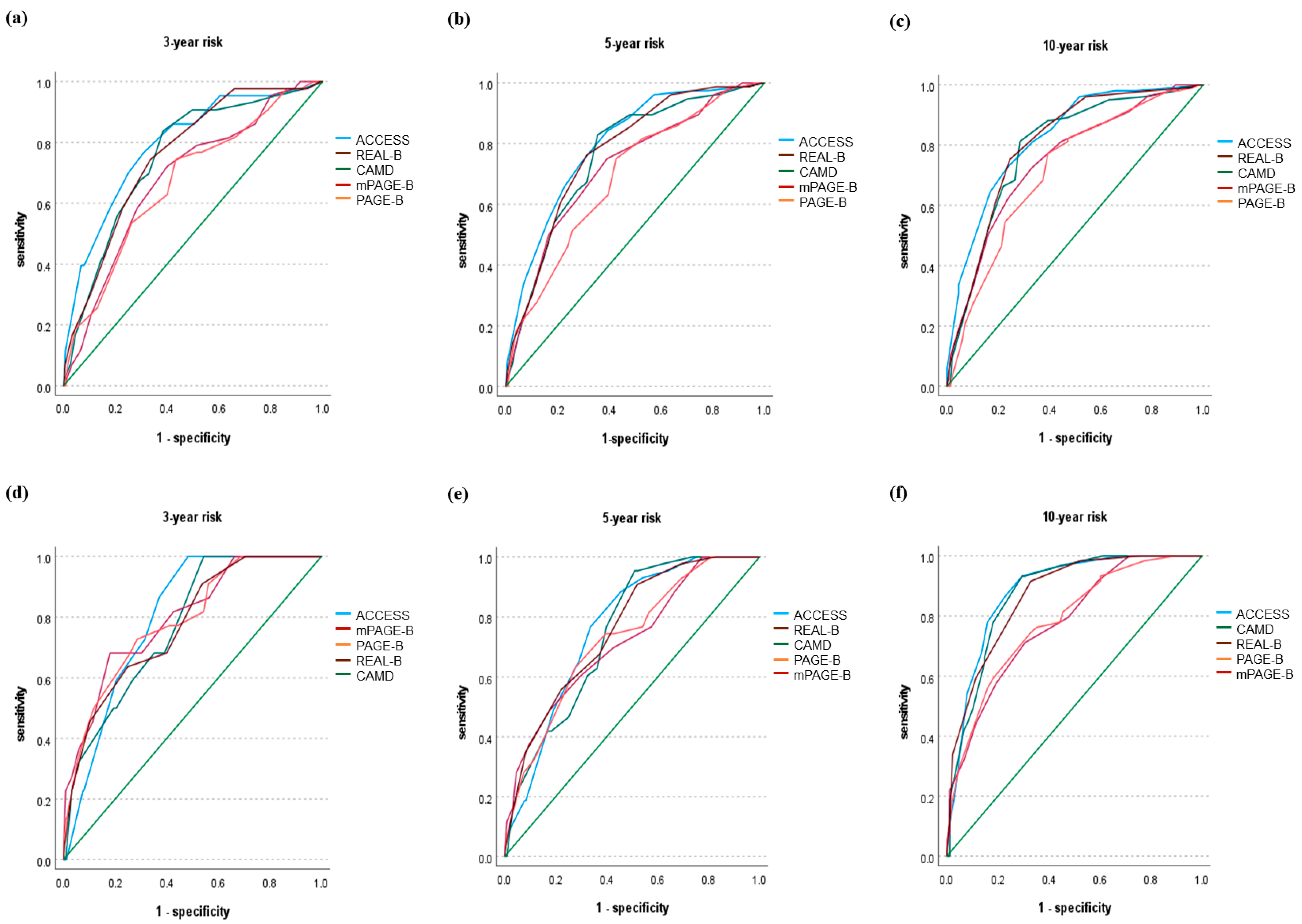
3.6. Validation of the ACCESS-HCC Score
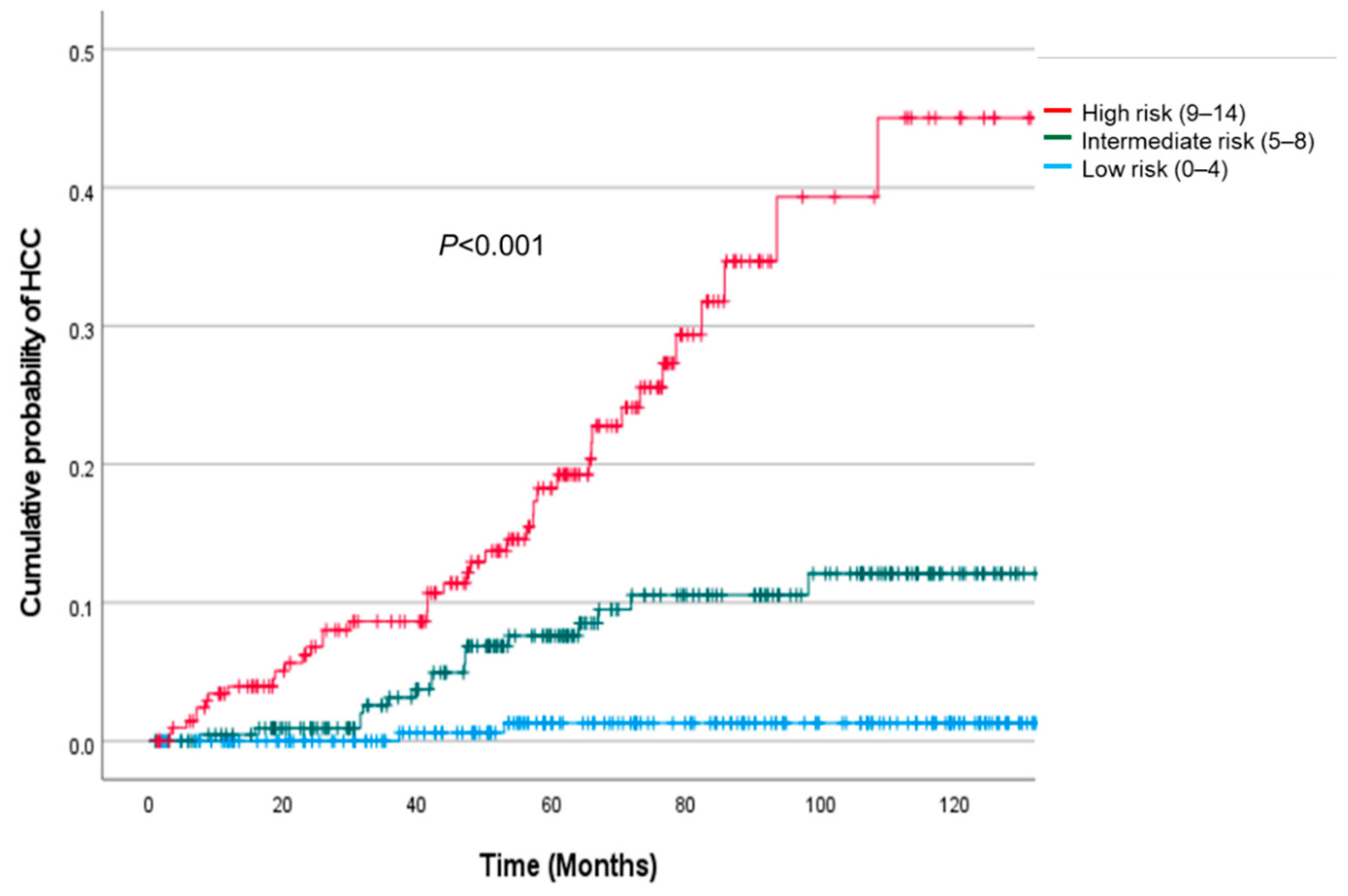
3.7. Risk Stratification Using the ACCESS-HCC Score
3.8. High-Risk Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.L.; Chan, H.L.; Mak, C.W.; Lee, S.K.; Ip, Z.M.; Lam, A.T.; Iu, H.W.; Leung, J.M.; Lai, J.W.; Lo, A.O.; et al. Entecavir treatment reduces hepatic events and deaths in chronic hepatitis B patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Seko, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Long-term entecavir treatment reduces hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2013, 58, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.H.; Hu, T.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Chuang, W.L.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Su, W.W.; Chen, M.Y.; Peng, C.Y.; et al. Four-year entecavir therapy reduces hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhotic events and mortality in chronic hepatitis B patients. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Yang, H.I.; Le, A.; Henry, L.; Nguyen, N.; Lee, M.H.; Zhang, J.; Wong, C.; Wong, C.; Trinh, H. Reduced Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic and Noncirrhotic Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Treated with Tenofovir-A Propensity Score-Matched Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringelhan, M.; McKeating, J.A.; Protzer, U. Viral hepatitis and liver cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20170339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W. Long Term Efficacy of Antiviral Therapy: Mortality and Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 74, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Sypsa, V.; Dalekos, G.; Yurdaydin, C.; van Boemmel, F.; Buti, M.; Goulis, J.; Calleja, J.L.; Chi, H.; Manolakopoulos, S.; et al. Eight-year survival in chronic hepatitis B patients under long-term entecavir or tenofovir therapy is similar to the general population. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Lampertico, P.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Lok, A. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving nucleos(t)ide therapy: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Chan, H.L.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.; Lampertico, P. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B: Assessment and modification with current antiviral therapy. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachogiannakos, J.; Papatheodoridis, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients under antiviral therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8822–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Sun, J.; Innes, H.; Toyoda, H.; Xie, Q.; Mo, S.; Sypsa, V.; Guha, I.N.; Kumada, T.; et al. aMAP risk score predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Sypsa, V.; Dalekos, G.N.; Yurdaydin, C.; Van Boemmel, F.; Buti, M.; Calleja, J.L.; Chi, H.; Goulis, J.; Manolakopoulos, S.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma prediction beyond year 5 of oral therapy in a large cohort of Caucasian patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Yip, T.C.; Ho, H.J.; Wong, V.W.; Huang, Y.T.; El-Serag, H.B.; Lee, T.Y.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T.; Wong, G.L.; et al. Development of a scoring system to predict hepatocellular carcinoma in Asians on antivirals for chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, M.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.U.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, B.K. An optimized hepatocellular carcinoma prediction model for chronic hepatitis B with well-controlled viremia. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Chan, S.L.; Mo, F.; Chan, T.C.; Loong, H.H.; Wong, G.L.; Lui, Y.Y.; Chan, A.T.; Sung, J.J.; Yeo, W.; et al. Clinical scoring system to predict hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B carriers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Tanaka, Y.; Fong, D.Y.; Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.; Yuen, J.C.; But, D.Y.; Chan, A.O.; Wong, B.C.; Mizokami, M.; et al. Independent risk factors and predictive score for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.; Dalekos, G.; Sypsa, V.; Yurdaydin, C.; Buti, M.; Goulis, J.; Calleja, J.L.; Chi, H.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Mangia, G.; et al. PAGE-B predicts the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B on 5-year antiviral therapy. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.I.; Yuen, M.F.; Chan, H.L.; Han, K.H.; Chen, P.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Chen, C.J.; Wong, V.W.; Seto, W.K. Risk estimation for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B (REACH-B): Development and validation of a predictive score. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.I.; Yeh, M.L.; Wong, G.L.; Peng, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Trinh, H.N.; Cheung, K.S.; Xie, Q.; Su, T.H.; Kozuka, R.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness from the Asia Pacific Rim Liver Consortium for HBV Risk Score for the Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Treated With Oral Antiviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganne-Carrié, N.; Ziol, M.; de Ledinghen, V.; Douvin, C.; Marcellin, P.; Castera, L.; Dhumeaux, D.; Trinchet, J.C.; Beaugrand, M. Accuracy of liver stiffness measurement for the diagnosis of cirrhosis in patients with chronic liver diseases. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolondi, L.; Gramantieri, L. From liver cirrhosis to HCC. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2011, 6 (Suppl. S1), 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.H.; Choe, W.H.; Choi, M.S.; Chung, W.J.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 93–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginès, P.; Krag, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Solà, E.; Fabrellas, N.; Kamath, P.S. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Kato, N. Advances in ultrasound diagnosis in chronic liver diseases. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 216–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buderer, N.M. Statistical methodology: I. Incorporating the prevalence of disease into the sample size calculation for sensitivity and specificity. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1996, 3, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, M.; Jun, B.G.; Kim, T.S.; Suk, K.T.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Cheon, G.J.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Modified PAGE-B score predicts the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asians with chronic hepatitis B on antiviral therapy. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.I.; Kim, H.S.; Yang, B.K.; Kang, J.G.; Shin, W.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Jang, M.K. Predictive factors for risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in immune inactive chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.K.; Cheong, J.Y.; Cho, S.W.; Cho, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, D.J.; Hwang, S.G.; Yang, J.M.; Park, Y.N. Liver stiffness measurement for the diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Korean J. Hepatol. 2007, 13, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Association; National Cancer Center. 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 227–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, P.S.; Trinh, H.; Garcia, R.T.; Phan, J.T.; Ha, N.B.; Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, K.; Keeffe, E.B.; Nguyen, M.H. Significant prevalence of histologic disease in patients with chronic hepatitis B and mildly elevated serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.Q.; Schiff, E.R.; Kowdley, K.V.; Min, A.D.; Shiffman, M.L.; Lee, W.M.; Goodman, Z.D.; Dau, L.O.; Peschell, K.J.; Fagan, E.A.; et al. Histologic evidence of active liver injury in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal range or minimally elevated alanine aminotransferase levels. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, E.L.; Park, H.; Kwon, J.H.; Sinn, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.W. Comparison of clinical practice guidelines for the management of chronic hepatitis B: When to start, when to change, and when to stop. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Derivation Cohort (n = 1239) | Validation Cohort (n = 656) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | ||
| Male sex | 736 (59.4) | 393 (59.9) | 0.831 |
| Age, mean (SD) | 47.72 (10.95) | 48.63 (10.92) | 0.084 |
| Antiviral agent | 0.243 | ||
| Entecavir | 760 (61.7) | 421 (64.5) | |
| Tenofovir | 471 (38.3) | 232 (35.5) | |
| HTN | 161 (13.0) | 74 (11.3) | 0.282 |
| DM | 129 (10.4) | 72 (11.0) | 0.705 |
| Alcohol drinking a | 193 (15.6) | 92 (14.0) | 0.184 |
| CKD | 33 (2.7) | 26 (4.0) | 0.121 |
| Liver cirrhosis b | 452 (36.5) | 262 (39.9) | 0.140 |
| Decompensation | 105 (8.8) | 57 (9.0) | 0.918 |
| Liver stiffness (kPa),c median (IQR) | 9.90 (6.10–17.30) | 9.95 (6.10–17.30) | 0.891 |
| HBV DNA (IU/mL), median (IQR) | 1.84 × 106 (7.50 × 104–3.26 × 107) | 1.88 × 106 (6.87 × 104–3.19 × 107) | 0.080 |
| HBeAg | 625 (51.6) | 348 (54.5) | 0.223 |
| HBeAb | 553 (46.7) | 294 (47.6) | 0.704 |
| PLT × 103/uL, median (IQR) | 157 (114–210) | 152 (113–201) | 0.058 |
| Albumin (g/dL), median (IQR) | 4.1 (3.7–4.4) | 4.1 (3.7–4.4) | 0.401 |
| ALT (U/L), median (IQR) | 87 (44–180) | 77 (44–160) | 0.165 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 0.90 (0.69–1.30) | 0.90 (0.69–1.31) | 0.602 |
| INR, median (IQR) | 1.08 (1.00–1.16) | 1.07 (1.00–1.18) | 0.435 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 0.80 (0.60–0.90) | 0.70 (0.68–0.90) | 0.350 |
| Na (mmol/L), mean (SD) | 139.55 (2.88) | 139.52 (2.82) | 0.845 |
| AFP (ng/mL), median (IQR) | 5.01 (2.70–13.05) | 5.00 (2.70–14.30) | 0.904 |
| Ascites | 65 (5.3) | 47 (7.2) | 0.158 |
| HEP d | |||
| 1 | 1122 (99.7) | 587 (100.0) | 0.238 |
| 2 | 2 (0.2) | - | |
| 3 | 1 (0.1) | - | |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Multivariate-Adjusted Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Multivariate-Adjusted Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value |
| Age | ||||
| <40 | Referent | <0.0001 | Referent | <0.0001 |
| 40–49 | 1.762 (0.668–4.651) | 0.253 | 1.771 (0.671–4.675) | 0.248 |
| ≥50 | 3.557 (1.381–9.158) | 0.009 | 3.682 (1.445–9.381) | 0.006 |
| HTN | 1.276 (0.766–2.126) | 0.350 | ||
| DM | 1.225 (0.711–2.112) | 0.465 | ||
| Alcohol a | 1.947 (1.247–3.041) | 0.003 | 1.954 (1.263–3.022) | 0.003 |
| Liver cirrhosis b | 2.898 (1.792–4.687) | <0.0001 | 2.974 (1.865–4.743) | <0.0001 |
| Liver stiffness c | ||||
| <9.7 kPa | Referent | 0.01 | Referent | 0.001 |
