The Role of Selected Serpins in Gastrointestinal (GI) Malignancies
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers
1.2. The Structure and Functions of Serpins
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
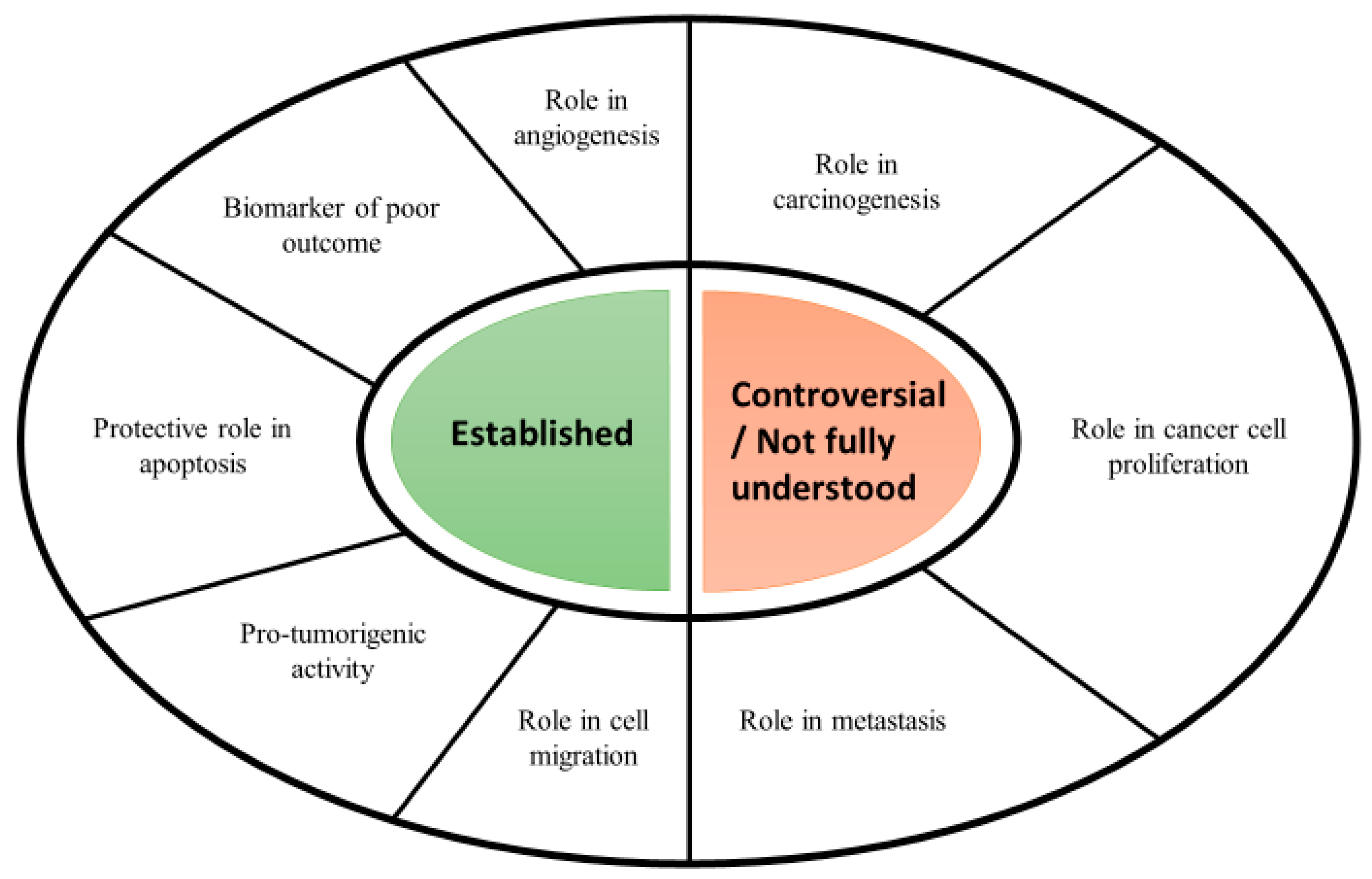
3.1. Serpins in Cancer
3.2. The Role of Serpins in GI Cancers
3.2.1. SERPIN A1 (Serpin Family A Member 1)—A1AT (Alpha-1-Antitrypsin)
3.2.2. SERPIN A12 (Serpin Family A Member 12)—Vaspin
3.2.3. SERPIN B5 (Serpin Family B Member 5)—Maspin
3.2.4. SERPIN E1 (Serpin Family E Member 1)—PAI-1 (Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1)
3.2.5. SERPIN F1 (Serpin Family F Member 1)—PEDF (Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor)
3.3. Serpins as Target for Cancer Therapy and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sensoy, I. A review on the food digestion in the digestive tract and the used in vitro models. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, G.; Meoni, G.; Amedei, A.; Tenori, L. Metabolomics profile in gastrointestinal cancers: Update and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2514–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Mullins, C.S.; Schafmayer, C.; Zeißig, S.; Linnebacher, M. A global assessment of recent trends in gastrointestinal cancer and lifestyle-associated risk factors. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Abnet, C.C.; Neale, R.E.; Vignat, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global Burden of 5 Major Types of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 335–349.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizdar, Ö.; Kılıçkap, S. Global Epidemiology of Gastrointestinal Cancers; Yalcin, S., Philip, P.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Thrift, A.P. Global burden and epidemiology of Barrett oesophagus and oesophageal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.; Jenab, M.; Gunter, M.J. Adiposity and gastrointestinal cancers: Epidemiology, mechanisms and future directions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMenamin, Ú.C.; McCain, S.; Kunzmann, A.T. Do smoking and alcohol behaviours influence GI cancer survival? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Meyerhardt, J.A. Obesity and Energy Balance in GI Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4217–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, L.; Galletti, F.; Strazzullo, P. Dietary salt intake and risk of gastric cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. 2014, 159, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.L.; Yu, S.J. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J. Surg. 2018, 41, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuzsen, T.; Kazaz, N.; Tanriverdi, Ö.; Akman, T.; Davis, M.P. Symptom Management in Gastrointestinal Cancers; Yalcin, S., Philip, P.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 669–685. [Google Scholar]
- Pullmer, R.; Linden, W.; Rnic, K.; Vodermaier, A. Measuring symptoms in gastrointestinal cancer: A systematic review of assessment instruments. Support Care Cancer 2014, 22, 2941–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, P.; Islami, F.; Anandasabapathy, S.; Freedman, N.D.; Kamangar, F. Gastric cancer: Descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntz, S.; Krieghoff-Henning, E.; Kather, J.N.; Jutzi, T.; Höhn, J.; Kiehl, L.; Hekler, A.; Alwers, E.; von Kalle, C.; Fröhling, S.; et al. Gastrointestinal cancer classification and prognostication from histology using deep learning: Systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 155, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katabathina, V.S.; Menias, C.O.; Khanna, L.; Murphy, L.; Dasyam, A.K.; Lubner, M.G.; Prasad, S.R. Hereditary Gastrointestinal Cancer Syndromes: Role of Imaging in Screening, Diagnosis, and Management. Radiographics 2019, 39, 1280–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaosmanoglu, A.D.; Onur, M.R.; Arellano, R.S. Imaging in Gastrointestinal Cancers; Yalcin, S., Philip, P.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 445–464. [Google Scholar]
