Silodosin Improves Pain and Urinary Frequency in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria, Classification, and Nomenclature for Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: An ESSIC Proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colemeadow, J.; Sahai, A.; Malde, S. Clinical management of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: A review on current recommendations and emerging treatment options. Res. Rep. Urol. 2020, 12, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groat, W.C.; Yoshimura, N. Changes in afferent activity after spinal cord injury. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2010, 29, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, D.A.; Nickel, J.C.; Wong, J.; Pontari, M.; Moldwin, R.; Mayer, R.; Carr, L.K.; Doggweiler, R.; Yang, C.C.; Mishra, N.; et al. Mapping of pain phenotypes in female patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis and controls. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towner, R.A.; Smith, N.; Saunders, D.; Lerner, M.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Hurst, R.E. Assessing bladder hyper-permeability biomarkers in vivo using molecularly-targeted MRI. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 10, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lovick, T.A. Central control of visceral pain and urinary tract function. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2016, 200, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihan, A.; Cihan, E.; Çakmak, B. Perceived Stress and Accompanying Low Urine pH Are in Relation to Bladder Pain Syndrome. J. Urol. Surg. 2021, 8, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.C.; Tripp, D.A.; Pontari, M.; Moldwin, R.; Mayer, R.; Carr, L.K.; Doggweiler, R.; Yang, C.C.; Mishra, N.; Nordling, J. Childhood sexual trauma in women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: A case control study. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2011, 5, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.-D.; Lee, M.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Ho, H.L.; Wu, H.-C. Childhood trauma perpetrated by close others, psychiatric dysfunction, and urological symptoms in patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J. Psychosom. Res. 2017, 93, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrua, A.; Pinto, R.; Birder, L.A.; Cruz, F. Sympathetic nervous system and chronic bladder pain: A new tune for an old song. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matos, R.; Serrão, P.; Rodriguez, L.; Birder, L.A.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. The water avoidance stress induces bladder pain due to a prolonged alpha1A adrenoceptor stimulation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, L.; Capogrosso, P.; Capitanio, U.; Martini, A.; Briganti, A.; Salonia, A.; Montorsi, F. Silodosin: An Update on Efficacy, Safety and Clinical Indications in Urology. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Hoe, K.-O.; Shin, J.H.; Choo, M.-S. Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and the efficacy of antimuscarinic treatment. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2017, 58, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrua, A.; Pinto, R.; Taylor, A.; Canelas, A.