Videolaryngoendoscopic and Stroboscopic Evaluation in Predicting the Malignancy Risk of Vocal Fold Leukoplakia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.2.1. Inter-Rater and Intra-Rater Agreement
3.2.2. Univariate Analysis
3.2.3. Multivariate Analysis
3.2.4. Diagnostic Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Huang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, F.; He, C.; Li, S.; Shao, J. The usefulness of narrow-band imaging for the diagnosis and treatment of vocal fold leukoplakia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Shi, F. A new classification of vocal fold leukoplakia by morphological appearance guiding the treatment. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018, 138, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.; Ongkasuwan, J.; Martinez, J.; Sandulache, V.; Deng, D.; Jiang, J.; Sikora, A.; Altman, K.W. Biomarkers for Malignant Potential in Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: A State of the Art Review. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2021, 164, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Eun, Y.-G.; Park, I.-S. The Value of I-Scan Image-Enhanced Endoscopy in the Diagnosis of Vocal Cord Leukoplakia. J. Korean Soc. Laryngol. Phoniatr. Logop. 2018, 29, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.K.; Chan, C.J.; Grandis, J.R.; Takata, T.; Slootweg, P.J. Squamous cell carcinoma. In WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumors; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; ISBN 978-92-832-2438-9. [Google Scholar]
- Young, C.K.; Lin, W.N.; Lee, L.Y.; Lee, L.A.; Hsin, L.J.; Liao, C.T.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, I.H.; Fang, T.J. Laryngoscopic characteristics in vocal leukoplakia: Inter-rater reliability and correlation with histology grading. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, E62–E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.P. Vocal fold leukoplakia: Incidence, management, and prevention. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 25, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostev, K.; Jacob, L.; Kalder, M.; Sesterhenn, A.; Seidel, D. Association of laryngeal cancer with vocal cord leukoplakia and associated risk factors in 1,184 patients diagnosed in otorhinolaryngology practices in Germany. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 8, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Jiang, T.; Chen, X. Differences in gene expression profile between vocal cord Leukoplakia and normal larynx mucosa by gene chip. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2018, 47, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Matsuzaki, H.; Makiyama, K.; Oshima, T. Inferior Surface Leukoplakia of Vocal Folds: Risk of Recurrence: A Preliminary Study. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odell, E.; Eckel, H.E.; Simo, R.; Quer, M.; Paleri, V.; Klussmann, J.P.; Remacle, M.; Sjögren, E.; Piazza, C. European Laryngological Society position paper on laryngeal dysplasia Part I: Aetiology and pathological classification. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.J.; Wu, T.T.; Cao, Z.Z.; Zhou, S.H.; Bao, Y.Y.; Shen, L.F. Role and mechanism of Glut-1 and H+/K+-ATPase expression in pepsin-induced development of vocal cord leukoplakia. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2022, 279, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H.T. Possible association between Helicobacter pylori infection and vocal fold leukoplakia. Head Neck 2018, 40, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, L.; Sun, M.J.; Du, J.; Zhang, W. Detecting Laryngopharyngeal Reflux by Immunohistochemistry of Pepsin in the Biopsies of Vocal Fold Leukoplakia. J. Voice 2018, 32, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrel, R.; Uro Coste, E.; Costes-Martineau, V.; Woisard, V.; Atallah, I.; Remacle, M. Vocal-fold leukoplakia and dysplasia. Mini-review by the French Society of Phoniatrics and Laryngology (SFPL). Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2020, 137, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, R.S.; Heckman, W.W.; Isenberg, J.; Thibeault, S.L.; Dailey, S.H. Genetic characterization of vocal fold lesions: Leukoplakia and Carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenberg, J.S.; Crozier, D.L.; Dailey, S.H. Institutional and comprehensive review of laryngeal leukoplakia. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2008, 117, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staníková, L.; Šatanková, J.; Kučová, H.; Walderová, R.; Zeleník, K.; Komínek, P. The role of narrow-band imaging (NBI) endoscopy in optical biopsy of vocal cord leukoplakia. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyduck, A.; Brosch, S.; Pickhard, A.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Reiter, R. The Efficiency of (videolaryngo) stroboscopy in Detecting T1a Glottic Carcinoma and Its Preliminary Stages. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 131, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, U.H.; Wong, E.; Smith, M.; Singh, N.; Palme, C.E.; Smith, M.C.; Riffat, F. Validity of narrow band imaging in the detection of oral and oropharyngeal malignant lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.J.; Lin, W.N.; Lee, L.Y.; Young, C.K.; Lee, L.A.; Chang, K.P.; Liao, C.T.; Li, H.Y.; Yen, T.C. Classification of vocal fold leukoplakia by clinical scoring. Head Neck 2016, 38, E1998–E2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Cheng, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Xie, M.; Li, C.; Chen, X.L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, H.T. Relationship between laryngoscopic and pathological characteristics of vocal cords leukoplakia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H. A morphological classification for vocal fold leukoplakia. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 85, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluss, R.; Faraggi, D.; Reiser, B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point. Biom. J. 2005, 47, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. Landis amd Koch1977_agreement of categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.J.; Lee, K.L.; Ingersoll, G.M. An introduction to logistic regression analysis and reporting. J. Educ. Res. 2002, 96, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Bao, Y.Y.; Zhou, S.H.; Yao, H.T.; Chen, Z. Relationship Between Pepsin Expression and Dysplasia Grade in Patients With Vocal Cord Leukoplakia. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2021, 164, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, M.M.; Diaz, J.; Patel, M.; Lloyd, A.T.; Rosow, D.E. Glottic Keratosis: Significance and Identification of Laryngoscopic Findings. OTO Open 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Xu, W.; Yang, Q.; Hu, R. Clinicopathological parameters associated with histological background and recurrence after surgical intervention of vocal cord leukoplakia. Medicine 2017, 96, e7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraniti, C.; Chianetta, E.; Greco, G.; Mat Lazim, N.; Verro, B. The Impact of Narrow-band Imaging on the Pre- And Intra- operative Assessments of Neoplastic and Preneoplastic Laryngeal LesionsA Systematic Review. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 25, e471–e478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cheng, L.; Li, C.J.; Chen, J.; Shu, Y.L.; Wu, H.T. Nonsurgical Treatment for Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: An Analysis of 178 Cases. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6958250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen Goktas, S.; Dogan, R.; Yenigun, A.; Calim, O.F.; Ozturan, O.; Tugrul, S. A new approach to vocal cord leukoplakia and evaluation of proton pump ınhibitor treatment. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, W.; Ma, H.; Feng, L.; Shi, Q.; Lian, M.; Wang, R.; Hou, L. The value of narrow band imaging combined with stroboscopy for the detection of applanate indiscernible early-stage vocal cord cancer. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018, 138, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vecchia, C.; Zhang, Z.F.; Altieri, A. Alcohol and laryngeal cancer: An update. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2008, 17, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, B.; Rasid, N.S.A.; Lazim, N.M.; Volgger, V.; Betz, C.S.; Mohammad, Z.W.; Hassan, N.F.H.N. Ni endoscopic classification for Storz Professional Image Enhancement System (SPIES) endoscopy in the detection of upper aerodigestive tract (UADT) tumours. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, S.; Lu, L.; Wang, M.; Qian, X. Diagnostic Value and Pathological Correlation of Narrow Band Imaging Classification in Laryngeal Lesions. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020, 100, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, F.; Ralli, M.; Di Stadio, A.; Greco, A.; Pellini, R.; de Vincentiis, M. Role of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy in Preoperative Evaluation of Laryngeal Leukoplakia: A Review of the Literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, T.; Saito, K.; Yabe, H.; Ogawa, K. Phonosurgical resection using submucosal infusion technique for precancerous laryngeal leukoplakia. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabrillac, E.; Dupret-Bories, A.; Vairel, B.; Woisard, V.; De Bonnecaze, G.; Vergez, S. Narrow-Band Imaging in oncologic otorhinolaryngology: State of the art. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2021, 138, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żurek, M.; Rzepakowska, A.; Osuch-Wójcikiewicz, E.; Niemczyk, K. Learning curve for endoscopic evaluation of vocal folds lesions with narrow band imaging. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 85, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
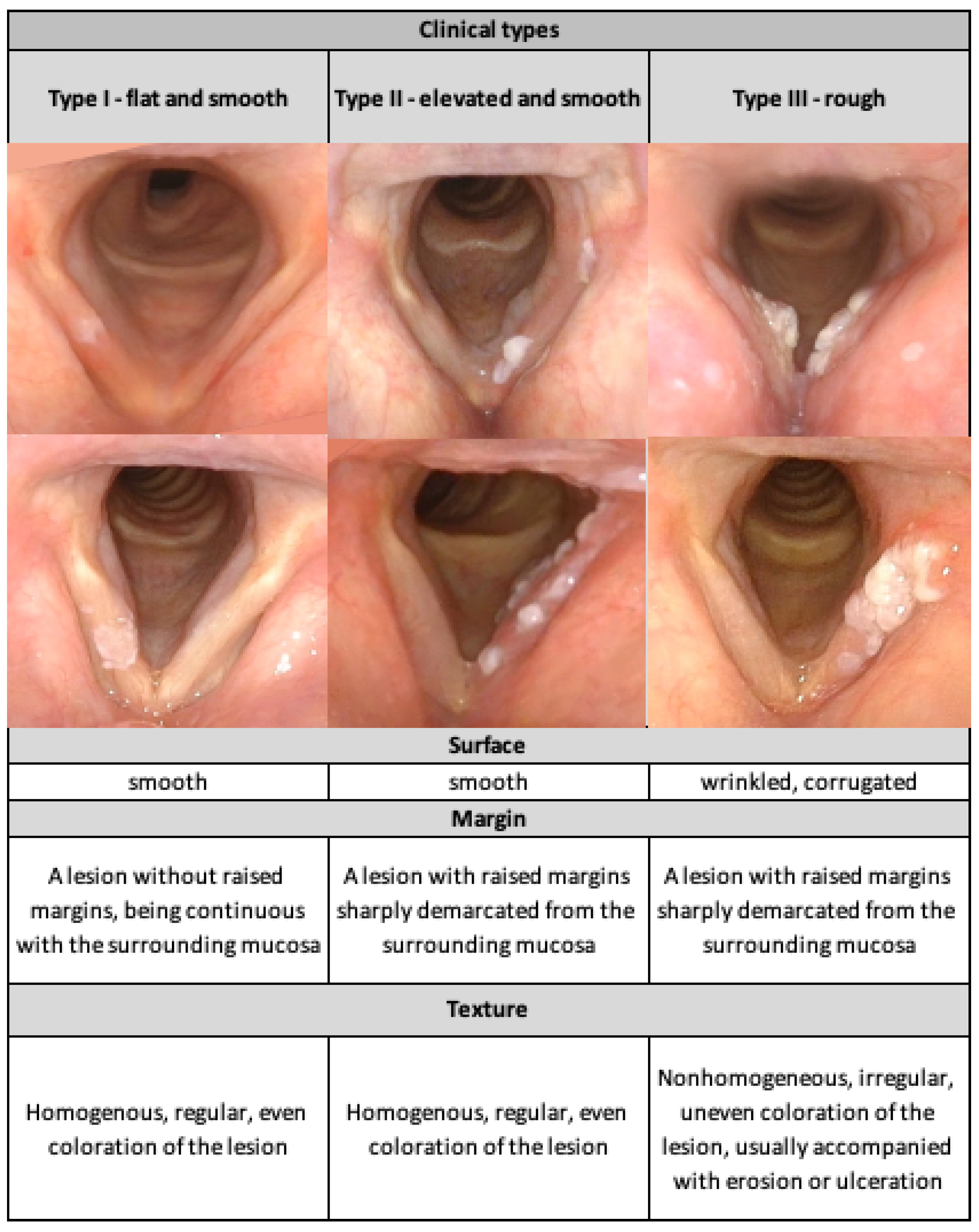

| VLE Classification | Type I: Flat and Smooth N (%) | Type II: Elevated and Smooth N (%) | Type III: Elevated and Rough N (%) | Total N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 37 (30.08) | 60 (48.78%) | 26 (21.14) | 123 (100) | |
| Gender | Male | 26 (26.80) | 51 (52.58%) | 20 (20.62) | 97 (78.86) |
| Female | 11 (42.31) | 9 (34.62%) | 6 (23.08) | 26 (21.14) | |
| Age | Mean (range; SD) | 56.08 (38–76; 11.409) | 64.55 (45–85; 8.852) | 65.38 (55–80; 6.777) | 62.18 (38–85; 10.097) |
| Smoking | No | 9 (56.25) | 5 (31.25) | 2 (12.50) | 16 (13.00) |
| Yes | 28 (26.17) | 55 (51.40) | 24 (22.43) | 107 (87.00) | |
| Alcohol consumption | No | 15 (36.59) | 20 (48.78) | 6 (14.63) | 41 (33.33) |
| Yes | 22 (26.83) | 40 (48.78) | 20 (24.39) | 82 (66.67) | |
| Localization | Unilateral | 16 (21.92) | 36 (49.32) | 21 (28.77) | 73 (59.35) |
| Bilateral | 21 (42.00) | 24 (48.00) | 5 (10.00) | 50 (40.65) | |
| Focality | Unifocal | 26 (35.62) | 36 (49.32) | 11 (15.07) | 73 (59.35) |
| Multifocal | 11 (22.00) | 24 (48.00) | 15 (30.00) | 50 (40.65) | |
| Anterior commissure involvement | No | 30 (41.10) | 33 (45.21) | 10 (13.69) | 73 (59.35) |
| Yes | 7 (14.00) | 27 (54.00) | 16 (32.00) | 50 (40.65) | |
| Inferior edge involvement | No | 27 (42.19) | 32 (50.00) | 5 (7.81) | 64 (52.03) |
| Yes | 10 (16.95) | 28 (47.46) | 21 (35.59) | 59 (47.97) | |
| Mucosal wave presence | No | 1 (1.85) | 34 (62.96) | 19 (35.19) | 54 (43.90) |