- Bouri, S.; Martin, J. Investigation of iron deficiency anaemia. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, N.S.S.; Rings, E.H.H.M.; Blijlevens, N.M.A.; Tissing, W.J.E. Biomarkers and non-invasive tests for gastrointestinal mucositis. Support Care Cancer 2017, 25, 2933–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.S.; Guo, X.Y.; Sun, K. Recent advances in blood-based and artificial intelligence-enhanced approaches for gastrointestinal cancer diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5666–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, W.M.; Yu, M.; Markowitz, S.D. Epigenetic Alterations in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Current and Emerging Use for Biomarkers of Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 690–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Olmos, D.; Tabernero, J. Prognostic and predictive roles for circulating biomarkers in gastrointestinal cancer. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorica, F.; Stefanelli, A.; Pascale, G.; Fisichella, R. Elderly gastrointestinal cancer patients and radiochemotherapy: A review. Clin. Ter. 2014, 165, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludmir, E.B.; Palta, M.; Willett, C.G.; Czito, B.G. Total neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer: An emerging option. Cancer 2017, 123, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanani, A.; Veen, T.; Søreide, K. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy in primary and metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Nakajima, M. Treatments for esophageal cancer: A review. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 61, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordry, N.; Astaras, C.; Ongaro, M.; Goossens, N.; Frossard, J.L.; Koessler, T. Recent advances in gastrointestinal cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4493–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Reichardt, P. An updated review of the treatment landscape for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer 2021, 127, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macha, M.A.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Krishn, S.R.; Pai, P.; Rachagani, S.; Jain, M.; Batra, S.K. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) as biomarker(s) for prognosis and diagnosis of gastrointestinal (GI) cancers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 5287–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, K.L.; Bhatia, V.; Agarwal, P.; Kumar, A. Gastrointestinal Cancers: Molecular Genetics and Biomarkers. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 4513860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryvalap, Y.; Czyzyk, J. The Role of Proteases and Serpin Protease Inhibitors in β-Cell Biology and Diabetes. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.C.; Abreu, P.A.; Geraldo, R.B.; Martins, R.C.; dos Santos, R.; Loureiro, N.I.; Cabral, L.M.; Rodrigues, C.R. Looking at the proteases from a simple perspective. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Yaron, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Ambadapadi, S. Overview of Serpins and Their Roles in Biological Systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1826, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.J. Serpins in cartilage and osteoarthritis: What do we know? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gent, D.; Sharp, P.; Morgan, K.; Kalsheker, N. Serpins: Structure, function and molecular evolution. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.H.; Zhang, Q.; McGowan, S.; Buckle, A.M.; Silverman, G.A.; Wong, W.; Rosado, C.J.; Langendorf, C.G.; Pike, R.N.; Bird, P.I.; et al. An overview of the serpin superfamily. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Askew, D.J.; Silverman, G.A. Intracellular and extracellular serpins modulate lung disease. J. Perinatol. 2008, 28 (Suppl. 3), S127–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Yaron, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Macaulay, C.; McFadden, G. Serpins: Development for Therapeutic Applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1826, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Jin, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Lee, D.J.; Chaft, J.E.; Kris, M.G.; Huse, J.T.; Brogi, E.; et al. Serpins promote cancer cell survival and vascular co-option in brain metastasis. Cell 2014, 156, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Singh, P.; Azhar, A.; Naseem, A.; Rashid, Q.; Kabir, M.A.; Jairajpuri, M.A. Serpin Inhibition Mechanism: A Delicate Balance between Native Metastable State and Polymerization. J. Amino Acids 2011, 2011, 606797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.; Iaccarino, L.; Ghirardello, A.; Bassi, N.; Pontisso, P.; Punzi, L.