Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia—A Review and Case Presentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology and Symptoms of CHI
3. Diagnosis of HH
Differential Diagnosis
4. Treatment
- -
- Stabilise blood glucose levels at >60 mg/dL;
- -
- Prevent neuroglycopaenia (manifested in hypothermia, apnoea, feeding problems, Cyanosis, tremor, convulsions, apathy, and coma);
- -
- Prevent long-term neurological problems (such as epilepsy, physical and psychological developmental delay, and microcephaly).
4.1. Diazoxide
4.2. Octreotide
4.3. Lanreotide
4.4. Glucagon
4.5. Acarbose
4.6. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Inhibitors
4.7. Potential New Therapies
5. Dietary Treatment
6. Surgical Treatment
7. Influence of CHH on Postnatal Development and QoL
8. Case Report
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| HH | hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia |
| ABCC8 | ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 8 |
| KCNJ11 | Potassium Inwardly-Rectifying Channel Subfamily J Member 11 |
| GLUD1 | Glutamate Dehydrogenase 1 |
| GCK | Glucokinase |
| HADH | Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase |
| SLC16A1 | Solute Carrier Family 16 Member 1 |
| MCT-1 | Monocarboxylate Transporter Subtype 1 |
| UCP2 | Uncoupling Protein 2 |
| HNF4A | Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4A |
| HNF1A | Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1A |
| HK1 | Hexokinase 1 |
| PGM1 | Phosphoglucomutase 1 |
| PMM2 | Phosphomannomutase 2CHI–Congenital hiperinsulinism |
| GLUT-2 | Glucose Transporter 2SUR1–Sylfonylourea Receptor 1 |
| CHH | Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia |
| (18)F-DOPA PET | Fluorine-18-dihydroxyphenyloalanine Positron Emission Tomography |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| SSTR2 | somatostatin receptor 2 |
| SSTR5 | somatostatin receptor 5 |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| mTOR | mammalian Target of Rapamycin |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HRQoL | Health-related quality of life |
| CAH | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| MS-MLPA | Methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification |
| WES | Whole exome sequencing |
| PHHI | Persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia of infancy |
| CGM | Continuous glucose monitoring |
| FGM | Flash glucose monitoring |
References
- Senniappan, S.; Shanti, B.; James, C.; Hussain, K. Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia: Genetic Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Management. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2012, 35, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roženková, K.; Güemes, M.; Shah, P.; Hussain, K. The Diagnosis and Management of Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galcheva, S.; Demirbilek, H.; Al-Khawaga, S.; Hussain, K. The Genetic and Molecular Mechanisms of Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, E.; Shah, P. Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia—An Overview of a Complex Clinical Condition. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.A.; Nessa, A.; Hussain, K. Molecular Mechanisms of Congenital Hyperinsulinism. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, R119–R129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gϋemes, M.; Rahman, S.A.; Kapoor, R.R.; Flanagan, S.; Houghton, J.A.L.; Misra, S.; Oliver, N.; Dattani, M.T.; Shah, P. Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia in Children and Adolescents: Recent Advances in Understanding of Pathophysiology and Management. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, K.; De León, D.D. Hyperinsulinism in the Neonate. Clin. Perinatol. 2018, 45, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, K.; Maejima, Y. KATP Channel Mutations and Neonatal Diabetes. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Rahman, S.A.; Demirbilek, H.; Güemes, M.; Hussain, K. Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia in Children and Adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasawa, K.; Miyakawa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Adachi, E.; Shidei, T.; Sutani, A.; Gau, M.; Nakagawa, R.; Taki, A.; Kashimada, K.; et al. Marked Clinical Heterogeneity in Congenital Hyperinsulinism Due to a Novel Homozygous ABCC8 Mutation. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021, 94, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franco, E.; Saint-Martin, C.; Brusgaard, K.; Knight Johnson, A.E.; Aguilar-Bryan, L.; Bowman, P.; Arnoux, J.B.; Larsen, A.R.; May, S.; Greeley, S.A.W.; et al. Update of Variants Identified in the Pancreatic β-Cell KATP Channel Genes KCNJ11 and ABCC8 in Individuals with Congenital Hyperinsulinism and Diabetes. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 884–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamkin, D.H. Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 22, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galcheva, S.; Al-Khawaga, S.; Hussain, K. Diagnosis and Management of Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 551–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treglia, G.; Mirk, P.; Giordano, A.; Rufini, V. Diagnostic Performance of Fluorine-18-Dihydroxyphenylalanine Positron Emission Tomography in Diagnosing and Localizing the Focal Form of Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2012, 42, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewat, T.I.; Johnson, M.B.; Flanagan, S.E. Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Current Laboratory-Based Approaches to the Genetic Diagnosis of a Heterogeneous Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, K.E.; Becker, S.; Boyajian, L.; Shyng, S.L.; MacMullen, C.; Hughes, N.; Ganapathy, K.; Bhatti, T.; Stanley, C.A.; Ganguly, A. Genotype and Phenotype Correlations in 417 Children with Congenital Hyperinsulinism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E355–E363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohnike, K.; Wieland, I.; Barthlen, W.; Vogelgesang, S.; Empting, S.; Mohnike, W.; Meissner, T.; Zenker, M. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation of Patients with KATP Channel Mutations from the German Registry for Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2014, 81, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vain, N.E.; Chiarelli, F.; Palermo, T.; Isidro, S.; Mejía, R.; Aires, B.; Sanatorio Trinidad Palermo, H. Neonatal Hypoglycaemia: A Never-Ending Story? Neonatology 2021, 118, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.; Platt, M.W. The Investigation and Management of Neonatal Hypoglycaemia. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2005, 10, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.S.; Stanley, C.A.; De Leon, D.D.; Harris, D.; Haymond, M.W.; Hussain, K.; Levitsky, L.L.; Murad, M.H.; Rozance, P.J.; Simmons, R.A.; et al. Recommendations from the Pediatric Endocrine Society for Evaluation and Management of Persistent Hypoglycemia in Neonates, Infants, and Children. