Sub-Muscular Direct-to-Implant Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Previously Irradiated Patients Avoiding the Use of ADM: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
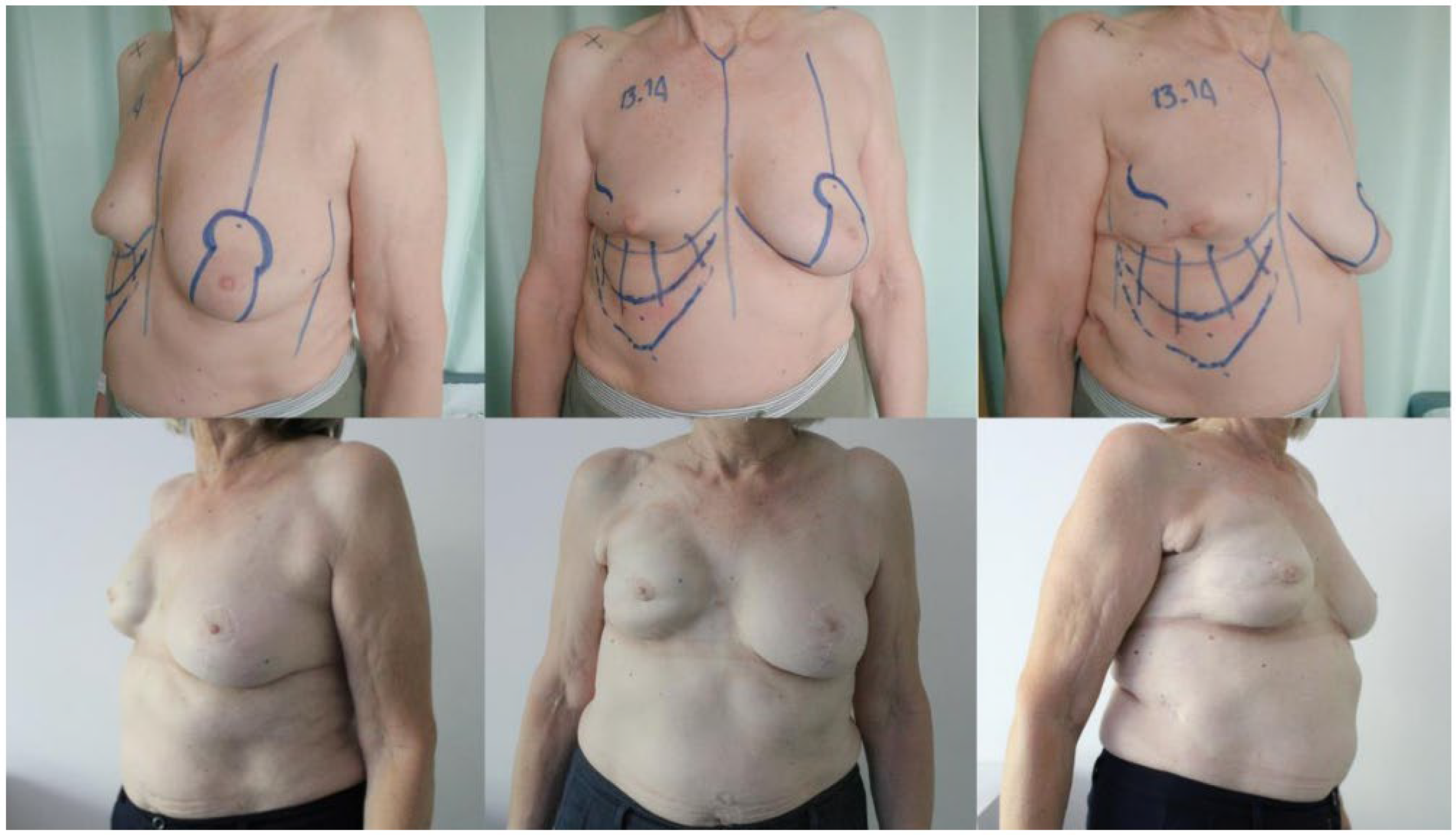
2.1. Surgical Technique
2.2. Statistical Analysis
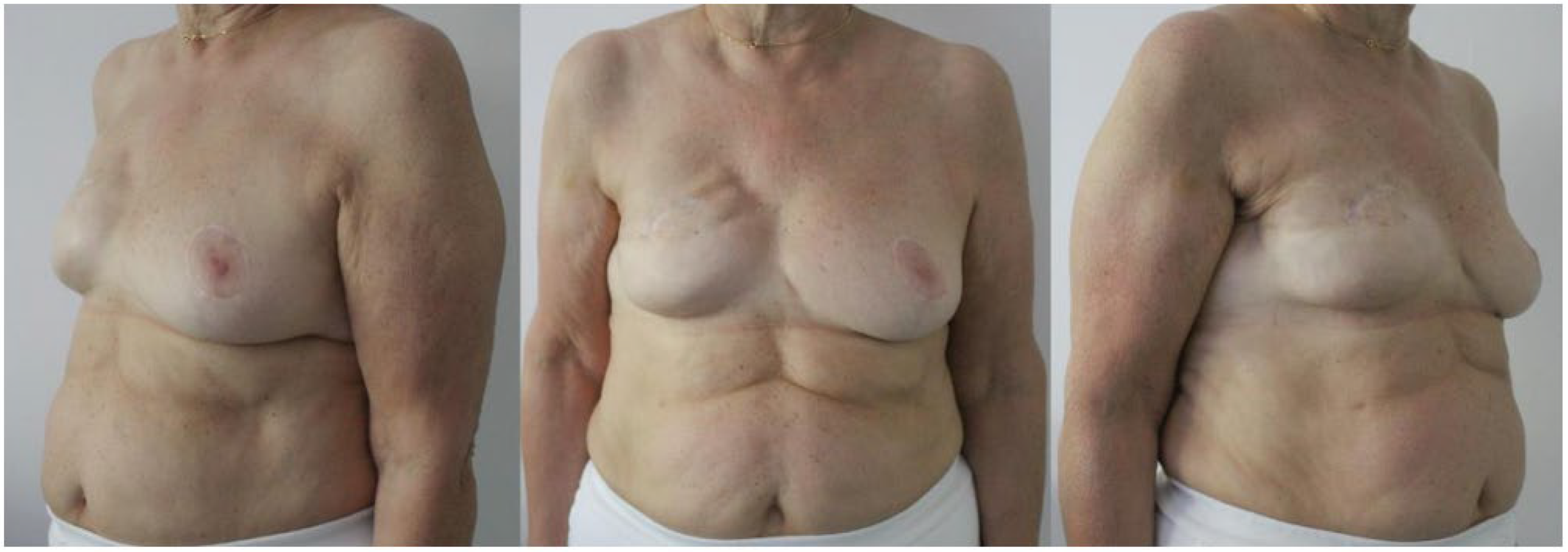
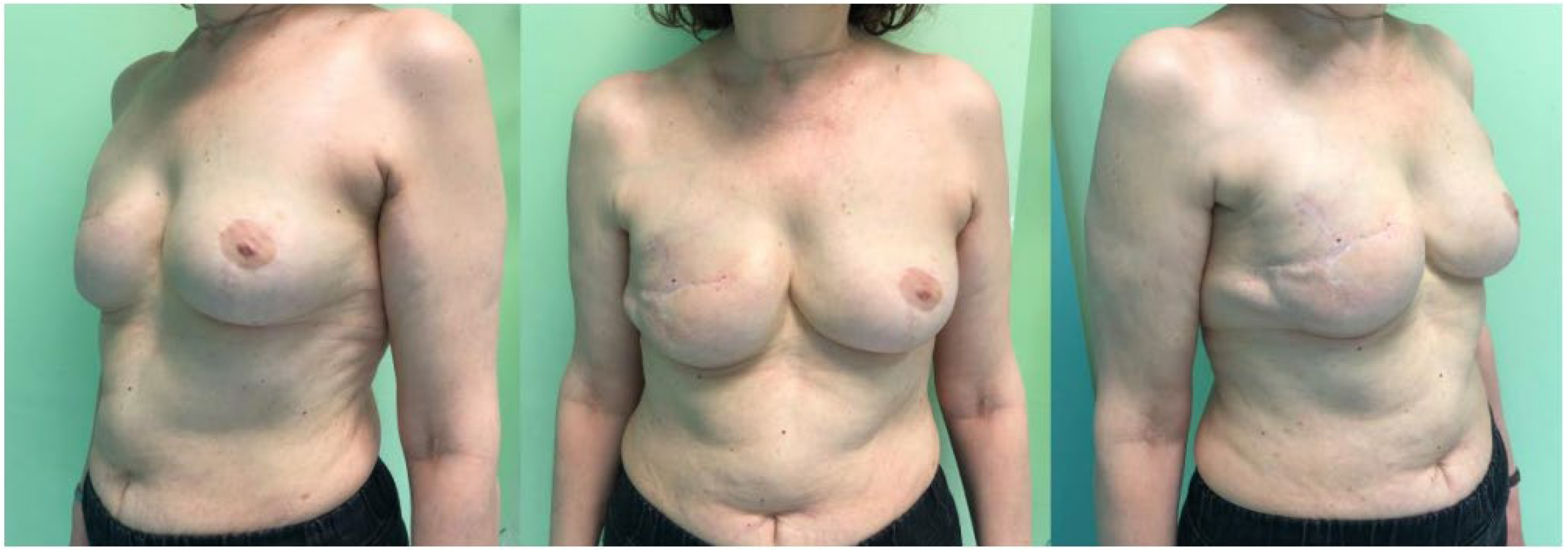
3. Results
Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeSantis, C.; Ma, J.; Bryan, L.; Jemal, A. Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzi, F.; Rietjens, M.; Soresina, M.; Rossetto, F.; Bosco, R.; Vento, A.R.; Monti, S.; Petit, J.Y. Immediate breast reconstruction in the elderly: Can it be considered an integral step of breast cancer treatment? The experience of the European Institute of Oncology, Milan. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2010, 63, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltahir, Y.; Werners, L.L.; Dreise, M.M.; van Emmichoven, I.A.; Jansen, L.; Werker, P.M.; de Bock, G.H. Quality-of-life outcomes between mastectomy alone and breast reconstruction: Comparison of patient-reported BREAST-Q and other health-related quality-of-life measures. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 201e–209e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, G.; Martin Sanchez, A.; Di Leone, A.; Magno, S.; Moschella, F.; Accetta, C.; Masetti, R. New trends in breast cancer surgery: A therapeutic approach increasingly efficacy and respectful of the patient. G. Chir. 2015, 36, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.P.; Soysal, S.D.; Zeindler, J.; Kappos, E.A.; Babst, D.; Schwab, F.; Kurzeder, C.; Haug, M. Current standards in oncoplastic breast conserving surgery. Breast 2017, 34 (Suppl. S1), S78–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.R.; Losken, A.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Schuster, D.M.; Switchenko, J.M.; Mister, D.; Godette, K.; Torres, M.A. Local recurrence patterns in breast cancer patients treated with oncoplastic reduction mammaplasty and radiotherapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.E.; Pain, S.J.; Peley, G. Treatment of recurrent breast cancer following breast conserving surgery. Breast J. 2013, 19, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.M.; Golshan, M. Management of In-Breast Tumor Recurrence. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2846–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, C.; Wang, K.; Asthana, R.; Drost, L.; Lam, H.; Lee, J.; Vesprini, D.; Leung, E.; DeAngelis, C.; Chow, E. Radiation-induced Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Trials. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e825–e840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, B.; Marx, M.; Untch, M.; Faridi, A. Breast Reconstruction Following Cancer Treatment. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2015, 112, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, G.L.; Heidemann, L.N.; Bille, C.; Sorensen, J.A.; Thomsen, J.B. Nipple sparing mastectomy and the evolving direct to implant breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2018, 7, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, P.G.; Snell, L.; Heerdt, A.; McCarthy, C. Immediate tissue expander/implast breast reconstruction after salvage mastectomy for cancer recurrence following lumpectomy/irradiation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusic, A.L.; Reavey, P.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Scott, A.; McCarthy, C.; Cano, S.J. Measuring patient outcomes in breast augmentation: Introducing the BREAST-Q Augmentation module. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009, 36, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Momeni, A.; Luan, J.; Chung, M.T.; Wright, E.; Lee, G.K. Quality of life and patient satisfaction after microsurgical abdominal flap versus staged expander/implant breast reconstruction: A critical study of unilateral immediate breast reconstruction using patient-reported outcomes instrument BREAST-Q. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayi, A.C.; Agha, R.A.; Sieber, B.A.; Orgill, D.P. Impact of Obesity on Outcomes in Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2018, 34, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Slater, K.; Papsdorf, M.; Van Laeken, N.; Zhong, T.; Hazen, A.; Vidal, D.; Macadam, S.A. Autologous Breast Reconstruction in Women Older Than 65 Years Versus Women Younger Than 65 Years: A Multi-Center Analysis. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechter, S.; Arad, E.; Inbal, A.; Friedman, O.; Gur, E.; Barnea, Y. DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction Complication Rate in Previously Irradiated Internal Mammary Nodes. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2018, 34, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, P.; Koolen, P.G.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Paul, M.A.; Dikmans, R.E.; Schermerhorn, M.L.; Lee, B.T.; Lin, S.J. Analyzing Regional Differences over a 15-Year Trend of One-Stage versus Two-Stage Breast Reconstruction in 941,191 Postmastectomy Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 1e–14e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, J.D.; Fischer, J.P.; Nelson, J.A.; Serletti, J.M.; Wu, L.C. Direct-to-implant breast reconstruction: An analysis of 1612 cases from the ACS-NSQIP surgical outcomes database. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2014, 48, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, P.G.; McCarthy, C.M. A single surgeon’s 12-year experience with tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction: Part II. An analysis of long-term complications, aesthetic outcomes, and patient satisfaction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, D.R.; Garvey, P.B.; Qi, J.; Hamill, J.B.; Kim, H.M.; Pusic, A.L.; Kronowitz, S.J.; Wilkins, E.G.; Butler, C.E.; Clemens, M.W. Direct-to-Implant versus Two-Stage Tissue Expander/Implant Reconstruction: 2-Year Risks and Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Prospective, Multicenter Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.H.; Scott, A.M.; Price, A.N.; Miller, H.C.; Klassen, A.F.; Jhanwar, S.M.; Mehrara, B.J.; Disa, J.J.; McCarthy, C.; Matros, E.; et al. Psychosocial and Sexual Well-Being Following Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy and Reconstruction. Breast J. 2016, 22, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdanasari, A.T.; Abu-Ghname, A.; Raj, S.; Winocour, S.J.; Largo, R.D. Update in Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2019, 33, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoum, G.E.; Salama, L.; Niemierko, A.; Vieira, B.L.; Belkacemi, Y.; Colwell, A.S.; Winograd, J.; Smith, B.; Ho, A.; Taghian, A.G. Single Stage Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction Has Lower Complication Rates Than Tissue Expander and Implant and Comparable Rates to Autologous Reconstruction in Patients Receiving Postmastectomy Radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 106, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, D.L.; Chiu, J.; Restifo, R.J.; Ward, B.A.; Haffty, B.; Ariyan, S. Breast reconstruction in previously irradiated patients using tissue expanders and implants: A potentially unfavorable result. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1998, 40, 360–363, discussion 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.R.; Schusterman, M.A.; Kroll, S.S.; Miller, M.J.; Reece, G.P.; Robb, G.L.; Ainslie, N. Reconstruction and the radiated breast: Is there a role for implants? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 1111–1115, discussion 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persichetti, P.; Cagli, B.; Simone, P.; Cogliandro, A.; Fortunato, L.; Altomare, V.; Trodella, L. Implant breast reconstruction after salvage mastectomy in previously irradiated patients. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2009, 62, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contant, C.M.; van Geel, A.N.; van der Holt, B.; Griep, C.; Wai, R.T.J.; Wiggers, T. Morbidity of immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) after mastectomy by a subpectorally placed silicone prosthesis: The adverse effect of radiotherapy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 26, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, O.; Andersen, M.; Siim, E. Breast reconstruction and tissue expansion in irradiated versus not irradiated women after mastectomy. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand Surg. 1996, 30, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, E.A.; Wilkins, E.G.; Strawderman, M.; Cederna, P.; Goldfarb, S.; Vicini, F.A.; Pierce, L.J. Complications and patient satisfaction following expander/implant breast reconstruction with and without radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 49, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Summa, P.G.; Tay, S.K.; Stevens, R.; Doughty, J.C.; Bramhall, R.J. Neo-adjuvant radiotherapy (NART) in breast reconstruction—The future for autologous reconstruction in locally advanced disease? J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2018, 71, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.L.; Parikh, P.M.; Reisin, E.; Menon, N.G. Acellular dermis-assisted breast reconstruction. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.S.; Verma, K.; Rosen, H.; Lipsitz, S.; Morris, D.; Kenney, P.; Eriksson, E. Implant-based breast reconstruction using acellular dermal matrix and the risk of postoperative complications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmander, F.; Lagergren, J.; Johansson, H.; Roy, P.G.; Brandberg, Y.; Frisell, J. Effect of Immediate Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy with and without Acellular Dermal Matrix among Women with Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2127806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgarello, M.; Visconti, G.; Barone-Adesi, L. Fat grafting and breast reconstruction with implant: Another option for irradiated breast cancer patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, Y.; Werners, L.L.; Dreise, M.M.; van Emmichoven, I.A.Z.; Werker, P.M.; de Bock, G.H. Which breast is the best? Successful autologous or alloplastic breast reconstruction: Patient-reported quality-of-life outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.B.; Lang, J.E.; Peric, M.; Yang, H.; Artenstein, D.; Chan, L.S.; Schooler, W.G.; Carey, J.N. Breast reconstruction satisfaction rates at a large county hospital. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2014, 72 (Suppl. S1), S61–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable Total Patients (n = 18) | No. of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Mean age, years (range) | 68 ± 1.8 (50–74) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Hypertension | 5 (28%) |
| Smoking | 4 (22%) |
| Diabetes | 2 (11%) |
| Hypothyroidism | 1 (5%) |