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Doria, A. Serpins, immunity and autoimmunity: Old molecules, new functions. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanrattana, W.; Maas, C.; de Maat, S. SERPINs-From Trap to Treatment. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Lomas, D.A. The molecular aetiology of the serpinopathies. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gettins, P.G.; Olson, S.T. Inhibitory serpins. New insights into their folding, polymerization, regulation and clearance. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2273–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hazari, Y.M.; Bashir, A.; Habib, M.; Bashir, S.; Habib, H.; Qasim, M.A.; Shah, N.N.; Haq, E.; Teckman, J.; Fazili, K.M. Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency: Genetic variations, clinical manifestations and therapeutic interventions. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 773, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. The Evolution of Carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 165, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistritto, G.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Ceci, C.; Garufi, A.; D’Orazi, G. Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: Function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging 2016, 8, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, H.J.; Strange, R.; Schedin, P.J. Apoptosis in the genesis and prevention of cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark. Prev. 1992, 1, 597–602. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Peng, P.; Li, J.; Deng, H.; Zhan, N.; Zeng, Z.; Dong, W. SERPINH1 regulates EMT and gastric cancer metastasis via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 3574–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; McGowan, P.M.; Harbeck, N.; Thomssen, C.; Schmitt, M. uPA and PAI-1 as biomarkers in breast cancer: Validated for clinical use in level-of-evidence-1 studies. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, P.A. PAI-1—A potential therapeutic target in cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2007, 8, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, S.; Koyama, K.; Shima, J.; Tonai, K.; Goto, Y.; Koinuma, T.; Nunomiya, S. Thrombomodulin, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Protein C Levels, and Organ Dysfunction in Sepsis. Crit. Care Explor. 2019, 1, e0013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatkowska, M.; Szemraj, J.; Cierniewski, C.S. Induction of PAI-1 expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha in endothelial cells is mediated by its responsive element located in the 4G/5G site. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubala, M.H.; DeClerck, Y.A. The plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 paradox in cancer: A mechanistic understanding. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placencio, V.R.; DeClerck, Y.A. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Cancer: Rationale and Insight for Future Therapeutic Testing. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, T.; Urano, T.; Umemura, K. PAI-1, progress in understanding the clinical problem and its aetiology. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 157, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filleur, S.; Nelius, T.; de Riese, W.; Kennedy, R.C. Characterization of PEDF: A multi-functional serpin family protein. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 106, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, N.; Brook, E.; Dass, C.R.; Chan, A.; Dharmarajan, A. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor and Sex Hormone-Responsive Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra, S.P.; Notario, V. The effects of PEDF on cancer biology: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, J.M.; Penno, M.A.; Weiland, F.; Klingler-Hoffmann, M.; Zuber, A.; Boussioutas, A.; Ernst, M.; Hoffmann, P. Identification and validation of novel candidate protein biomarkers for the detection of human gastric cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1844, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, J.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Lin, Y.D.; Ho, W.Y.; Moi, S.H. Effect of Baseline Characteristics and Tumor Burden on Vaspin Expression and Progressive Disease in Operable Colorectal Cancer. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, S. The promise and challenge toward the clinical application of maspin in cancer. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 2733–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Xiong, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, B.; He, K.; Huang, C. Identification of peptide regions of SERPINA1 and ENOSF1 and their protein expression as potential serum biomarkers for gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5109–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Cheng, C.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, D.C.; Hsieh, J.S.; Lee, S.C.; Wang, W.M. Discovery of tumor markers for gastric cancer by proteomics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulos, D.; Tzonou, A.; Kalapothaki, V.; Sparos, L.; Kremastinou, T.; Skoutari, M. Alpha 1-antitrypsin and survival in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 45, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaberie, H.; Hosseini, S.V.; Naghibalhossaini, F. Evaluation of Alpha 1-Antitrypsin for the Early Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.R.; Xie, L.Q.; Xu, Y.; Cai, S.J.; Yao, J.; Yang, P.Y.; Lu, H.J. Direct-S: A directed mass spectrometry method for biomarker verification in native serum. Analyst 2015, 140, 3654–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żelechowska, P.; Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, E.; Kusowska, A.; Kozłowska, E. The role of adipokines in the modulation of lymphoid lineage cell development and activity: An overview. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazgan-Simon, M.; Kukla, M.; Zuwała-Jagiełło, J.; Derra, A.; Bator, M.; Menżyk, T.; Lekstan, A.; Grzebyk, E.; Simon, K. Serum visfatin and vaspin levels in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazeli, M.S.; Dashti, H.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Assadi, M.; Aminian, A.; Keramati, M.R.; Nabipour, I. Circulating levels of novel adipocytokines in patients with colorectal cancer. Cytokine 2013, 62, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Duan, R.; Zhang, J.; Du, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, N. Effects of vaspin on pancreatic β cell secretion via PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Dzinic, S.; Li, S.; Fang, F.; Wu, N.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, Y. Elevated maspin expression is associated with better overall survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63581, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; Yang, Y.M.; Li, X.H.; Dong, F.; Li, Y. Maspin expression and its clinicopathological significance in tumorigenesis and progression of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeren, N.; Emmink, B.L.; Koerkamp, M.J.; van Hooff, S.R.; Goos, J.A.; van Houdt, W.J.; de Wit, M.; Prins, A.M.; Piersma, S.R.; Pham, T.V.; et al. Maspin is a marker for early recurrence in primary stage III and IV colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, H.M.; Pu, H.W.; Ma, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Ma, H.; Chen, X. Expression of Bmi-1 and PAI-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5533–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yang, L.Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xu, X.; Hao, J.J.; Wang, M.R. PAI-1 overexpression promotes invasion and migration of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Hereditas 2020, 42, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Peng, H.