How to Recognize and Treat Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Prevalence, Pathophysiology, and Risk Factors of SIBO
- Gastrointestinal antimicrobial defense mechanisms connected with the production of hydrochloric acid (which may be deficient due to atrophic gastritis, long-term proton pump inhibitor use, or gastric resection), pancreatic enzyme secretion (impaired in chronic pancreatitis or cystic fibrosis), bile, and mucosal immunity (compromised in AIDS or insufficient immunoglobulin A secretion);
- Gastrointestinal motility. Motility disorders impair small intestinal clearance due to the absence of phase III of the migrating motor complex and retrograde peristalsis. Such disorders may be due to primary visceral neuropathy or myopathy (intestinal pseudo-obstruction) or, much more commonly, secondary neuropathy (e.g., in diabetes; amyloidosis; scleroderma; Parkinson’s disease; iatrogenic effects of drugs, such as opioids or anticholinergic and antidiarrheal agents);
- Gastrointestinal tract anatomy. Anatomical anomalies include small intestinal diverticuli, strictures, adhesions, and interloop fistulae; secondary structural anomalies, which are often a result of Crohn’s disease, radiotherapy, or surgical interventions (gastrojejunostomy, colectomy, or ileocecal valve resection).
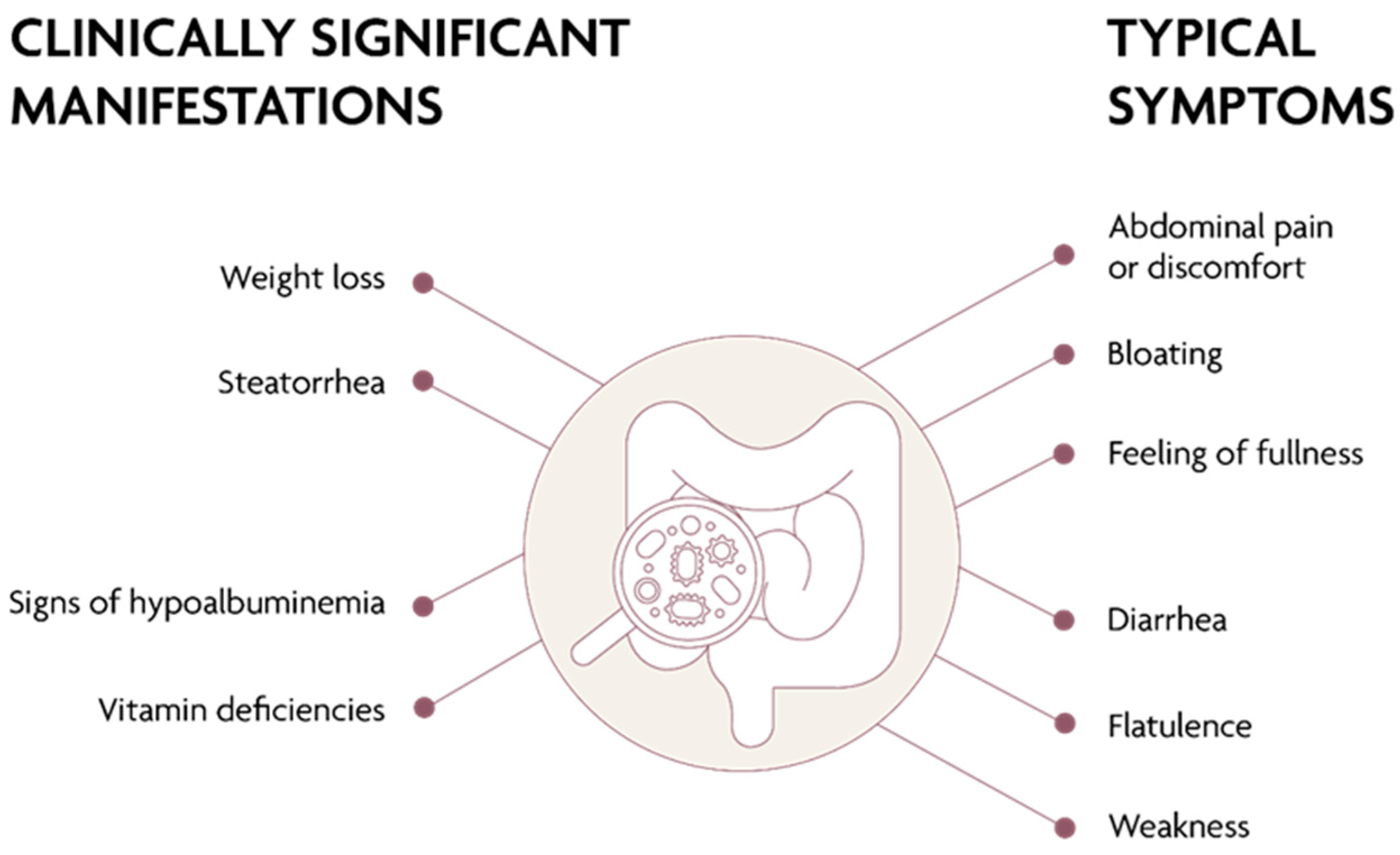
3. Clinical Presentation of SIBO
4. SIBO Diagnostics
5. SIBO Treatment
5.1. Diet
5.2. Antibiotic Therapy
5.3. Probiotics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrett, C.R., Jr.; Holt, P.R. Postgastrectomy blind loop syndrome: Megaloblastic anemia secondary to malabsorption of folic acid. Am. J. Med. 1966, 41, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, G.; Gompertz, D.; Schönsby, H.; Tabaqchali, S.; Booth, C.C. The metabolic and nutritional consequences of bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1972, 25, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajicek, E.J.; Hansel, S.L. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Primary Care Review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.C.; Bhagatwala, J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Clinical features and therapeutic management: Clinical features and therapeutic management. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, W.; Pimentel, M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Irritable Bowel Syndrome–An Update. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achufusi, T.G.O.; Sharma, A.; Zamora, E.A.; Manocha, D. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Comprehensive Review of Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment Methods. Cureus 2020, 12, e8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.; Pimentel, M.; Rao, S.S. How to Test and Treat Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: An Evidence-Based Approach. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.; Shin, A.; Teagarden, S.; Xu, H.; Gupta, A.; Siwiec, R.; Nelson, D.; Wo, J.M. Risk Factors Associated with Upper Aerodigestive Tract or Coliform Bacterial Overgrowth of the Small Intestine in Symptomatic Patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 54, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, A.S.; Gao, X.; Bohm, M.; Lin, H.; Gupta, A.; Nelson, D.E.; Toh, E.; Teagarden, S.; Siwiec, R.; Dong, Q.; et al. Characterization of Proximal Small Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Suspected Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, E.; Shaw, C.; Whelan, K.; Andreyev, H.J.N. Review article: Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth–Prevalence, clinical features, current and developing diagnostic tests, and treatment. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Saad, R.J.; Long, M.D.; Rao, S.S.C. ACG Clinical Guideline: Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, R.S.; Ruff, K.C.; Malhotra, A.; Herrick, L.; Locke, G.R.; Harmsen, W.S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Talley, N.J.; Saito, Y.A. Clinical predictors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth by duodenal aspirate culture. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Kim, J.J.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Dai, N. Prevalence and predictors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Talley, N.J.; Jones, M.; Kendall, B.J.; Koloski, N.; Walker, M.M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, M.; Veneto, G.; Malservisi, S.; Corazza, G.R. Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth and Metabolic Bone Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2001, 46, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaie, A.; Buresi, M.; Lembo, A.; Lin, H.; McCallum, R.; Rao, S.; Schmulson, M.; Valdovinos, M.; Zakko, S.; Pimentel, M. Hydrogen and Methane-Based Breath Testing in Gastrointestinal Disorders: The North American Consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.A.; Baker, J.R.; Wamsteker, E.J.; Saad, R.; DiMagno, M.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Common in Chronic Pancreatitis and Associates with Diabetes, Chronic Pancreatitis Severity, Low Zinc Levels, and Opiate Use. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, C.P.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Kumar, S.; Goel, A.; Misra, A.; Mohindra, S.; Choudhuri, G. Frequency and Factors Associated with Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Cirrhosis of the Liver and Extra Hepatic Portal Venous Obstruction. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, A.; Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Mulak, A.; Lipiński, M.; Małecka-Panas, E.; Reguła, J.; Rydzewska, G. Guidelines on the management of irritable bowel syndrome: In memory of Professor Witold Bartnik. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2018, 13, 259–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, A.; Rao, S.S.C.; Gulley, D.; Jacobs, C.; Lee, Y.Y.; Badger, C. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: Duodenal aspiration vs glucose breath test. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmidt, E.; Smyrk, T.C.; Boswell, C.L.; Enders, F.T.; Oxentenko, A.S. Increasing duodenal intraepithelial lymphocytosis found at upper endoscopy: Time trends and associations. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 80, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remes-Troche, J.M.; Adames, K.; Castillo-Rodal, A.I.; Ramírez, T.; Barreto-Zuñiga, R.; Lopez-Vidal, Y.; Uscanga, L.F. Intraepithelial γδ+ Lymphocytes: A Comparative Study Between Celiac Disease, Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth, and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.; Tang, J.; Pyleris, E.; Pistiki, A.; Barbatzas, C.; Brown, J.; Lee, C.C.; Harkins, T.T.; Kim, G.; Weitsman, S.; et al. Molecular assessment of differences in the duodenal microbiome in subjects with irritable bowel syndrome. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.; Shah, A.; Jones, M.P.; Koloski, N.; Talley, N.J.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G. Methane positive small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1933313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losurdo, G.; Leandro, G.; Ierardi, E.; Perri, F.; Barone, M.; Principi, M.; Di Leo, A. Breath Tests for the Non-invasive Diagnosis of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, B.T.; Wald, A. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Syndrome: A Guide for the Appropriate Use of Breath Testing. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Szarka, L.A. Every Breath Test You Take: Practical Advice on Breath Testing Used to Detect Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, J.; Ford, A.C.; Yuan, Y.; Chey, W.D.; Lacy, B.E.; Saito, Y.A.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Moayyedi, P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Evaluating the Efficacy of a Gluten-Free Diet and a Low FODMAPS Diet in Treating Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.; Reed, D.E.; Schneider, T.; Dang, F.; Keshteli, A.H.; De Palma, G.; Madsen, K.; Bercik, P.; Vanner, S. FODMAPs alter symptoms and the metabolome of patients with IBS: A randomised controlled trial. Gut 2017, 66, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, C.J.; Staudacher, H.M.; Ford, A.C. Efficacy of a low FODMAP diet in irritable bowel syndrome: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gut 2021, 71, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.; Constantino, T.; Kong, Y.; Bajwa, M.; Rezaei, A.; Park, S. A 14-Day Elemental Diet Is Highly Effective in Normalizing the Lactulose Breath Test. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M.; Murray, J.A.; Pimentel, M. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, E.C.; Gabrielli, M.; Scarpellini, E.; Lupascu, A.; Novi, M.; Sottili, S.; Vitale, G.; Cesario, V.; Serricchio, M.; Cammarota, G.; et al. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Recurrence After Antibiotic Therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X. Efficacy of rifaximin in treating with small intestine bacterial overgrowth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, L.; Scarpignato, C. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Rifaximin is effective and safe for the treatment of small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Zocco, M.A.; D’Aversa, F.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A. Eubiotic properties of rifaximin: Disruption of the traditional concepts in gut microbiota modulation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Cash, B.D.; Lembo, A.; Wolf, R.A.; Israel, R.J.; Schoenfeld, P. Repeat Rifaximin for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: No Clinically Significant Changes in Stool Microbial Antibiotic Sensitivity. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinler, J.K.; Taweechotipatr, M.; Rognerud, C.L.; Ou, C.N.; Tumwasorn, S.; Versalovic, J. Human-derived probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri demonstrate antimicrobial activities targeting diverse enteric bacterial pathogens. Anaerobe 2008, 14, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Yin, R.; Du, S.; Ye, F.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; et al. In vitro evaluation of the probiotic and functional potential of Lactobacillus strains isolated from fermented food and human intestine. Anaerobe 2014, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Rastall, R.A.; Gibson, G.R.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Chatzifragkou, A. Adhesion mechanisms mediated by probiotics and prebiotics and their potential impact on human health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, N.R.F.; Ramos, M.R.Z.; de Oliveira Carlos, L.; da Cruz, M.R.R.; Taconeli, C.A.; Filho, A.J.B.; Nassif, L.S.; Schieferdecker, M.E.M.; Campos, A.C.L. Effects of Probiotics Supplementation on Gastrointestinal Symptoms and SIBO after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Collinot, G.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.O.; Martínez-Bencomo, M.A.; Carranza-Muleiro, R.A.; Jara, L.J.; Vera-Lastra, O.; Montes-Cortes, D.H.; Medina, G.; Cruz-Domínguez, M.P. Effectiveness of Saccharomyces boulardii and Metronidazole for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Systemic Sclerosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventogiannis, K.; Gkolfakis, P.; Spithakis, G.; Tsatali, A.; Pistiki, A.; Sioulas, A.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Triantafyllou, K. Effect of a Preparation of Four Probiotics on Symptoms of Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Association with Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Saadi, M.; Ramsey, F.V.; Schey, R.; Parkman, H.P. Effect of Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 (Align) on the Lactulose Breath Test for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Qu, C.; Wang, B.; Liang, S.; Zeng, B. Probiotics for Preventing and Treating Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A meta-analysis and systematic review of current evidence. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.C.; Rehman, A.; Yu, S.; De Andino, N.M. Brain fogginess, gas and bloating: A link between SIBO, probiotics and metabolic acidosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Period before the Breath Test | Drugs/Activities to Be Avoided |
|---|---|
| 4 weeks | Oral or intravenous antibiotics Prokinetic agents |
| 2 weeks | Probiotics |
| 1 week | Proton pump inhibitors |
| 48 h | Motility regulators: loperamide, metoclopramide, trimebutine |
| 24 h | Alcohol Fiber (particularly non-soluble fiber) |
| 12 h | Oral food intake (only water is allowed) |
| The morning on the day of the test | Smoking Physical exertion Food Regularly used medications are allowed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Cukrowska, B. How to Recognize and Treat Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206017
Skrzydło-Radomańska B, Cukrowska B. How to Recognize and Treat Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206017
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkrzydło-Radomańska, Barbara, and Bożena Cukrowska. 2022. "How to Recognize and Treat Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206017
APA StyleSkrzydło-Radomańska, B., & Cukrowska, B. (2022). How to Recognize and Treat Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 6017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206017