| 9.7 ≤ LS < 14.9 kPa | 1.284 (0.710–2.323) | 0.409 | 1.314 (0.728–2.371) | 0.365 |
| ≥14.9 kPa | 2.122 (1.268–3.551) | 0.004 | 2.340 (1.440–3.804) | <0.0001 |
| ALT < 80 | 1.696 (1.119–2.573) | 0.013 | 1.633 (1.081–2.466) | 0.020 |
| PLT < 150,000 | 0.926 (0.584–1.468) | 0.745 | ||
| Alb < 3.5 | 1.174 (0.751–1.834) | 0.482 | ||
| AFP ≥ 10 | 1.292 (0.849–1.965) | 0.232 | ||
| Parameter | Beta-Coefficient | ACCESS Score |
|---|---|---|
| Age | <40: 0 | |
| 0.572 | 40–49: 2 | |
| 1.304 | ≥50: 4 | |
| Alcohol a | No: 0 | |
| 0.670 | Yes: 2 | |
| Liver cirrhosis b | No: 0 | |
| 1.090 | Yes: 3 | |
| Liver stiffness c | <9.7 kPa: 0 | |
| 0.273 | 9.7 ≤ LS < 14.9 kPa: 1 | |
| 0.850 | ≥14.9 kPa: 3 | |
| ALT | ≥80: 0 | |
| 0.490 | <80: 2 |
| Prediction Model | Time-Dependent AUROC (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Year Risk Prediction | 5-Year Risk Prediction | 10-Year Risk Prediction | |
| ACCESS | 0.798 (0.737–0.860) | 0.762 (0.701–0.824) | 0.883 (0.830–0.937) |
| PAGE-B | 0.787 (0.695–0.879) | 0.725 (0.649–0.802) | 0.782 (0.707–0.856) |
| mPAGE-B | 0.797 (0.706–0.889) | 0.720 (0.638–0.801) | 0.777 (0.702–0.851) |
| REAL-B | 0.772 (0.680–0.864) | 0.757 (0.689–0.825) | 0.867 (0.811–0.923) |
| CAMD | 0.770 (0.689–0.852) | 0.747 (0.685–0.810) | 0.874 (0.819–0.930) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Shin, S.K.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Yim, H.J.; Yim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, Y.S.; et al. Long-Term Prediction Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Antiviral Therapy: Based on Data from Korean Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226613
Lee JH, Shin SK, Kang SH, Kim TH, Yim HJ, Yim SY, Lee Y-S, Jung YK, Kim JH, Seo YS, et al. Long-Term Prediction Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Antiviral Therapy: Based on Data from Korean Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226613
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Hun, Seung Kak Shin, Seong Hee Kang, Tae Hyung Kim, Hyung Joon Yim, Sun Young Yim, Young-Sun Lee, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, and et al. 2022. "Long-Term Prediction Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Antiviral Therapy: Based on Data from Korean Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226613
APA StyleLee, J. H., Shin, S. K., Kang, S. H., Kim, T. H., Yim, H. J., Yim, S. Y., Lee, Y.-S., Jung, Y. K., Kim, J. H., Seo, Y. S., Yeon, J. E., Kwon, O. S., Um, S. H., & Byun, K. S. (2022). Long-Term Prediction Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Receiving Antiviral Therapy: Based on Data from Korean Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226613