| Depression | 3 (17%) |
| GERD | 3 (17%) |
| Autoimmune disease | 3 (17%) |
| Others | 4 (22%) |
| Interval from previous radiotherapy, years (range) | 15 ± 2 (2–24) |
| Type of mastectomy | |
| SSM | 5 (28%) |
| NSM | 13 (72%) |
| Axillary dissection | |
| With BCS | 7 (39%) |
| With salvage mastectomy | 2 (11%) |
| Type of implant | |
| Anatomical shape textured silicone size (range) | 308 cc ± 7 cc (270–350) |
| Contralateral procedure | |
| Mastopexy | 3 (17%) |
| Breast reduction | 6 (33%) |
| QUART | 1 (5%) |
| Mean hospital stay, days (range) | 2 ± 0.2 (2–4) |
| Time to heal, days (range) | 20 ± 2 (14–38) |
| Adjuvant treatment | |
| Hormonotherapy | 9 (69%) |
| Trastuzumab | 1 (8%) |
| Follow up, months | 30 ± 2 |
| Variable Total Patients (n = 18) | |
|---|---|
| BREAST-Q | |
| Satisfaction (breast) | 62.4 (50–74) |
| Psychosocial wellness | 65.8 (47–83) |
| Sexual well-being | 43 (14–62) |
| Physical impact (chest) | 69.3 (55–85) |
| Overall satisfaction with outcome | 87.1 (76–100) |
| VAS | |
| Patients, result (range) | 6.9 (5–9) |
| Surgeon, result (range) | 5.4 (3–8) |
| Variable Total Patients (n = 18) | No. of Patients |
|---|---|
| Early complications: | |
| Wound dehiscence | 4 (22%) |
| Superficial mastectomy flap necrosis | 3 (17%) |
| Late complications: | |
| Capsular contracture | |
| Baker 2 | 4 (22%) |
| Baker 3 | 3 (17%) |
| Rippling | 2 (11%) |
| Secondary procedure | |
| Autologous fat grafting | 3 (17%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacchioni, L.; Sapino, G.; Lusetti, I.L.; Zaccaria, G.; Di Summa, P.G.; De Santis, G. Sub-Muscular Direct-to-Implant Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Previously Irradiated Patients Avoiding the Use of ADM: A Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195856
Pacchioni L, Sapino G, Lusetti IL, Zaccaria G, Di Summa PG, De Santis G. Sub-Muscular Direct-to-Implant Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Previously Irradiated Patients Avoiding the Use of ADM: A Preliminary Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195856
Chicago/Turabian StylePacchioni, Lucrezia, Gianluca Sapino, Irene Laura Lusetti, Giovanna Zaccaria, Pietro G. Di Summa, and Giorgio De Santis. 2022. "Sub-Muscular Direct-to-Implant Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Previously Irradiated Patients Avoiding the Use of ADM: A Preliminary Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195856
APA StylePacchioni, L., Sapino, G., Lusetti, I. L., Zaccaria, G., Di Summa, P. G., & De Santis, G. (2022). Sub-Muscular Direct-to-Implant Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Previously Irradiated Patients Avoiding the Use of ADM: A Preliminary Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195856