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Su, N.; Tang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Cui, L.; Hu, P.; et al. Silencing of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 suppresses colorectal cancer progression and liver metastasis. Surgery 2015, 158, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Märkl, B.; Renk, I.; Oruzio, D.V.; Jähnig, H.; Schenkirsch, G.; Schöler, C.; Ehret, W.; Arnholdt, H.M.; Anthuber, M.; Spatz, H. Tumour budding, uPA and PAI-1 are associated with aggressive behaviour in colon cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 102, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Yang, X.; Shao, C.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, R.; Cai, W.; Ma, J.; Yang, Z.; Gao, G. Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits angiogenesis and growth of gastric carcinoma by down-regulation of VEGF. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, E.K.; Akpınar, M.Y.; Doğan, Ö.; Göktaş, Z.; Sapmaz, F.P.; Şimşek, G.G.; Uzman, M.; Nazlıgül, Y. Clinical Significance of Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor, Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha, and Progranulin Levels in Patients with Gastric Cancer and Gastric Precancerous Lesions. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2019, 50, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principe, D.R.; DeCant, B.; Diaz, A.M.; Mangan, R.J.; Hwang, R.; Lowy, A.; Shetuni, B.B.; Sreekumar, B.K.; Chung, C.; Bentrem, D.J.; et al. PEDF inhibits pancreatic tumorigenesis by attenuating the fibro-inflammatory reaction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28218–28234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wågsäter, D.; Löfgren, S.; Zar, N.; Hugander, A.; Dimberg, J. Pigment epithelium-derived factor expression in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Investig. 2010, 28, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Li, M.; Zhan, T.; Yao, Y.; Shen, J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J. Prognostic role of serum AZGP1, PEDF and PRDX2 in colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bteich, M. An overview of albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein main characteristics: Highlighting the roles of amino acids in binding kinetics and molecular interactions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchera, A.; Alomari, E.; Bruno, S. Augmentation Therapy with Alpha-1 Antitrypsin: Present and Future of Production, Formulation, and Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 385–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödl, W.; Büchler, R.; Wendler, S.; Reinhold, P.; Muckova, P.; Reindl, J.; Rhode, H. Acute phase proteins as promising biomarkers: Perspectives and limitations for human and veterinary medicine. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.Q.; Zhao, C.; Cai, S.J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, L.Y.; Bian, J.S.; Shen, C.P.; Lu, H.J.; Yang, P.Y. Novel proteomic strategy reveal combined alpha1 antitrypsin and cathepsin D as biomarkers for colorectal cancer early screening. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4701–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernacka, K.; Kuryliszyn-Moskal, A.; Sierakowski, S. The levels of alpha 1-antitrypsin and alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the sera of patients with gastrointestinal cancers during diagnosis. Cancer 1988, 62, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiker, J.T.; Klöting, N.; Kovacs, P.; Kuettner, E.B.; Sträter, N.; Schultz, S.; Kern, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Vaspin inhibits kallikrein 7 by serpin mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova, R.; Tankova, T. The role of vaspin in the development of metabolic and glucose tolerance disorders and atherosclerosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 823481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Guan, Z. Vaspin deficiency failed to promote the proliferation of BMSCs in osteoarthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 24, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pich, K.; Respekta, N.; Dawid, M.; Mlyczynska, E.; Kurowska, P.; Rak, A. New insights into cell apoptosis and proliferation: The potential role of vaspin. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 72, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulatos, G.S.; Spyrou, N.; Kadillari, J.; Psallida, S.; Dalamaga, M. The Role of Adipokines in Breast Cancer: Current Evidence and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, S.; Sansoni, V.; Ziemann, E.; Lombardi, G. Another Weapon against Cancer and Metastasis: Physical-Activity-Dependent Effects on Adiposity and Adipokines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shan, P.F.; Shen, J.; Liang, Q.H.; Cui, R.R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Wu, S.S.; Lu, Q.; et al. Vaspin attenuates the apoptosis of human osteoblasts through ERK signaling pathway. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalkhali-Ellis, Z. Maspin: The new frontier. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7279–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockett, J.; Yin, S.; Li, X.; Meng, Y.; Sheng, S. Tumor suppressive maspin and epithelial homeostasis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 97, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, S. A role of novel serpin maspin in tumor progression: The divergence revealed through efforts to converge. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 209, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenstine, T.M.; Seftor, R.E.; Khalkhali-Ellis, Z.; Seftor, E.A.; Pemberton, P.A.; Hendrix, M.J. Maspin: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Multiple functions of maspin in tumor progression and mouse development. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Zheng, H.; Tsuneyama, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nomoto, K.; Xu, H.; Takano, Y. Paradoxical expression of maspin in gastric carcinomas: Correlation with carcinogenesis and progression. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurzu, S.; Jung, I. Subcellular Expression of Maspin in Colorectal Cancer: Friend or Foe. Cancers 2021, 13, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Guan, X.; Guo, H.; Xiong, G.; Yang, K.; Wang, K.; Bai, Y. Association between SNPs in Serpin gene family and risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 6231–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Chang, L.L. Maspin suppresses cell invasion and migration in gastric cancer through inhibiting EMT and angiogenesis via ITGB1/FAK pathway. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banias, L.; Jung, I.; Bara, T.; Fulop, Z.; Simu, P.; Simu, I.; Satala, C.; Gurzu, S. Immunohistochemical-Based molecular subtyping of colorectal carcinoma using maspin and markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, M.; Ćelap, I. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in acute coronary syndromes. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2019, 491, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Faria, C.A.; Zanette, D.L.; Silva, W.A., Jr.; Ribeiro-Paes, J.T. PAI-1 inhibition by simvastatin as a positive adjuvant in cell therapy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Pahor, M.; Incalzi, R.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1): A key factor linking fibrinolysis and age-related subclinical and clinical conditions. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 28, e72–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 and atherothrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1879–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Koma, Y.I.; Higashino, N.; Kodama, T.; Tanigawa, K.; Shimizu, M.; Fujikawa, M.; Nishio, M.; Shigeoka, M.; Kakeji, Y.; et al. PAI-1 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma promotes the invasion of cancer cells and the migration of macrophages. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, N.M.; Joyce, M.R.; Murphy, J.M.; Barry, F.P.; O’Brien, T.; Kerin, M.J.; Dwyer, R.M. Impact of mesenchymal stem cell secreted PAI-1 on colon cancer cell migration and proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombran-Tink, J. The neuroprotective and angiogenesis inhibitory serpin, PEDF: New insights into phylogeny, function, and signaling. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2131–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Yamagishi, S.I.; Sata, M. Structure-function relationships of PEDF. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Cheng, R.; Benyajati, S.; Ma, J.X. PEDF and its roles in physiological and pathological conditions: Implication in diabetic and hypoxia-induced angiogenic diseases. Clin. Sci. 2015, 128, 805–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yu, X.; Gao, T.; Feng, J.; Hong, H.; Yin, H.; Zhou, T.; Qi, W.; et al. The contrary intracellular and extracellular functions of PEDF in HCC development. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Jin, Q.; Zeng, J.; Yu, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Gong, D.; He, L.; Tan, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Combined Tumor- and Neovascular-“Dual Targeting” Gene/Chemo-Therapy Suppresses Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25753–25769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.J.; Gong, C.Y.; Luo, S.T.; Zhang, D.M.; Zhang, S.; Shi, H.S.; Lu, L.; Yan, H.X.; He, S.S.; Li, D.D.; et al. AAV-Mediated human PEDF inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in murine colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis model. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Wang, J.J.; Gao, G.; Parke, K.; Ma, J.X. Pigment epithelium-derived factor downregulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and inhibits VEGF-VEGF receptor 2 binding in diabetic retinopathy. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zeng, J.; Huang, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Liao, X.; Song, X. Cancer-Targeted PEDF-DNA therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Huang, S. Role of urokinase receptor in tumor progression and development. Theranostics 2013, 3, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, R.; Morgese, F.; Onofri, A.; Mazzanti, P.; Pistelli, M.; Ballatore, Z.; Savini, A.; De Lisa, M.; Caramanti, M.; Rinaldi, S.; et al. Role of maspin in cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, R.; Fernández, A.M.; Ellis, V. Maspin inhibits cell migration in the absence of protease inhibitory activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46845–46848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, Z.; Jung, I.; Szalman, K.; Banias, L.; Bara, T.J.; Gurzu, S. Interaction of arylsulfatases A and B with maspin: A possible explanation for dysregulation of tumor cell metabolism and invasive potential of colorectal cancer. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 3990–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadhead, M.L.; Dass, C.R.; Choong, P.F. In vitro and in vivo biological activity of PEDF against a range of tumors. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 13, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadhead, M.L.; Dass, C.R.; Choong, P.F. Cancer cell apoptotic pathways mediated by PEDF: Prospects for therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Serpin | Alternative Name | GI Cancer | Significance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SERPINA1 | A1AT | GC |
| [64,65,66,67,68,69] |
| PC |
| |||
| CRC |
| |||
| SERPINA12 | Vaspin | HCC |
| [70,71,72] |
| CRC |
| |||
| SERPINB5 | Maspin | ESCC |
| [73,74,75] |
| GC |
| |||
| CRC |
| |||
| SERPINE1 | PAI-1 | ESCC |
| [76,77,78,79] |
| CRC |
| |||
| SERPINF1 | PEDF | GC |
| [80,81,82,83,84] |
| PC |
| |||
| CRC |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pączek, S.; Mroczko, B. The Role of Selected Serpins in Gastrointestinal (GI) Malignancies. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206225
Pączek S, Mroczko B. The Role of Selected Serpins in Gastrointestinal (GI) Malignancies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):6225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206225
Chicago/Turabian StylePączek, Sara, and Barbara Mroczko. 2022. "The Role of Selected Serpins in Gastrointestinal (GI) Malignancies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 6225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206225
APA StylePączek, S., & Mroczko, B. (2022). The Role of Selected Serpins in Gastrointestinal (GI) Malignancies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 6225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206225