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A.; Cruz, C.D.; Birder, L.A.; Cruz, F. Can the adrenergic system be implicated in the pathophysiology of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis? A clinical and experimental study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2015, 34, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, R.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Coelho, A.; Ferreira, S.; Silva, C.; Igawa, Y.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. Bladder pain induced by prolonged peripheral alpha 1A adrenoceptor stimulation involves the enhancement of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 activity and an increase of urothelial adenosine triphosphate release. Acta Physiol. 2016, 218, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, B.; Serrão, P.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. Effect of Water Avoidance Stress on serum and urinary NGF levels in rats: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications for BPS/IC patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothrock, N.E.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Kreder, K.J.; Ratliff, T.; Zimmerman, B. Stress and symptoms in patients with interstitial cystitis: A life stress model. Urology 2001, 57, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgendorf, S.K.; Kreder, K.J.; Rothrock, N.E.; Ratliff, T.L.; Zimmerman, B. Stress and Symptomatology in patients wuth interstitial cystitis: A laboratory stress model. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
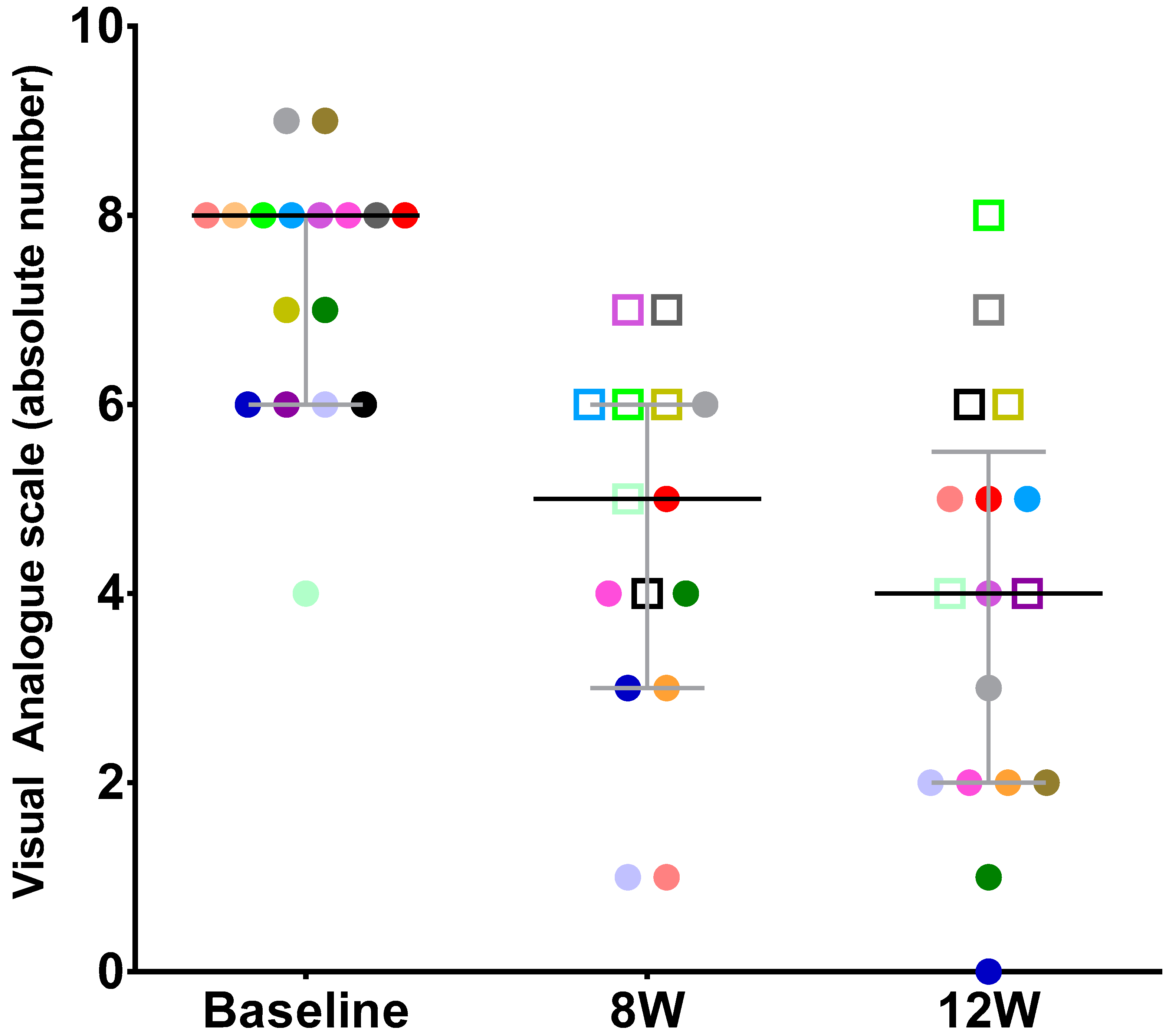


| Baseline Median (P25, P75) | W12 Median (P25, P75) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pain VAS | 8.00 (6.00; 8.00) | 4.00 (2.00; 5.50) | 0.001 |
| Total Voiding Frequency | 14.00 (13.00; 21.00) | 9.00 (7.50; 11.00) | 0.001 |
| Nocturia | 4.00 (2.00; 5.50) | 2.00 (1.00; 3.00) | 0.001 |
| MVV | 175.00 (150.00; 250.00) | 250.00 (200.00; 350.00) | 0.03 |
| OSS | 26.00 (24.00; 28.00) | 19.00 (14.00; 22.50) | 0.001 |
| QoL | 5.00 (4.25; 6.00) | 3.00 (2.00; 4.00) | 0.001 |
| Demographics | Responders | Non-Responders | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 49.0 (35.0; 67.0) | 58.8 (49.0; 64.0) | 0.52 |
| Baseline VAS | 8.00 (7,00; 8.00) | 6.50 (5.50; 8.00) | 0.09 |
| Total Urinary Frequency | 14.00 (13.00; 19.00) | 15.00 (12.50; 24.50) | 0.81 |
| Nocturia | 4.00 (3.00; 5.00) | 3.00 (1.75; 8.00) | 0.81 |
| MVV | 150.00 (150.00; 250.00) | 200.00 (150.00; 265.00) | 0.78 |
| OSS | 24.00 (27.00; 29.00) | 25.00 (23.50; 27.50) | 0.24 |
| QoL | 5.00 (4.00; 6.00) | 4.50 (6.00; 3.80) | 0.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abreu-Mendes, P.; Araújo-Silva, B.; Charrua, A.; Cruz, F.; Pinto, R. Silodosin Improves Pain and Urinary Frequency in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195659
Abreu-Mendes P, Araújo-Silva B, Charrua A, Cruz F, Pinto R. Silodosin Improves Pain and Urinary Frequency in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195659
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbreu-Mendes, Pedro, Beatriz Araújo-Silva, Ana Charrua, Francisco Cruz, and Rui Pinto. 2022. "Silodosin Improves Pain and Urinary Frequency in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195659
APA StyleAbreu-Mendes, P., Araújo-Silva, B., Charrua, A., Cruz, F., & Pinto, R. (2022). Silodosin Improves Pain and Urinary Frequency in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195659