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamkin, D.H. Metabolic Screening and Postnatal Glucose Homeostasis in the Newborn. Pediatr. Clin. 2015, 62, 385–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Banerjee, I.; Morris, A.A.M. Recognition, Assessment and Management of Hypoglycaemia in Childhood. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douillard, C.; Mention, K.; Dobbelaere, D.; Wemeau, J.L.; Saudubray, J.M.; Vantyghem, M.C. Hypoglycaemia Related to Inherited Metabolic Diseases in Adults. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, P.C.; Heksch, R.; Cossen, K.; De Leon, D.D.; Kamboj, M.K.; Marks, S.D.; Marshall, B.A.; Miller, R.; Page, L.; Stanley, T.; et al. Management and Appropriate Use of Diazoxide in Infants and Children with Hyperinsulinism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 3750–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, V.B.; Kalitsi, J.; Hickey, A.; Flanagan, S.E.; Kapoor, R.R. Exceptional Diazoxide Sensitivity in Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia Due to a Novel HNF4A Mutation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2019, 2019, 19-0013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.; Key, L.; Swindall, A.; Gaston, K.; Talati, A.J. The Danger of Diazoxide in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2021, 12, 20420986211011338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbilek, H.; Hussain, K. Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Diagnosis and Treatment Update. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizu, R.; Nishimura, K.; Sato, R.; Kosaki, K.; Tanaka, T.; Tanigawara, Y.; Hasegawa, T. Population Pharmacokinetics of Diazoxide in Children with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 88, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, C.; Hashmi, L.A.; Yau, D.; Salomon-Estebanez, M.; Ruiz, D.P.; Hall, C.; O’Shea, E.; Stokes, H.; Foster, P.; Flanagan, S.E.; et al. Longitudinal Auxological Recovery in a Cohort of Children with Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boodhansingh, K.E.; Kandasamy, B.; Mitteer, L.; Givler, S.; De Leon, D.D.; Shyng, S.L.; Ganguly, A.; Stanley, C.A. Novel Dominant KATP Channel Mutations in Infants with Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Validation by in Vitro Expression Studies and in Vivo Carrier Phenotyping. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2019, 179, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiff, S.; Babb, C.; Guemes, M.; Dastamani, A.; Gilbert, C.; Flanagan, S.E.; Ellard, S.; Barton, J.; Dattani, M.; Shah, P. Partial Diazoxide Responsiveness in a Neonate with Hyperinsulinism Due to Homozygous ABCC8 Mutation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2019, 2019, 18-0120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, M.; Shimodera, M.; Maeda, Y.; Iwakura, M.; Hara, M. Safety and Effectiveness, Including Intelligence Prognosis, of Diazoxide inpediatric Patients with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia: Special Survey in Japan (Long-Term, All-Case Survey). Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2018, 27, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartorelli, C.; Gargano, N.; Leonetti, G.; Zanchetti, A. Hypotensive and Renal Effects of Diazoxide, a Sodiumretaining Benzothiadiazine Compound. Circulation 1963, 27, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.D.; Dudash, K.; Escobar, C.; Freel, C.; Harrison, T.; McMillan, C.; Puia-Dumitrescu, M.; Cotten, C.M.; Benjamin, R.; Clark, R.H.; et al. Prevalence and Safety of Diazoxide in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.; Ellen Vajravelu, M.; Givler, S.; Mitteer, L.; Avitabile, C.M.; Lord, K.; De León, D.D. Prevalence of Adverse Events in Children with Congenital Hyperinsulinism Treated with Diazoxide. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timlin, M.R.; Black, A.B.; Delaney, H.M.; Matos, R.I.; Percival, C.S. Development of Pulmonary Hypertension during Treatment with Diazoxide: A Case Series and Literature Review. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2017, 38, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylat, R.I. Pulmonary Hypertension Occurring with Diazoxide Use in a Preterm Infant with Hypoglycemia. Drug. Healthc. Patient Saf. 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.T.; Tillman, K.A.; Kindel, S.J.; Handler, S.S. Diazoxide-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension in a Patient with Noncompaction Cardiomyopathy. Pulm. Circ. 2021, 11, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shono, T.; Shono, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Taguchi, S.; Masuda, M.; Muramori, K.; Taguchi, T. Congenital Hyperinsulinism Associated with Hirschsprung’s Disease—A Report of an Extremely Rare Case. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, B.; Saraswathi, S.; Hussain, K. Somatostatin Analogues for the Treatment of Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 11, 2042018820965068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunt, M.; Dale, O.; Smith, P.A. Somatostatin Inhibits Oxidative Respiration in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männistö, J.M.E.; Jääskeläinen, J.; Otonkoski, T.; Huopio, H. Long-Term Outcome and Treatment in Persistent and Transient Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Finnish Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Kawakita, R.; Yokoya, S.; Ogata, T.; Ozono, K.; Arisaka, O.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kusuda, S.; Masue, M.; Nishibori, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Octreotide for the Treatment of Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Prospective, Open-Label Clinical Trial and an Observational Study in Japan Using a Nationwide Registry. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Rahman, S.A.; McElroy, S.; Gilbert, C.; Morgan, K.; Hinchey, L.; Senniappan, S.; Levy, H.; Amin, R.; Hussain, K. Use of Long-Acting Somatostatin Analogue (Lanreotide) in an Adolescent with Diazoxide-Responsive Congenital Hyperinsulinism and Its Psychological Impact. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2015, 84, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khnen, P.; Marquard, J.; Ernert, A.; Meissner, T.; Raile, K.; Wannenmacher, G.; Blankenstein, O. Long-Term Lanreotide Treatment in Six Patients with Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2012, 78, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastamani, A.; Guëmes, M.; Pitfield, C.; Morgan, K.; Rajab, M.; Rottenburger, C.; Bomanji, J.; De Coppi, P.; Dattani, M.; Shah, P. The Use of a Long-Acting Somatostatin Analogue (Lanreotide) in Three Children with Focal Forms of Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 91, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundarapandian, M.M.; Juliana, C.A.; Chai, J.; Haslett, P.A.; Fitzgerald, K.; de León, D.D. Activation of Protein Kinase A (PKA) Signaling Mitigates Congenital Hyperinsulinism Associated Hypoglycemia in the Sur1-/- Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohnike, K.; Blankenstein, O.; Pfuetzner, A.; Pötzsch, S.; Schober, E.; Steiner, S.; Hardy, O.T.; Grimberg, A.; Van Waarde, W.M. Long-Term Non-Surgical Therapy of Severe Persistent Congenital Hyperinsulinism with Glucagon. Horm. Res. 2008, 70, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Giugliano, D. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Relationships of Acarbose. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1996, 30, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, G.; Antonia, D.; Michael, A.; Kate, M.; Sian, E.; Sarah, F.E.; Mehul, D.; Pratik, S. Sirolimus: Efficacy and Complications in Children with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulke, M.H.; Bergsland, E.K.; Yao, J.C. Glycemic Control in Patients with Insulinoma Treated with Everolimus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haliloğlu, B.; Tüzün, H.; Flanagan, S.E.; Çelik, M.; Kaya, A.; Ellard, S.; Özbek, M.N. Sirolimus-Induced Hepatitis in Two Patients with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2018, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankhala, K.; Mita, A.; Kelly, K.; Mahalingam, D.; Giles, F.; Mita, M. The Emerging Safety Profile of MTOR Inhibitors, a Novel Class of Anticancer Agents. Target. Oncol. 2009, 4, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuntaş, Y. Postprandial Reactive Hypoglycemia. Sisli Etfal Hastan. Tip Bul. 2019, 53, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroni, L.; Palucci, A.; Biscontini, G.; Cherubini, V. Early Diagnosis of Focal Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Fluorine-18-Labeled l-Dihydroxyphenylalanine Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Study. World J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 20, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghe, D.; Gunatilake, S.S.C.; Dassanyake, V.E.; Garusinghe, C.; Ganewaththa, E.; Appuhamy, C.; Somasundaram, N.P.; Sivaganesh, S. Seeking the Unseen: Localization and Surgery for an Occult Sporadic Insulinoma. Ann. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Surg. 2020, 24, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, B.; Lübke, H.J.; Frieling, T.; Strohmeyer, G.; Starke, A.A.R. Prospective Study on the Detection of Insulinomas by Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Endoscopy 1996, 28, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.S. Gastrointestinal Endocrine Tumours. Insulinoma. Baillieres. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1996, 10, 645–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lairmore, T.C.; Moley, J.F.; Lairmore, T.C.; Surgery, O. Endocrine Pancreatic Tumors. Scand. J. Surg. 2004, 93, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, A.; Krausch, M.M.; Anlauf, M.; Wieben, D.; Braunstein, S.; Klöppel, G.; Röher, H.D.; Knoefel, W.T. Diffuse Nesidioblastosis as a Cause of Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia in Adults: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Surgery 2007, 141, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.A.; Miranda, A.C.; Maior, M.S.; de Mello, R.V.; Bandeira, F. Nesidioblastosis Associated with Pancreatic Heterotopia as a Differential Diagnosis of Hypoglycemia: A Literature Review and Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e922778-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, E.; Demirbilek, H.; Houghton, J.A.; Ellard, S.; Flanagan, S.E.; Hussain, K. Congenital Hyperinsulinism and Evolution to Sulfonylurearesponsive Diabetes Later in Life Due to a Novel Homozygous p.L171F ABCC8 Mutation. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2019, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, I.; Forsythe, L.; Skae, M.; Avatapalle, H.B.; Rigby, L.; Bowden, L.E.; Craigie, R.; Padidela, R.; Ehtisham, S.; Patel, L.; et al. Feeding Problems Are Persistent in Children with Severe Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, C.; Hall, C.; Wilson, S.; Gilligan, N.; O’Shea, E.; Salomon-Estebanez, M.; Dunne, M.; Banerjee, I. Delayed Resolution of Feeding Problems in Patients with Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajravelu, M.E.; Congdon, M.; Mitteer, L.; Koh, J.; Givler, S.; Shults, J.; De León, D.D. Continuous Intragastric Dextrose: A Therapeutic Option for Refractory Hypoglycemia in Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 91, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avatapalle, H.B.; Banerjee, I.; Shah, S.; Pryce, M.; Nicholson, J.; Rigby, L.; Caine, L.; Didi, M.; Skae, M.; Ehtisham, S.; et al. Abnormal Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Are Common in Children with Transient Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männistö, J.M.E.; Jääskeläinen, J.; Huopio, H. Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsutani, N.; Furuta, H.; Matsuno, S.; Oku, Y.; Morita, S.; Uraki, S.; Doi, A.; Furuta, M.; Iwakura, H.; Ariyasu, H.; et al. Identification of a Compound Heterozygous Inactivating ABCC8 Gene Mutation Responsible for Young-onset Diabetes with Exome Sequencing. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huopio, H.; Otonkoski, T.; Vauhkonen, I.; Reimann, F.; Ashcroft, F.M.; Laakso, M. A New Subtype of Autosomal Dominant Diabetes Attributable to a Mutation in the Gene for Sulfonylurea Receptor 1. Lancet 2003, 361, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.R.; Flanagan, S.E.; James, C.T.; McKiernan, J.; Thomas, A.M.; Harmer, S.C.; Shield, J.P.; Tinker, A.; Ellard, S.; Hussain, K. Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia and Diabetes Mellitus due to Dominant ABCC8/KCNJ11 Mutations. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulhadi-Atwan, M.; Bushman, J.D.; Tornovsky-Babaey, S.; Perry, A.; Abu-Libdeh, A.; Glaser, B.; Shyng, S.L.; Zangen, D.H. Novel De Novo Mutation in Sulfonylurea Receptor 1 Presenting as Hyperinsulinism in Infancy Followed by Overt Diabetes in Early Adolescence. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouron-Hryciuk, J.; Stoppa-Vaucher, S.; Busiah, K.; Bouthors, T.; Antoniou, M.C.; Jacot, E.; Brusgaard, K.; Christesen, H.T.; Hussain, K.; Dwyer, A.; et al. Congenital Hyperinsulinism: 2 Case Reports with Different Rare Variants in ABCC8. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 26, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbilek, H.; Galcheva, S.; Vuralli, D.; Al-Khawaga, S.; Hussain, K. Ion Transporters, Channelopathies, and Glucose Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, A.G.; Melikian, M.; Globa, E.; Detlefsen, S.; Rasmussen, L.; Petersen, H.; Brusgaard, K.; Rasmussen, A.H.; Mortensen, M.B.; Christesen, H.T. The Difficult Management of Persistent, Non-Focal Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Retrospective Review from a Single, Tertiary Center. Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 21, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
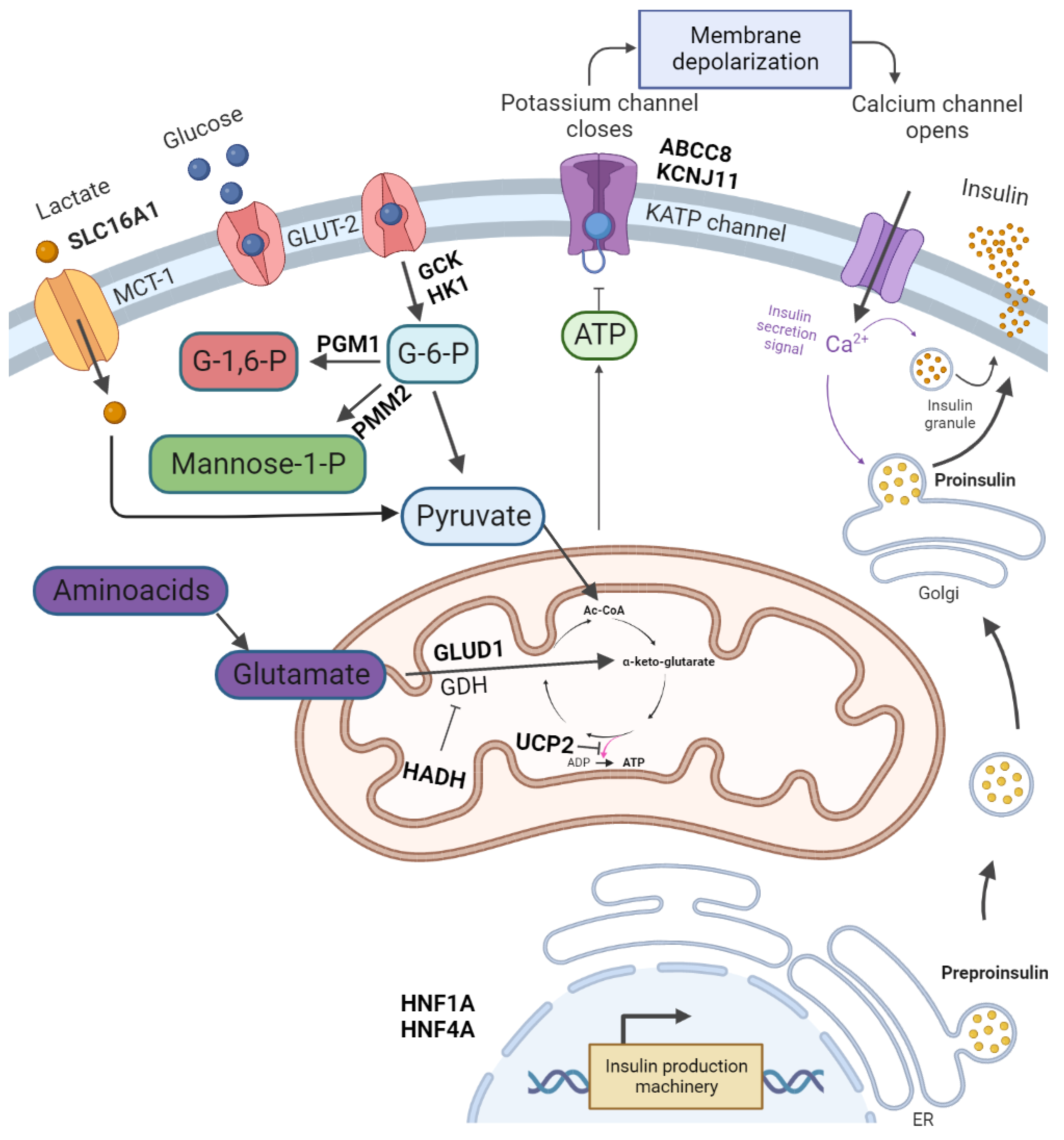
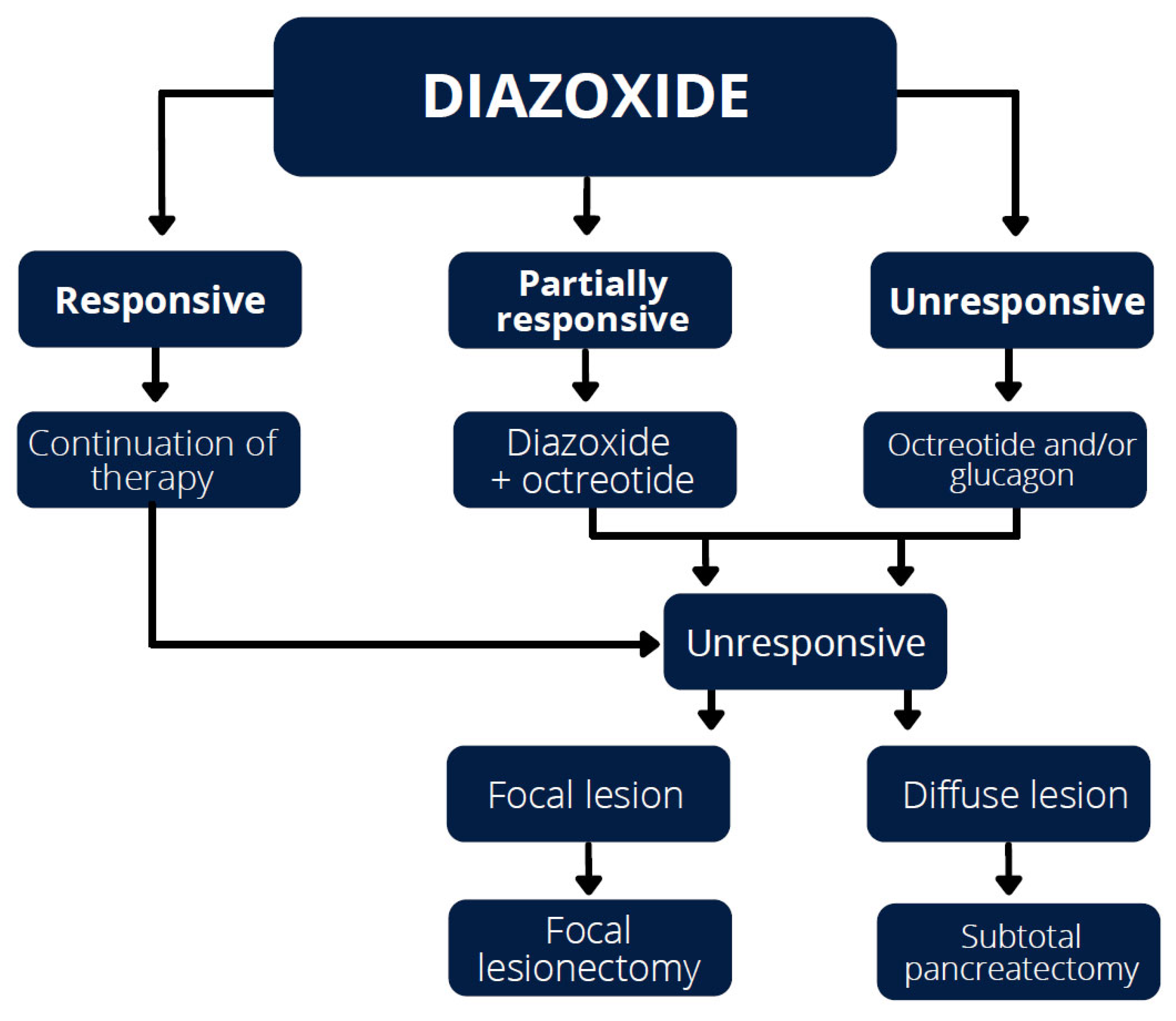
| Gene | Full Gene Name | Diazoxide Responsiveness |
|---|---|---|
| ABCC8 | ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 8 | Yes/No |
| KCNJ11 | Potassium Inwardly-Rectifying Channel Subfamily J Member 11 | No |
| GLUD1 | Glutamate Dehydrogenase 1 | Yes |
