Recombinant Thrombopoietin Effectively Shortens the Time to Response and Increases Platelet Counts in Elderly Patients with Severe Immune Thrombocytopenia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
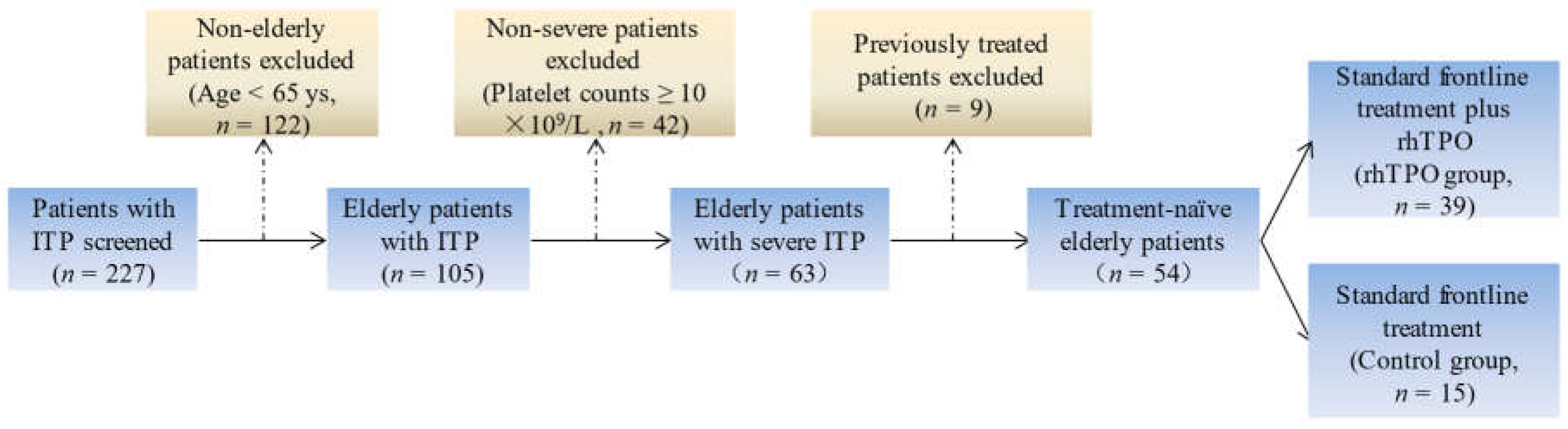
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Outcome Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Response Rate
3.2. Time to Initial Response
3.3. Peak Platelet Counts
3.4. Factors Related to the Time to Initial Response
3.5. Adverse Events
3.6. Efficacy Comparison with Non-Elderly Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Provan, D.; Arnold, D.M.; Bussel, J.B.; Chong, B.H.; Cooper, N.; Gernsheimer, T.; Ghanima, W.; Godeau, B.; González-López, T.J.; Grainger, J.; et al. Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3780–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, N.; Ghanima, W. Immune Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, E.; Fanin, R.; Cooper, N.; Zaja, F. Management of immune thrombocytopenia in elderly patients. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 58, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, B.; Ji, L.; Chen, P.; Li, F.; Cao, J.; Ke, Y.; Yuan, L.; Min, Z.; et al. Interleukin (IL)-1 family cytokines could differentiate primary immune thrombocytopenia from systemic lupus erythematosus-associated thrombocytopenia. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-G.; Bai, X.-C.; Chen, F.-P.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Dai, K.-S.; Fang, M.-Y.; Feng, J.-M.; Gong, Y.-P.; Guo, T.; Guo, X.-H.; et al. Chinese guidelines for treatment of adult primary immune thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 107, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahévas, M.; Michel, M.; Godeau, B. How we manage immune thrombocytopenia in the elderly. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shao, X.; Ou, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Ji, L.; Zhuang, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, D.; Qiao, T.; et al. Neutrophils contribute to elevated BAFF levels to modulate adaptive immunity in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia by CD62P and PSGL1 interaction. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2022, 11, e1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, F.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhan, Y.; Ji, L.; Gao, S.; Meng, Y.; Li, F.; Zou, S.; et al. The expression profile of toll-like receptor signaling molecules in CD19+ B cells from patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 176, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, L.; Ji, L.; Li, F.; Zhan, Y.; Wu, B.; Ke, Y.; Chen, P.; Hua, F.; Yuan, L.; et al. Intestinal microbiota dysbiosis play a role in pathogenesis of patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Thromb. Res. 2020, 190, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, F.; Ji, L.; Shao, X.; Wu, B.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, C.; Min, Z.; Ke, Y.; et al. The abnormal function of CD39+ regulatory T cells could be corrected by high-dose dexamethasone in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zufferey, A.; Kapur, R.; Semple, J.W. Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Mechanisms in Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP). J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanima, W.; Cooper, N.; Rodeghiero, F.; Godeau, B.; Bussel, J.B. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists: Ten years later. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puavilai, T.; Thadanipon, K.; Rattanasiri, S.; Ingsathit, A.