Video Laryngoscopy Using King Vision™ aBlade™ and Direct Laryngoscopy in Paediatric Airway Management: A Randomized Controlled Study about Device Learning by Anaesthesia Residents
Abstract
1. Introduction
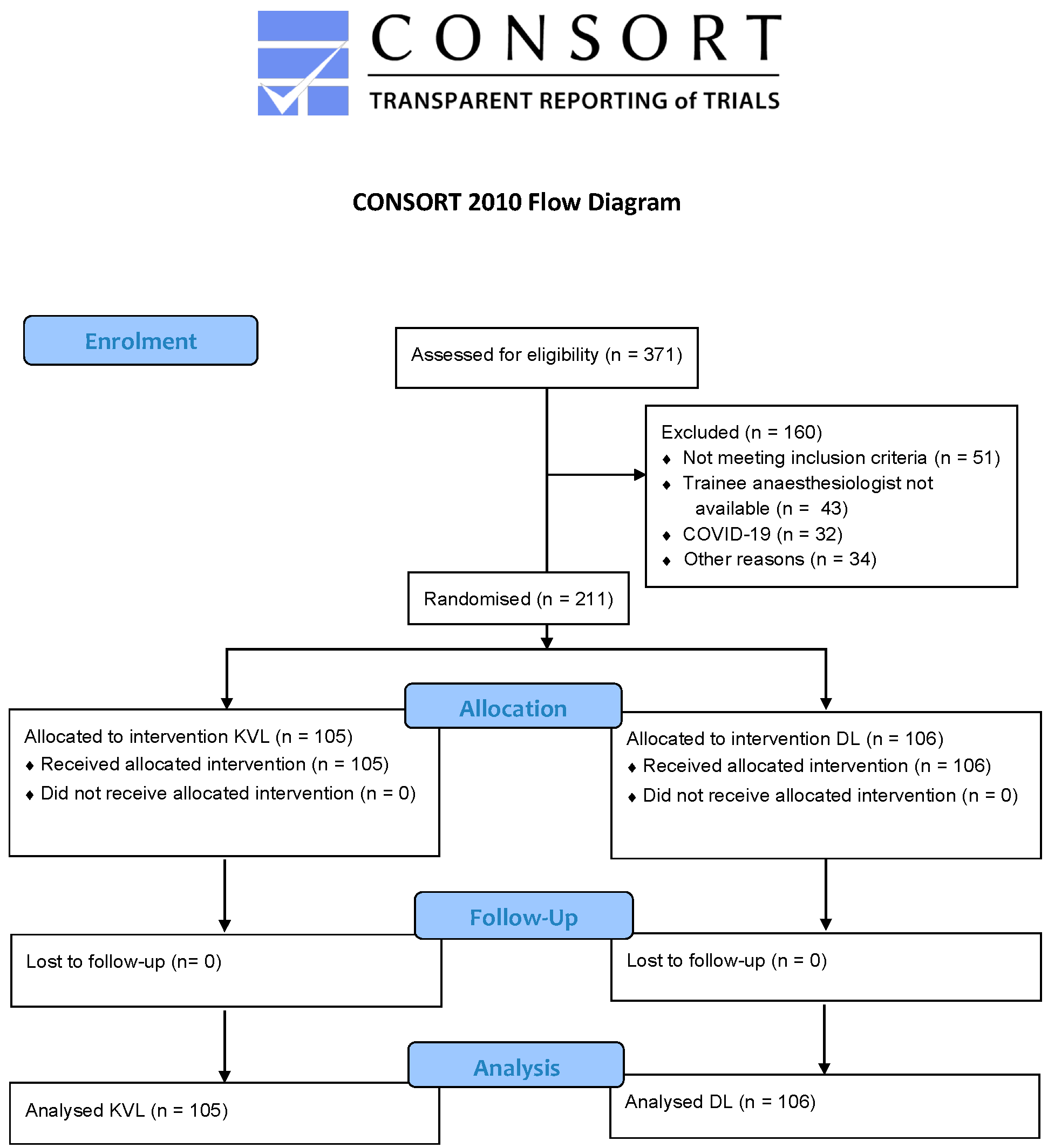
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Trainee Characateristics
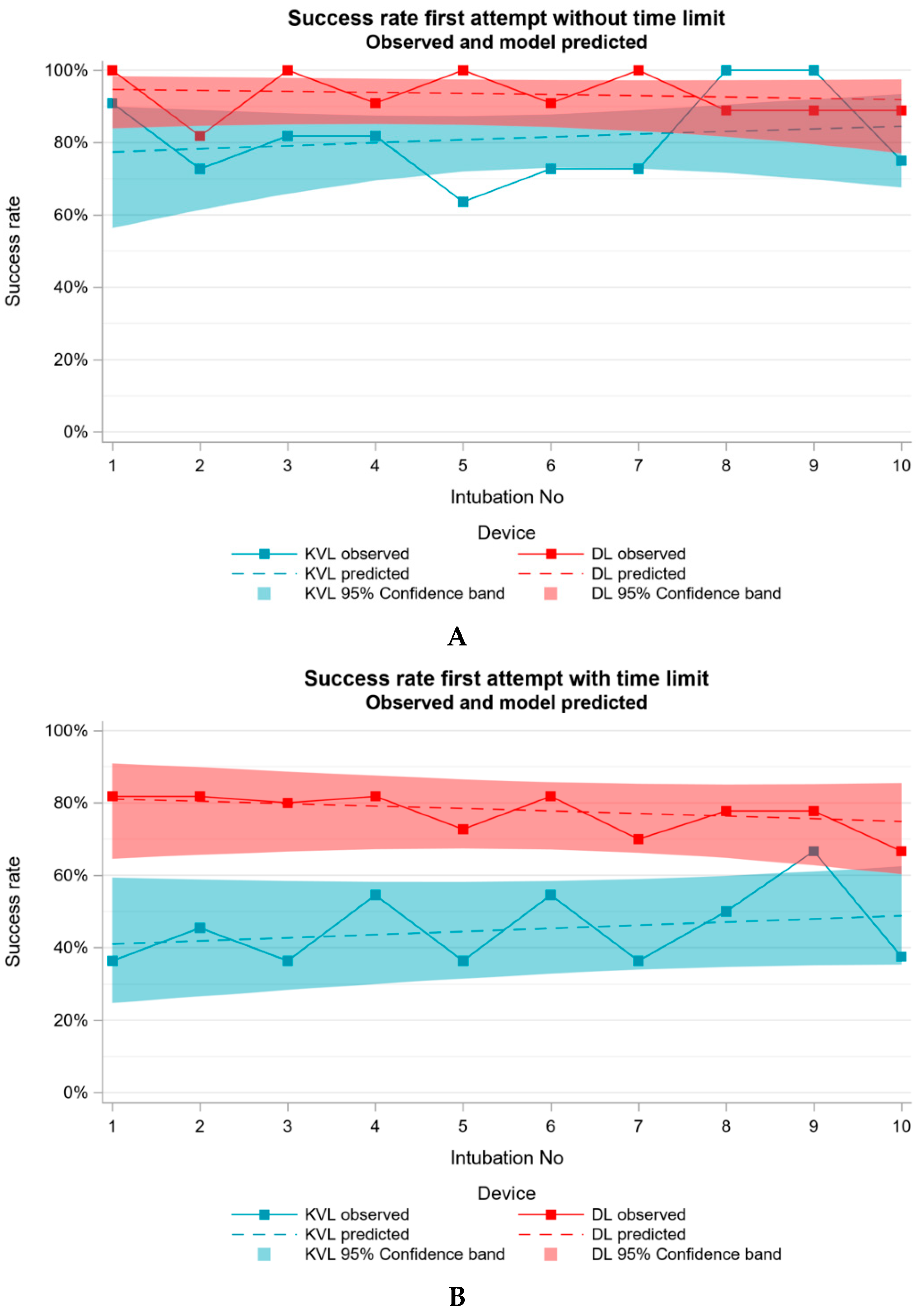
3.2. Primary Endpoint–First Attempt Success Rate with and without Time Limit
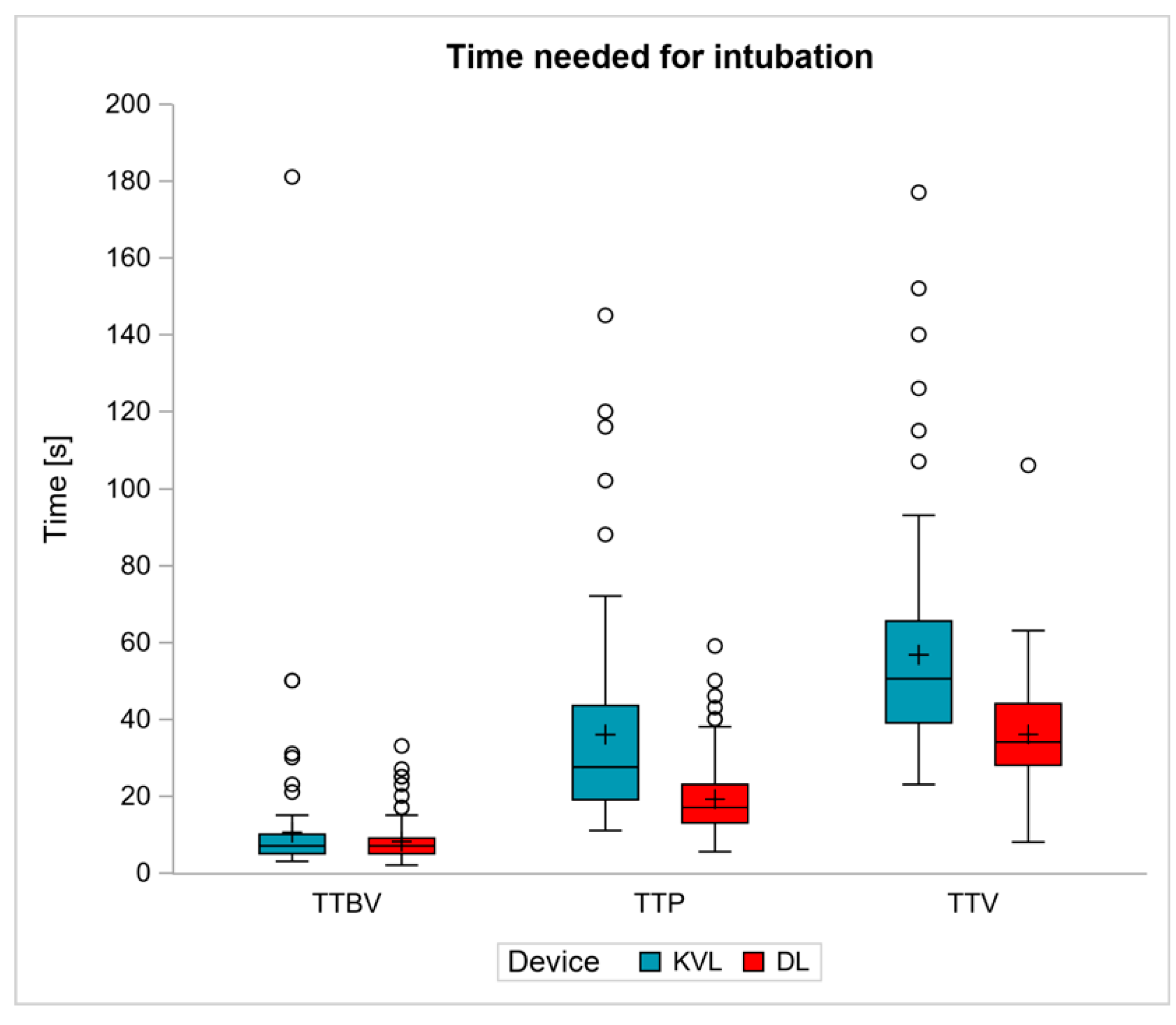
3.3. Secondary Endpoint–Time Needed for the Intubation Steps
3.4. Further Endpoints–Intubation Difficulties and Usability of Device
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiadjoe, J.E.; Nishisaki, A.; Jagannathan, N.; Hunyady, A.I.; Greenberg, R.S.; Reynolds, P.I.; Matuszczak, M.E.; Rehman, M.A.; Polaner, D.; Szmuk, P.; et al. Airway management complications in children with difficult tracheal intubation from the Pediatric Difficult Intubation (PeDI) registry: A prospective cohort analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, N.; Sequera-Ramos, L.; Sohn, L.; Huang, A.; Sawardekar, A.; Wasson, N.; Miriyala, A.; De Oliveira, G.S. Randomized comparison of experts and trainees with nasal and oral fibreoptic intubation in children less than 2 yr of age. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.F.; Healy, D.; Kheterpal, S.; Fu, R.F.; Dillman, D.; Brambrink, A.M. Routine Clinical Practice Effectiveness of the Glidescope in Difficult Airway Management: An Analysis of 2004 Glidescope Intubations, Complications, and Failures from Two Institutions. Anesthesiology 2011, 114, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavus, E.; Neumann, T.; Doerges, V.; Moeller, T.; Scharf, E.; Wagner, K.; Bein, B.; Serocki, G. First Clinical Evaluation of the C-MAC D-Blade Videolaryngoscope During Routine and Difficult Intubation. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 112, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiadjoe, J.E.; Gurnaney, H.; Dalesio, N.M.; Sussman, E.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Stricker, P.A. A Prospective Randomized Equivalence Trial of the GlideScope Cobalt® Video Laryngoscope to Traditional Direct Laryngoscopy in Neonates and Infants. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, N.; Hajduk, J.; Sohn, L.; Huang, A.; Sawardekar, A.; Albers, B.; Bienia, S.; De Oliveira, G. Randomized equivalence trial of the King Vision aBlade videolaryngoscope with the Miller direct laryngoscope for routine tracheal intubation in children < 2 yr of age. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-T.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, S.-D. A comparison of GlideScope® videolaryngoscopy and direct laryngoscopy for nasotracheal intubation in children. Pediatr. Anesth. 2011, 21, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-T.; Na, H.-S.; Bae, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, S.D. GlideScope video laryngoscope: A randomized clinical trial in 203 paediatric patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, Y.-H.; Byon, H.-J.; Han, W.-K.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, J.-T. A comparative trial of the GlideScope(R) video laryngoscope to direct laryngoscope in children with difficult direct laryngoscopy and an evaluation of the effect of blade size. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, M.; Seal, R.F.; Spady, D.; Csanyi-Fritz, Y.; Robinson, J.L. Randomized trial of success of pediatric anesthesiologists learning to use two video laryngoscopes. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2013, 23, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, J.-B.; Donati, F.; Drolet, P. Review article: Video-laryngoscopy: Another tool for difficult intubation or a new paradigm in airway management? Can. J. Anesth. 2012, 60, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepho, T.; Cavus, E.; Noppens, R.; Byhahn, C.; Dörges, V.; Zwissler, B.; Timmermann, A. S1 guidelines on airway management: Guideline of the German Society of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine. Anaesthesist 2015, 64 (Suppl. S1), 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepho, T.; Fortmueller, K.; Heid, F.M.; Schmidtmann, I.; Werner, C.; Noppens, R.R. Performance of the C-MAC video laryngoscope in patients after a limited glottic view using Macintosh laryngoscopy. Anaesthesia 2011, 66, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redel, A.; Karademir, F.; Schlitterlau, A.; Frommer, M.; Scholtz, L.-U.; Kranke, P.; Kehl, F.; Roewer, N.; Lange, M. Validation of the glidescope video laryngoscope in pediatric patients. Pediatric. Anesth. 