The Evolution of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Its Current Use in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Older Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evolution of Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fracture
3. Rationale for Use of RTSA for the Treatment of PHFs
4. Current Controversies in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Elderly
5. Evidence for the Use of RTSA in PHF Compared to Other Surgical Treatments
5.1. RTSA versus Nonoperative Treatment
5.2. RTSA versus Internal Fixation
5.3. RTSA versus Hemiarthroplasty
5.4. Cost Effectiveness Analysis
6. Complications of RTSA
7. Special Considerations for RTSA for Fractures
7.1. Press Fit versus Cemented Humeral Stems
7.2. Standard Humeral Stem versus Fracture Stem
7.3. Tuberosity Healing and Its Influence on Outcomes of RTSA
7.4. Timing of RTSA
7.5. RTSA as a Salvage Procedure
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khatib, O.; Onyekwelu, I.; Zuckerman, J.D. The Incidence of proximal humeral fractures in New York state from 1990 through 2010 with an emphasis on operative management in patients aged 65 years or older. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.S.; Price, N.; Graves, S.; Hatton, A.; Taylor, F.J. Nationwide trends in management of proximal humeral fractures: An analysis of 77,966 cases from 2008 to 2017. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.J.; Sing, D.C.; Feeley, B.T.; Ma, C.B.; Zhang, A.L. Proximal humerus fragility fractures: Recent trends in nonoperative and operative treatment in the Medicare population. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannus, P.; Palvanen, M.; Niemi, S.; Parkkari, J.; Jarvinen, M.; Vuori, I. Increasing number and incidence of osteoporotic fractures of the proximal humerus in elderly people. BMJ 1996, 313, 1051–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handoll, H.H.; Keding, A.; Corbacho, B.; Brealey, S.D.; Hewitt, C.; Rangan, A. Five-year follow-up results of the PROFHER trial comparing operative and non-operative treatment of adults with a displaced fracture of the proximal humerus. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangan, A.; Handoll, H.; Brealey, S.; Jefferson, L.; Keding, A.; Martin, B.C.; Goodchild, L.; Chuang, L.-H.; Hewitt, C.; Torgerson, D.; et al. Surgical vs. nonsurgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: The PROFHER randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015, 313, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, D.; Jaeger, M.; Izadpanah, K.; Strohm, P.C.; Suedkamp, N.P. Proximal humeral fracture treatment in adults. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bufquin, T.; Hersan, A.; Hubert, L.; Massin, P. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly: A prospective review of 43 cases with a short-term follow-up. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2007, 89, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazeneuve, J.-F.; Cristofari, D.-J. Grammont reversed prosthesis for acute complex fracture of the proximal humerus in an elderly population with 5 to 12 years follow-up. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 2006, 92, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, H.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, T.; Araki, A.; Hosoi, T.; Sawabe, M. Reviewing the definition of “Elderly”. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2006, 6, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neer, C.S.; Brown, T.H.; McLaughlin, H.L. Fracture of the neck of the humerus with dislocation of the head fragment. Am. J. Surg. 1953, 85, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neer, C.S. The classic: Articular replacement for the humeral head. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.N.; Butt, M.S. Treatment of comminuted proximal humerus fractures with shoulder hemiarthroplasty in elderly patients. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2005, 71, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldman, R.T.; Koval, K.J.; Cuomo, F.; Gallagher, M.A.; Zuckerman, J.D. Functional outcome after humeral head replacement for acute three- and four-part proximal humeral fractures. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 1995, 4, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralinger, F.; Schwaiger, R.; Wambacher, M.; Farrell, E.; Menth-Chiari, W.; Lajtai, G.; Hübner, C.; Resch, H. Outcome after primary hemiarthroplasty for fracture of the head of the humerus. A retrospective multicentre study of 167 patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2004, 86, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, P.; Krishnan, S.G.; Tinsi, L.; Walch, G.; Coste, J.S.; Molé, D. Tuberosity malposition and migration: Reasons for poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for displaced fractures of the proximal humerus. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2002, 11, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, A.; Brorson, S.; Olsen, B.S.; Rasmussen, J.V. Ten-year follow-up of stemmed hemiarthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fractures. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, R.W.; Pugely, A.J.; Martin, C.T.; Gao, Y.; Wolf, B.R.; Hettrich, C.M. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty in the United States: A comparison of national volume, patient demographics, complications, and surgical indications. Iowa Orthop. J. 2015, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, D.; de la Fuente, G. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for a 4-part proximal humerus fracture. J. Orthop. Trauma 2016, 30 Suppl 2, S9–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routman, H.D.; Flurin, P.H.; Wright, T.W.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Hamilton, M.A.; Roche, C.P. Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Prosthesis Design Classification System. Bull. Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2015, 73 (Suppl. 1), S5–S14. [Google Scholar]
- Boileau, P.; Watkinson, D.J.; Hatzidakis, A.M.; Balg, F. Grammont reverse prosthesis: Design, rationale, and biomechanics. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2005, 14, 147S–161S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boileau, P.; Alta, T.D.; Decroocq, L.; Sirveaux, F.; Clavert, P.; Favard, L.; Chelli, M. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for acute fractures in the elderly: Is it worth reattaching the tuberosities? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.H.; Wilder, J.H.; Ofa, S.A.; Lee, O.C.; Savoie, F.H.; O’Brien, M.J.; Sherman, W.F. Trending a decade of proximal humerus fracture management in older adults. JSES Int. 2022, 6, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, I.R.; Amin, A.K.; White, T.O.; Robinson, C.M. Proximal humeral fractures: Current concepts in classification, treatment and outcomes. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2011, 93, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoll, H.H.G.; Brorson, S. Interventions for treating proximal humeral fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 11, CD000434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinlugtenbelt, Y.V.; Bhandari, M. Cochrane in CORR (®): Interventions for treating proximal humeral fractures in adults (review). Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 2750–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.N.; Bjørdal, J.; Wagle, T.M.; Karlberg, A.C.; Lien, O.A.; Eilertsen, L.; Mader, K.; Apold, H.; Larsen, L.B.; Madsen, J.E.; et al. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty is superior to plate fixation at 2 years for displaced proximal humeral fractures in the elderly: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2020, 102, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, E.Ö.; Ekholm, C.; Salomonsson, B.; Demir, Y.; Olerud, P. Collaborators in the SAPF study group reverse total shoulder arthroplasty provides better shoulder function than hemiarthroplasty for displaced 3- and 4-part proximal humeral fractures in patients aged 70 years or older: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiá-Forcada, E.; Cebrián-Gómez, R.; Lizaur-Utrilla, A.; Gil-Guillén, V. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fractures. A blinded, randomized, controlled, prospective study. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopiz, Y.; Alcobía-Díaz, B.; Galán-Olleros, M.; García-Fernández, C.; Picado, A.L.; Marco, F. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty versus nonoperative treatment for 3- or 4-part proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: A prospective randomized controlled trial. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivot, M.; Lami, D.; Bizzozero, P.; Galland, A.; Argenson, J.-N. Three- and four-part displaced proximal humeral fractures in patients older than 70 years: Reverse shoulder arthroplasty or nonsurgical treatment? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simovitch, R.; Flurin, P.-H.; Wright, T.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Roche, C.P. Quantifying success after total shoulder arthroplasty: The minimal clinically important difference. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2018, 27, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberson, T.A.; Granade, C.M.; Hunt, Q.; Griscom, J.T.; Adams, K.J.; Momaya, A.M.; Kwapisz, A.; Kissenberth, M.J.; Tolan, S.J.; Hawkins, R.J.; et al. Nonoperative management versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty for treatment of 3- and 4-part proximal humeral fractures in older adults. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2017, 26, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Karlin, E.; Boin, M.A.; Dankert, J.F.; Larose, G.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Virk, M.S. Operative treatment of proximal humeral fractures with reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in patients ≥65 years old: A critical analysis review. JBJS Rev. 2022, 10, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, P.N.; Slikker, W.; Mall, N.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Rahman, Z.; Enriquez, D.; Nicholson, G.P. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fracture: Comparison to open reduction-internal fixation and hemiarthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardella, A.; Ascione, F.; Mocchi, M.; Berlusconi, M.; Romano, A.M.; Oliva, F.; Maradei, L. Reverse total shoulder versus angular stable plate treatment for proximal humeral fractures in over 65 years old patients. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2017, 7, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiwe, R.M.; Kohrs, B.J.; Callegari, J.; Harm, R.G.; Hill, M.A.; Boyle, M.S. Open reduction internal fixation vs. reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of acute displaced proximal humerus fractures. Semin. Arthroplast. JSES 2020, 30, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, A.; Harth, J.; Hoffmann, R.; Gramlich, Y. Surgical treatment of complex proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: A matched-pair analysis of angular-stable plating vs. reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2020, 29, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, A.; Wincheringer, D.; Harth, J.; Schmidt-Horlohé, K.; Hoffmann, R.; Gramlich, Y. Complications after surgical treatment of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly-an analysis of complication patterns and risk factors for reverse shoulder arthroplasty and angular-stable plating. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciani, P.; Procaccini, R.; Rotini, M.; Pettinari, F.; Gigante, A. Angular stable plate versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures in elderly patient. Musculoskelet Surg. 2022, 106, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, I.; Alessio-Mazzola, M.; Cerruti, P.; Sanguineti, F.; Formica, M.; Felli, L. Surgical management of complex proximal humeral fractures: Pinning, locked plate and arthroplasty: Clinical results and functional outcome on retrospective series of patients. Musculoskelet Surg. 2017, 101, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahuaca, B.I.; Simon, P.; Christmas, K.N.; Patel, S.; Gorman, R.A.; Mighell, M.A.; Frankle, M.A. Acute surgical management of proximal humerus fractures: ORIF vs. hemiarthroplasty vs. reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2020, 29, S32–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olerud, P.; Ahrengart, L.; Ponzer, S.; Saving, J.; Tidermark, J. Internal fixation versus nonoperative treatment of displaced 3-part proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2011, 20, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laas, N.; Engelsma, Y.; Hagemans, F.J.A.; Hoelen, M.A.; van Deurzen, D.F.P.; Burger, B.J. Reverse or hemi shoulder arthroplasty in proximal humerus fractures: A single-blinded prospective multicenter randomized clinical trial. J. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 35, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudi, P.; Campochiaro, G.; Serafini, F.; Gazzotti, G.; Matino, G.; Rovesta, C.; Catani, F. Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty: Comparative study of functional and radiological outcomes in the treatment of acute proximal humerus fracture. Musculoskelet Surg. 2014, 98 (Suppl. 1), 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnevialle, N.; Tournier, C.; Clavert, P.; Ohl, X.; Sirveaux, F.; Saragaglia, D.; la Société française de chirurgie orthopédique et traumatologique. Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty in 4-part displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: Multicenter retrospective study. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2016, 102, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, M.J.; Youn, S.-M.; Frampton, C.M.A.; Ball, C.M. Functional outcomes of reverse shoulder arthroplasty compared with hemiarthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fractures. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2013, 22, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuff, D.J.; Pupello, D.R. Comparison of hemiarthroplasty and reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am 2013, 95, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, G.E.; Johnston, P.S.; Pepe, M.D.; Tucker, B.S.; Ramsey, M.L.; Austin, L.S. Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for acute proximal humerus fractures in elderly patients. Orthopedics 2012, 35, e703–e708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Merwe, M.; Boyle, M.J.; Frampton, C.M.A.; Ball, C.M. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty compared with hemiarthroplasty in the treatment of acute proximal humeral fractures. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2017, 26, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.W.; Segal, B.S.; Turner, P.C.; Poon, P.C. Compa.arison of functional outcomes of reverse shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty in the primary treatment of acute proximal humerus fracture. ANZ J. Surg. 2010, 80, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterhoff, G.; O’Hara, N.N.; D’Cruz, J.; Sprague, S.A.; Bansback, N.; Evaniew, N.; Slobogean, G.P. A cost-effectiveness analysis of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for the management of complex proximal humeral fractures in the elderly. Value Health 2017, 20, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørdal, J.; Fraser, A.N.; Wagle, T.M.; Kleven, L.; Lien, O.A.; Eilertsen, L.; Mader, K.; Apold, H.; Larsen, L.B.; Madsen, J.-E.; et al. A cost-effectiveness analysis of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty compared with locking plates in the management of displaced proximal humerus fractures in the elderly: The delphi trial. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwachukwu, B.U.; Schairer, W.W.; McCormick, F.; Dines, D.M.; Craig, E.V.; Gulotta, L.V. Arthroplasty for the surgical management of complex proximal humerus fractures in the elderly: A cost-utility analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalik, H.A.; Humphries, B.; Zoratti, M.; Axelrod, D.; Kruse, C.; Ristevski, B.; Rajaratnam, K.; Gardner, M.; Tarride, J.-É.; Johal, H. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty is the most cost-effective treatment strategy for proximal humerus fractures in older adults: A cost-utility analysis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2022, 480, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobin, C.M.; Galdi, B.; Anakwenze, O.A.; Ahmad, C.S.; Levine, W.N. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the management of proximal humerus fractures. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2015, 23, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.; Klifto, C.S.; Ledbetter, L.; Bullock, G.S. Reverse Total shoulder arthroplasty clinical and patient-reported outcomes and complications stratified by preoperative diagnosis: A systematic review. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumstein, M.A.; Pinedo, M.; Old, J.; Boileau, P. Problems, complications, reoperations, and revisions in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: A systematic review. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2011, 20, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazeneuve, J.F.; Cristofari, D.-J. The reverse shoulder prosthesis in the treatment of fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, E.Y.; Rizkalla, J.; Montemaggi, P.; Majekodunmi, T.; Krishnan, S.G. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of cementless reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopiz, Y.; García-Fernandez, C.; Vallejo-Carrasco, M.; Garriguez-Pérez, D.; Achaerandio, L.; Tesoro-Gonzalo, C.; Marco, F. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fracture in the elderly. Cemented or uncemented stem? Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.A.; Guillermina, B.M.; Buljubasich, M.; Atala, N.; Tanoira, I.; Bongiovanni, S.; Ranalletta, M. Cemented versus uncemented reverse shoulder arthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fractures. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, B.; Aibinder, W.; Walters, J.; Sperling, J.; Throckmorton, T.; Sanchez-Sotelo, J.; Duquin, T. Outcomes of uncemented versus cemented reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures. Orthopedics 2019, 42, e236–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.O.; Ho, A.; Kalma, J.; Koueiter, D.; Esterle, J.; Marcantonio, D.; Wiater, J.M.; Wiater, B. Uncemented reverse total shoulder arthroplasty as initial treatment for comminuted proximal humerus fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, e263–e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.-M.; Deo, S.; Poon, P.C. Functional and radiologic outcomes of uncemented reverse shoulder arthroplasty in proximal humeral fractures: Cementing the humeral component is not necessary. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, e83–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, O.; Borbas, P.; Grubhofer, F.; Ek, E.T.; Pullen, C.; Treseder, T.; Ernstbrunner, L. Prosthesis designs and tuberosity fixation techniques in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: Influence on tuberosity healing in proximal humerus fractures. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.G.; Reineck, J.R.; Bennion, P.D.; Feher, L.; Burkhead, W.Z. Shoulder arthroplasty for fracture: Does a fracture-specific stem make a difference? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3317–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onggo, J.R.; Nambiar, M.; Onggo, J.D.; Hau, R.; Pennington, R.; Wang, K.K. Improved functional outcome and tuberosity healing in patients treated with fracture stems than nonfracture stems during shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fracture: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, J.; Neide, A.; Mick, P.; Brunnemer, U.; Schmidmaier, G.; Fischer, C. Functional outcome and CEUS-assessed deltoid muscle vitality after fracture-specific versus standard prosthetic design in reverse shoulder arthroplasty for trauma. J. Orthop. Res. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, R.; Flanagin, B.; Castagna, A.; Lo, E.Y.; Krishnan, S.G. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fracture using a dedicated stem: Radiological outcomes at a minimum 2 years of follow-up—Case series. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2015, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.-K.; Liao, J.-P.; Guo, J.-H.; Huang, F. Fracture-dedicated prosthesis promotes the healing rate of greater tuberosity in reverse shoulder arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 616104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imiolczyk, J.-P.; Moroder, P.; Scheibel, M. Fracture-specific and conventional stem designs in reverse shoulder arthroplasty for acute proximal humerus fractures—A retrospective, observational study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-J.; Kong, C.-G.; Park, S.-E.; Ji, J.-H.; Whang, W.-H.; Choi, B.-S. Non-fracture stem vs. fracture stem of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in complex proximal humeral fracture of asian elderly. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2019, 139, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simovitch, R.W.; Roche, C.P.; Jones, R.B.; Routman, H.D.; Marczuk, Y.; Wright, T.W.; Zuckerman, J.D. Effect of tuberosity healing on clinical outcomes in elderly patients treated with a reverse shoulder arthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, e39–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinet, D.; Clappaz, P.; Garbuio, P.; Tropet, Y.; Obert, L. Three or four parts complex proximal humerus fractures: Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse prosthesis: A comparative study of 40 cases. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2009, 95, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Juschka, M.; Hinkenjann, B.; Scherger, B.; Ostermann, P.A.W. Treatment of comminuted fractures of the proximal humerus in elderly patients with the delta III reverse shoulder prosthesis. J. Orthop. Trauma 2008, 22, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinet, D.; Cazeneuve, J.-F.; Boyer, E.; Menu, G.; Obert, L.; Ohl, X.; Bonnevialle, N.; Valenti, P.; Boileau, P. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for recent proximal humerus fractures: Outcomes in 422 cases. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2019, 105, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formaini, N.T.; Everding, N.G.; Levy, J.C.; Rosas, S. Tuberosity healing after reverse shoulder arthroplasty for acute proximal humerus fractures: The “black and tan” technique. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2015, 24, e299–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.P.; Mannan, S.S.; Dharmarajan, R.; Rangan, A. Tuberosity healing after reverse shoulder arthroplasty for complex proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients—Does it improve outcomes? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, e78–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
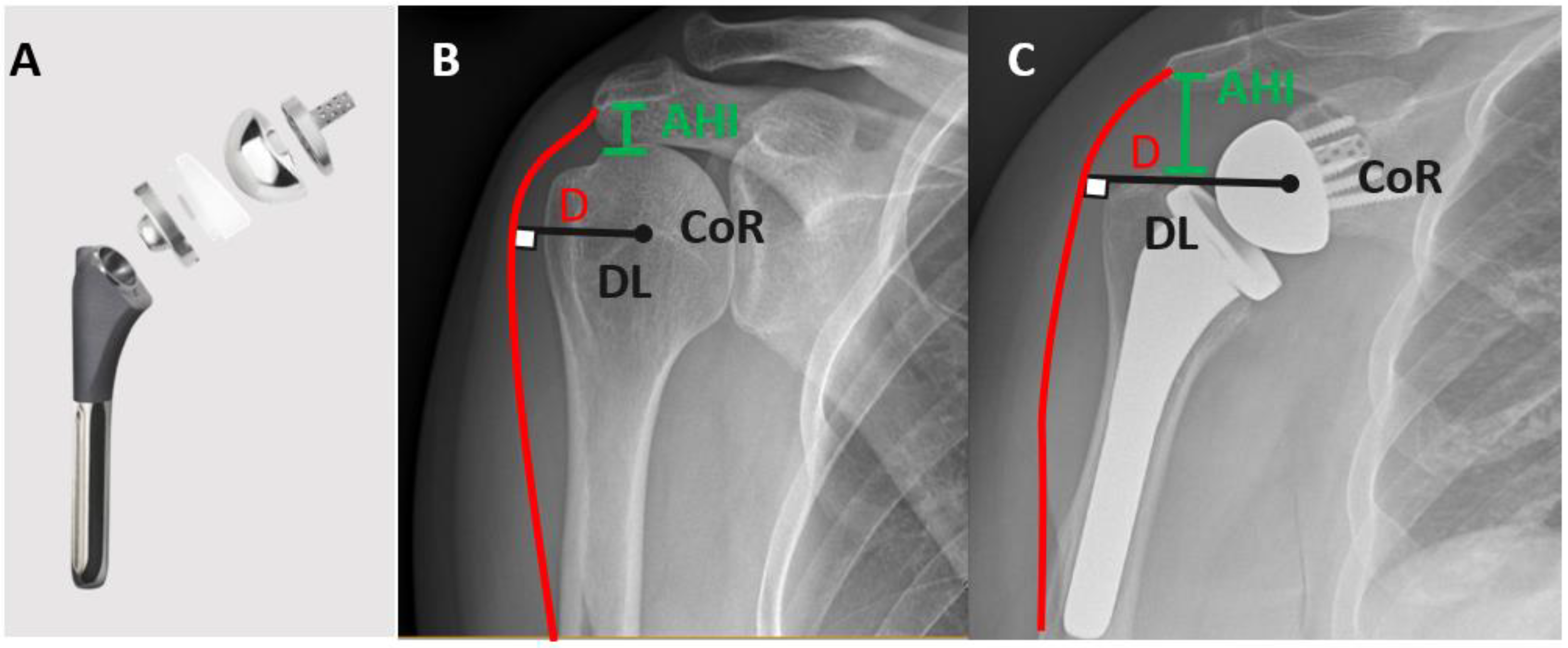
- O’Sullivan, J.; Lädermann, A.; Parsons, B.O.; Werner, B.; Steinbeck, J.; Tokish, J.M.; Denard, P.J. A systematic review of tuberosity healing and outcomes following reverse shoulder arthroplasty for fracture according to humeral inclination of the prosthesis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2020, 29, 1938–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
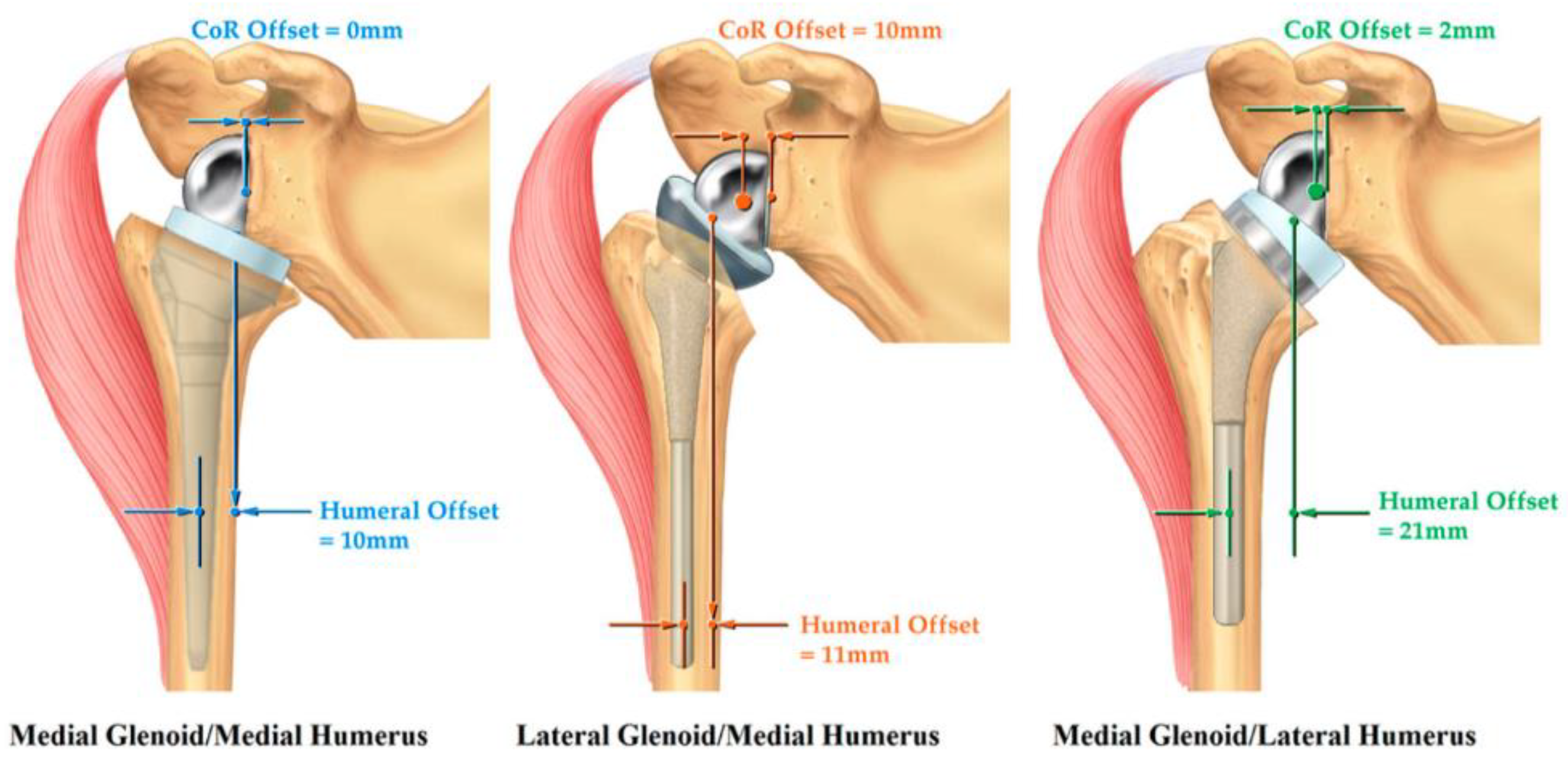
- Holschen, M.; Körting, M.; Khourdaji, P.; Bockmann, B.; Schulte, T.L.; Witt, K.-A.; Steinbeck, J. Treatment of proximal humerus fractures using reverse shoulder arthroplasty: Do the inclination of the humeral component and the lateral offset of the glenosphere influence the clinical outcome and tuberosity healing? Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knierzinger, D.; Heinrichs, C.H.; Hengg, C.; Konschake, M.; Kralinger, F.; Schmoelz, W. Biomechanical evaluation of cable and suture cerclages for tuberosity reattachment in a 4-part proximal humeral fracture model treated with reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2018, 27, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalzl, J.; Piepenbrink, M.; Buchner, J.; Picht, S.; Gerhardt, C.; Lehmann, L.-J. Tensioning device increases biomechanical stability of tuberosity fixation technique with cerclage sutures in reverse shoulder arthroplasty for fracture. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalzl, J.; Piepenbrink, M.; Buchner, J.; Picht, S.; Gerhardt, C.; Lehmann, L.-J. Higher primary stability of tuberosity fixation in reverse fracture arthroplasty with 135° than with 155° humeral inclination. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Yamada, S.; Kobori, Y.; Shiode, H. The clinical outcomes and tuberosity healing after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fracture using the turned stem tension band technique. J. Orthop. Sci. 2022, 27, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzer, G.; Yildiz, F.; Batar, S.; Binlaksar, R.; Elmadag, M.; Kus, G.; Bilsel, K. Does grafting of the tuberosities improve the functional outcomes of proximal humeral fractures treated with reverse shoulder arthroplasty? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2017, 26, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.H.; Figueiredo, S.; Marques, M.; Rodrigues, C.; Ramos, J.; Claro, R. Consolidação dos tubérculos na artroplastia reversa do ombro após fratura proximal do úmero: Existe melhoria nos resultados funcionais? Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2020, 55, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchia, M.T.; Austin, D.C.; Cozzolino, N.; Jacobowitz, L.; Bell, J.-E. Acute versus delayed reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures in the elderly population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, J.; Stenquist, D.S.; Mohamadi, A.; Weaver, M.J.; Dyer, G.S.M.; von Keudell, A. Acute versus delayed reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for the management of proximal humerus fractures. Injury 2021, 52, 2272–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, G.N.; Pugliese, M.; Leonidou, A.; Butt, F.; Jaibaji, M.; Megaloikonomos, P.D.; Consigliere, P.; Sforza, G.; Atoun, E.; Levy, O. Acute versus delayed reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: A consecutive cohort study. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, H.D.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Koh, J.L.; Strelzow, J.A.; Shi, L.L. Acute versus delayed reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the primary treatment of proximal humeral fractures. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, A.; Sholder, D.; Warrender, W.; Livesey, M.; Williams, G.; Abboud, J.; Namdari, S. Early versus late reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures: Does it matter? Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2017, 5, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, A.; Hohenberger, G.; Sauerschnig, M.; Niks, M.; Lipnik, G.; Mattiassich, G.; Zacherl, M.; Seibert, F.; Plecko, M. Effectiveness of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for primary and secondary fracture care: Mid-term outcomes in a single-centre experience. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubhofer, F.; Wieser, K.; Meyer, D.C.; Catanzaro, S.; Schürholz, K.; Gerber, C. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for failed open reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2017, 26, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, M.M.; Hussey, S.E.; Mighell, M.A. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty as a salvage procedure after failed internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus: Outcomes and complications. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliemann, B.; Theisen, C.; Kösters, C.; Raschke, M.J.; Weimann, A. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for type i fracture sequelae after internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.; King, J.J.; Farmer, K.W.; Struk, A.M.; Wright, T.W. Outcomes of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty as primary versus revision procedure for proximal humerus fractures. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.A.; Kwan, C.C.; Tjong, V.K.; Terry, M.A.; Sheth, U. Primary versus salvage reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for displaced proximal humerus fractures in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Arthroplast. 2020, 4, 247154922094973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastia-Forcada, E.; Lizaur-Utrilla, A.; Cebrian-Gomez, R.; Miralles-Muñoz, F.A.; Lopez-Prats, F.A. Outcomes of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: Primary arthroplasty versus secondary arthroplasty after failed proximal humeral locking plate fixation. J. Orthop. Trauma 2017, 31, e236–e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, S.F.; Wagner, E.R.; Houdek, M.T.; Cross, W.W.; Sánchez-Sotelo, J. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: Outcomes comparing primary reverse arthroplasty for fracture versus reverse arthroplasty after failed osteosynthesis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
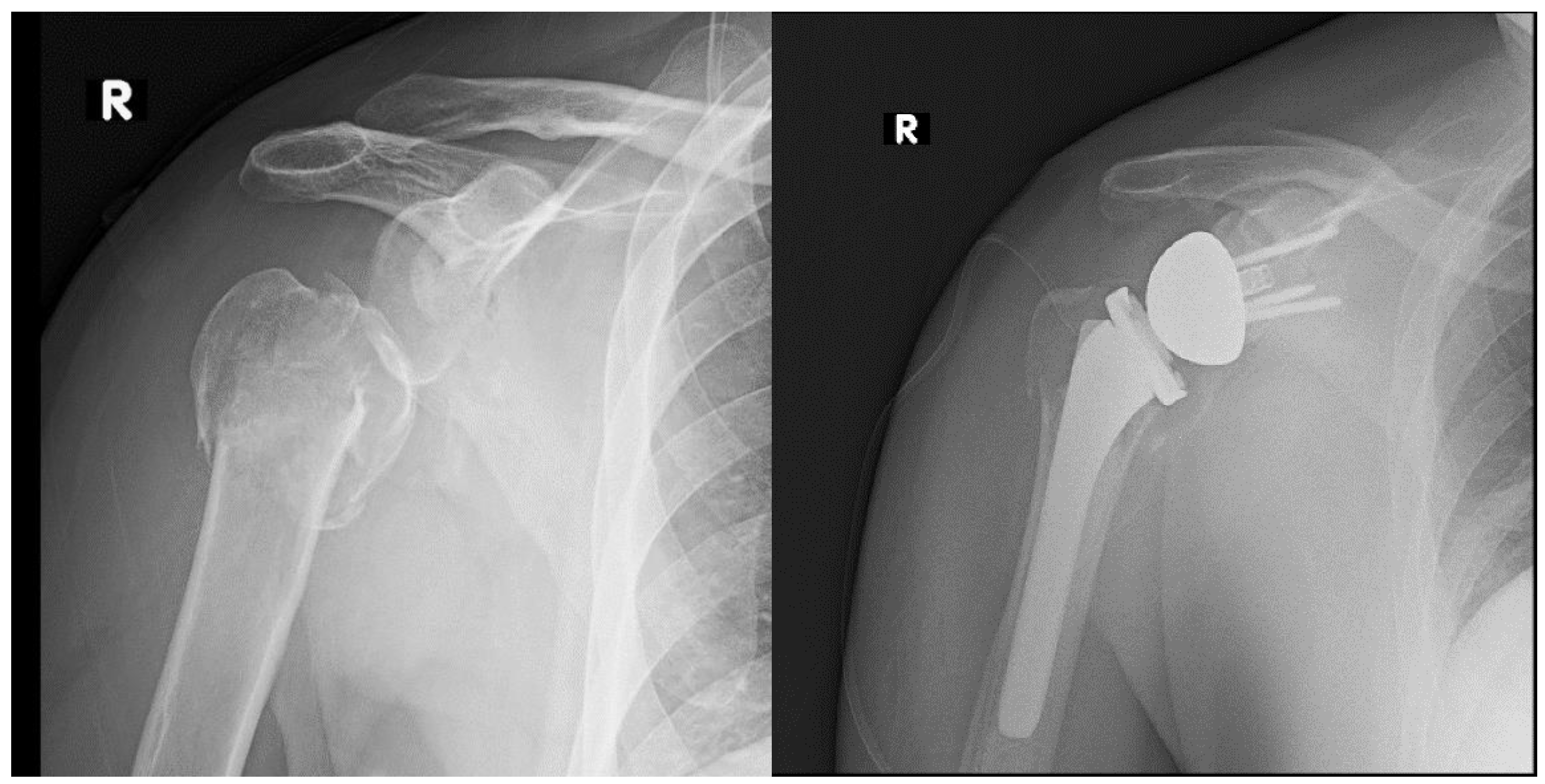
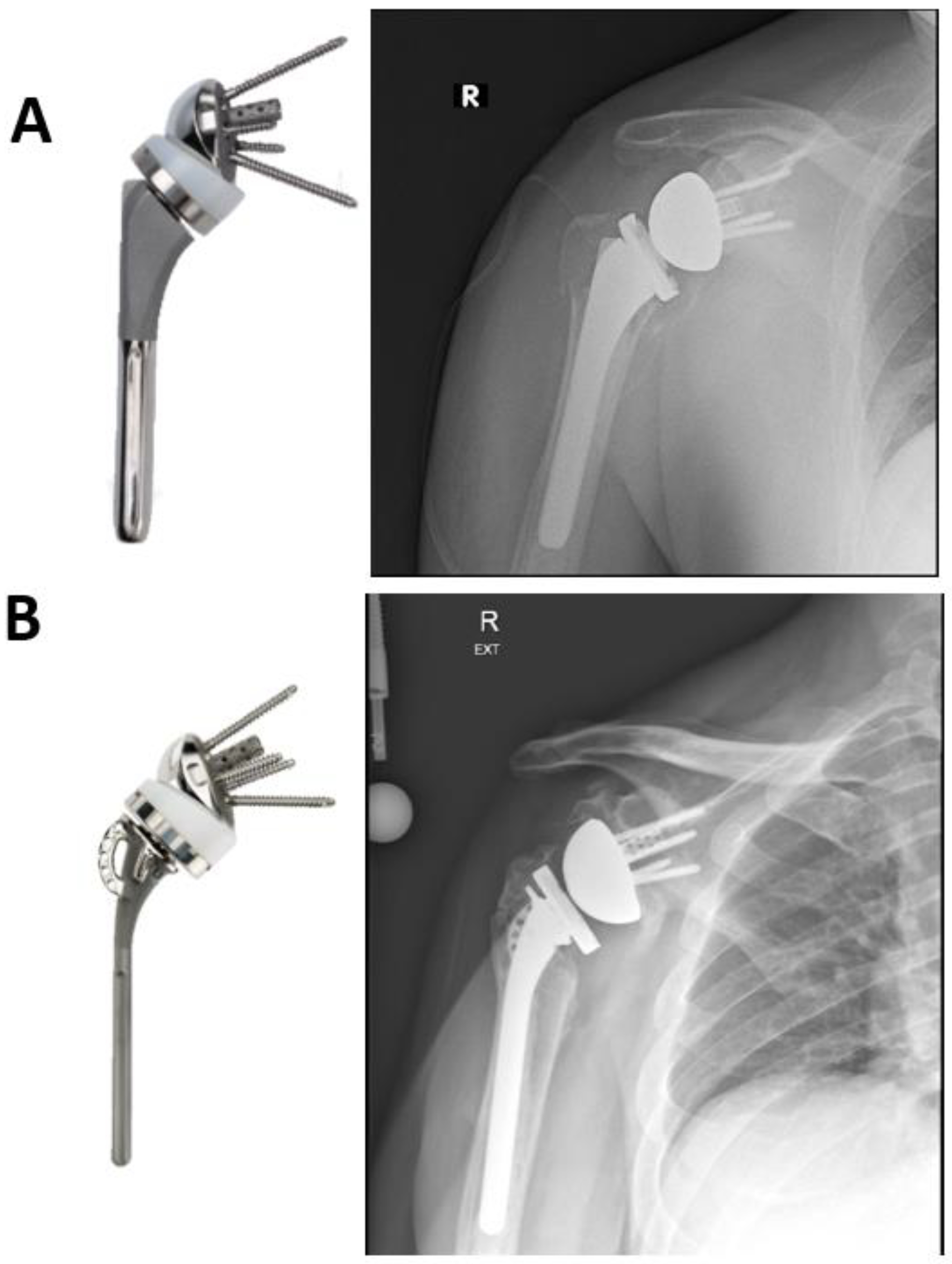
| Acute Fracture |
|
| Salvage Indications |
|
| Study | LOE | Patients | Age | PROMS | ROM FF | ROM ER | Complications | Revisions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chalmers | III | ORIF: 9 | 71 | ASES: 75 | 108 | 46 | Stiffness1 | 1 |
| 2014 [35] | RTSA: 9 | 77 | ASES: 80 | 133 | 41 | CRPS | 0 | |