| GCK | Glucokinase | Yes/No |
| HADH | Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase | Yes |
| SLC16A1 (MCT-1) | Solute Carrier Family 16 Member 1 (Monocarboxylate Transporter Subtype 1) | Yes/No |
| UCP2 | Uncoupling Protein 2 | Yes |
| HNF4A | Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4A | Yes |
| HNF1A | Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1A | Yes |
| HK1 | Hexokinase 1 | Yes |
| PGM1 | Phosphoglucomutase 1 | No |
| PMM2 | Phosphomannomutase 2 | Yes |
| Transient neonatal hypoglycemia caused by hyperinsulinism |
|
| Patent neonatal hypoglycemia | Inborn metabolic errors (impaired gluconeogenesis):
|
Congenital hyperinsulinism:
| |
Counter-regulatory hormone deficiency:
| |
Increased glucose requirement:
|
| Suggested Investigations in Differential Diagnosis |
|---|
| Complete blood count |
| Arterial blood gas |
| Blood glucose |
| Lactate |
| Pyruvate |
| Alanine |
| Glycerol |
| Ketone bodies |
| Plasma insulin |
| Free fatty acids |
| C-peptide |
| Plasma total and free carnitine, acylcarnitine profile |
| Ammonia |
| Electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine |
| Uric acid |
| Growth hormone |
| Cortisol |
| Thyroid hormones |
| IGF-1 |
| Galactosaemia screen |
| Ketones and organic acids in urine |
| Parameter | Level | Reference Range | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 46 | 50–200 | mg/dL |
| Insulin | 183.5 | 2.6–24.9 | µIU/mL |
| C-Peptide | 18.61 | 1–4 | ng/mL |
| Cortisol | 19.0 | 6.2–19.4 | µg/dL |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) | 14.5 | 0.7–15.2 | µIU/mL |
| Thyroxine (T4) | 2.31 | 0.86–2.49 | ng/dL |
| Growth hormone (GH) | 22.4 | 1.18–27 | ng/mL |
| Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) | 47.22 | 0–26 | ng/mL |
| Ammonia | 45.7 | 21–95 | µmol/L |
| Parameter | Before Surgery | After Surgery | Reference Ranges | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 46 | 105 | 50–160 | mg/dL |
| Insulin | 183.5 | 14.83 | 2.6–24.9 | µIU/mL |
| C-Peptide | 18.61 | 2.67 | 1.1–4.4 | µg/L |
| Lipase | - | 12 | 0–37 | U/L |
| Elastase in faeces | - | 432 | >200 | µg/g |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krawczyk, S.; Urbanska, K.; Biel, N.; Bielak, M.J.; Tarkowska, A.; Piekarski, R.; Prokurat, A.I.; Pacholska, M.; Ben-Skowronek, I. Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia—A Review and Case Presentation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206020
Krawczyk S, Urbanska K, Biel N, Bielak MJ, Tarkowska A, Piekarski R, Prokurat AI, Pacholska M, Ben-Skowronek I. Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia—A Review and Case Presentation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):6020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206020
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrawczyk, Sylwia, Karolina Urbanska, Natalia Biel, Michal Jakub Bielak, Agata Tarkowska, Robert Piekarski, Andrzej Igor Prokurat, Malgorzata Pacholska, and Iwona Ben-Skowronek. 2022. "Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia—A Review and Case Presentation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 6020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206020
APA StyleKrawczyk, S., Urbanska, K., Biel, N., Bielak, M. J., Tarkowska, A., Piekarski, R., Prokurat, A. I., Pacholska, M., & Ben-Skowronek, I. (2022). Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia—A Review and Case Presentation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 6020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206020