2009, 19, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, R.; Sung, W.; Sessler, D.I.; Sanchez, I.P.; Mendoza, M.L.; Mascha, E.J.; Niezgoda, J. Comparison of the Truview PCD™ and the GlideScope® video laryngoscopes with direct laryngoscopy in pediatric patients: A randomized trial. Can. J. Anesth. 2013, 60, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serocki, G.; Bein, B.; Scholz, J.; Dörges, V. Management of the predicted difficult airway: A comparison of conventional blade laryngoscopy with video-assisted blade laryngoscopy and the GlideScope. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 27, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadi, M.G.; Roddy, K.J.; Ghazal, E.A.; Um, M.; Neiheisel, A.J.; Applegate, R.L., 2nd. Comparison of the GlideScope Cobalt® and Storz DCI® Video Laryngoscopes in Children Younger Than 2 Years of Age During Manual In-Line Stabilization: A Randomized Trainee Evaluation Study. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2017, 33, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatten, A.; Litz, S.; Macmanus, B.; Launcelott, S.; Soder, C. A Comparison of the GlideScope Video Laryngoscope and Standard Direct Laryngoscopy in Children With Immobilized Cervical Spine. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2012, 28, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, D.; Komasawa, N.; Fujiwara, S.; Minami, T. Comparison of tube-guided and guideless videolaryngoscope for tracheal intubation during chest compression in a manikin: A randomized crossover trial. J. Anesth. 2015, 29, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Shimada, N.; Shiba, J.; Niwa, Y.; Takeuchi, M. Comparative study of the KingVision videolaryngoscope and Airwayscope using manikins. Masui 2014, 63, 927–930. [Google Scholar]
- Akihisa, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Koyama, Y.; Yamada, R.; Ogura, A.; Andoh, T. Comparison of intubation performance between the King Vision and Macintosh laryngoscopes in novice personnel: A randomized, crossover manikin study. J. Anesth. 