| Giardella | III | ORIF: 23 | 72.1 | CMS 52.9 | 112.8 | 47.4 * | NR | NR |
| 2017 [36] | RTSA: 21 | 77.2 | CMS 65.9 * | 133.3 * | 35.5 | NR | NR | |
| Greiwe | III | ORIF 25 | 73.3 | ASES: 81.1 | 121.4 | 43 | AVN:4; Screw cut out 2; Nerve palsy1; Delayed union 1; malunion 2 | 6 * |
| 2020 [37] | RTSA: 25 | 74.4 | ASES: 82.9 | 143.2 * | 46.8 | Tuberosity resorption 5 | 0 | |
| Klug | III | ORIF: 66 | NR | NR | NR | Stiffness 17, AVN: 6; loss of fixation 4; screw cut out 2; infection 1 PE 2; anemia 1 | 7 | |
| 2019 [39] | RTSA: 59 | NR | NR | NR | Stiffness 9; Instability 3; Axial nerve palsy 2; radiolucent line 2; 2; PE 2; anemia 1 | 3 | ||
| Klug | III | ORIF 30 | 72.5 | ASES: 83.4 CMS 81.4 DASH 14.3 * | 146 | 52 | Stiffness6; loss of fixation 2; screw cut out 1; infection1 | 6 |
| 2020 [38] | RTSA 30 | 73.9 | ASES: 74.6 CMS 69.9 DASH 25.3 | 133 | 39 | Axillary nerve1; dislocation 1; infection 1 | 1 | |
| Luciani | III | ORIF: 26 | 73 | CMS 65.85 DASH 18.99 | 125.75 | 28 * | AVN5; loss reduction3; infection1; hardware impingement 2; | 7 |
| 2022 [40] | RTSA: 22 | 75.5 | CMS 63.65 DASH 25.1 | 124.5 | 14.25 | Instability1; infection1 | 2 | |
| Repetto | III | ORIF: 19 | 65.3 | CMS 61.8 DASH 16.9 | 130.6 | 23.2 | AVN:4; Hardware impingement: 2; Transient circumflex nerve palsy 1 | 3 |
| 2017 [41] | RTSA: 27 | 71.2 | CMS 58.5 DASH 28.6 | 125 | 20.3 | Infection: 1; Hematoma: 1; Periprosthetic fracture: 1; Instability 2; | 3 | |
| Yahuaca | III | ORIF 211 | 61.6 | NR | 130 | Tuberosity nonunion 22 * | 17.50% | |
| 2020 [42] | RTSA: 106 | 73 | NR | 124 | Tuberosity nonunion 25 | 6.6% * |
| Study | LOE | Patients | Age | PROM | ROM FF | ROM ER | Tub Healing | Complications | Revisions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baudi | III | RTSA: 25 | 77 * | CMS 56.2 * DASH 40.4 | 131* | 15 | 84% * | 1 transient nerve palsy | NR |
| 2014 [45] | HA: 28 | 70 | CMS 42.3 DASH 46.1 | 89 | 23 | 27% | 2 septic infections; 1 Pulmonary Embolism; 3 Stiffness | NR | |
| Bonnevialle | III | RTSA: 41 | 78 * | CMS 57 DASH 28 | 130 * | 23 | 73% | 1 hematoma; 1 transient nerve injury; 2 HO | 0 |
| 2016 [46] | HA: 57 | 67 | CMS 54 DASH 30 | 112 | 28 | 72% | 11 stiffness; 1 HO; 1 infection; 1 transient nerve palsy | 1 | |
| Chalmers | III | RTSA: 9 | 77 | ASES 80 | 133 * | 41 | 100% | 1 Complex Regional pain Syndrome | 0 |
| 2014 [35] | HA: 9 | 72 | ASES 66 | 106 | 28 | 100% | 1 Ulnar nerve neuritis; 1 Stiffness | 0 | |
| Cuff | III | RTSA: 24 | NR | ASES 77 * | 139 * | 24 | 67% | 8 complications -not specify | 0 |
| 2013 [48] | HA: 23 | NR | ASES 62 | 100 | 25 | 57% | 9complications -not specify | 3 | |
| Garrigues | III | RTSA:10 | 80.5 * | ASES 81.1 | 121 * | 34 | 100% | none | 0 |
| 2012 [49] | HA:9 | 69.3 | ASES 37.4 | 91 | 31 | 22% | 2 transient nerve palsy; 1 periprosthetic fracture; 1 glenoid erosion | 3 | |
| Repetto | III | RTSA: 27 | 71.2 | CMS 58.5 DASH 33.8 | 125 | 20.3 | NR | 1 Cuff Failure; 2 Periprothetic fracture; 2 Stiffness | 3 |
| 2017 [41] | HA: 24 | 67.5 | CMS 48.4 DASH 28.6 | 103 | 16.5 | 79% | 2 Instability; 1 Periprosthetic fractures; 1 Hematoma; 1 Deep Infection | 7 | |
| Young | III | RTSA: 10 | 77.2 | ASES 65 | 115 | 49 | 90% | 0 | 0 |
| 2010 [51] | HA: 10 | 75.5 | ASES 67 | 108 | 48 | 80% | 1 stiffness; 1 infection | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larose, G.; Virk, M.S. The Evolution of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Its Current Use in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Older Population. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195832
Larose G, Virk MS. The Evolution of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Its Current Use in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Older Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195832
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarose, Gabriel, and Mandeep S. Virk. 2022. "The Evolution of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Its Current Use in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Older Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195832
APA StyleLarose, G., & Virk, M. S. (2022). The Evolution of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Its Current Use in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Older Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195832