| Yes | 36 (52.17) | 26 (37.68) | 7 (10.14) | 69 (56.10) | |
| Number of Cases | Type I—Flat and Smooth | Type II—Elevated and Smooth | Type III—Rough | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rater I | Rater II | Rater I | Rater II | Rater I | Rater II | Rater I | Rater II | |
| High-risk VFL | 2 | 2 | 30 | 25 | 15 | 20 | p < 0.001 * pa = 0.001 pb = 0.001 pc = 1.0 | p = 0.018 * pa = 0.004 pb = 0.002 pc = 1.0 |
| Low-risk VFL | 35 | 31 | 30 | 28 | 11 | 17 | ||
| Inter-rater agreement (Rater I vs. Rater II) | Cohen’s kappa = 0.826 p < 0.001 ** | |||||||
| Cohen’s Kappa | |
|---|---|
| VLE classification | |
| Inter-rater (Rater I—Rater II) | 0.826 (p < 0.001) 95%CI (0.748; 0.904) |
| Intra-rater I | 0.895 (p < 0.001) 95%CI (0.767; 1.024) |
| Intra-rater II | 0.875 (p < 0.001) 95%CI (0.749; 1.001) |
| Mucosal wave evaluation in VLS | |
| Inter-rater (Rater I—Rater II) | 0.785 (p < 0.001) 95%CI (0.608; 0.962) |
| Intra-rater I | 0.867 (p < 0.001) 95%CI (0.690; 1.043) |
| Intra-rater II | 0.816 (p < 0.001) 95%CI (0.640; 0.993) |
| Variable | p-Value [LR Test] | Included in Multivariate Analysis | OR [95%CI] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.049 | No | 1.040 (1.000; 1.081) |
| Age 60 yr. and older | 0.037 | Yes | 2.380 (1.054; 5.374) |
| Male gender | 0.079 | No | 2.44 (0.900; 6.616) |
| Unilateral leukoplakia localization | <0.001 | Yes | 4.11 (1.791; 9.439) |
| Unifocality of leukoplakia | 0.676 | No | 0.853 (0.406; 1.796) |
| Anterior commissure involvement | 0.066 | No | 2.07 (0.955; 4.217) |
| Inferior vocal fold edge involvement | 0.002 | Yes | 3.321 (1.550; 7.119) |
| Mucosal wave absence | <0.001 | Yes | 8.750 (3.791; 20.194) |
| Current or former smoking | 0.037 | Yes | 5.081 (1.100; 23.476) |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.010 | Yes | 3.071 (1.303; 7.238) |
| Type III in VLE classification | <0.001 | Yes | 19.207(4.344; 84.925) |
| Predictor | β | Wald’s χ2 | p | OR [95%CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | −5.410 | 3.617 | 0.057 | NA |
| Unilateral leukoplakia localization | 1.697 | 8.595 | 0.003 | 5.458 (1.755–16.973) |
| VLE classification—Type III | 2.231 | 6.112 | 0.013 | 9.314 (1.588–54.628) |
| Mucosal wave absence | 1.499 | 4.510 | 0.034 | 4.479 (1.123–17.870) |
| Alcohol consumption | 1.211 | 3.940 | 0.047 | 3.357 (1.015–11.101) |
| Regression model statistics | ||||
| Parameter | Test outcome | |||
| Wald’s test | χ2 = 26.149 Df = 10 p = 0.004 | |||
| Hosmer-Lemeshow test | 5.485 p = 0.705 | |||
| AIC | 128.357 | |||
| Clinical Classification | Proposed Cut-Off Value | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLE classification | Type III | 0.726 | 95.7% | 40.8% | 50.0% | 93.9% |
| The proposed logistic regression model for IPHRL | n/a | 0.861 | 80.9% | 73.7% | 65.5% | 86.2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leduchowska, A.; Morawska, J.; Pietruszewska, W. Videolaryngoendoscopic and Stroboscopic Evaluation in Predicting the Malignancy Risk of Vocal Fold Leukoplakia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195789
Leduchowska A, Morawska J, Pietruszewska W. Videolaryngoendoscopic and Stroboscopic Evaluation in Predicting the Malignancy Risk of Vocal Fold Leukoplakia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195789
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeduchowska, Agata, Joanna Morawska, and Wioletta Pietruszewska. 2022. "Videolaryngoendoscopic and Stroboscopic Evaluation in Predicting the Malignancy Risk of Vocal Fold Leukoplakia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195789
APA StyleLeduchowska, A., Morawska, J., & Pietruszewska, W. (2022). Videolaryngoendoscopic and Stroboscopic Evaluation in Predicting the Malignancy Risk of Vocal Fold Leukoplakia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195789