2014, 28, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, N.; Hayashi, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Takahashi, M.; Niwa, Y.; Takeuchi, M. The KINGVISION: Clinical assessment of performance in 50 patients. Masui 2013, 62, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.D.; Kovacs, G.; Reardon, P.M.; Law, J.A. Comparison of the king vision video laryngoscope with the macintosh laryngoscope. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 47, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, B.J.; Brown, C.A.; Grazioso, C.J.; Pozner, C.N.; Raja, A.S. Comparison of Video, Optical, and Direct Laryngoscopy by Experienced Tactical Paramedics. Prehospital Emerg. Care 2014, 18, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Q.E.; Amir, S.H.; Jamil, S.; Ahmad, S. A comparative evaluation of the Airtraq and King Vision video laryngoscope as an intubating aid in adult patients. Acta Anaesthesiol. Belg. 2015, 66, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yousif, S.; Machan, J.T.; Alaska, Y.; Suner, S. Airway Management in Disaster Response: A Manikin Study Comparing Direct and Video Laryngoscopy for Endotracheal Intubation by Prehospital Providers in Level C Personal Protective Equipment. Prehosp. Disaster. Med. 2017, 32, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manirajan, M.; Bidkar, P.U.; Sivakumar, R.K.; Lata, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Jha, A.K. Comparison of paediatric King Vision videolaryngoscope and Macintosh laryngoscope for elective tracheal intubation in children of age less than 1 year: A randomised clinical trial. Indian J. Anaesth. 2020, 64, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kriege, M.; Pirlich, N.; Ott, T.; Wittenmeier, E.; Dette, F. A comparison of two hyperangulated video laryngoscope blades to direct laryngoscopy in a simulated infant airway: A bicentric, comparative, randomized manikin study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, H. Pediatric video laryngoscope versus direct laryngoscope: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2014, 24, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, M.; Rangarajan, V.; Sawyer, T.L.; Napolitano, N.; Boyer, D.L.; Morrison, W.E.; Lockman, J.L.; Berg, R.A.; Nadkarni, V.M.; Nishisaki, A. The Development of Tracheal Intubation Proficiency Outside the Operating Suite During Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Fellowship Training: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Cumulative Sum Analysis. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. J. Soc. Crit. Care Med. World Fed. Pediatr. Intensive Crit. Care Soc. 2016, 17, e309–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelgadir, I.S.; Phillips, R.S.; Singh, D.; Moncreiff, M.P.; Lumsden, J.L. Videolaryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy for tracheal intubation in children (excluding neonates). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 5, Cd011413.d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patients | KVL | DL | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 105) | (n = 106) | ||
| Age; months | 49 [35–69] | 50 [35–73] | 0.7402 |
| Sex; male | 67 (64%) | 55 (52%) | 0.0947 |
| Weight; kg | 17 [13–20] | 17 [14–20] | 0.7249 |
| Height; cm | 105 [95–115] | 104 [95–117] | 0.8196 |
| ASA | 0.1786 | ||
| 1 | 66 (63%) | 77 (73%) | |
| 2 | 37 (35%) | 28 (26%) | |
| NA 1 | 2 (2%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Type of surgery | 0.0292 | ||
| Otorhinolaryngology | 90 (86%) | 77 (73%) | |
| Others (pediatric surgery, ophthalmology) | 15 (14%) | 29 (27%) | |
| Anaesthesia residents (n = 11) | |||
| Training status; months | 49 [45–56] | ||
| Practical year in anaesthesia | 10/11 (91%) | ||
| Clinical traineeship in anaesthesia | 9/11 (82%) | ||
| Age; years [range] | 31 [30–33] | ||
| Sex; male | 4/11 (36%) | ||
| Left-hander | 1/11 (9%) | ||
| Number of VL 2 in patients aged > 10 years | |||
| <100 | 3/11 (27%) | ||
| 100–499 | 7/11 (64%) | ||
| >500 | 1/11 (9%) | ||
| Number of VL 2 in children aged < 10 years | |||
| <10 | 6/11 (55%) | ||
| 10–49 | 5/11 (46%) | ||
| Intubation Attempt | KVL | DL | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 105) | (n = 106) | ||
| Oesophageal intubation at first attempt | 2 (2%) | 1 (1%) | 0.9098 |
| Timeout at first attempt | 51 (49%) | 19 (18%) | <0.0001 |
| Tube type: | 0.6262 | ||
| Murphy tube | 26 (25%) | 42 (40%) | |
| Armoured tube | 78 (74%) | 63 (59%) | |
| Other | 1 (1%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Airway manoeuvres: | 0.4079 | ||
| OELM 1 | 10 (10%) | 6 (6%) | |
| Position of head | 6 (6%) | 11 (10%) | |
| OELM 1 and position of head | 4 (4%) | 8 (8%) | |
| Cormack and Lehane Score I | 84 (80%) | 66 (62%) | <0.0001 |