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J.; Thakkinstian, A. Treatment efficacy for adult persistent immune thrombocytopenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 188, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.S.M.; Saleh, M.N.; Khelif, A.; Salama, A.; Portella, M.S.O.; Burgess, P.; Bussel, B. Safety and efficacy of long-term treatment of chronic/persistent ITP with eltrombopag: Final results of the EXTEND study. Blood 2017, 130, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Du, X.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, G. Safety and efficacy of eltrombopag plus pulsed dexamethasone as first-line therapy for immune thrombocytopenia. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, D.; Benzon, B.; Batinic, M.; Culic, S.; Roganovic, J.; Markic, J. Hypovitaminosis D Influences the Clinical Presentation of Immune Thrombocytopenia in Children with Newly Diagnosed Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audia, S.; Bonnotte, B. Emerging Therapies in Immune Thrombocytopenia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, J.-Q.; Chen, C.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Qiu, H.-Y.; Fu, C.-C.; Tang, X.-W.; Wu, D.-P.; et al. Recombinant Human Thrombopoietin Promotes Platelet Engraftment and Improves Prognosis of Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Aplastic Anemia after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Fan, L.; Fang, C.; Zhu, D.-X.; Dong, H.-J.; Wang, N.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Xu, W.; Li, J.-Y. The expression of SOX11, cyclin D1, cyclin D2, and cyclin D3 in B-cell lymphocytic proliferative diseases. Med. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, M.; Feng, J.; Fu, H.; Gao, H.; Han, Y.; He, A.; et al. 2021 Chinese consensus on the diagnosis and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia in pregnancy. Chin. Med J. 2022, 135, 887–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Qin, P.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Yang, R.; Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; et al. A novel recombinant human thrombopoietin therapy for the management of immune thrombocytopenia in pregnancy. Blood 2017, 130, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, M.; Qin, P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yuan, C.L.; Zhao, H.G.; Cui, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, F.; et al. A multicenter randomized open-label study of rituximab plus rhTPO vs rituximab in corticosteroid-resistant or relapsed ITP. Blood 2015, 125, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Hou, Y.; Qin, P.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; et al. High-dose dexamethasone plus recombinant human thrombopoietin vs high-dose dexamethasone alone as frontline treatment for newly diagnosed adult primary immune thrombocytopenia: A prospective, multicenter, randomized trial. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulis, G.; Palmaro, A.; Montastruc, J.-L.; Godeau, B.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M.; Sailler, L. Epidemiology of incident immune thrombocytopenia: A nationwide population-based study in France. Blood 2014, 124, 3308–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palandri, F.; Catani, L.; Auteri, G.; Bartoletti, D.; Fatica, S.; Fusco, A.; Reggiani, M.L.B.; Cavo, M.; Vianelli, N. Understanding how older age drives decision-making and outcome in Immune Thrombocytopenia. A single centre study on 465 adult patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Molony, J.T.; Cetin, K.; Wasser, J.S.; Altomare, I. Rate of bleeding-related episodes in elderly patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia: A retrospective cohort study. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Uzun, G.; Bakchoul, T. Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia: Novel Insights into Pathophysiology and Disease Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrès, E. Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Translational Research Model for Autoimmune Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Meng, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Hua, F. Decreased levels of immune-regulatory cytokines in patients with immune thrombocytopenia and long-lasting overexpression of these cytokines in the splenectomized patients. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 110, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeghiero, F. Is ITP a thrombophilic disorder? Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, Z.; Terriou, L.; Lega, J.-C.; Nove-Josserand, R.; Hié, M.; Amoura, Z.; Bussel, J.B.; Hamidou, M.; Rosenthal, E.; Lioger, B.; et al. Risk of thrombosis with anti-phospholipid syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus treated with thrombopoietin-receptor agonists. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | rhTPO Group (n = 39) | Control Group (n = 15) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years old) | 71.4 ± 8.9 | 75.0 ± 7.0 | 0.169 |
| Gender (male/female) | 14/25 | 10/5 | 0.066 |
| Baseline platelet (×109/L) | 3.0 (1.0, 8.0) | 3.0 (2.0, 7.0) | 0.861 |
| Bleeding score | 3.3 ± 2.1 | 4.2 ± 2.5 | 0.265 |
| Number of IVIg (%) | 33.3 (13/39) | 26.7 (4/15) | 0.751 |
| Number of platelet transfusions (%) | 38.5 (15/39) | 40.0 (6/15) | >0.999 |
| Total | p-Value | Without IVIg and Platelet Transfusion | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rhTPO (n = 39) | Control (n =1 5) | rhTPO (n = 17) | Control (n = 7) | |||
| Overall response rate (%) | 100.0 (39/39) | 93.3 (14/15) | 0.278 | 100.0 (17/17) | 85.7 (6/7) | 0.292 |
| Complete response rate (%) | 71.8 (28/39) | 73.3 (11/15) | >0.999 | 82.4 (14/17) | 42.9 (3/7) | 0.137 |
| Time to initial response (days) | 5.0 (3.0, 6.0) | 6.0 (4.0, 7.0) | 0.032 | 4.0 (3.0, 6.0) | 7.0 (4.0, 10.0) | 0.041 |
| Peak platelet counts (×109/L) | 141.0 (91.0, 253.0) | 127.0 (84.0, 209.0) | 0.276 | 159.0 (114.5, 263.0) | 84.0 (46.0, 104.0) | 0.003 |
| Time to peak platelet counts (days) | 8.3±2.9 | 8.8±1.7 | 0.544 | 7.8±3.2 | 8.7±2.4 | 0.487 |
| Elderly (n = 39) | Non-Elderly (n = 35) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall response rate (%) | 100.0 (39/39) | 100.0 (35/35) | >0.999 |
| Complete response rate (%) | 71.8 (28/39) | 82.9 (29/35) | 0.284 |
| Time to initial response (days) | 5.0 (3.0, 6.0) | 5.0 (4.0, 5.0) | 0.919 |
| Baseline platelet counts (×109/L) | 3.0 (1.0, 8.0) | 5.0 (3.0, 7.0) | 0.213 |
| Peak platelet counts (×109/L) | 141.0 (91.0, 253.0) | 199.0 (125.0, 384.0) | 0.115 |
| Time to peak platelet counts (days) | 8.3 ± 2.9 | 8.4 ± 2.5 | 0.851 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; Meng, Y.; Fan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Hua, F. Recombinant Thrombopoietin Effectively Shortens the Time to Response and Increases Platelet Counts in Elderly Patients with Severe Immune Thrombocytopenia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195763
Li Y, Sun L, Li F, Li Y, Hou Y, Meng Y, Fan X, Cheng Y, Hua F. Recombinant Thrombopoietin Effectively Shortens the Time to Response and Increases Platelet Counts in Elderly Patients with Severe Immune Thrombocytopenia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195763
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang, Lihua Sun, Feng Li, Ying Li, Yunhua Hou, Yahong Meng, Xiaohong Fan, Yunfeng Cheng, and Fanli Hua. 2022. "Recombinant Thrombopoietin Effectively Shortens the Time to Response and Increases Platelet Counts in Elderly Patients with Severe Immune Thrombocytopenia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195763
APA StyleLi, Y., Sun, L., Li, F., Li, Y., Hou, Y., Meng, Y., Fan, X., Cheng, Y., & Hua, F. (2022). Recombinant Thrombopoietin Effectively Shortens the Time to Response and Increases Platelet Counts in Elderly Patients with Severe Immune Thrombocytopenia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195763