| Cormack and Lehane Score II | 18 (17%) | 38 (36%) | |
| Cormack and Lehane Score III | - | 2 (2%) | |
| NA | 3 (3%) | - | |
| POGO 2 Scale 100% | 65 (62%) | 46 (43%) | 0.0495 |
| Fogging of camera | 57 (54%) | - | -- |
| Complications (oesophageal intubation, desaturation > 2%, bleeding, no visualization) | 39 (37%) | 7 (7%) | 0.2578 |
| Difficulties (tube too big, tube placement not possible, guide wire problem, blade too big, visualization problem, lip injury) | 36 (34%) | 8 (8%) | <0.0001 |
| Likert Scale rating usability of intubation: | <0.0001 | ||
| Very easy (1) | 13 (12%) | 71 (67%) | |
| Easy (2) | 32 (30%) | 30 (28%) | |
| Difficult (3) | 44 (42%) | 4 (4%) | |
| Very difficult (4) | 12 (11%) | - | |
| NA 3 | 4(4%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Mean [95% CI] 4 | 2.5 [2.3;2.7] | 1.4 [1.1;1.6] | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Epp, K.; Zimmermann, S.; Wittenmeier, E.; Kriege, M.; Dette, F.; Schmidtmann, I.; Pirlich, N. Video Laryngoscopy Using King Vision™ aBlade™ and Direct Laryngoscopy in Paediatric Airway Management: A Randomized Controlled Study about Device Learning by Anaesthesia Residents. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195676
Epp K, Zimmermann S, Wittenmeier E, Kriege M, Dette F, Schmidtmann I, Pirlich N. Video Laryngoscopy Using King Vision™ aBlade™ and Direct Laryngoscopy in Paediatric Airway Management: A Randomized Controlled Study about Device Learning by Anaesthesia Residents. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195676
Chicago/Turabian StyleEpp, Katharina, Sophie Zimmermann, Eva Wittenmeier, Marc Kriege, Frank Dette, Irene Schmidtmann, and Nina Pirlich. 2022. "Video Laryngoscopy Using King Vision™ aBlade™ and Direct Laryngoscopy in Paediatric Airway Management: A Randomized Controlled Study about Device Learning by Anaesthesia Residents" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195676
APA StyleEpp, K., Zimmermann, S., Wittenmeier, E., Kriege, M., Dette, F., Schmidtmann, I., & Pirlich, N. (2022). Video Laryngoscopy Using King Vision™ aBlade™ and Direct Laryngoscopy in Paediatric Airway Management: A Randomized Controlled Study about Device Learning by Anaesthesia Residents. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195676








